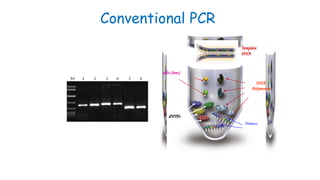
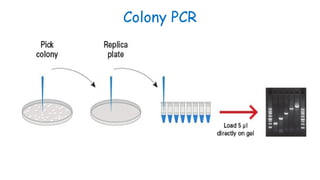
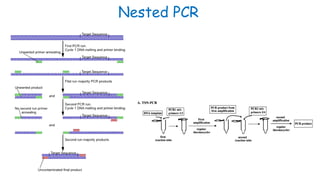
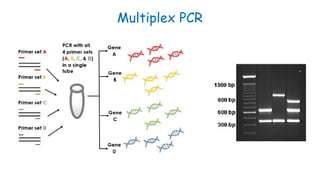
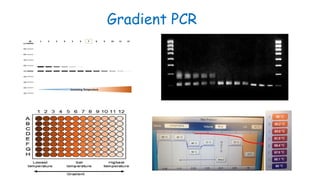
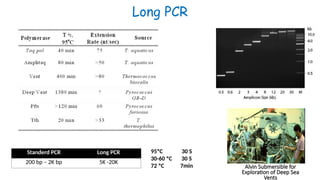
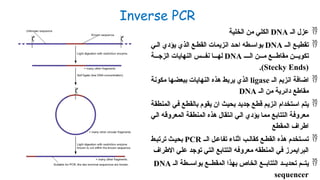
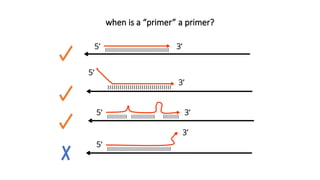
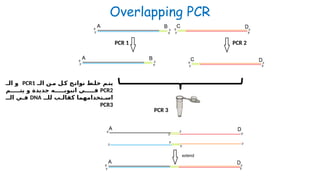
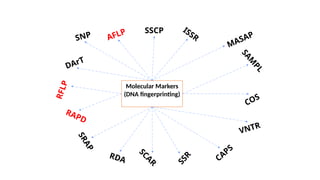
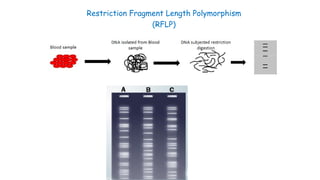
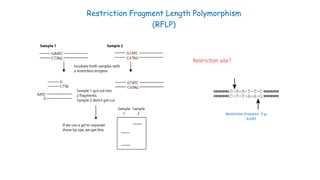
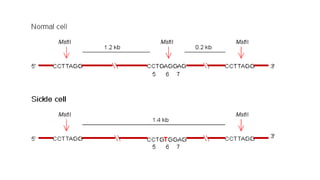
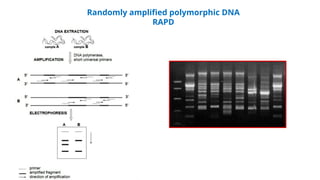
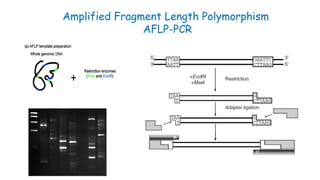
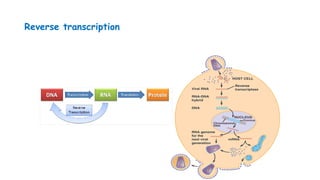
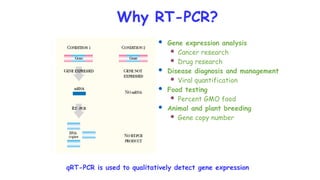
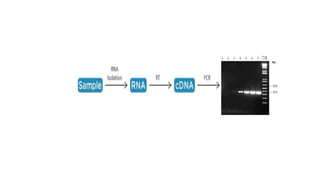
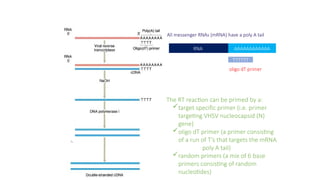
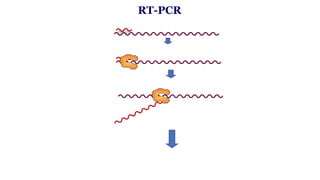
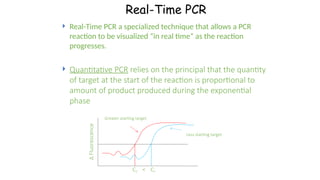
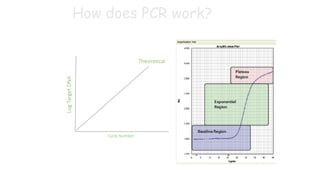
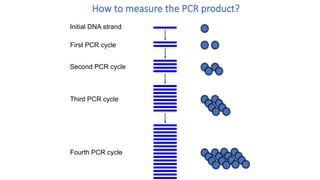
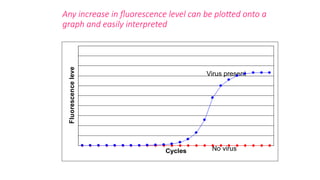
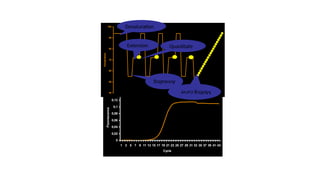
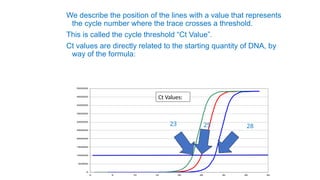
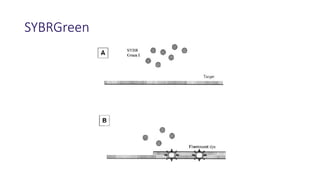
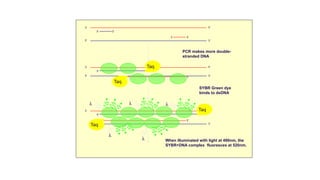
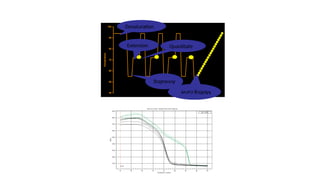
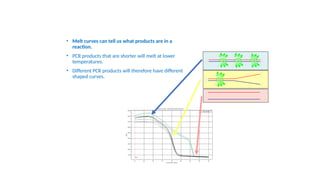
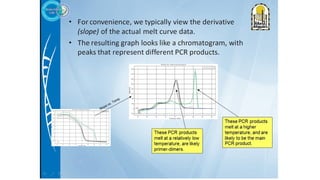
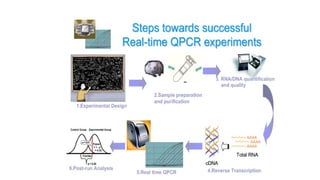
The document outlines various PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) types and their applications in molecular genetics, including colony, nested, multiplex, and long PCR. It also discusses techniques for DNA fingerprinting, such as RAPD and AFLP, as well as reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) for gene expression analysis and real-time PCR for monitoring reaction progress. Key concepts such as cycle threshold (Ct) values, fluorescence measurement, and melting curve analysis for product verification are also examined.