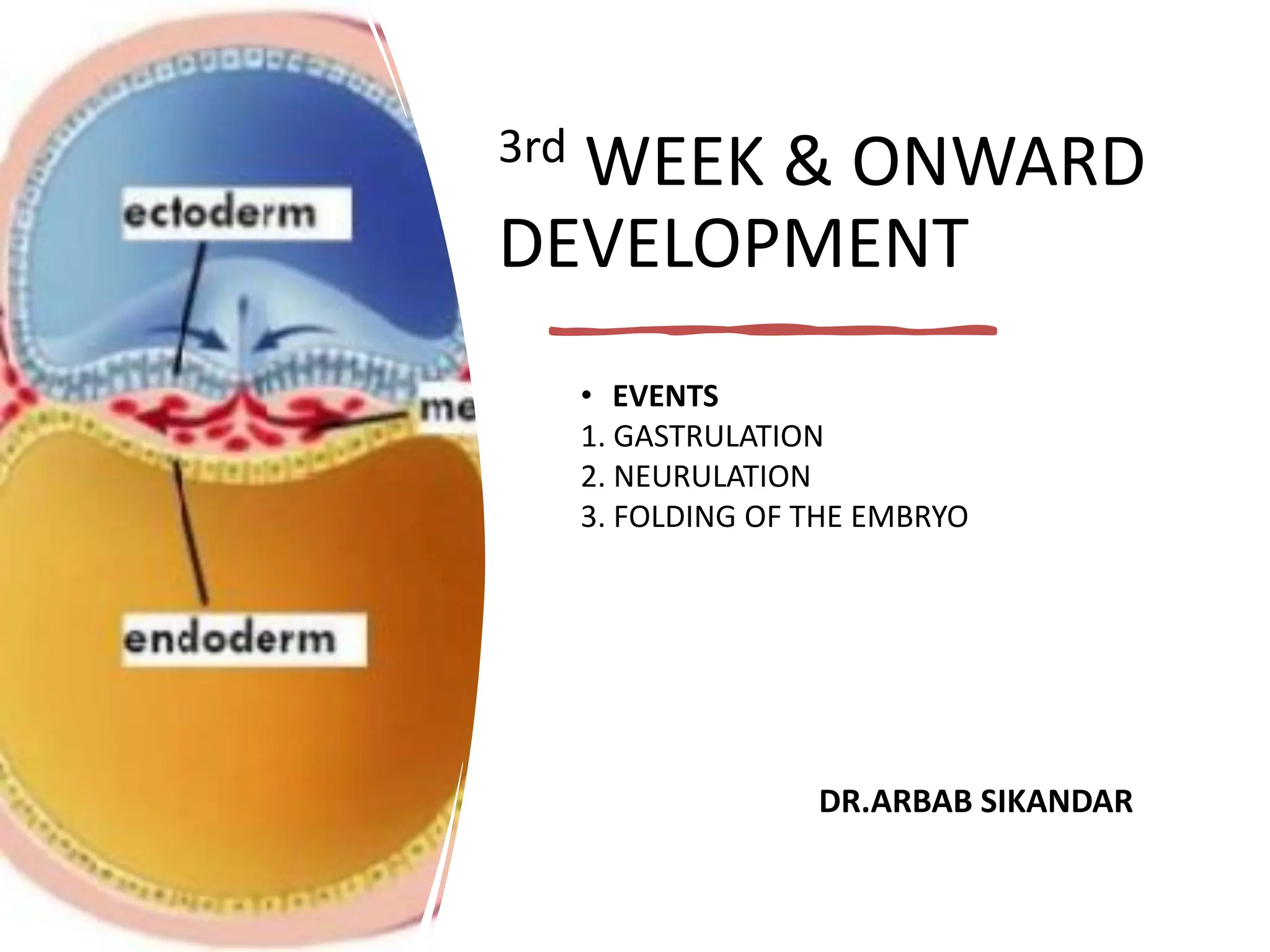
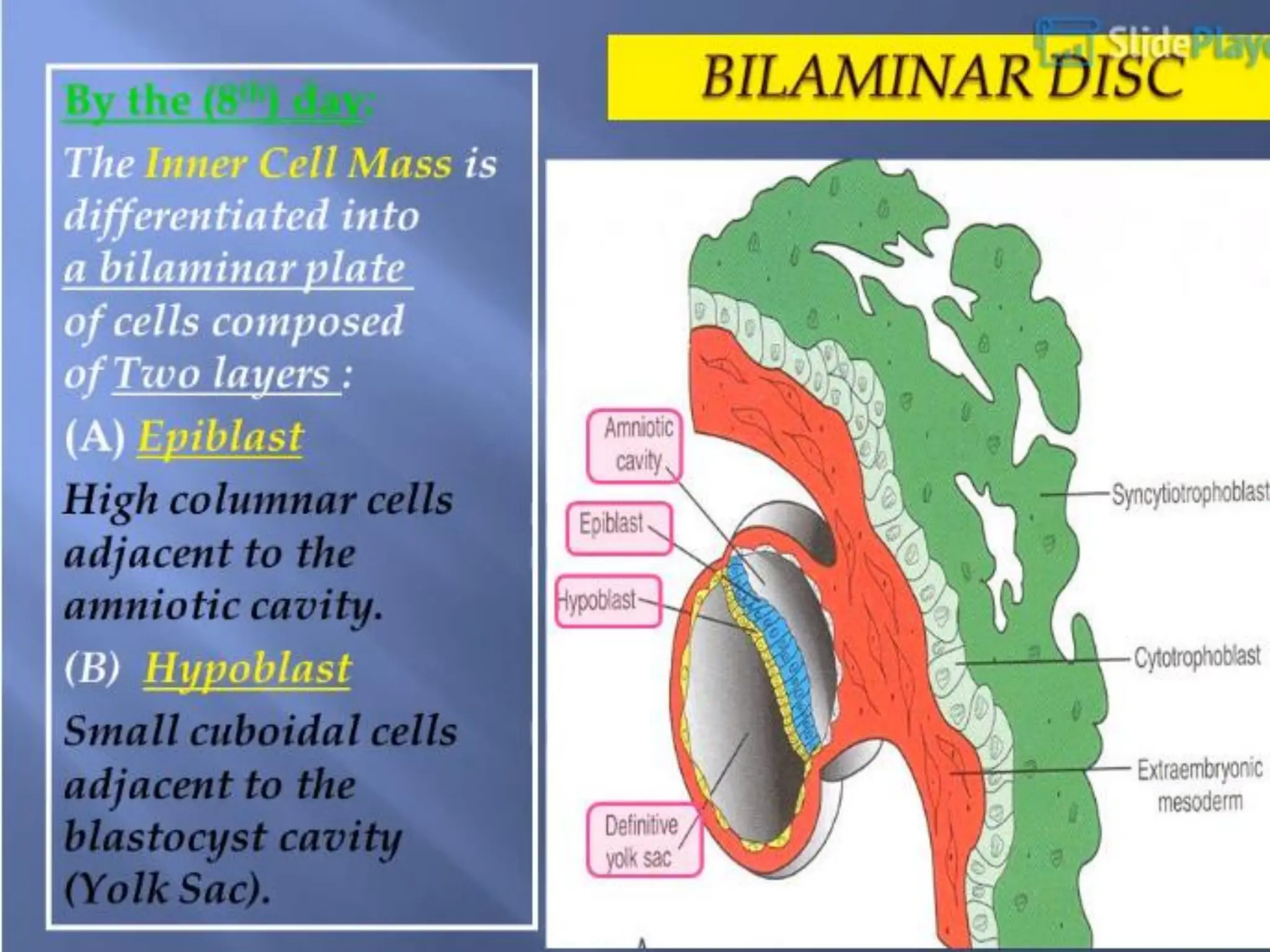
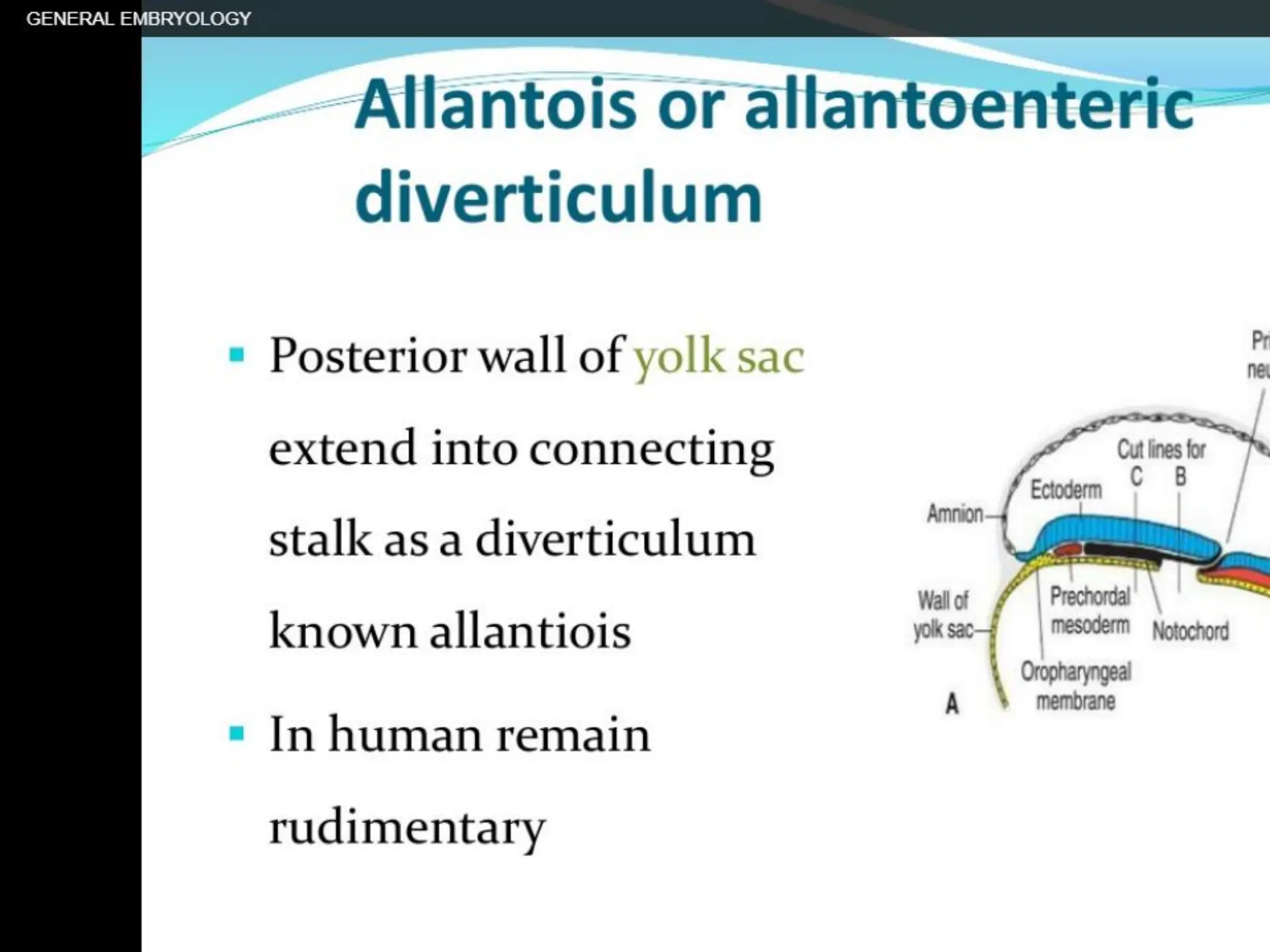
This document summarizes key developmental events that occur during the 3rd week of embryogenesis, including gastrulation, neurulation, and embryo folding. Specifically, it describes:
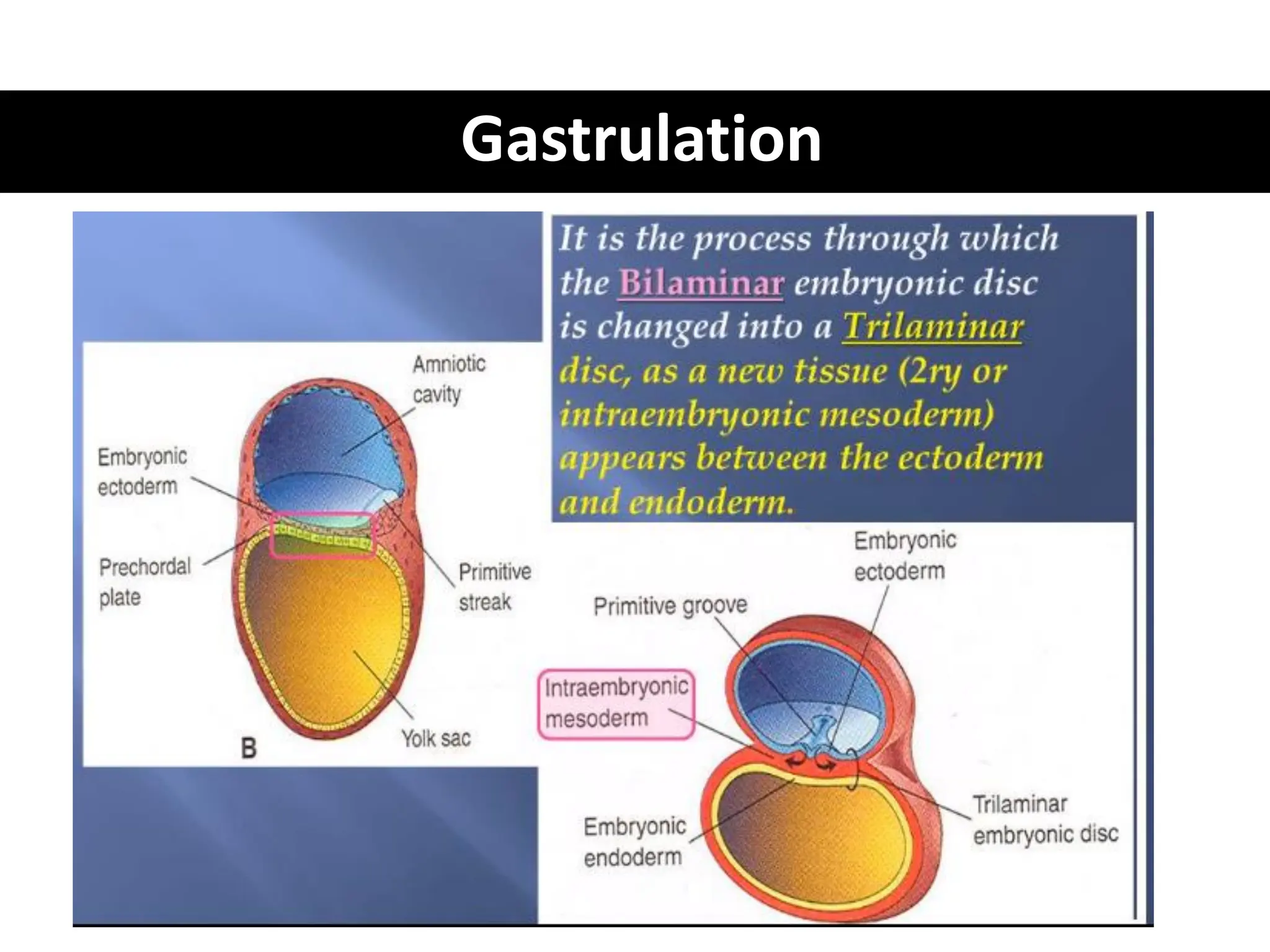
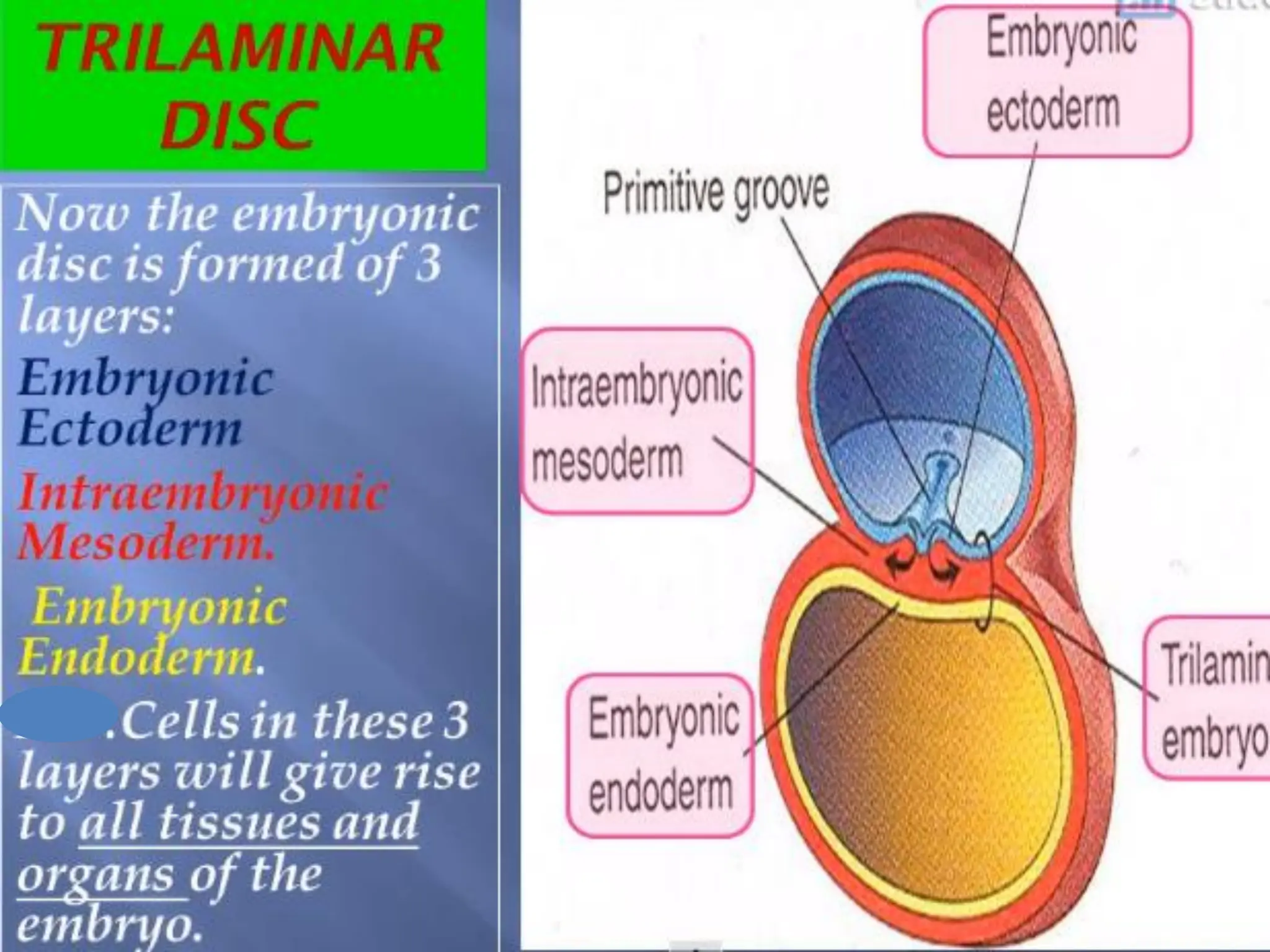
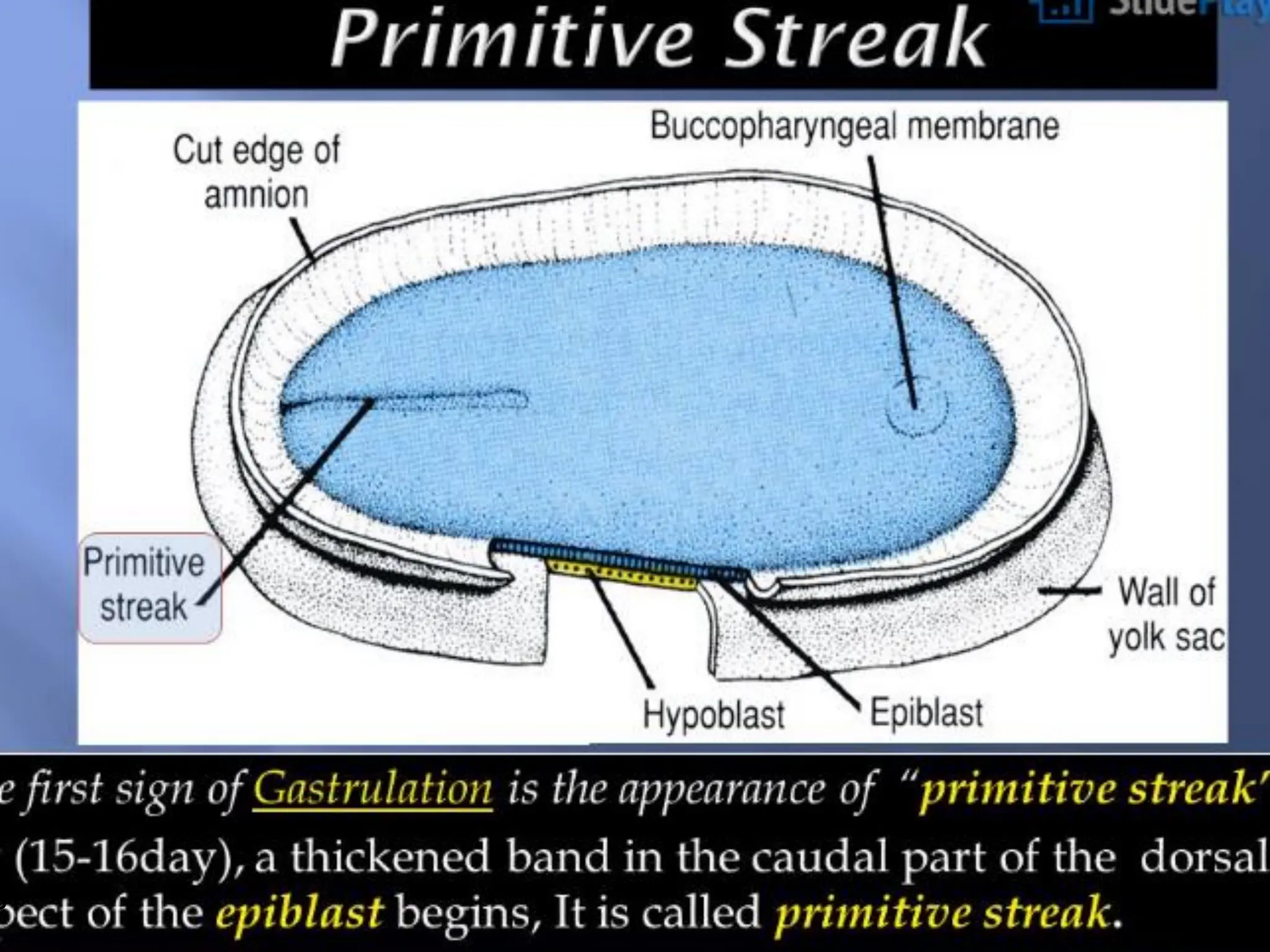
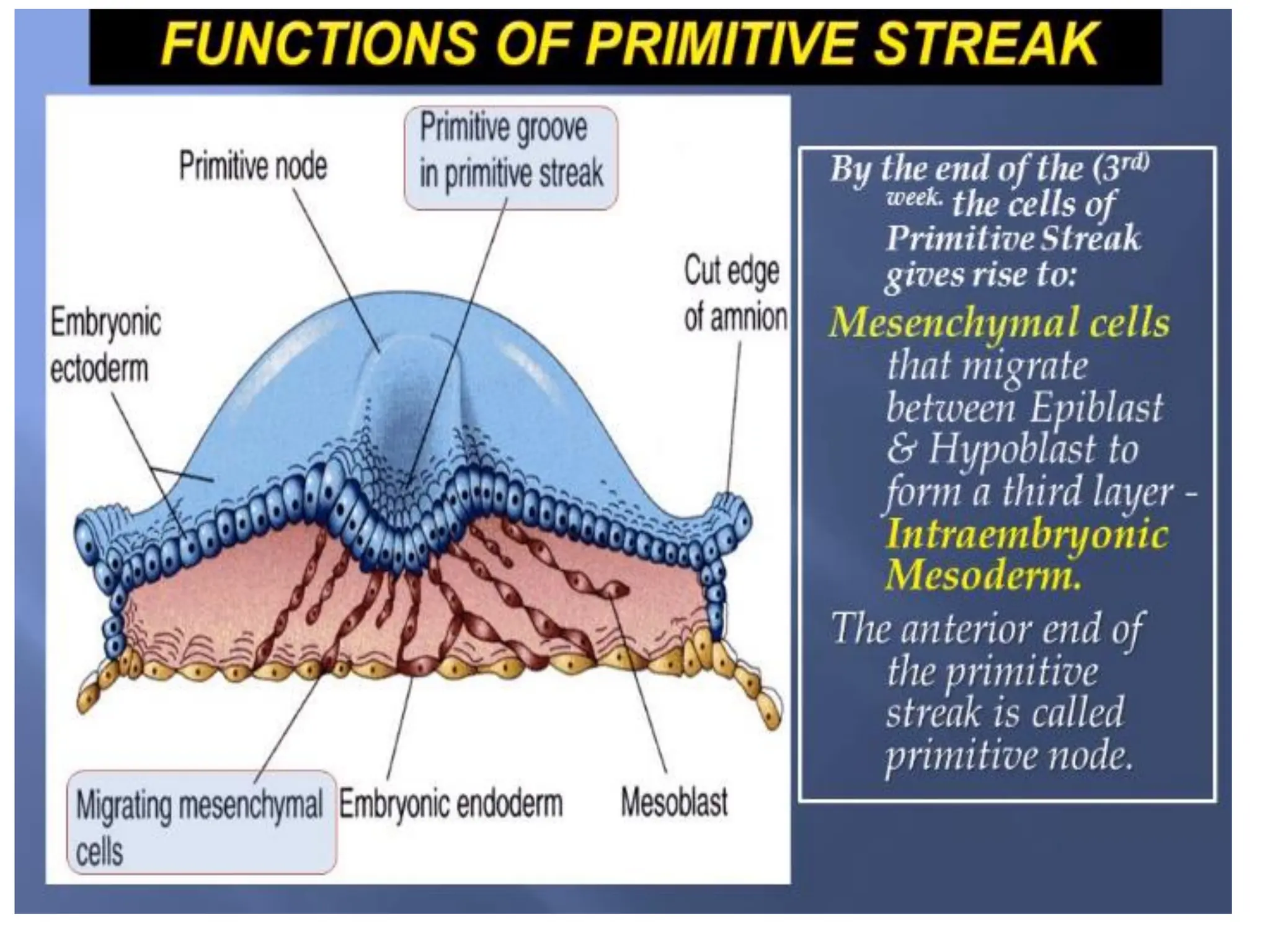
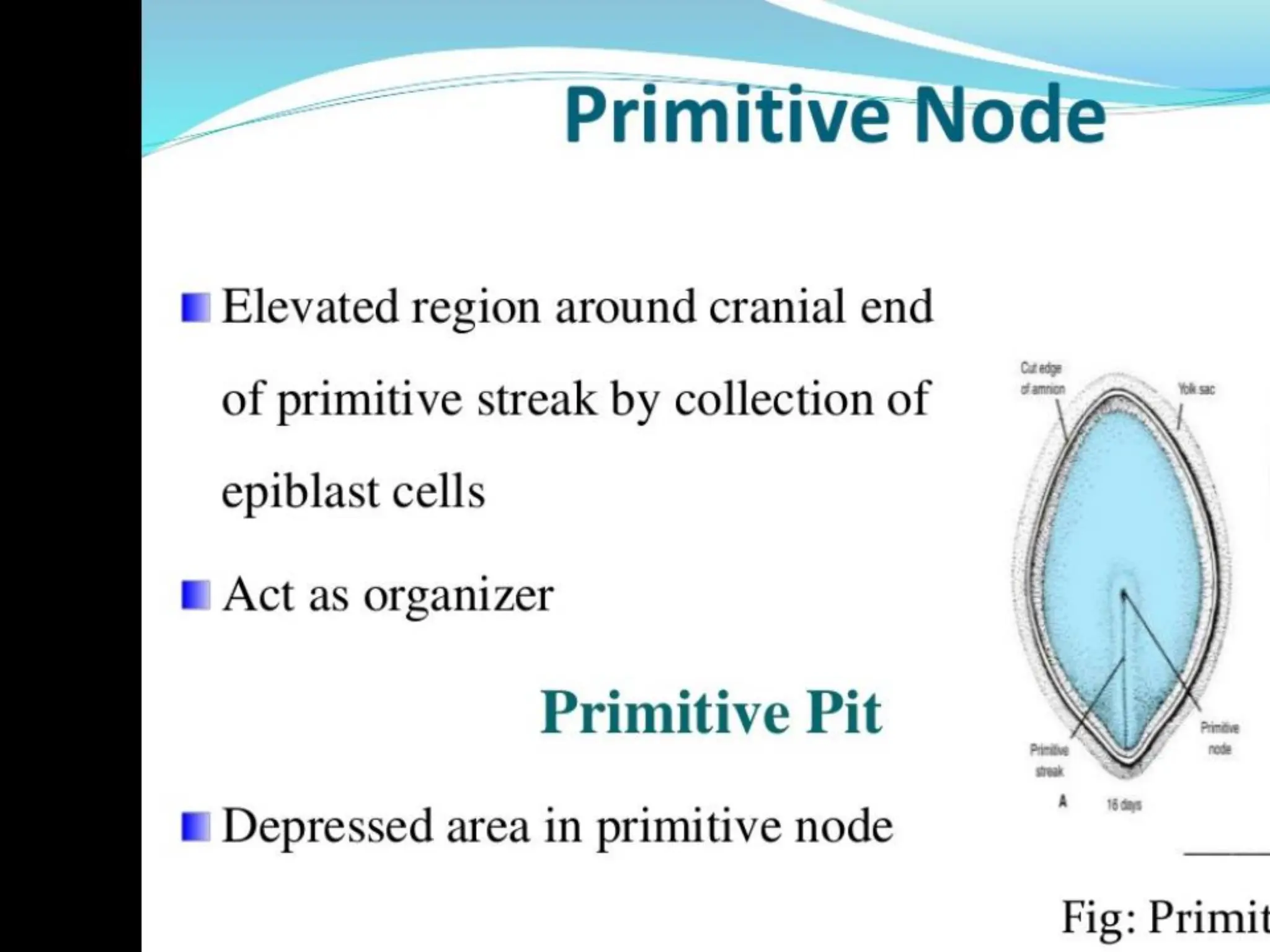
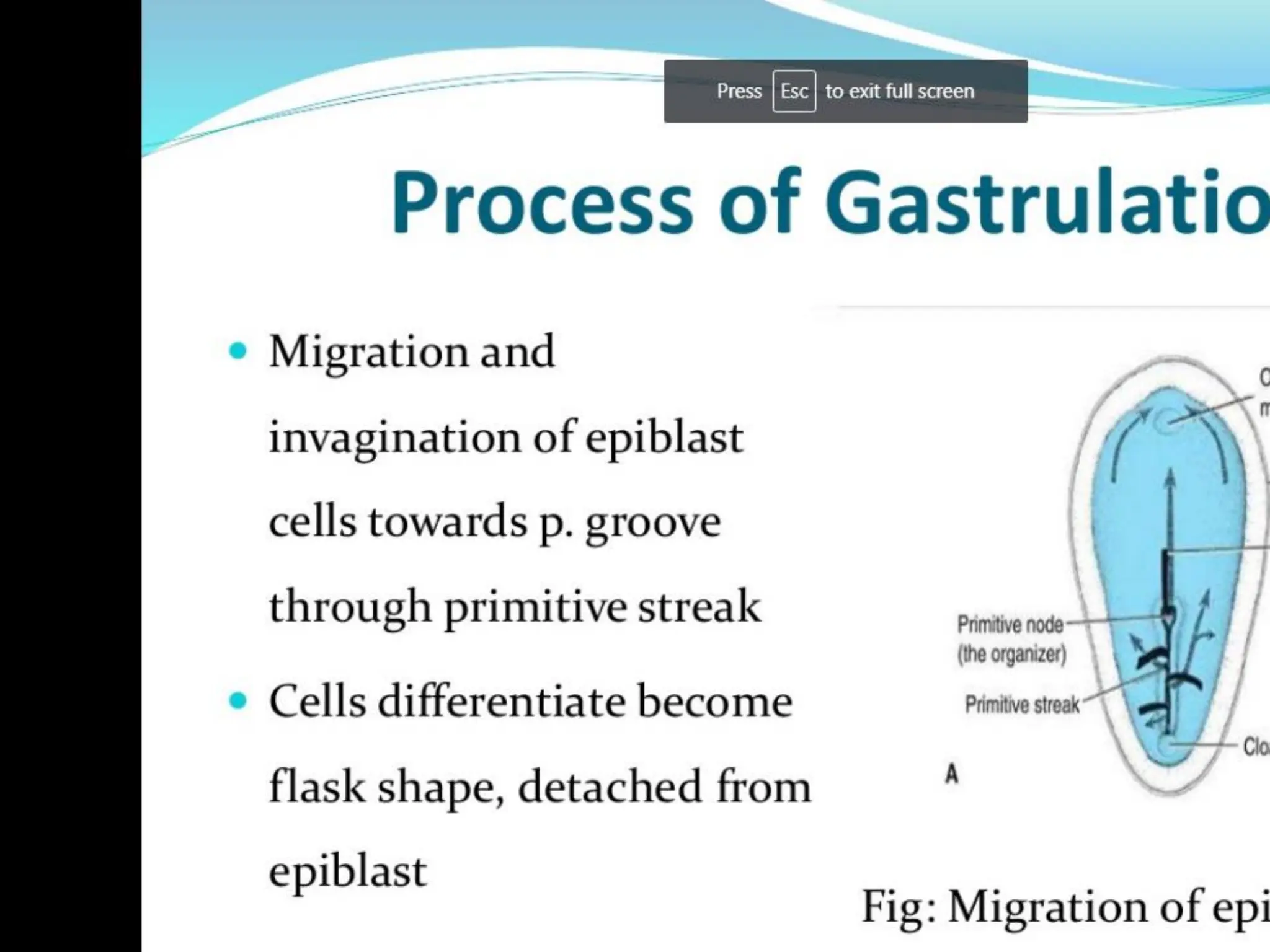
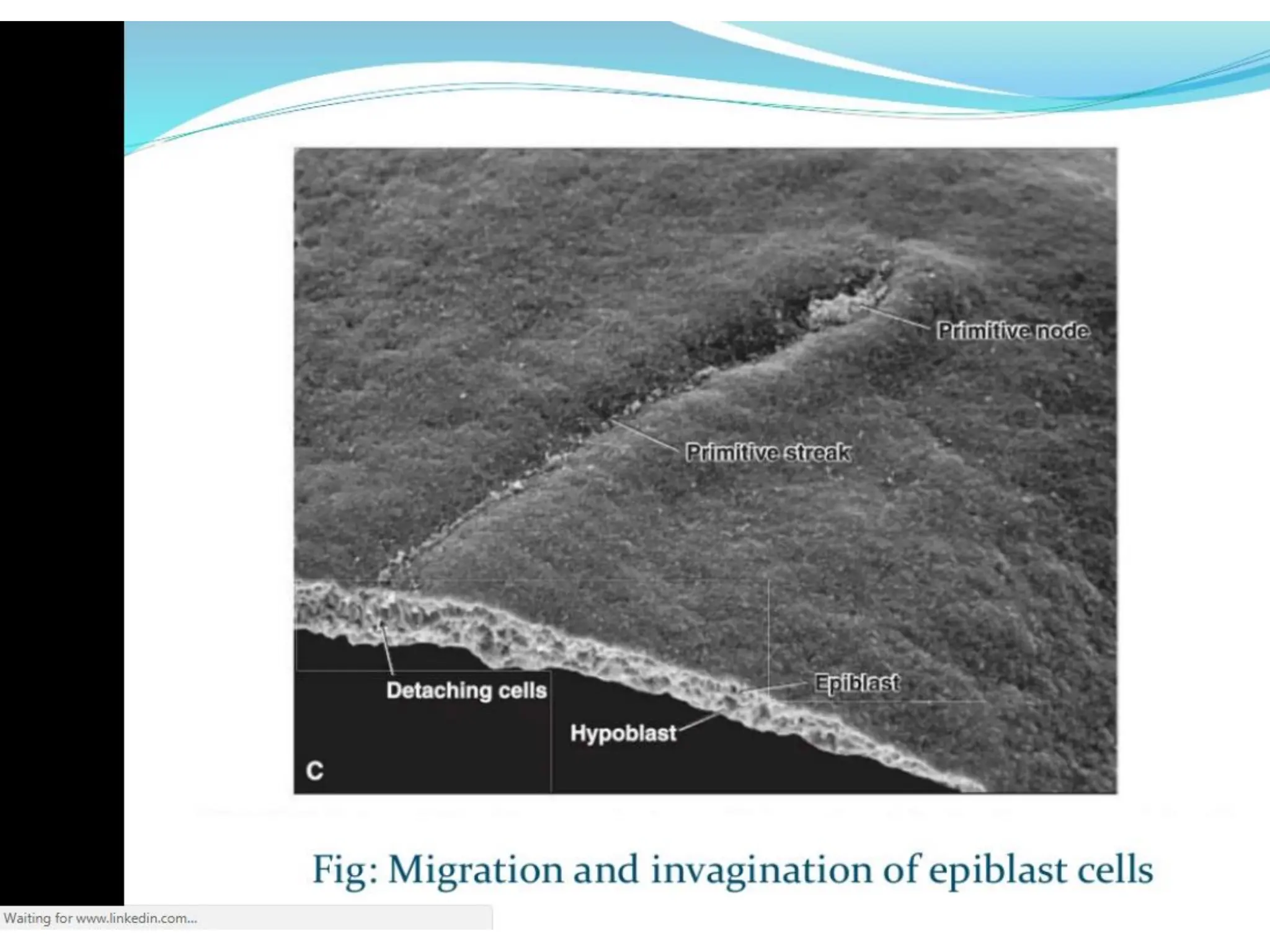
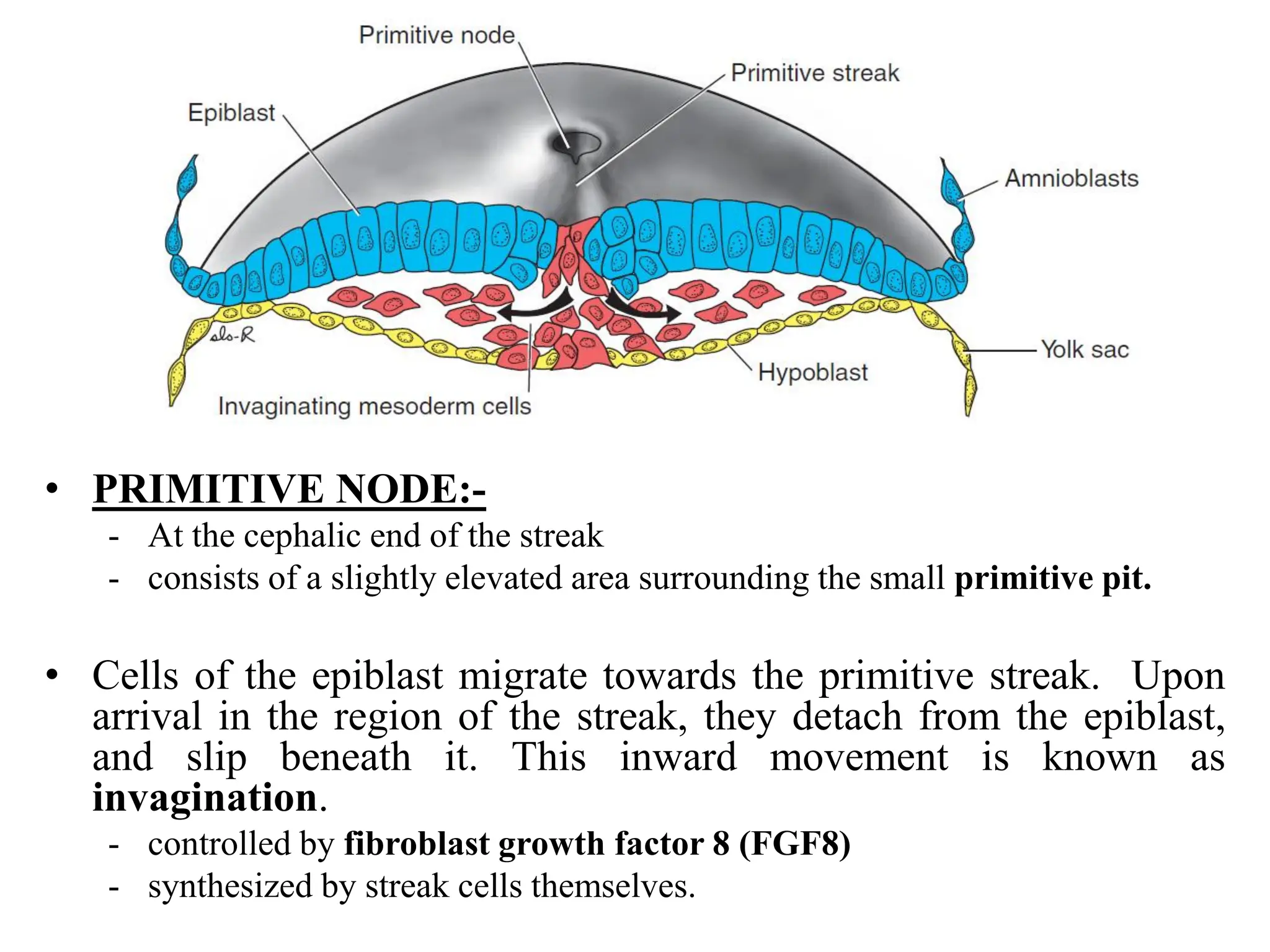
1. Gastrulation - the formation of the germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) through invagination of cells through the primitive streak, controlled by FGF8.
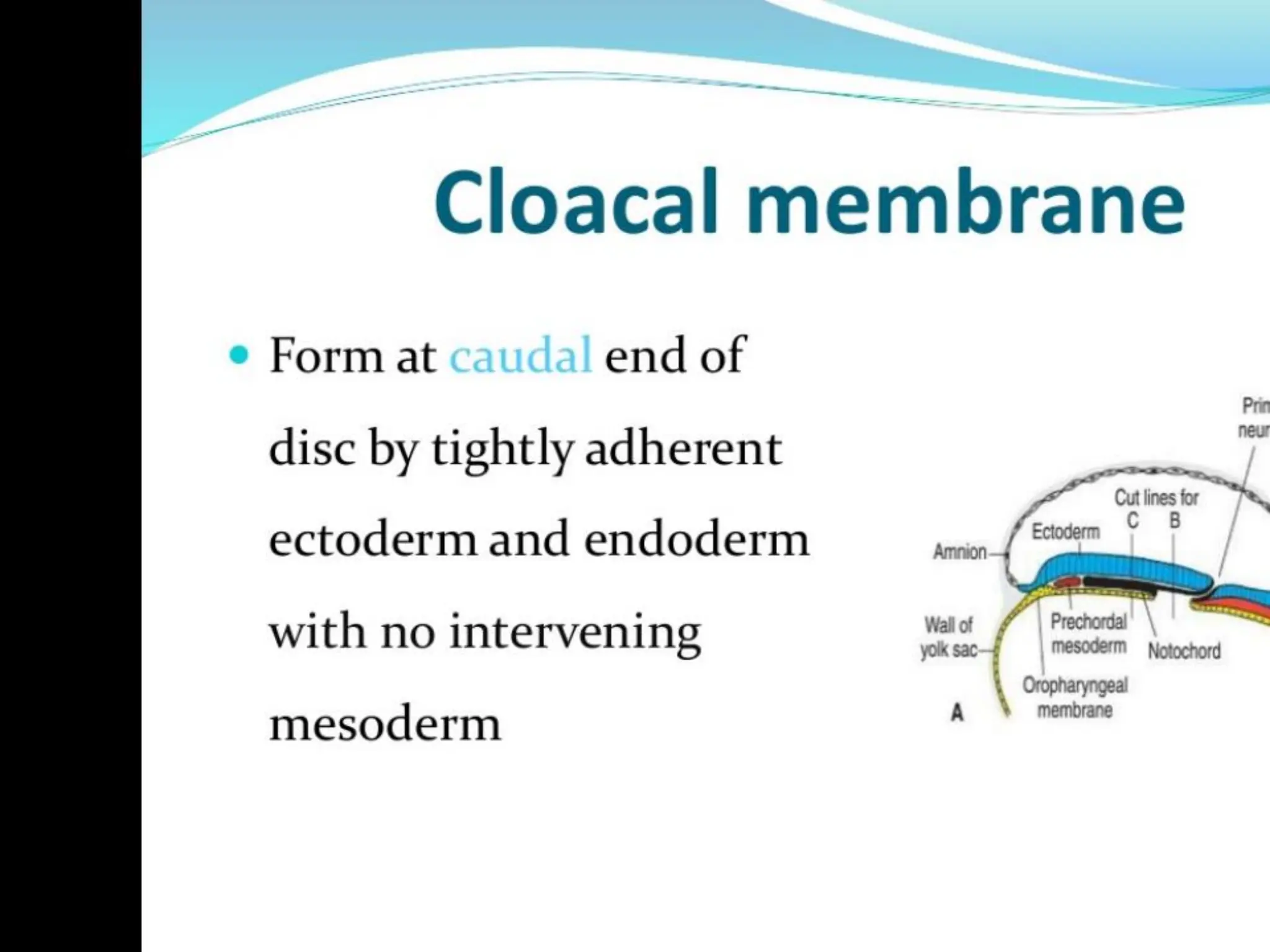
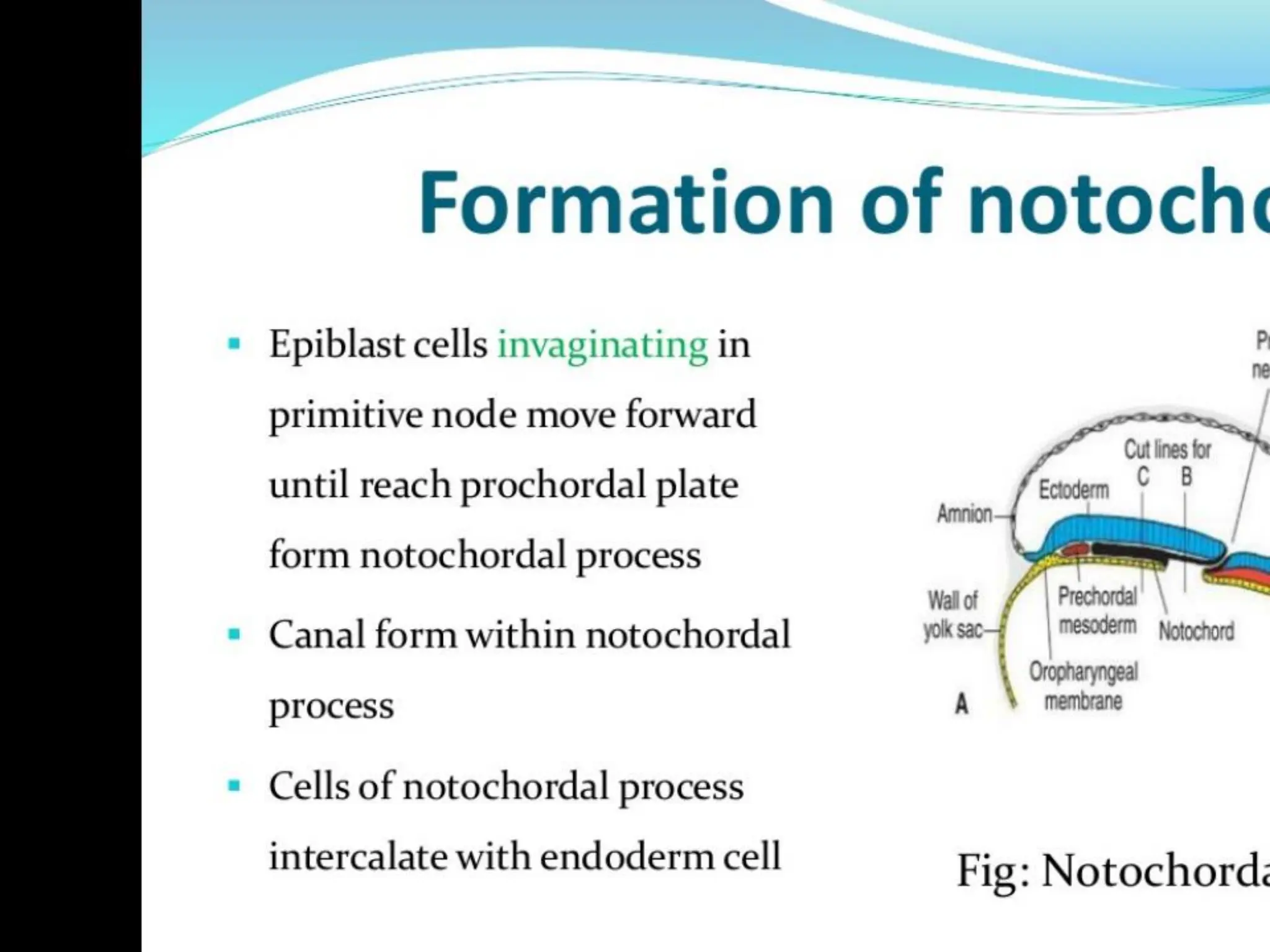
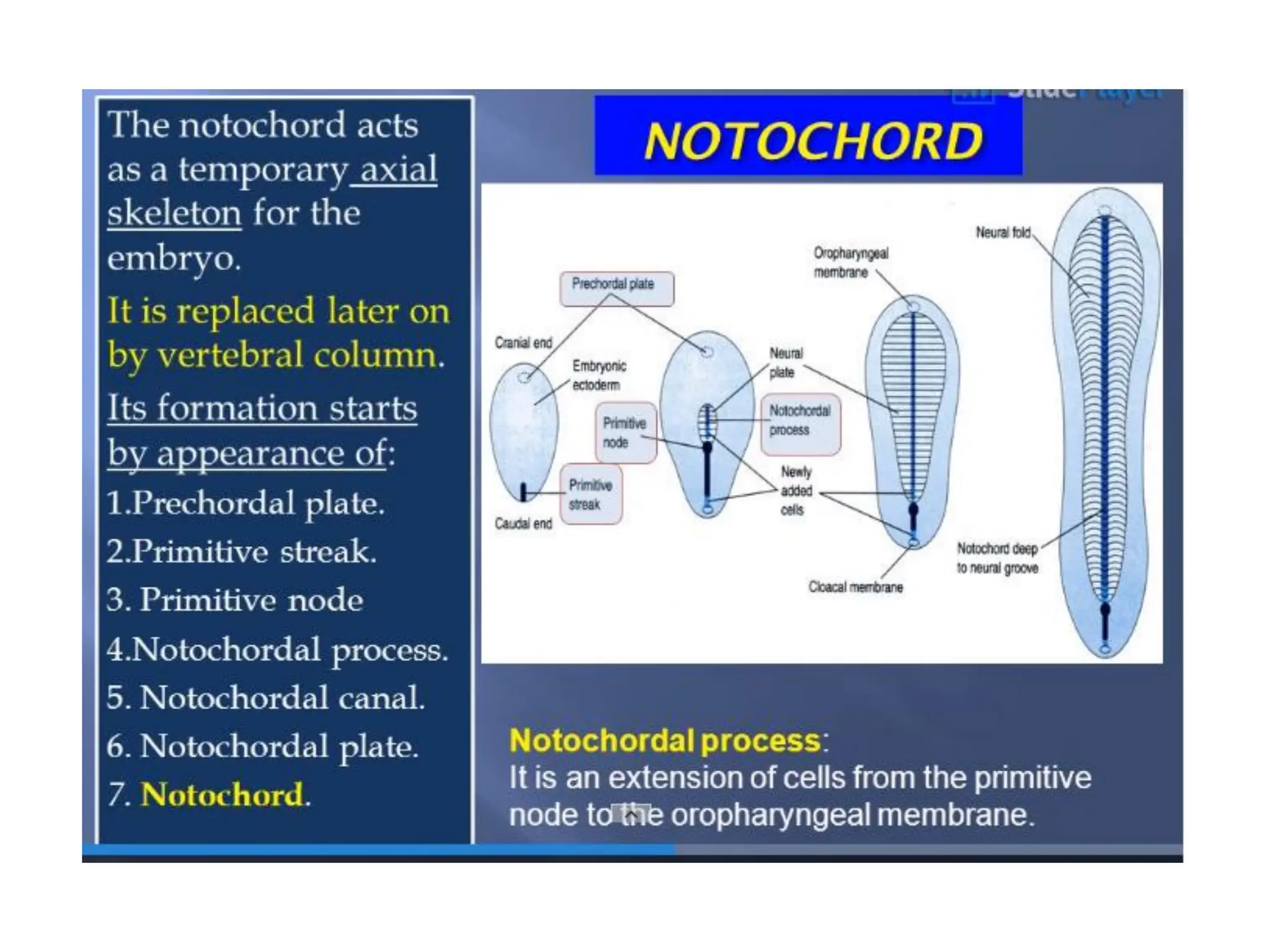
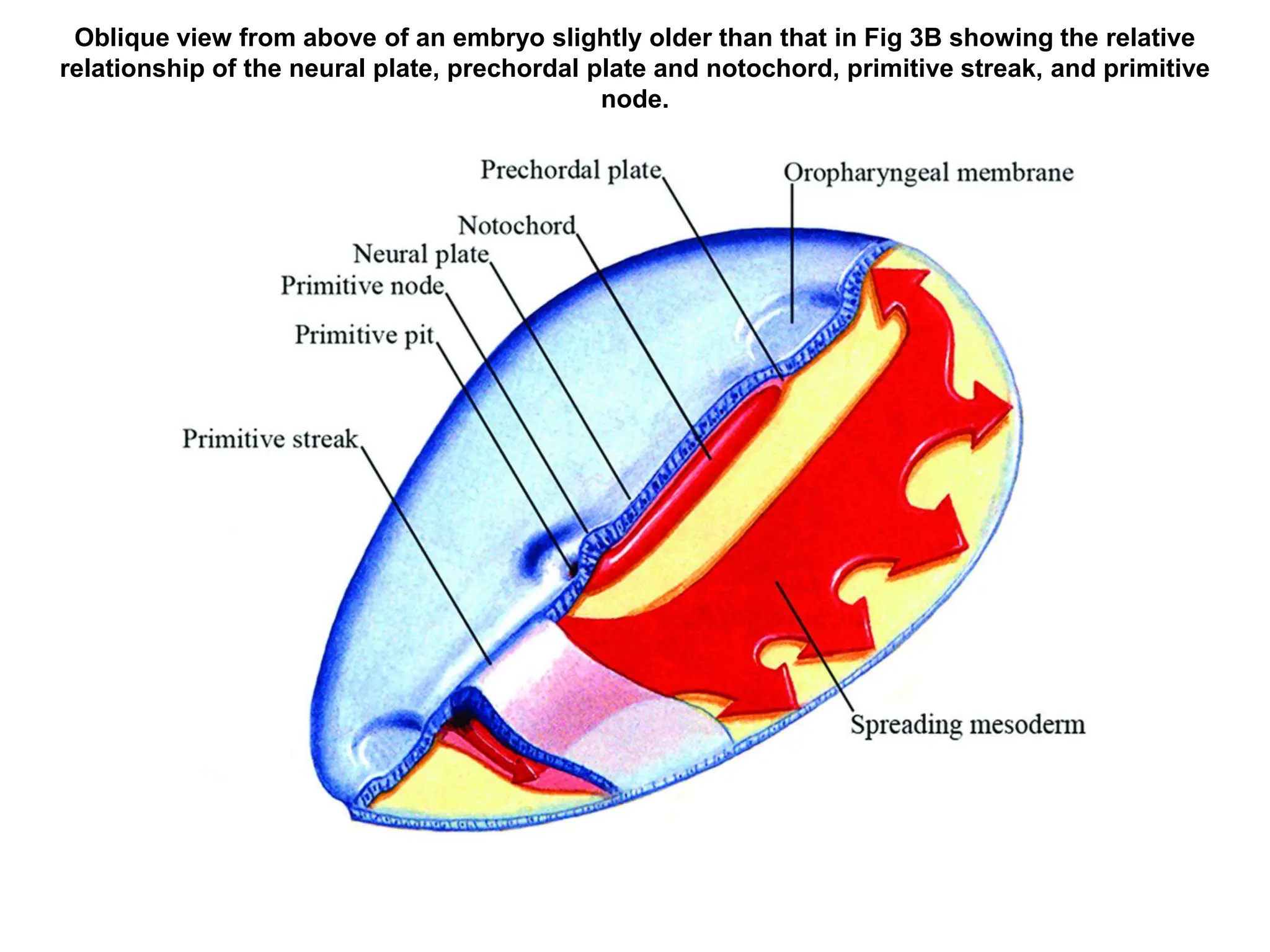
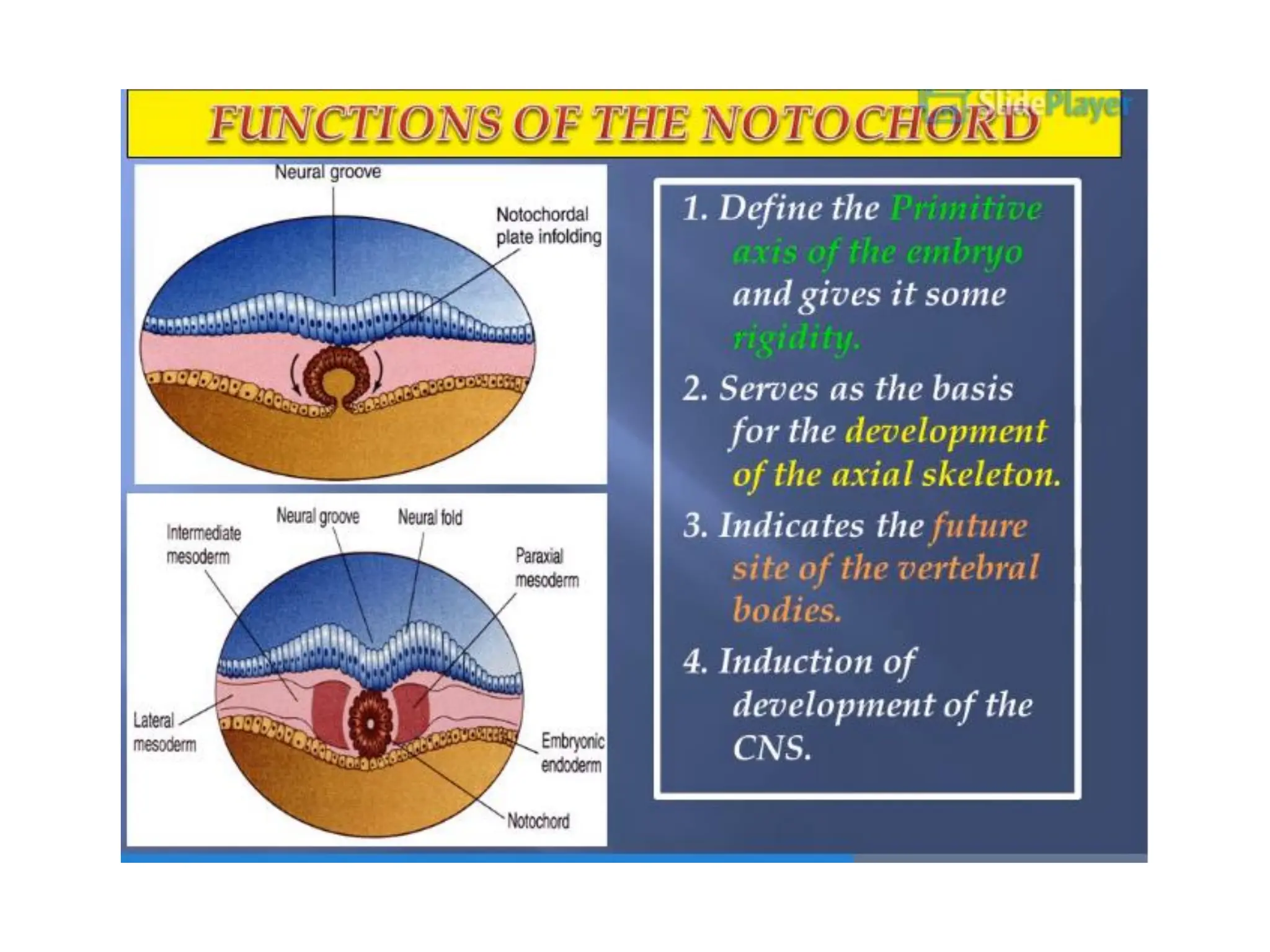
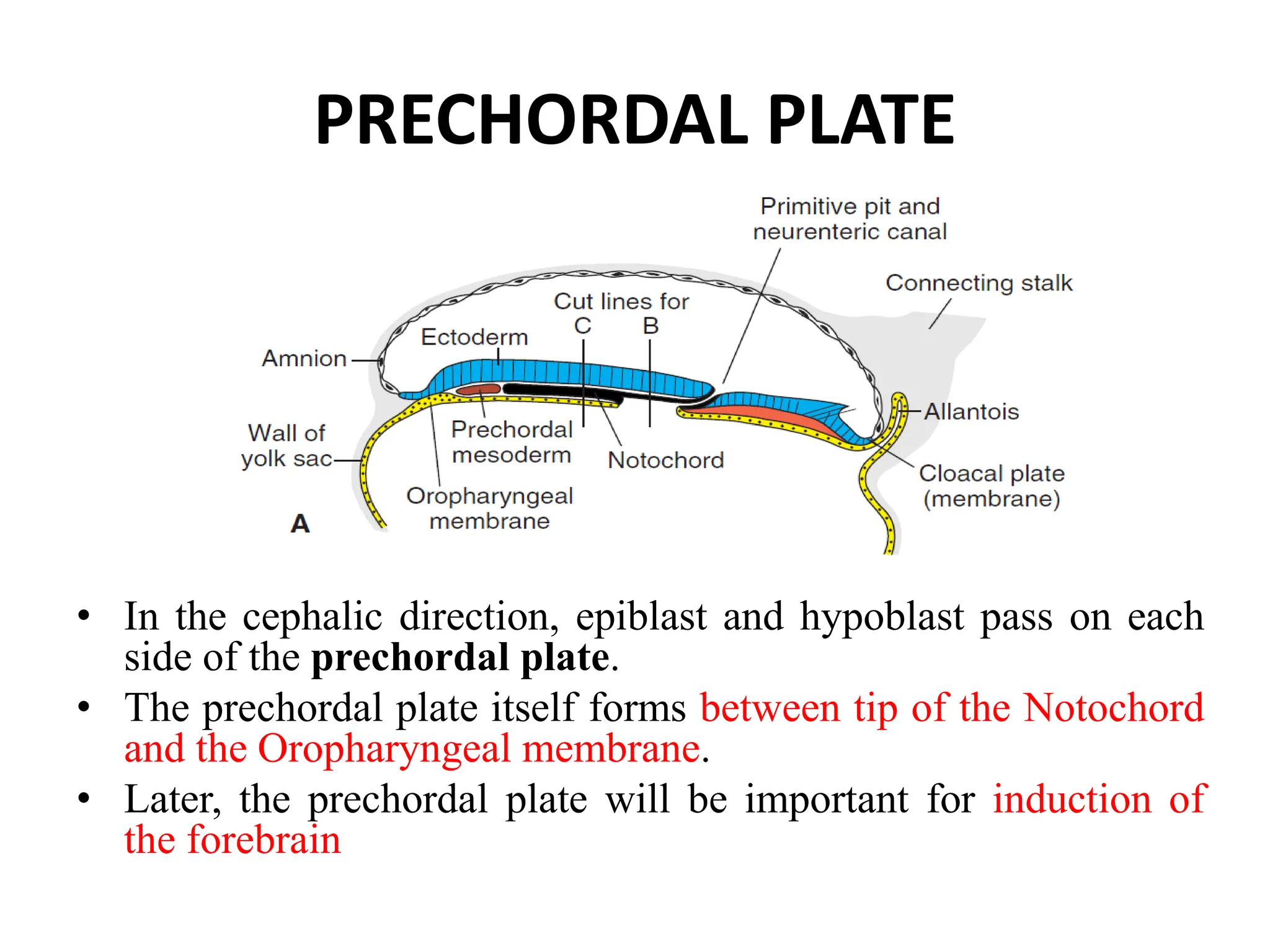
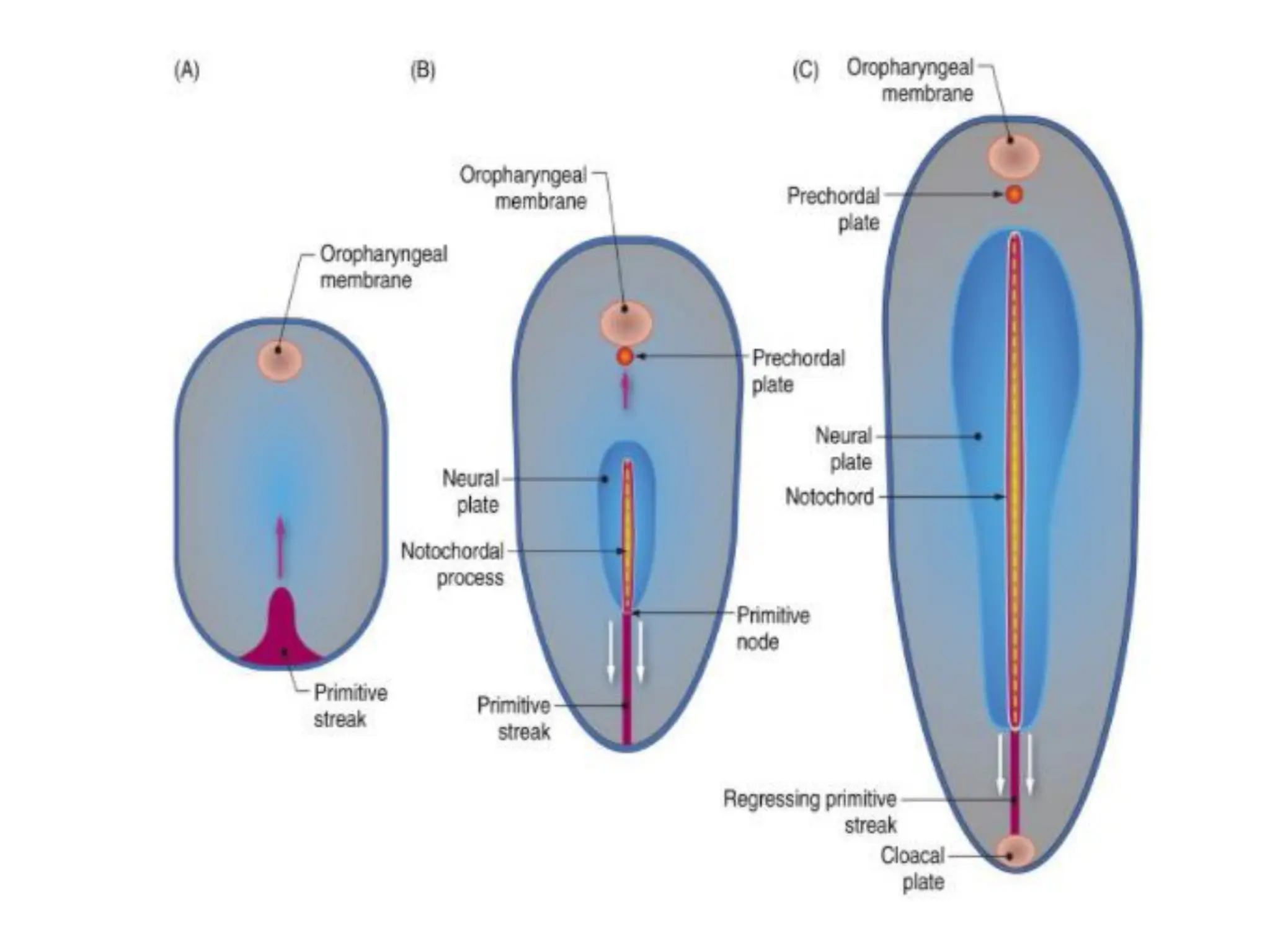
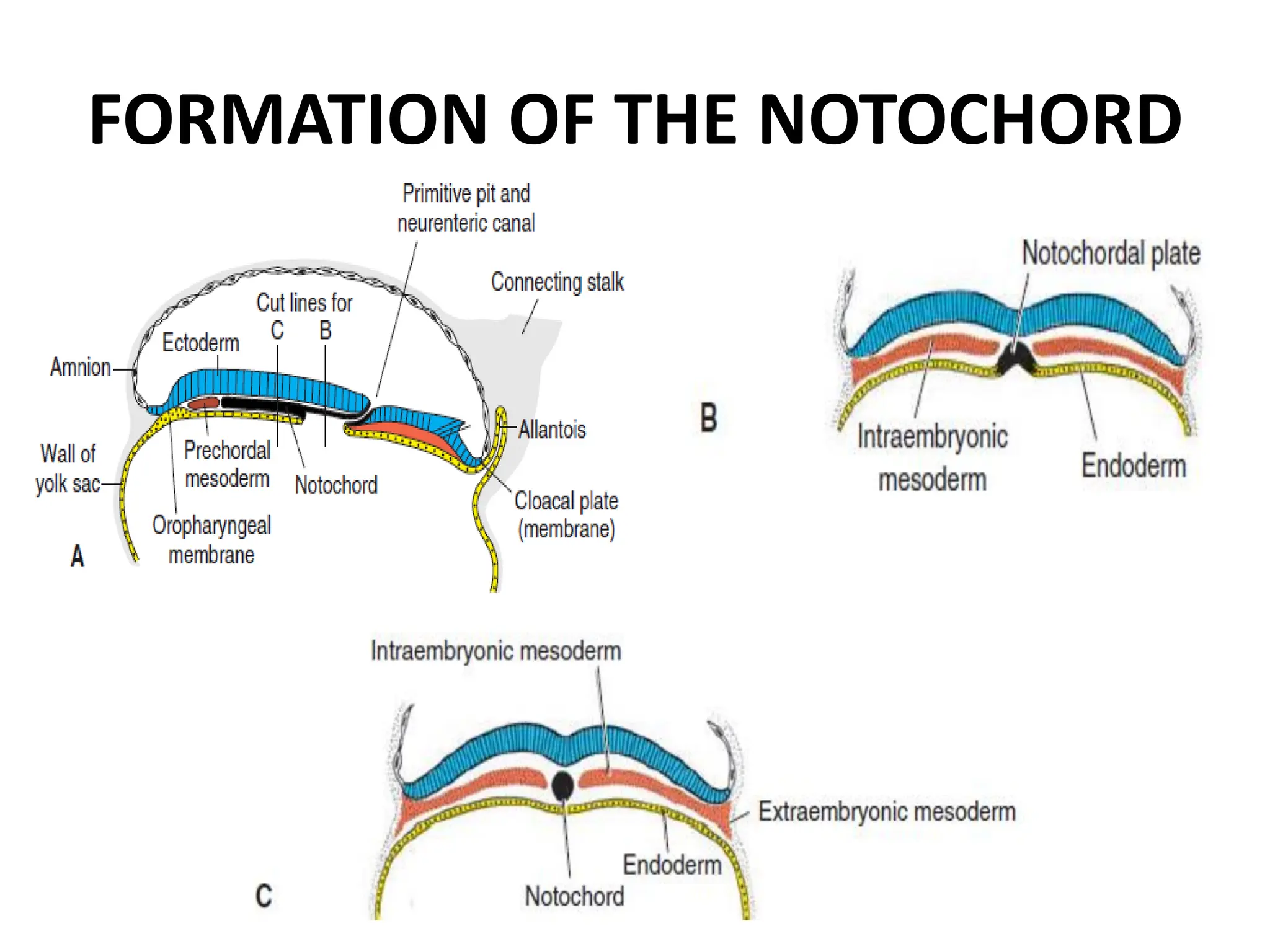
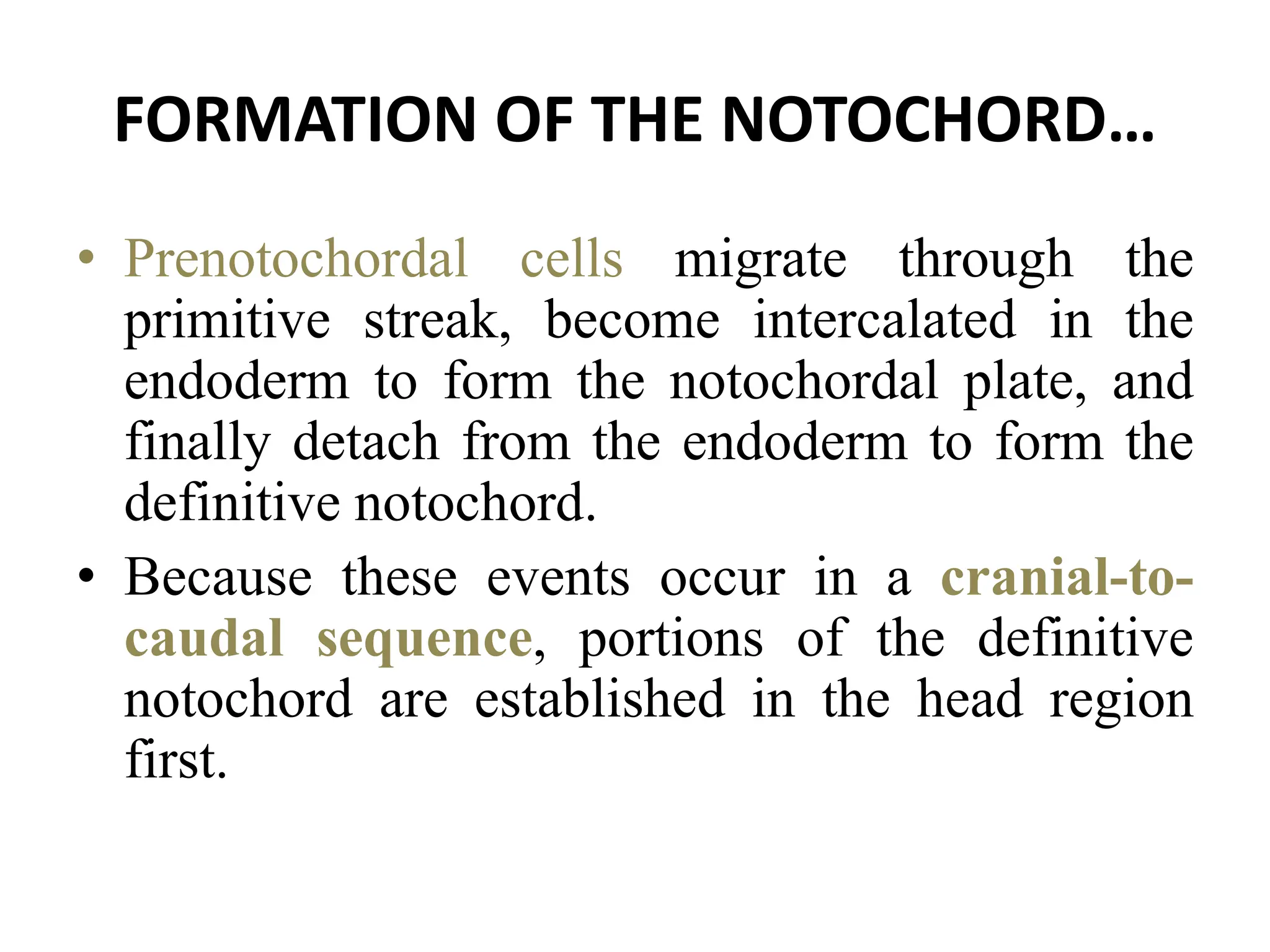
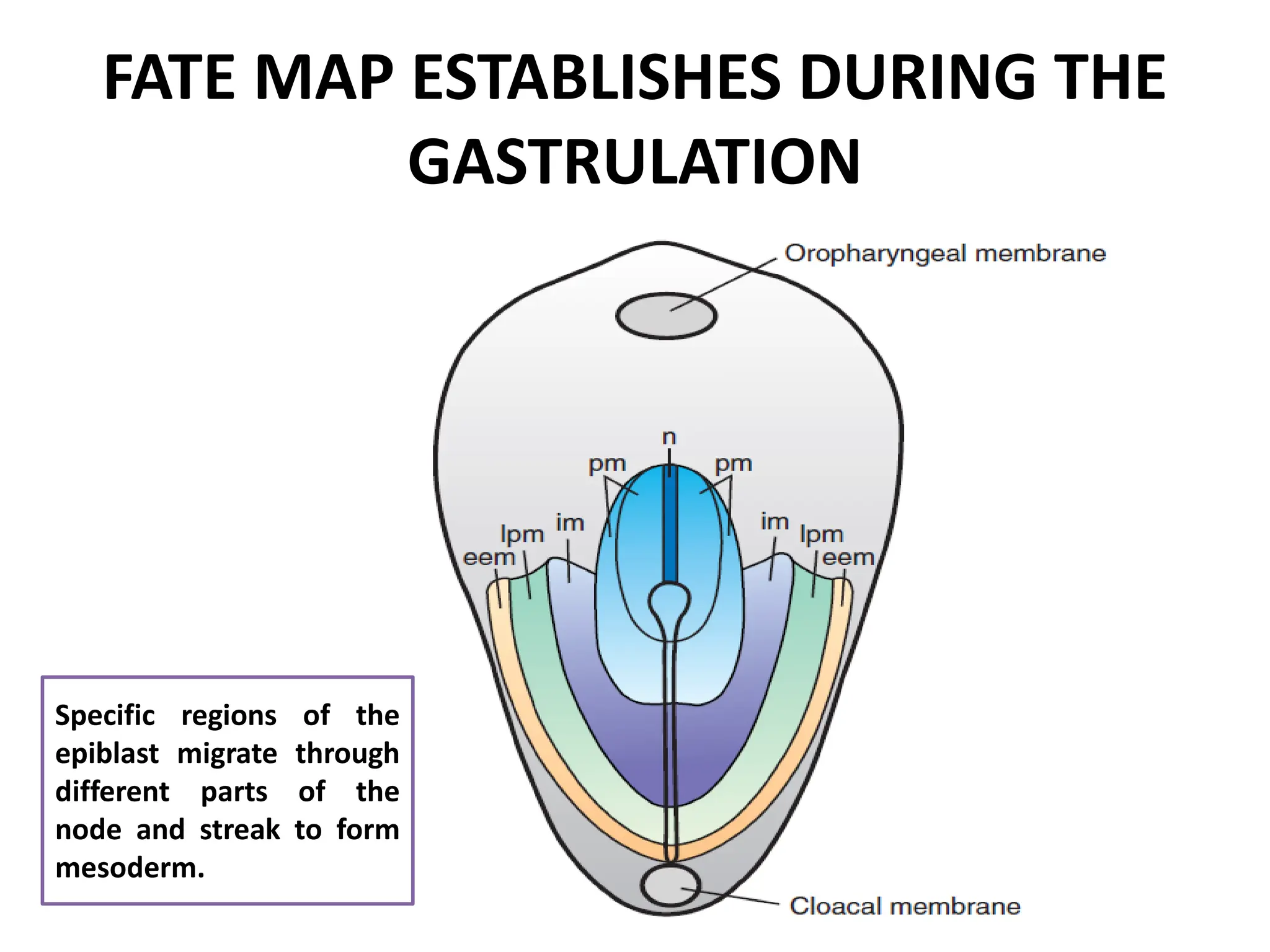
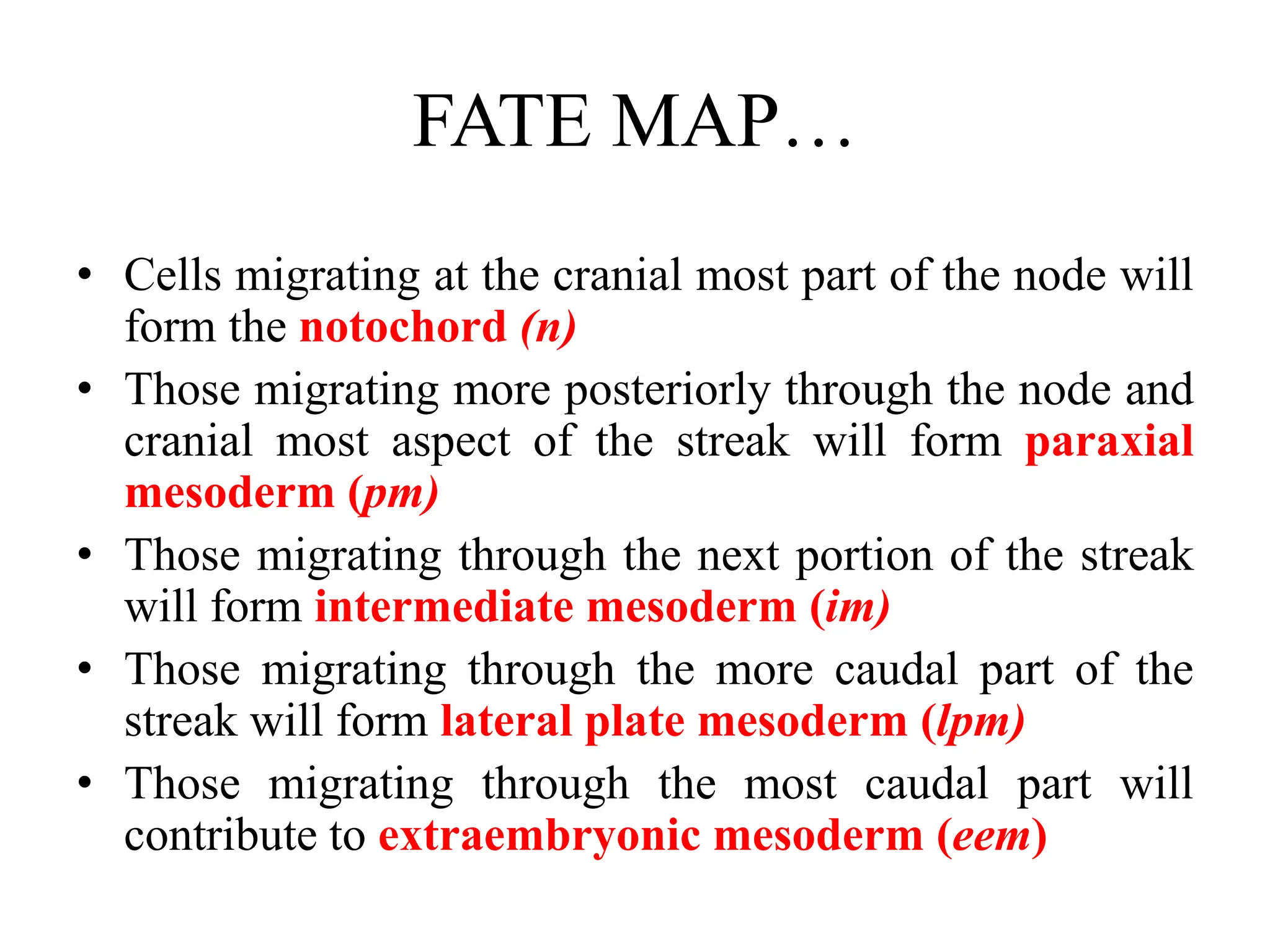
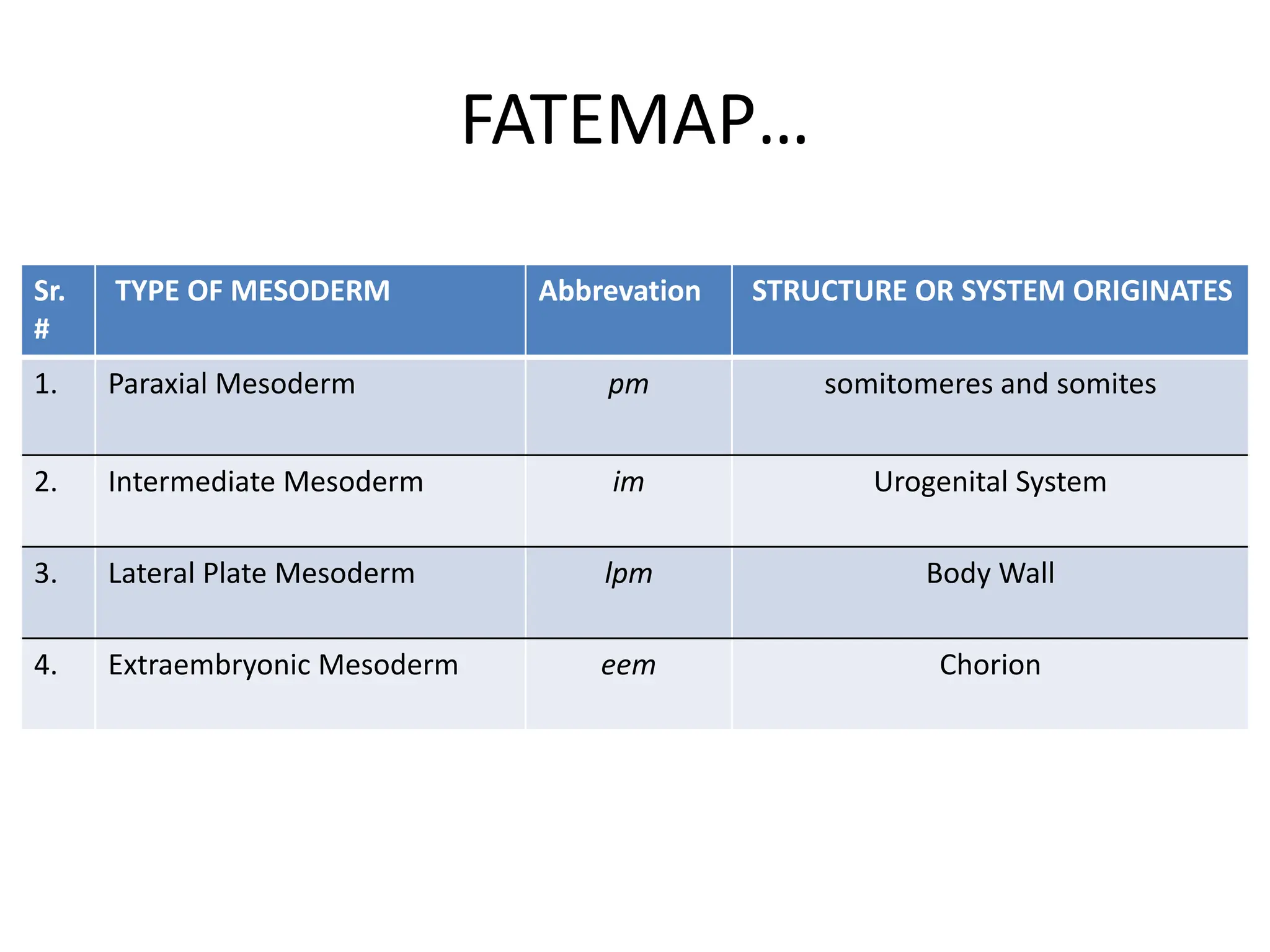
2. Formation of structures like the notochord and prechordal plate, and how the fate map is established during gastrulation to determine tissue origins.
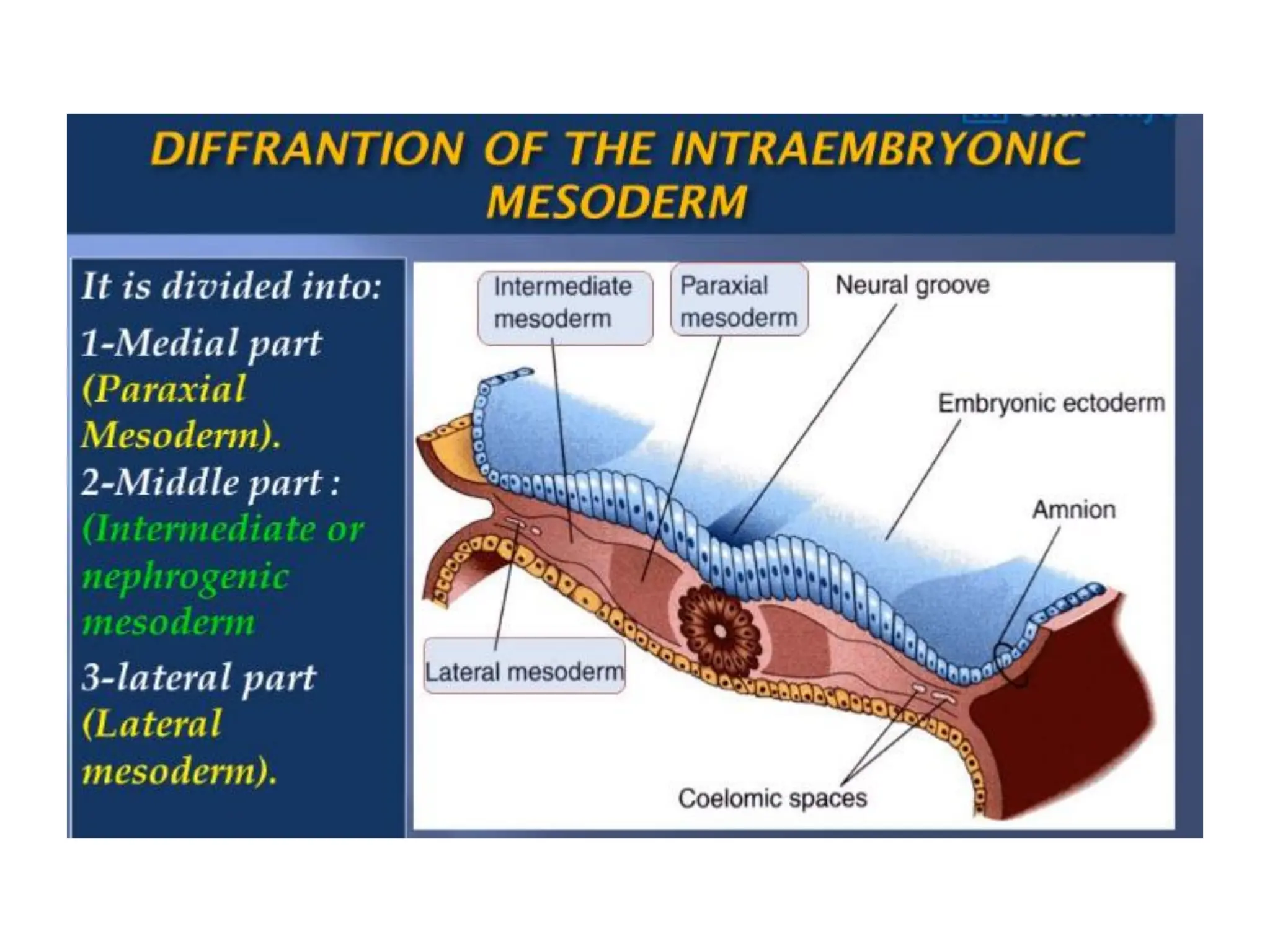
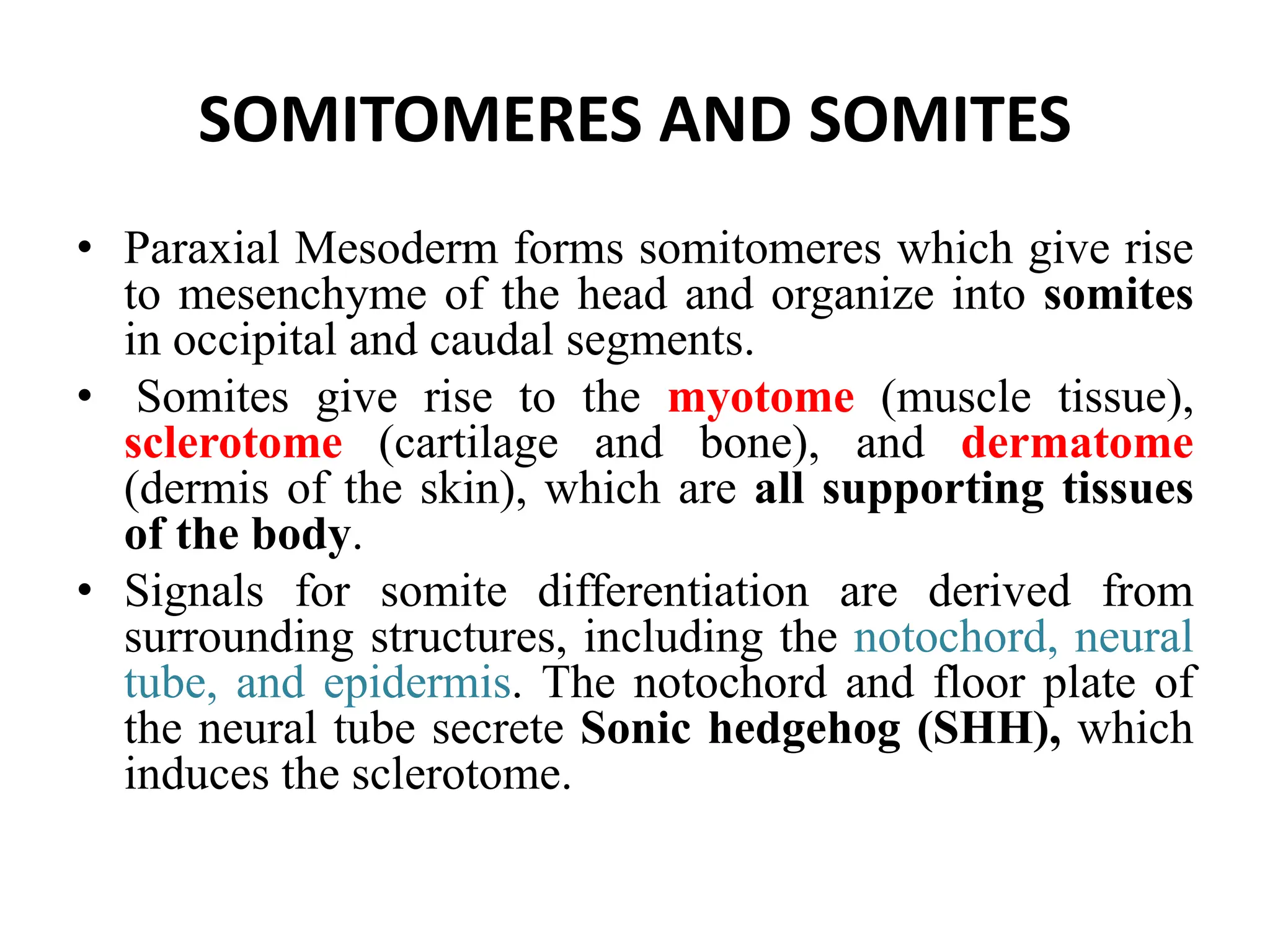
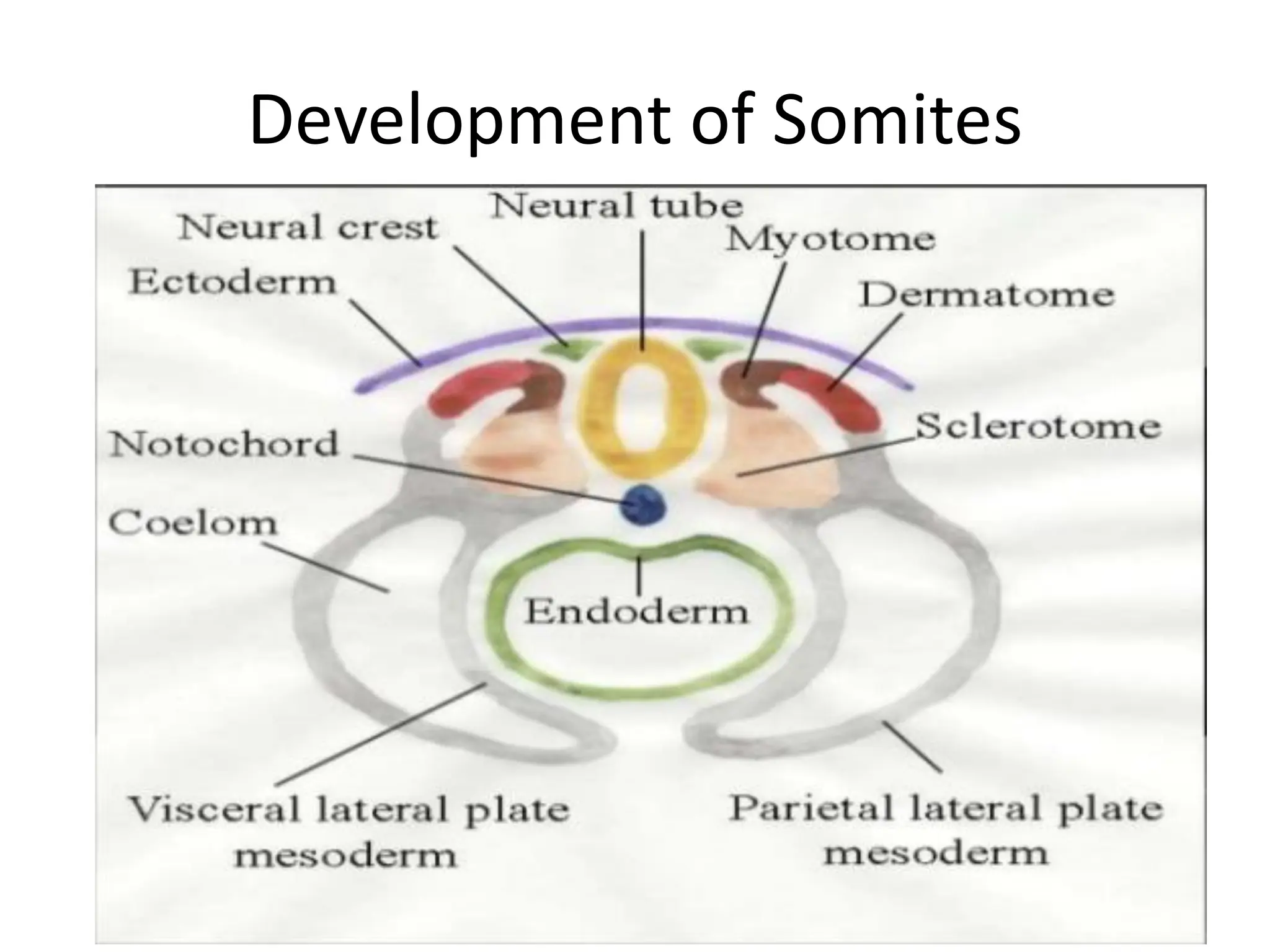
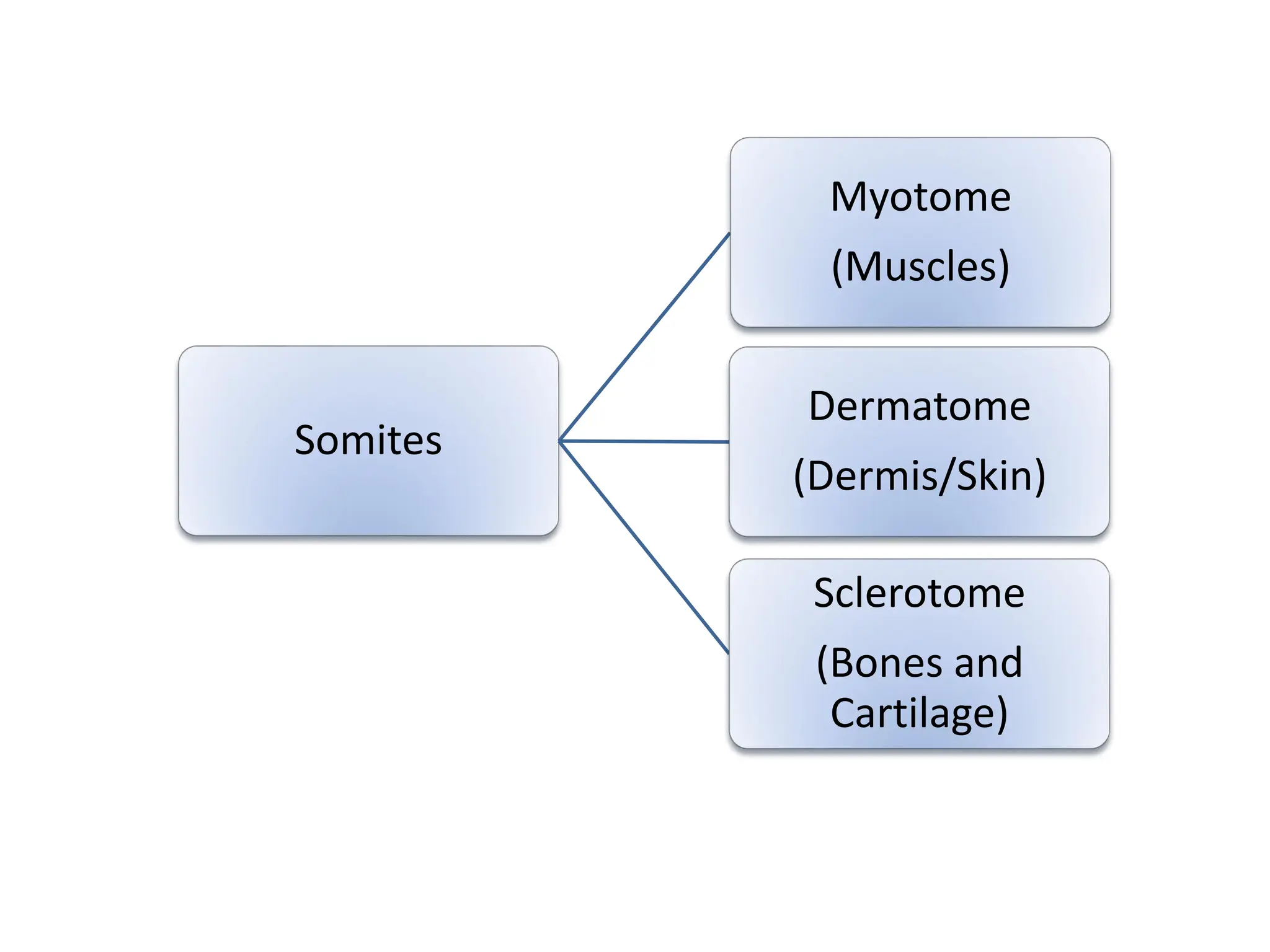
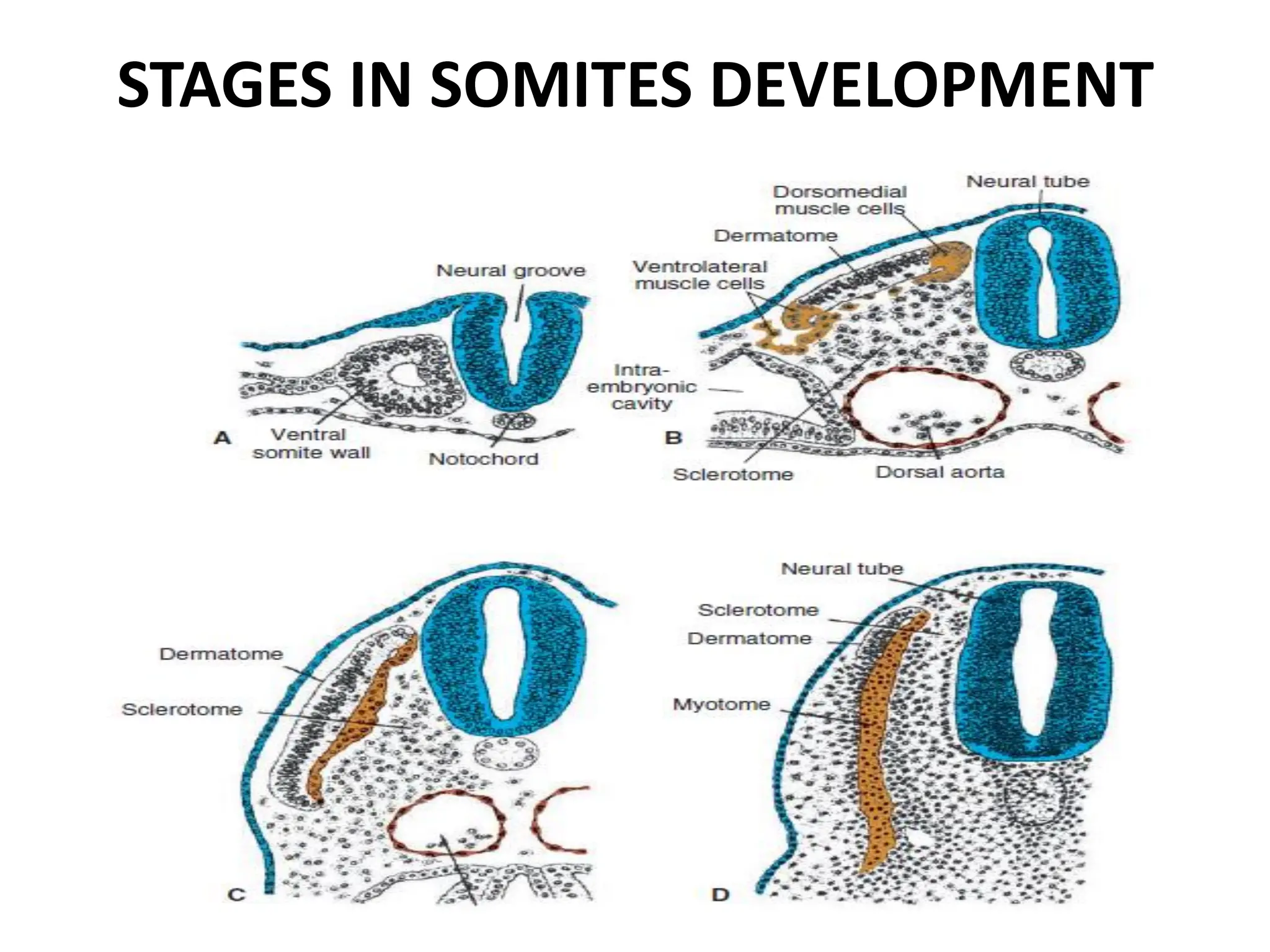
3. Somitomere and somite formation from the paraxial mesoderm, which will give rise to muscles, cartilage/bones, and skin