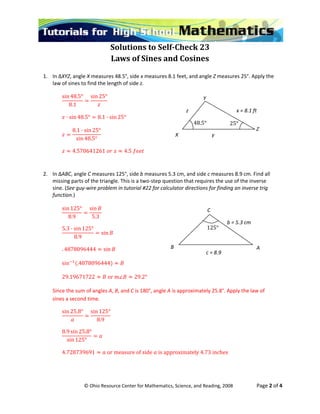
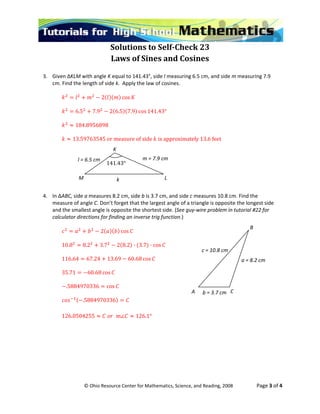
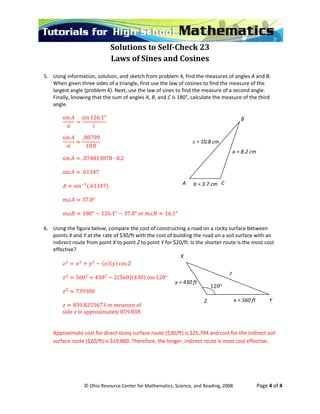
This document contains 6 problems involving the use of the Law of Sines and Law of Cosines to solve for missing parts of triangles. Problem 1 uses the Law of Sines to find the length of a side. Problem 2 uses the Law of Sines twice to find all missing parts of a triangle. Problem 3 uses the Law of Cosines to find the length of a side. Problems 4-5 use both laws to find all angle and side measures. Problem 6 compares the cost of two road routes using trigonometric formulas.