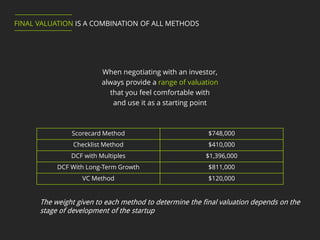
This document discusses 5 methods for valuing a startup company:
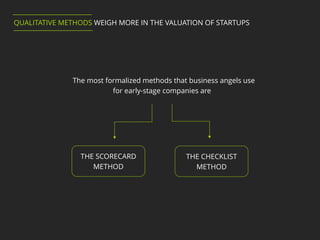
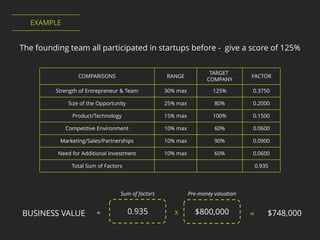
1. The Scorecard method compares a startup to already funded companies based on factors like management team and market opportunity.
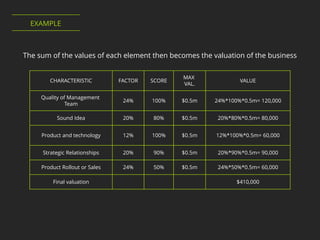
2. The Checklist method assigns fixed dollar values to elements like management team and product based on an investor's assessment.
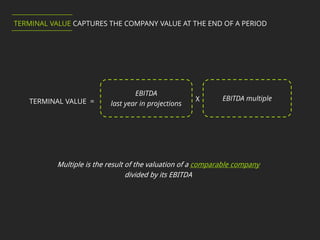
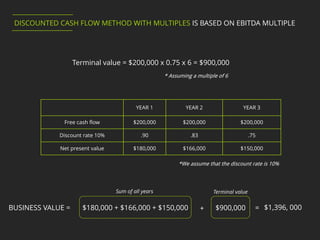
3. The Discounted Cash Flow method with Multiples values a company based on projected cash flows discounted to the present using a discount rate and a terminal value based on EBITDA multiples of comparable companies.
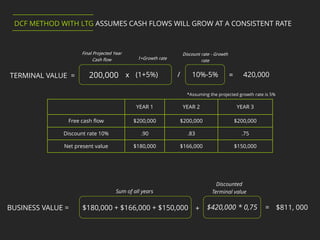
4. The Discounted Cash Flow method with Long-Term Growth values a company similarly but assumes cash flows will grow at a consistent long-term rate instead of using a terminal value.