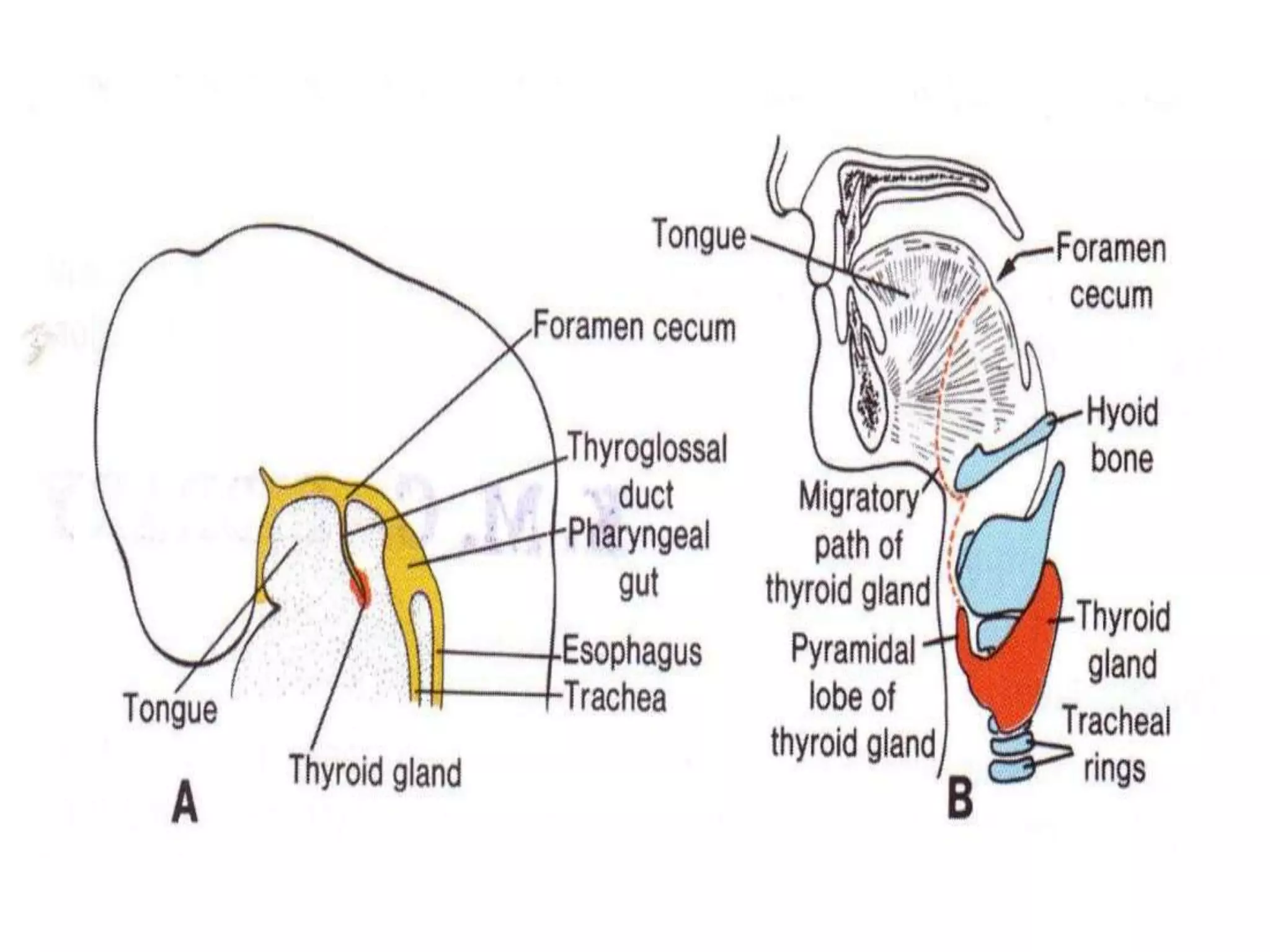
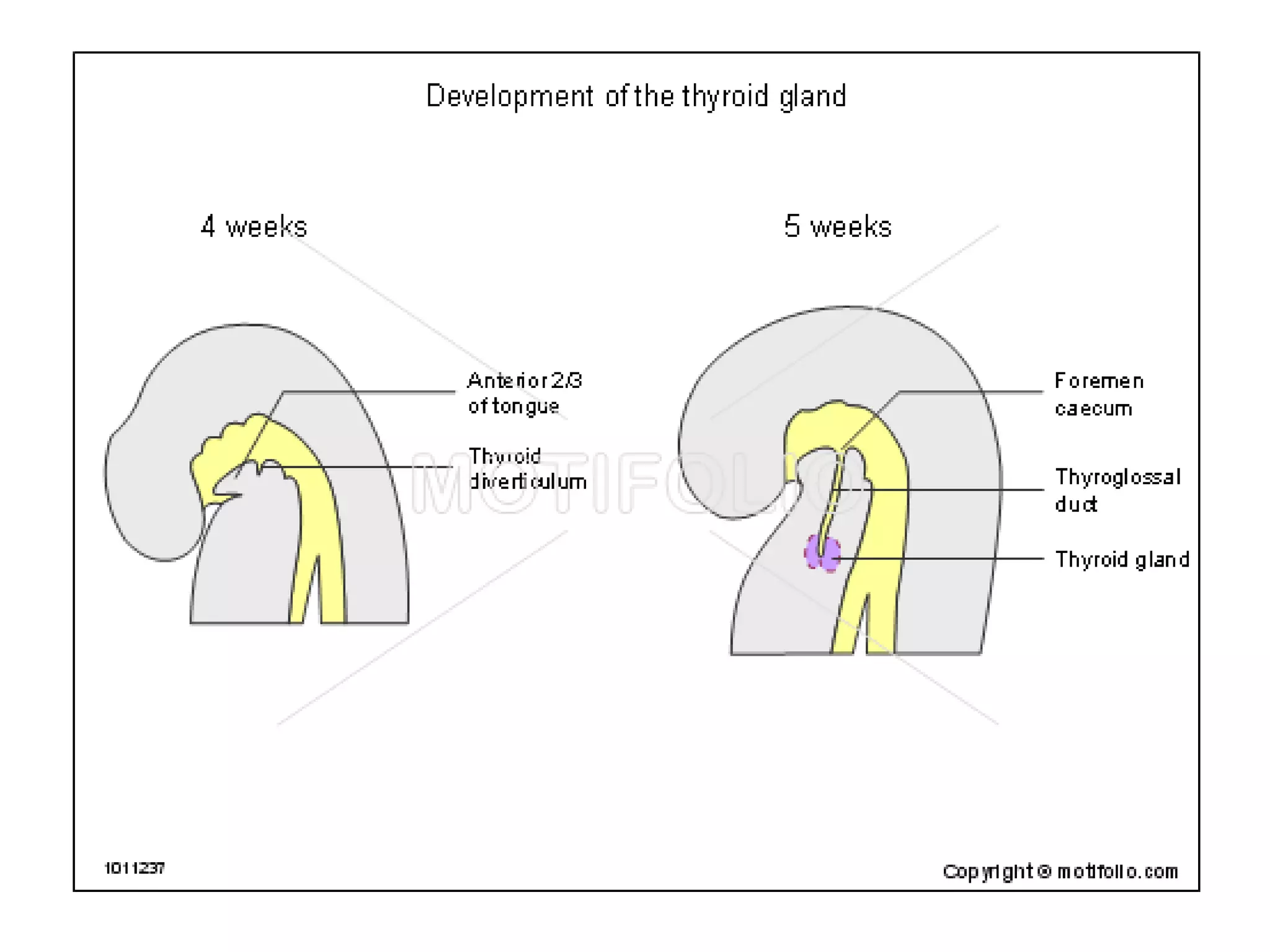
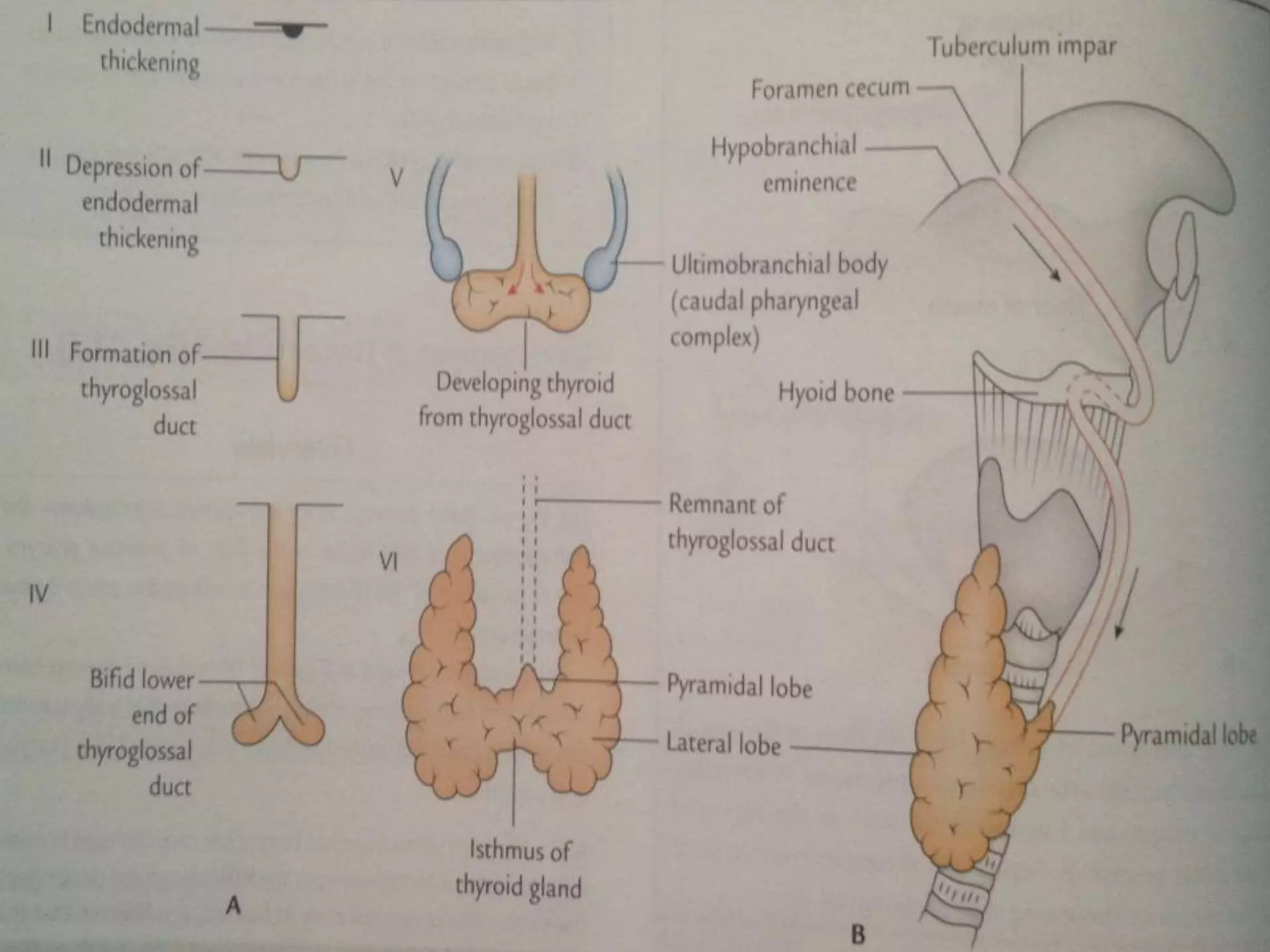
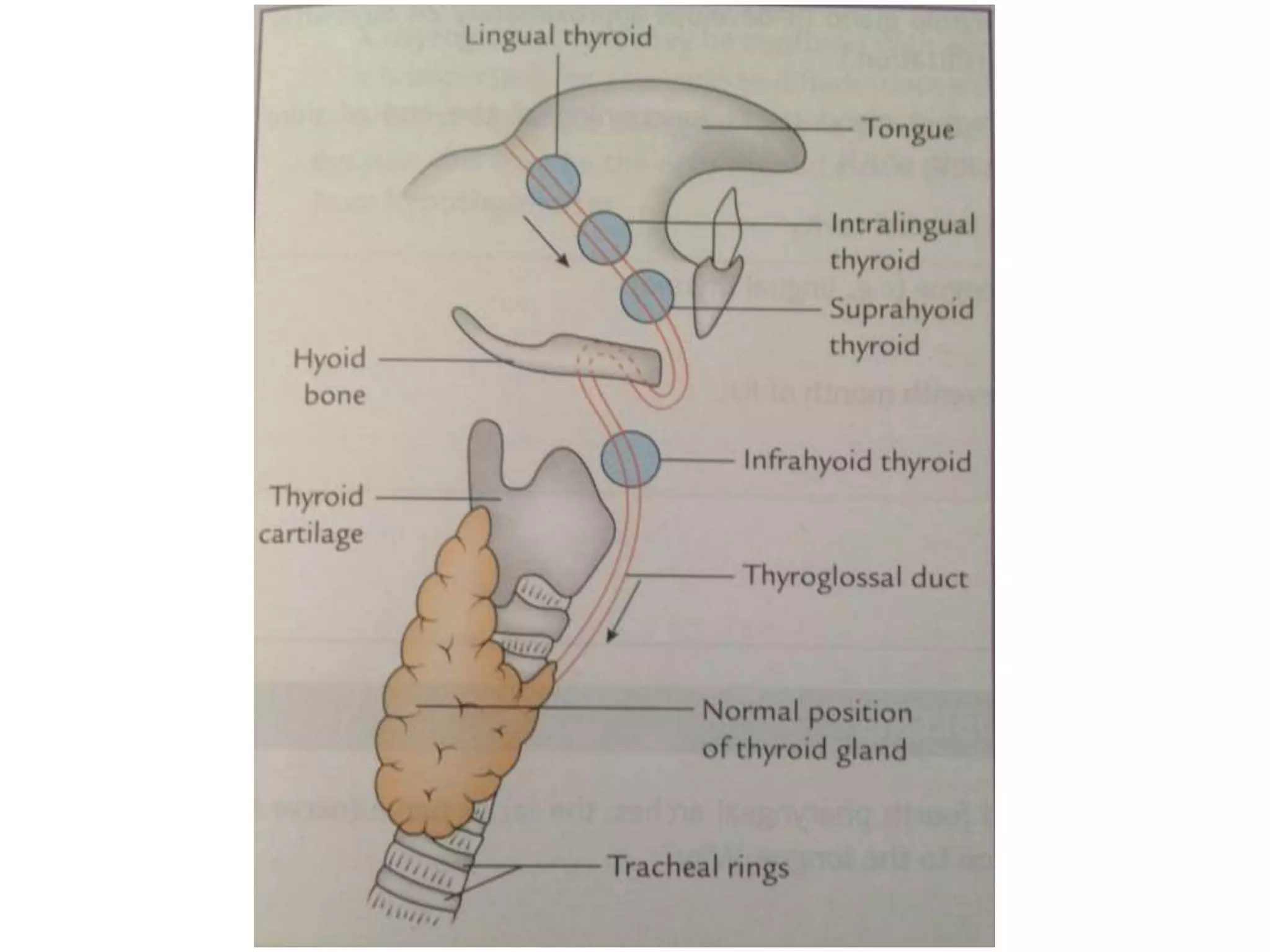
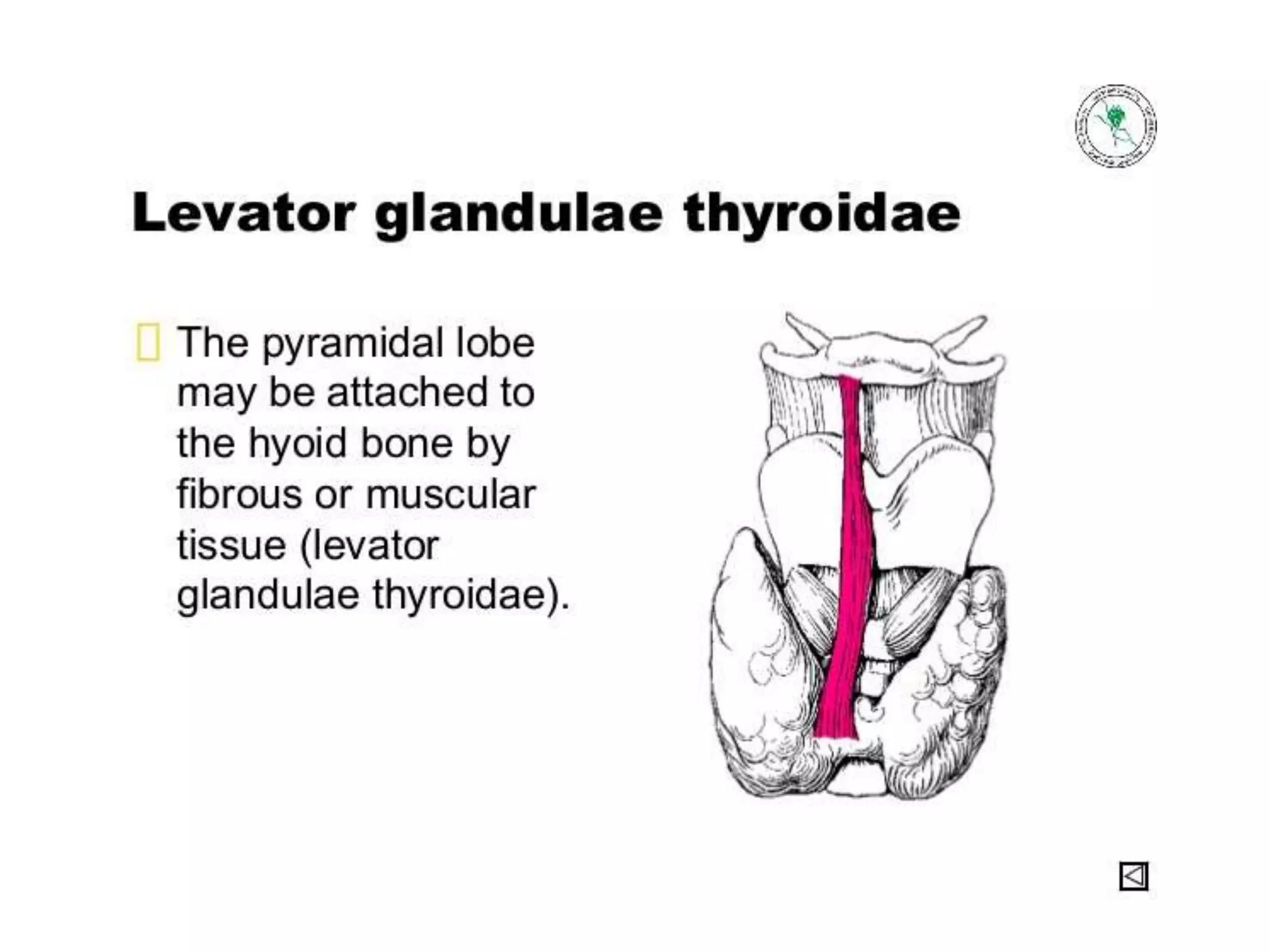
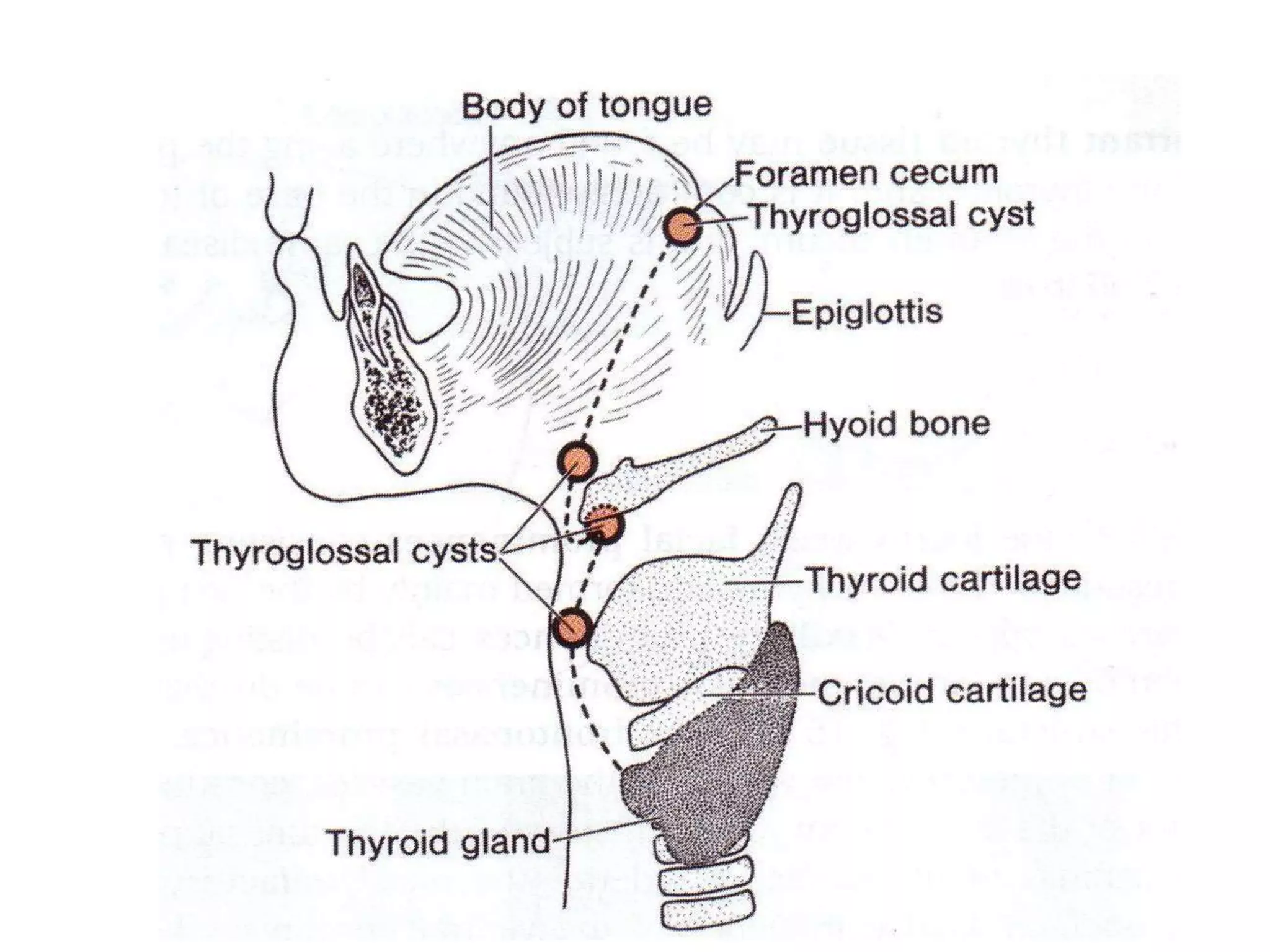
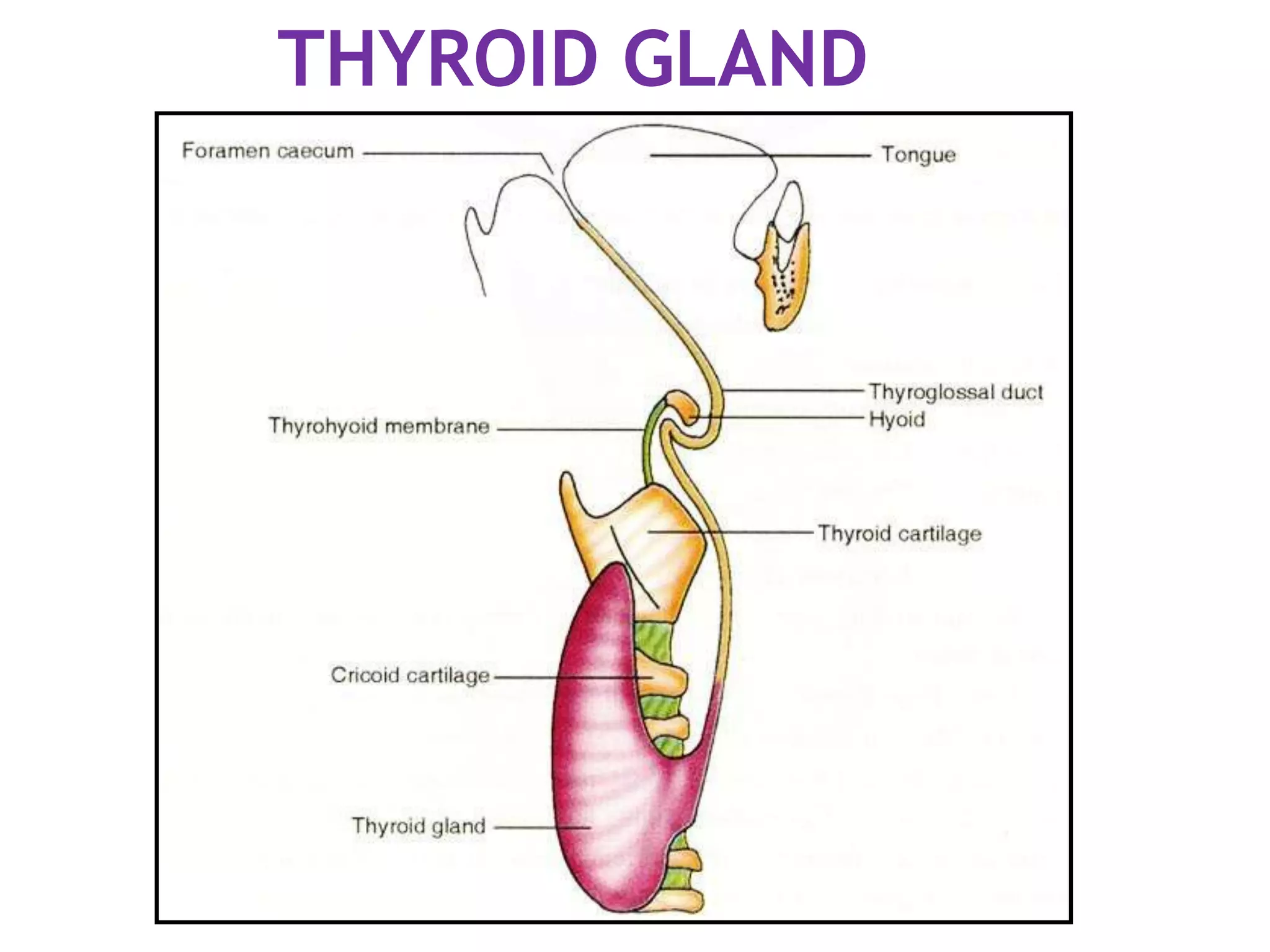
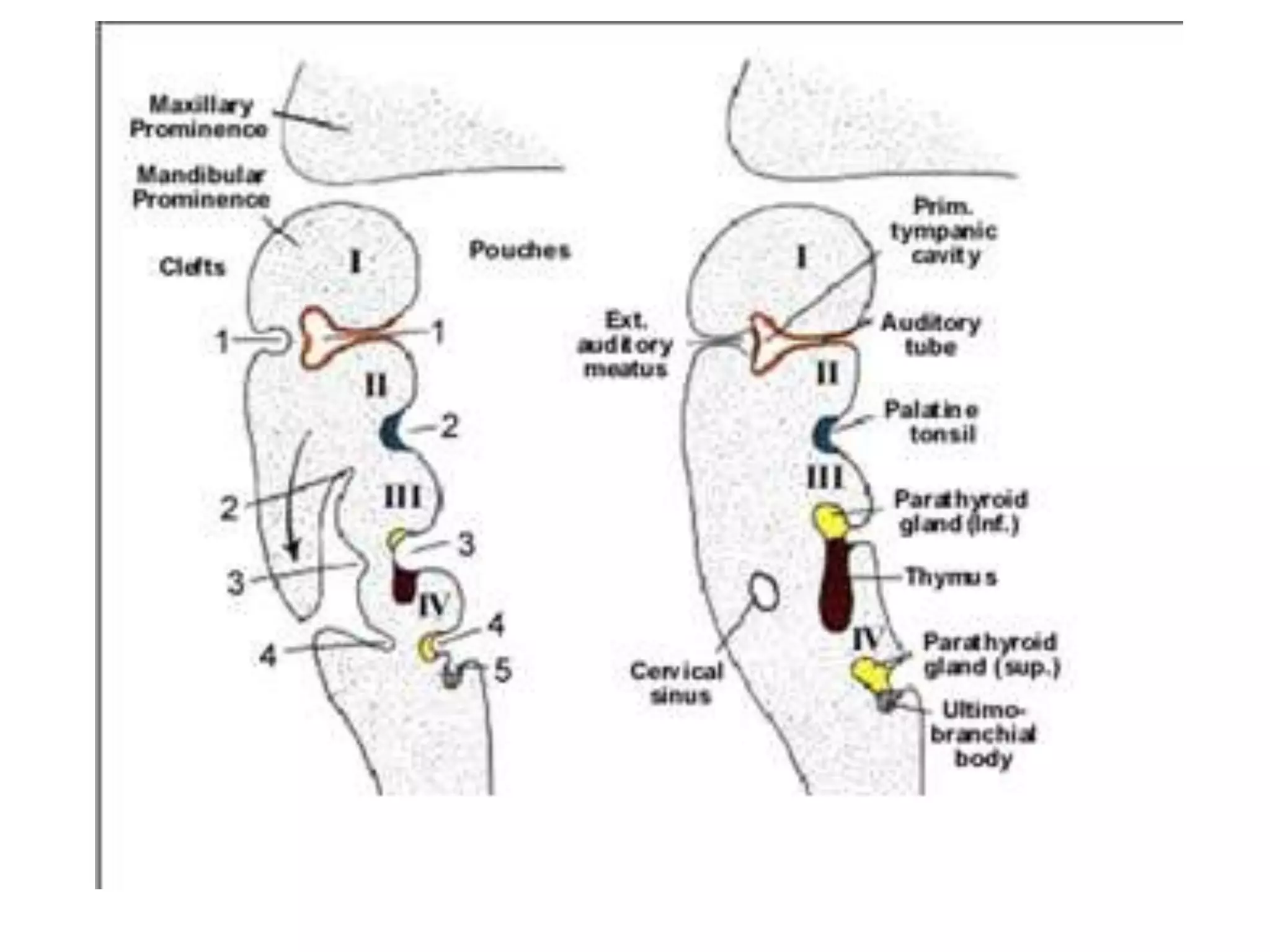
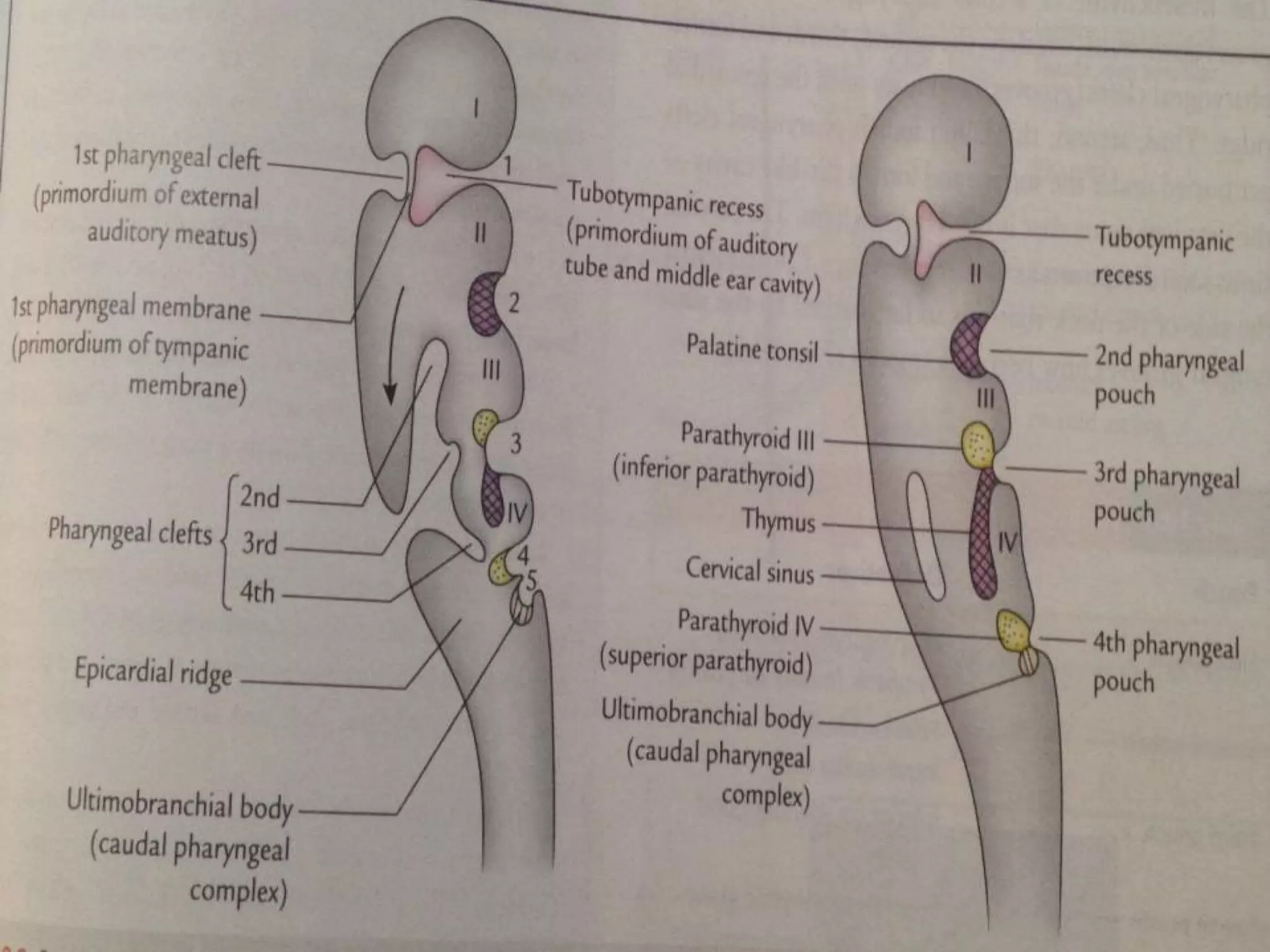
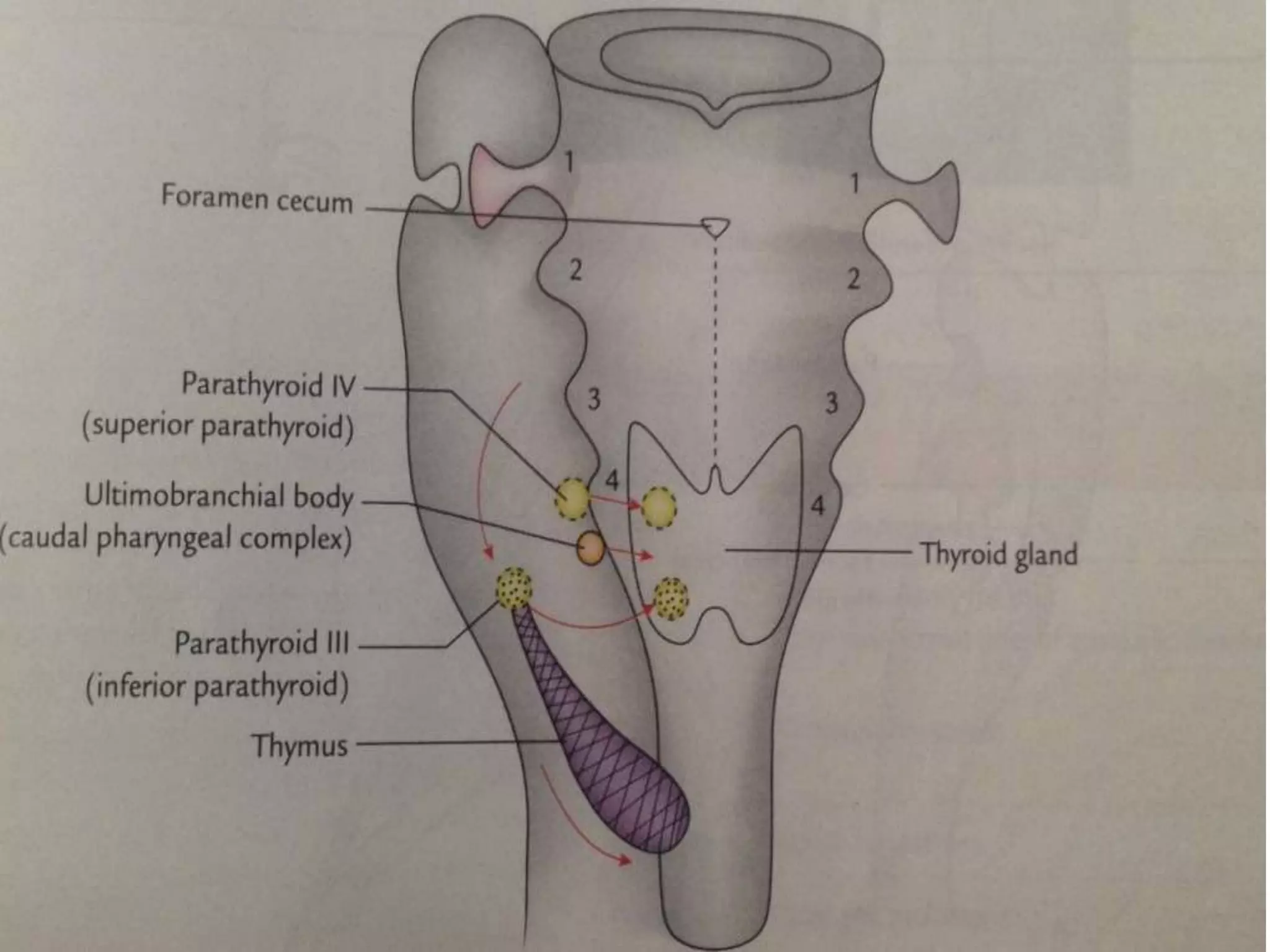
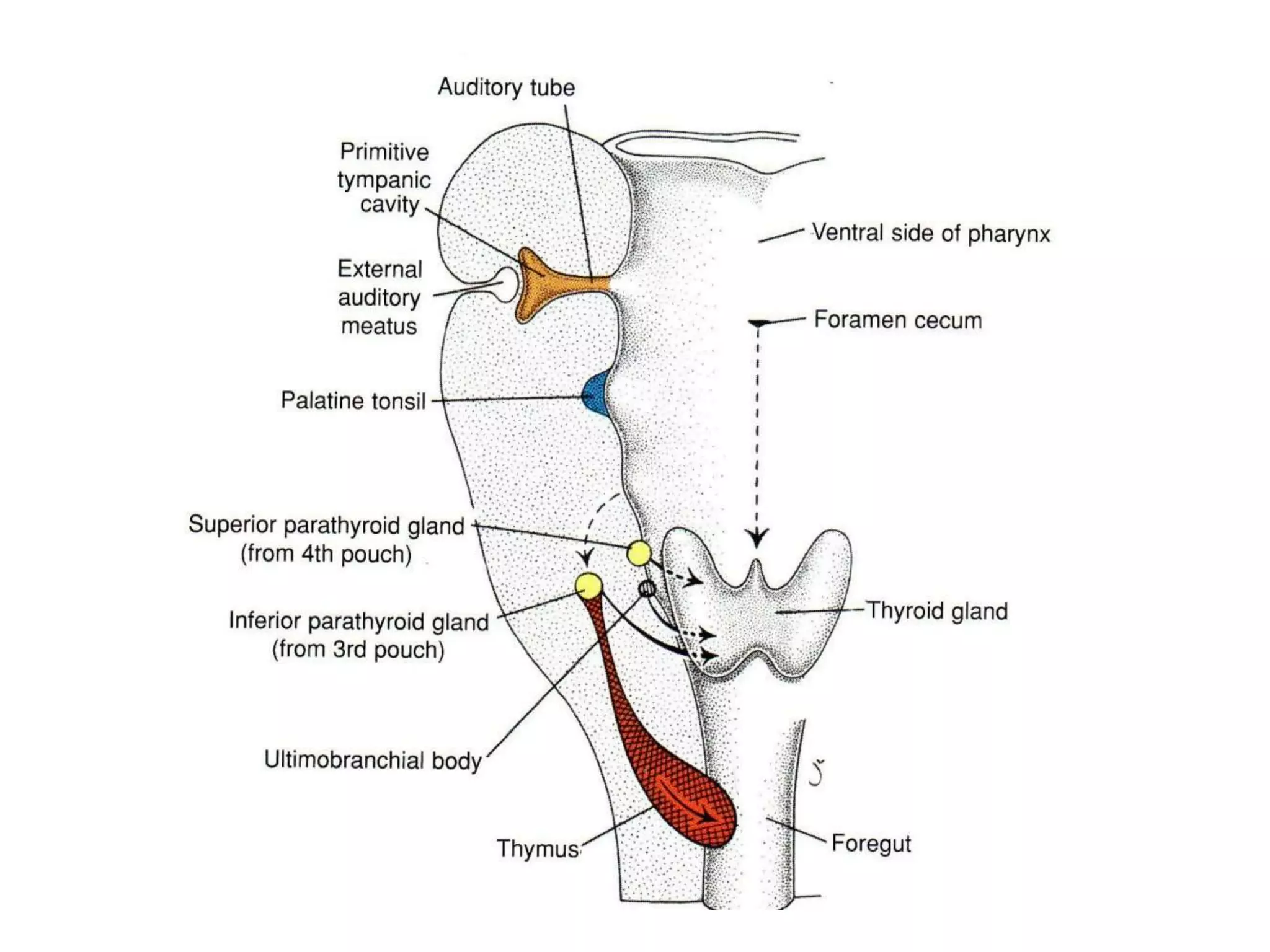
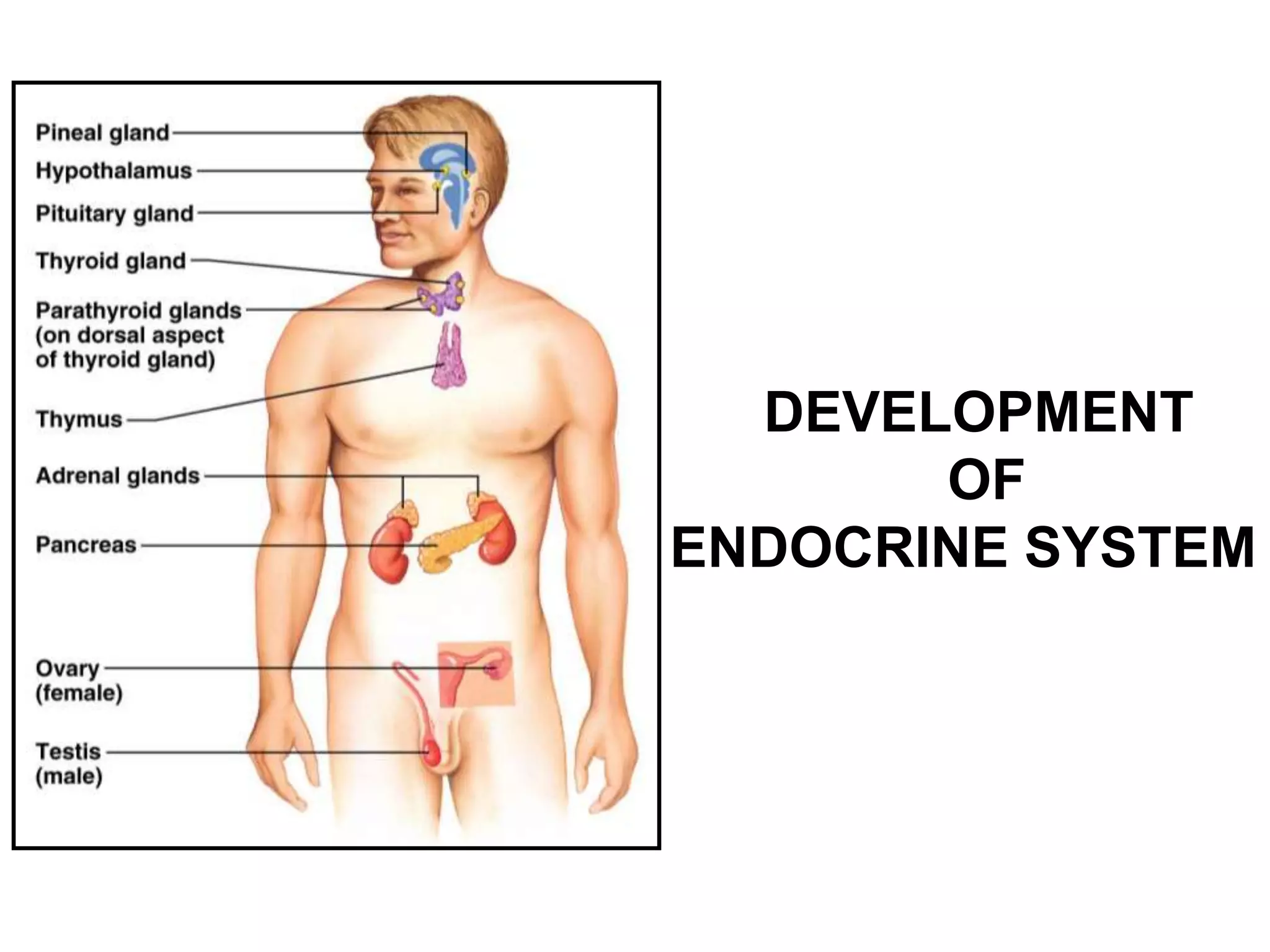
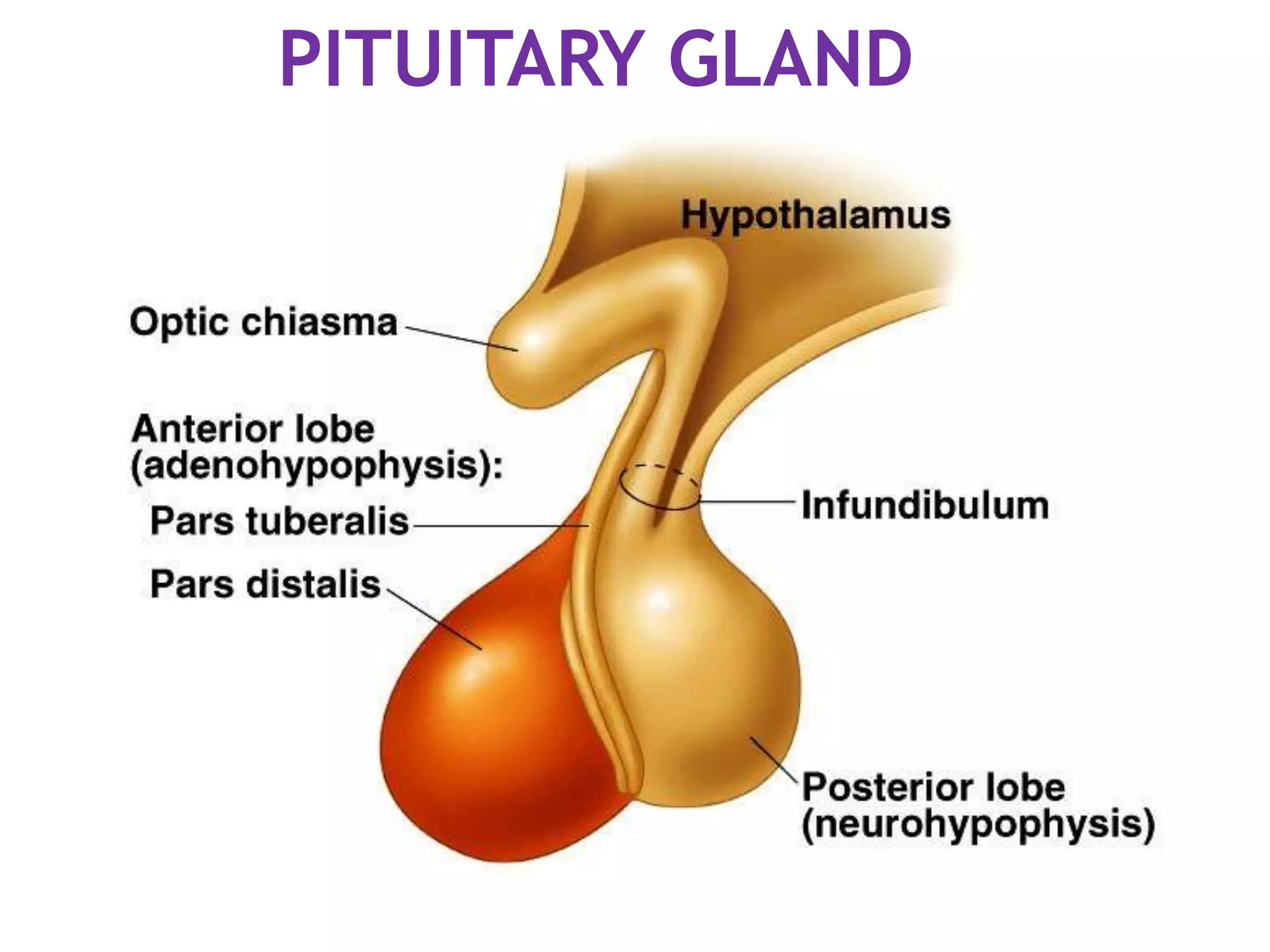
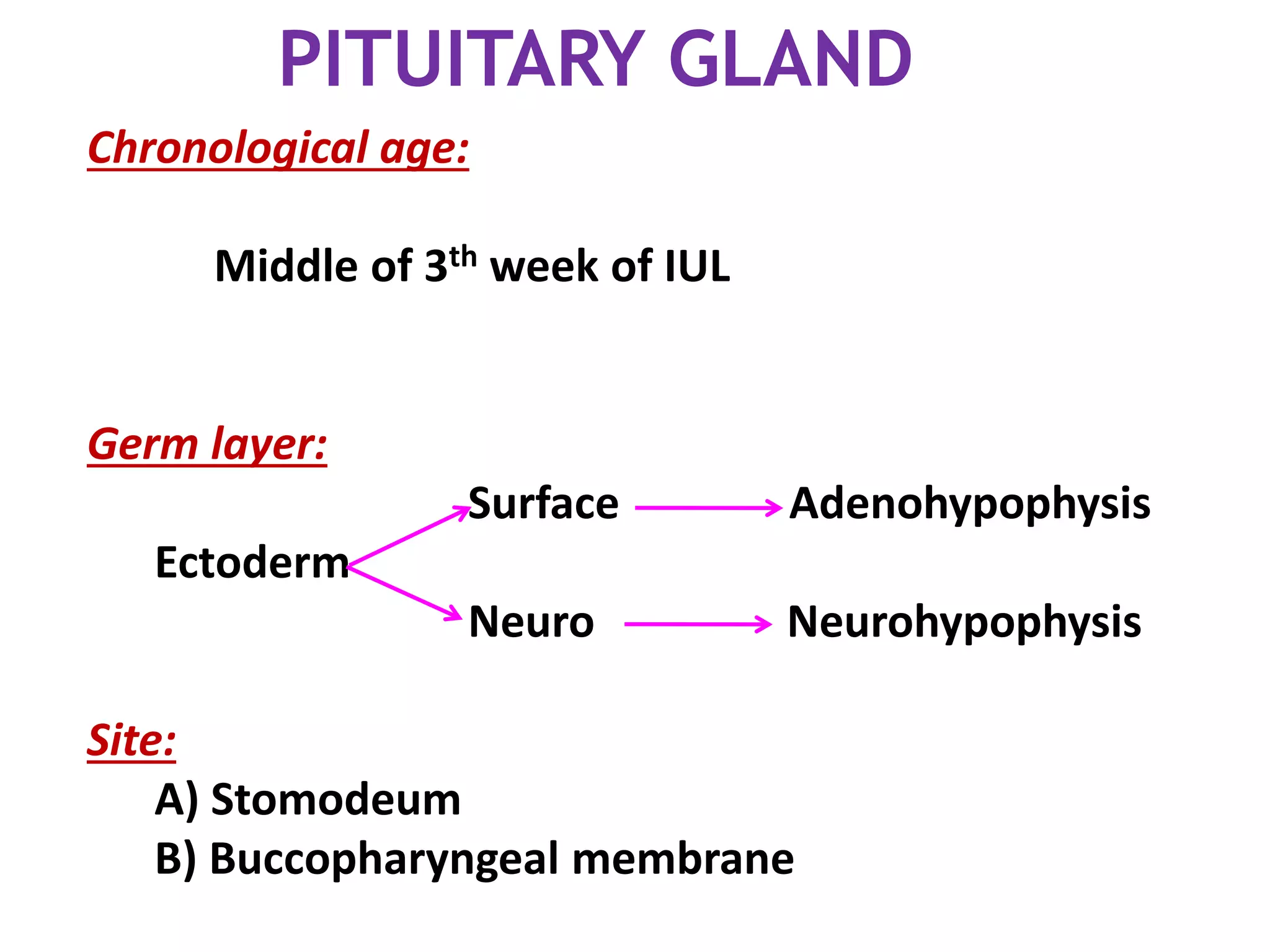
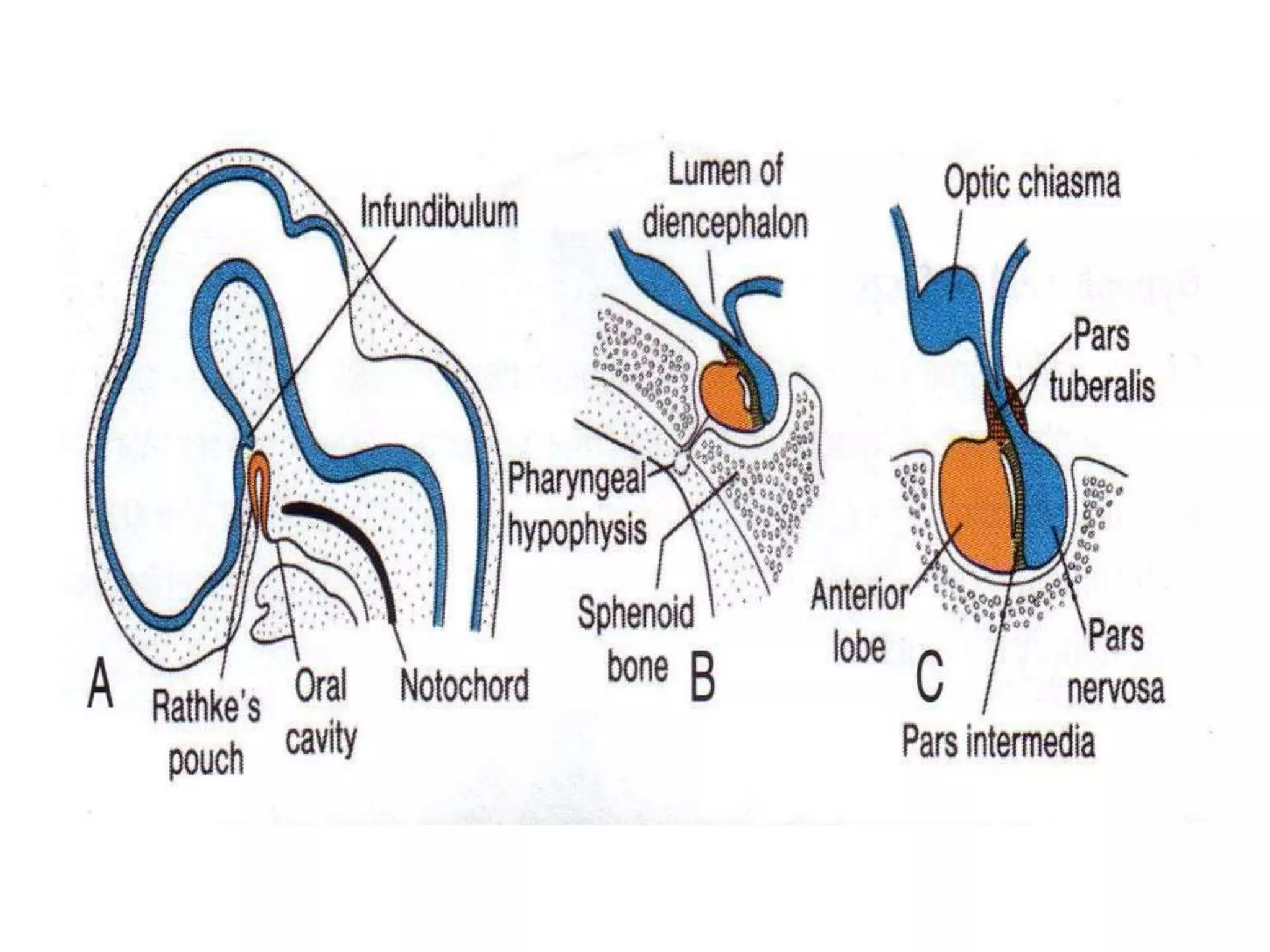
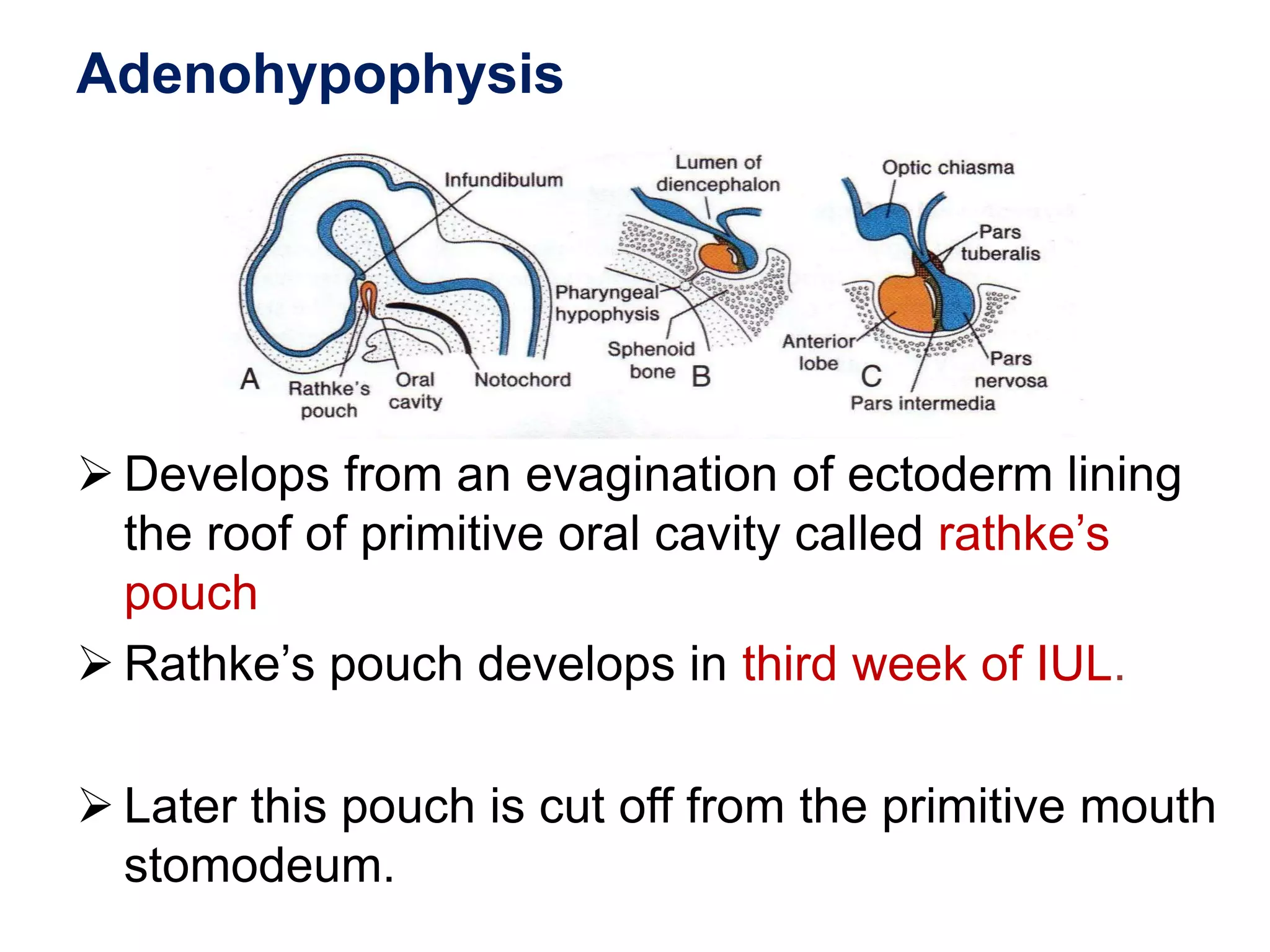
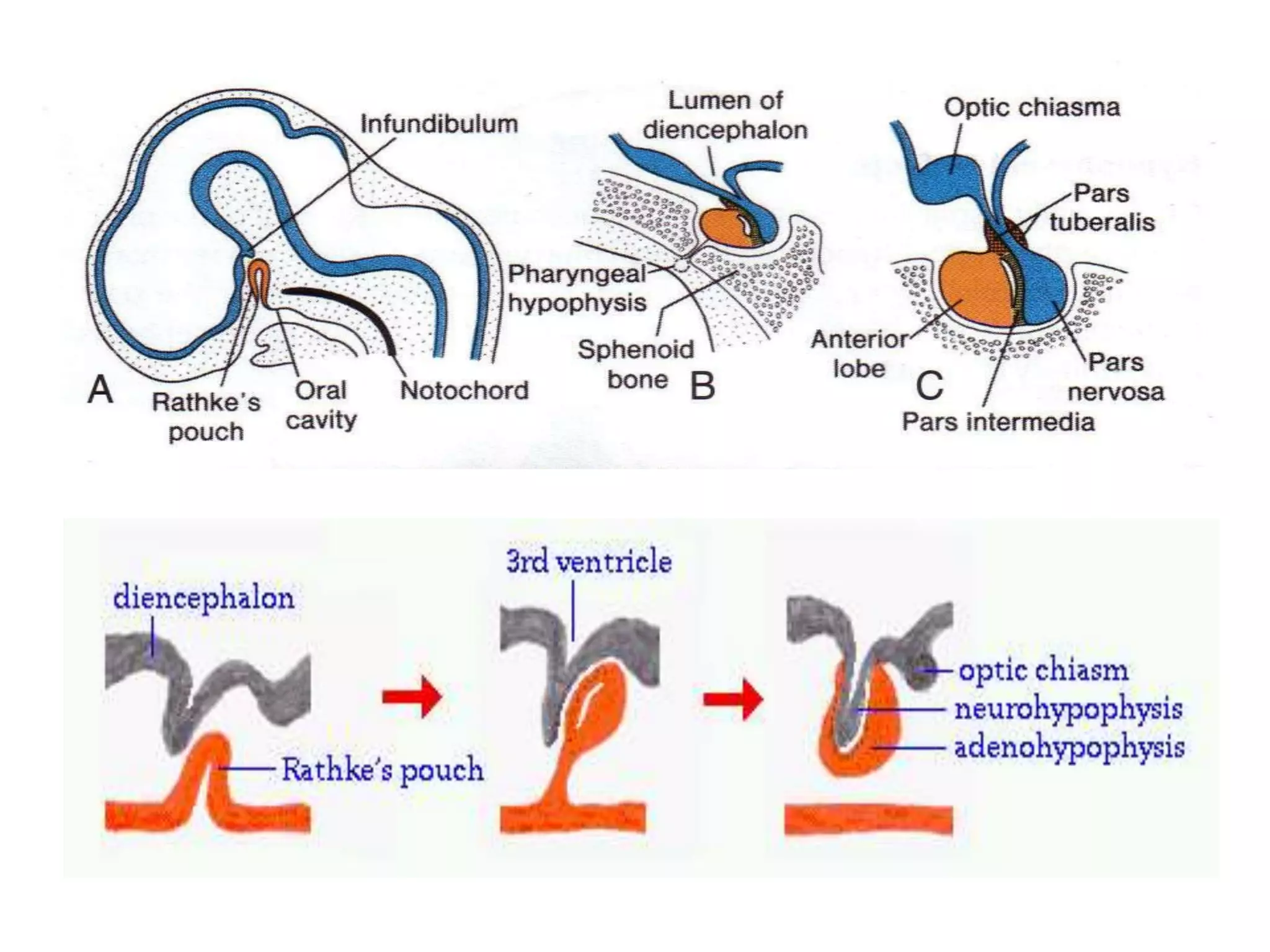
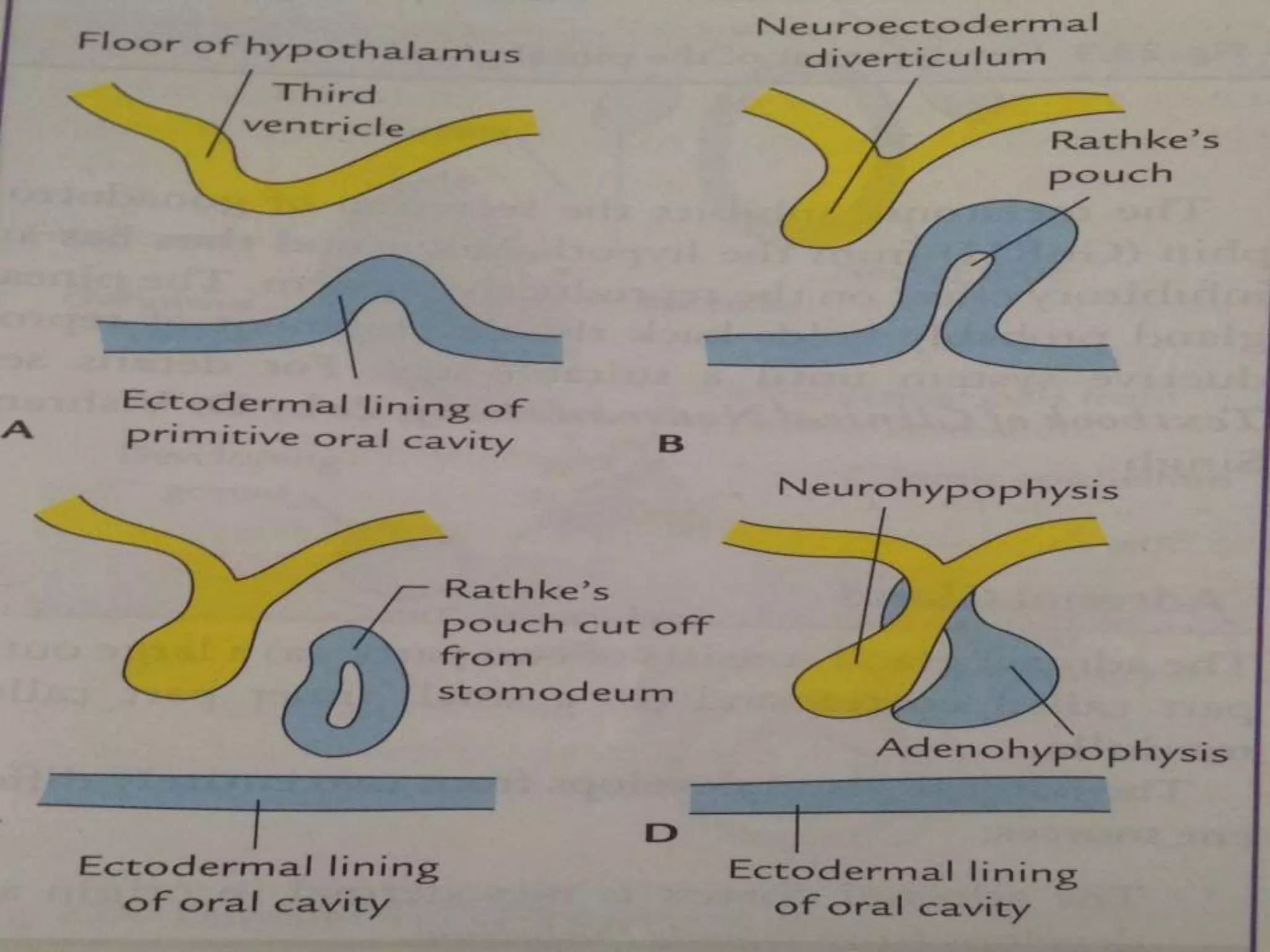
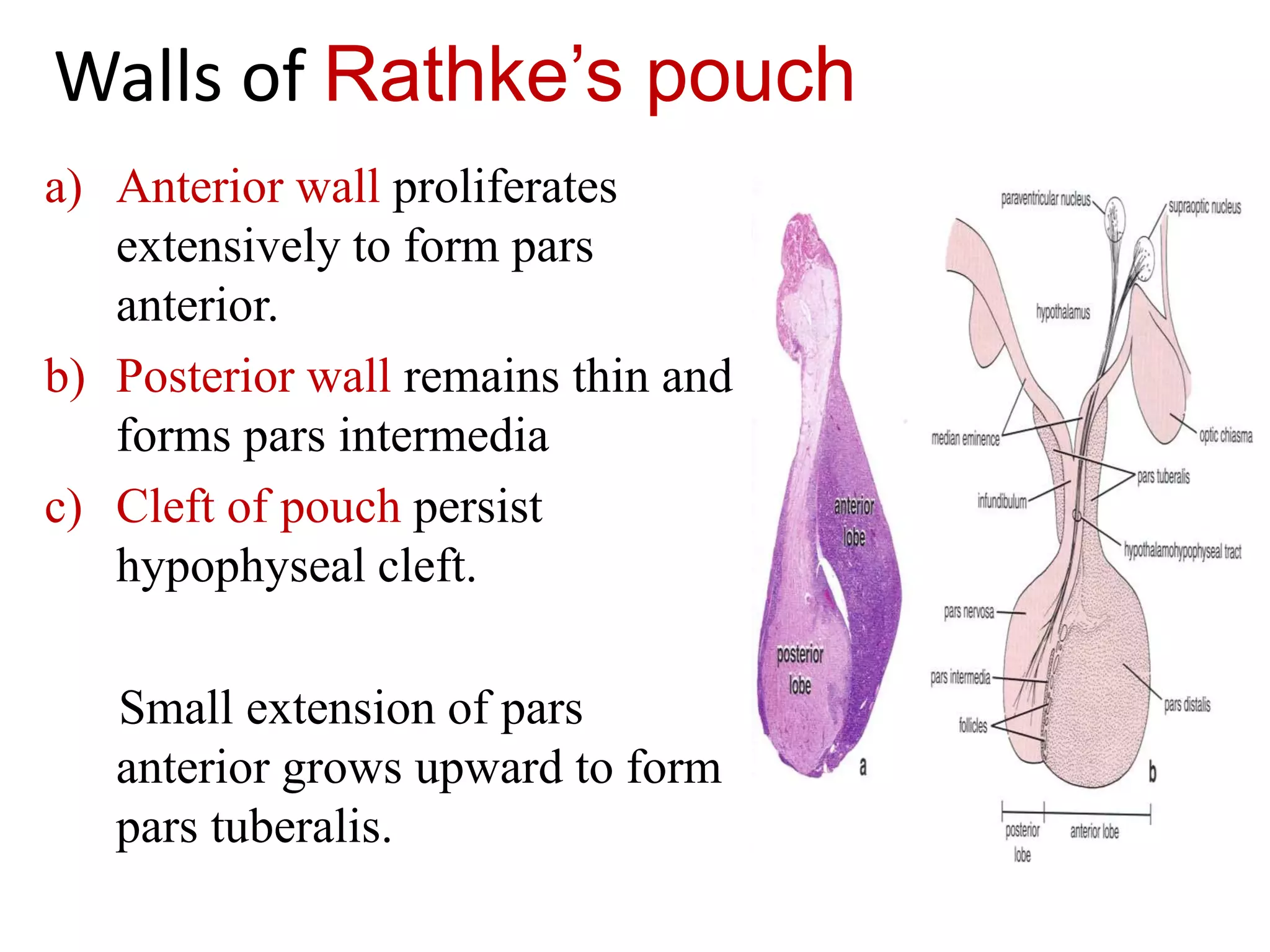
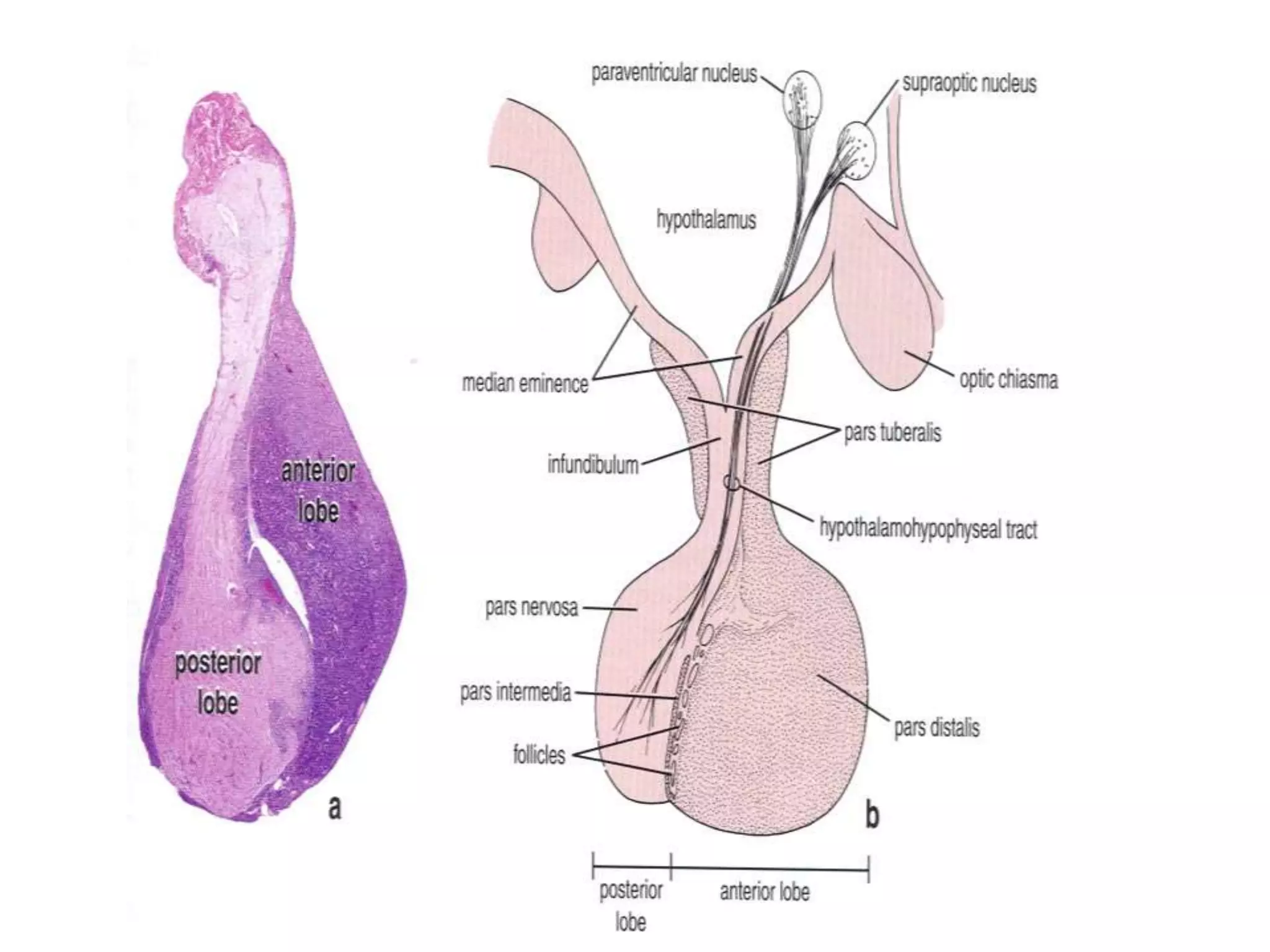
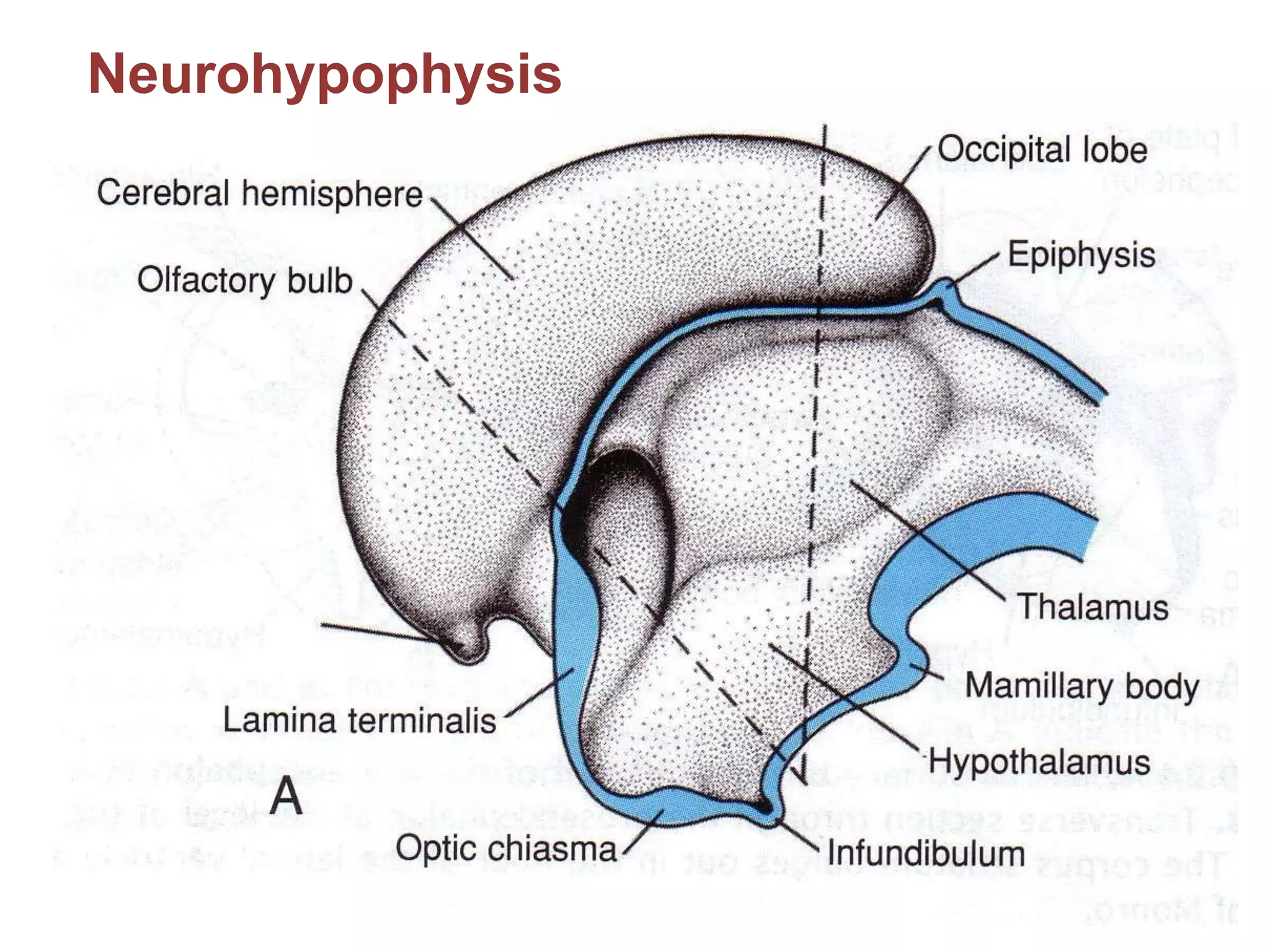
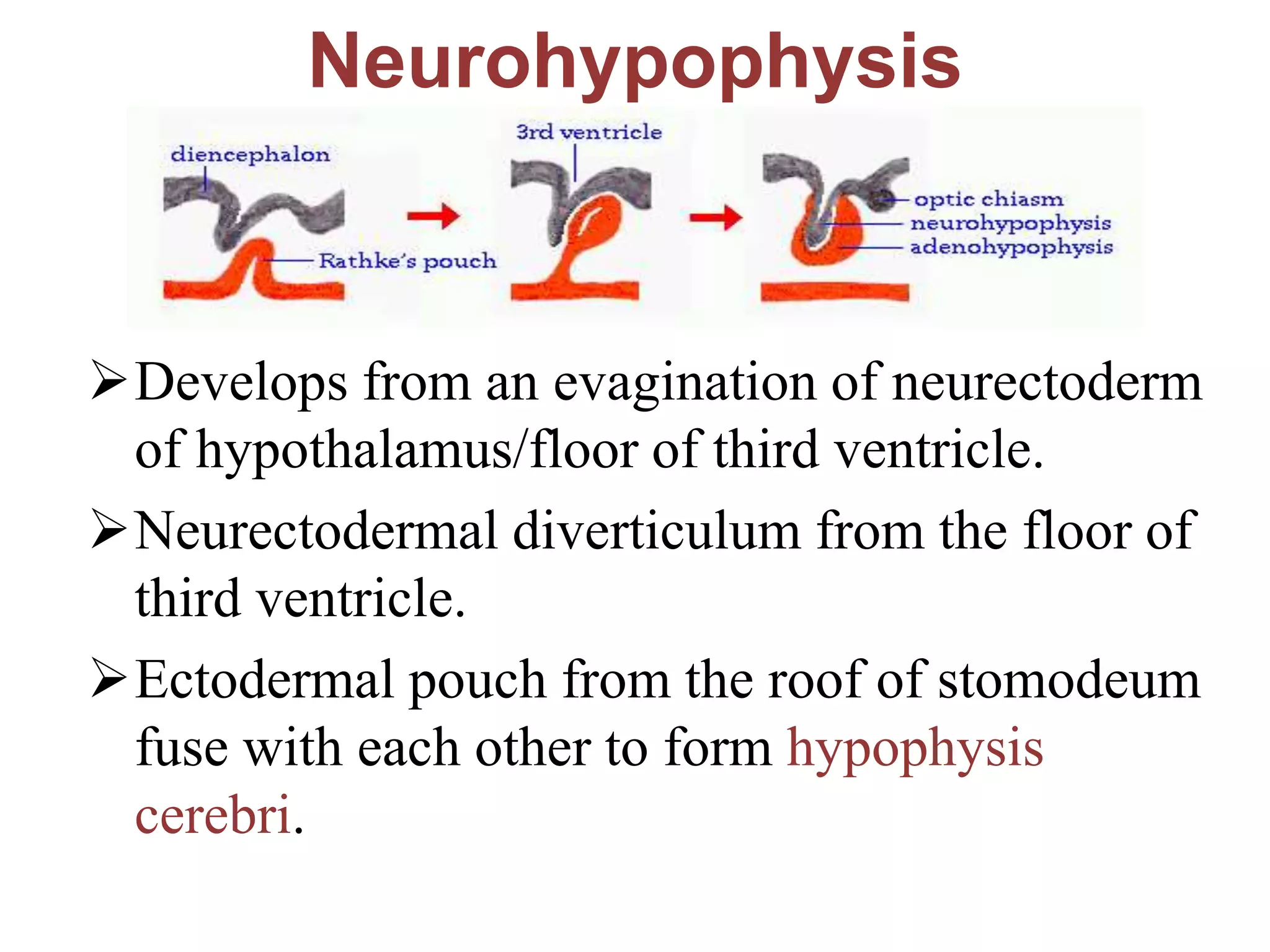
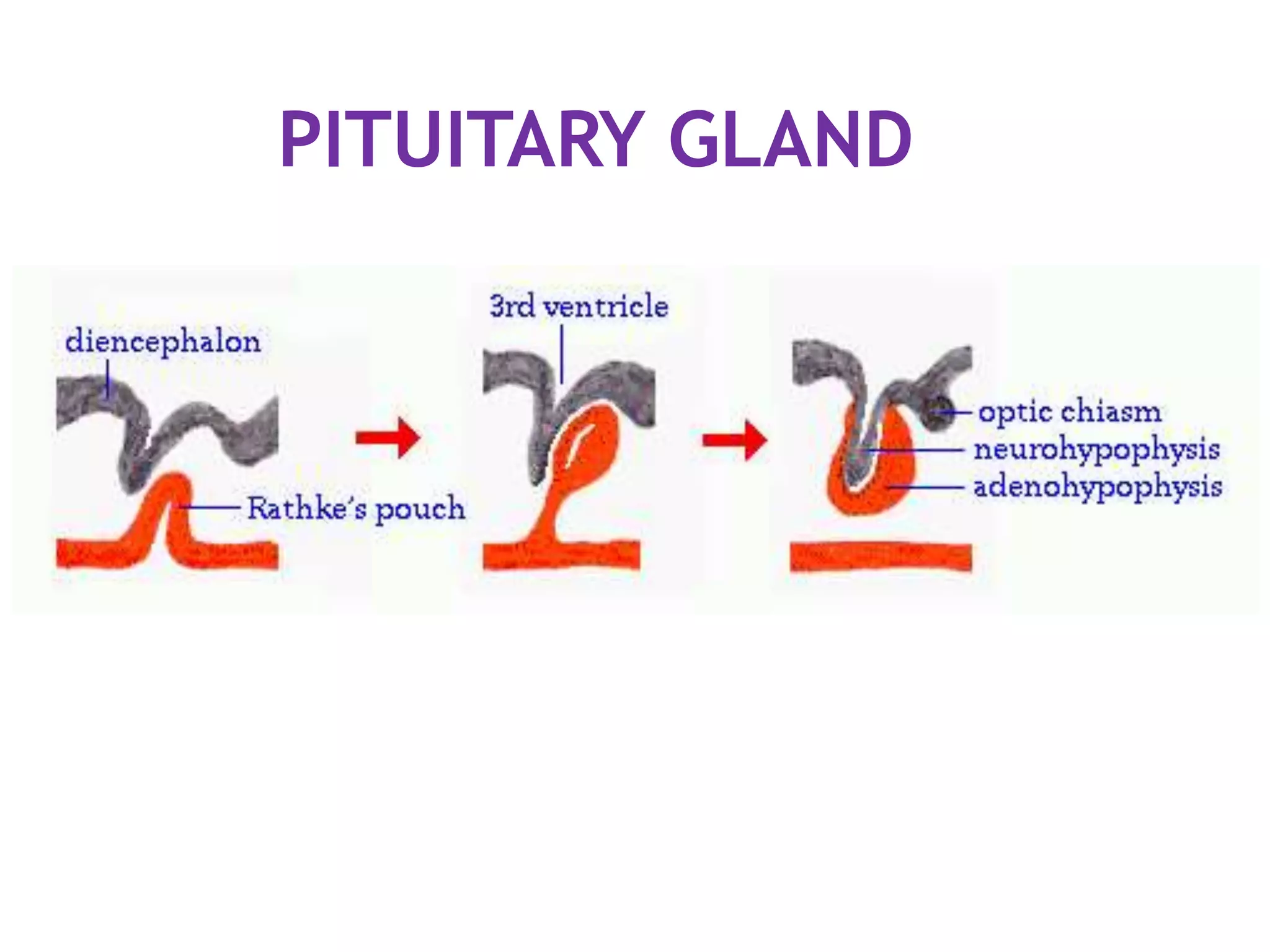
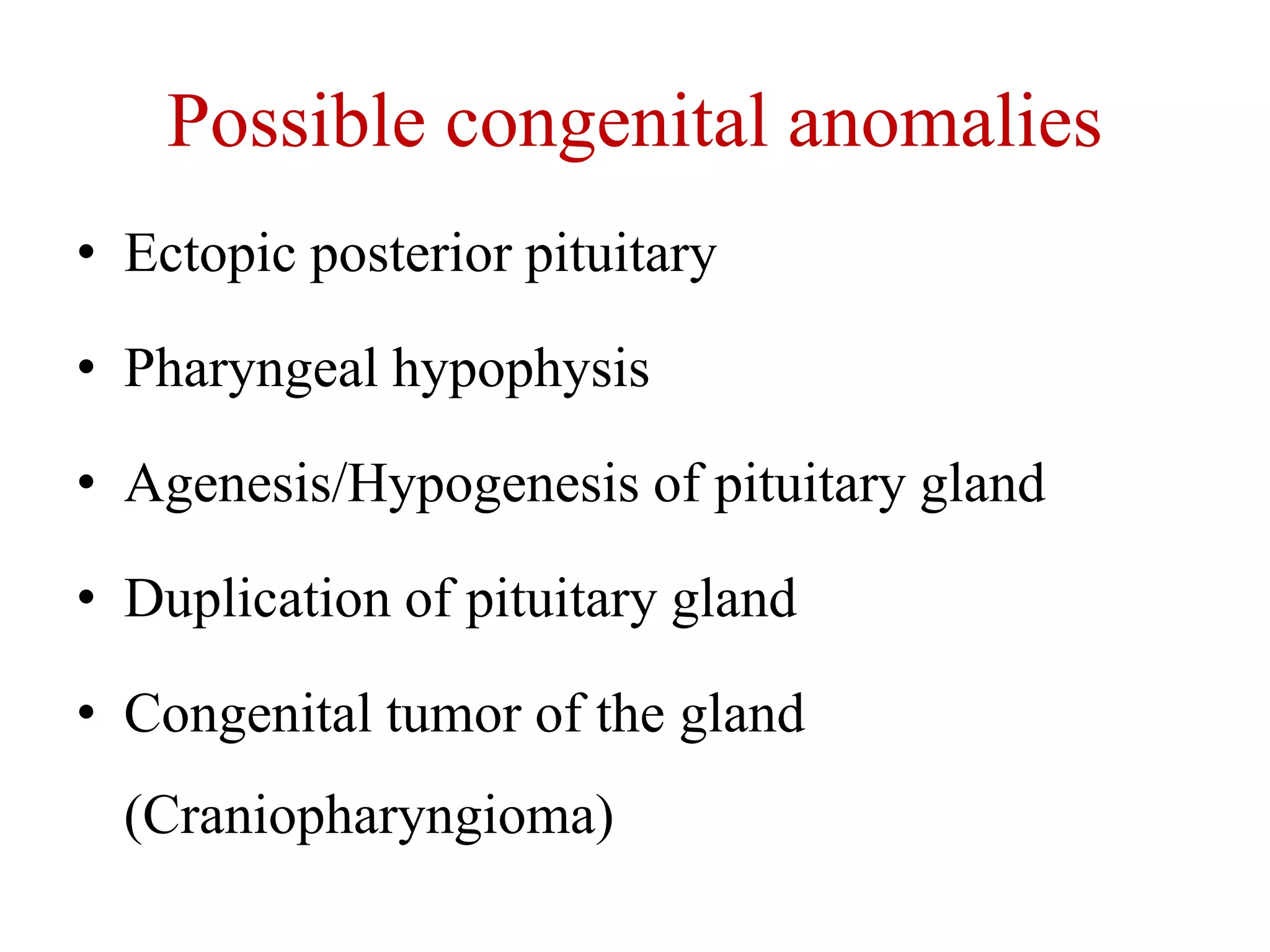
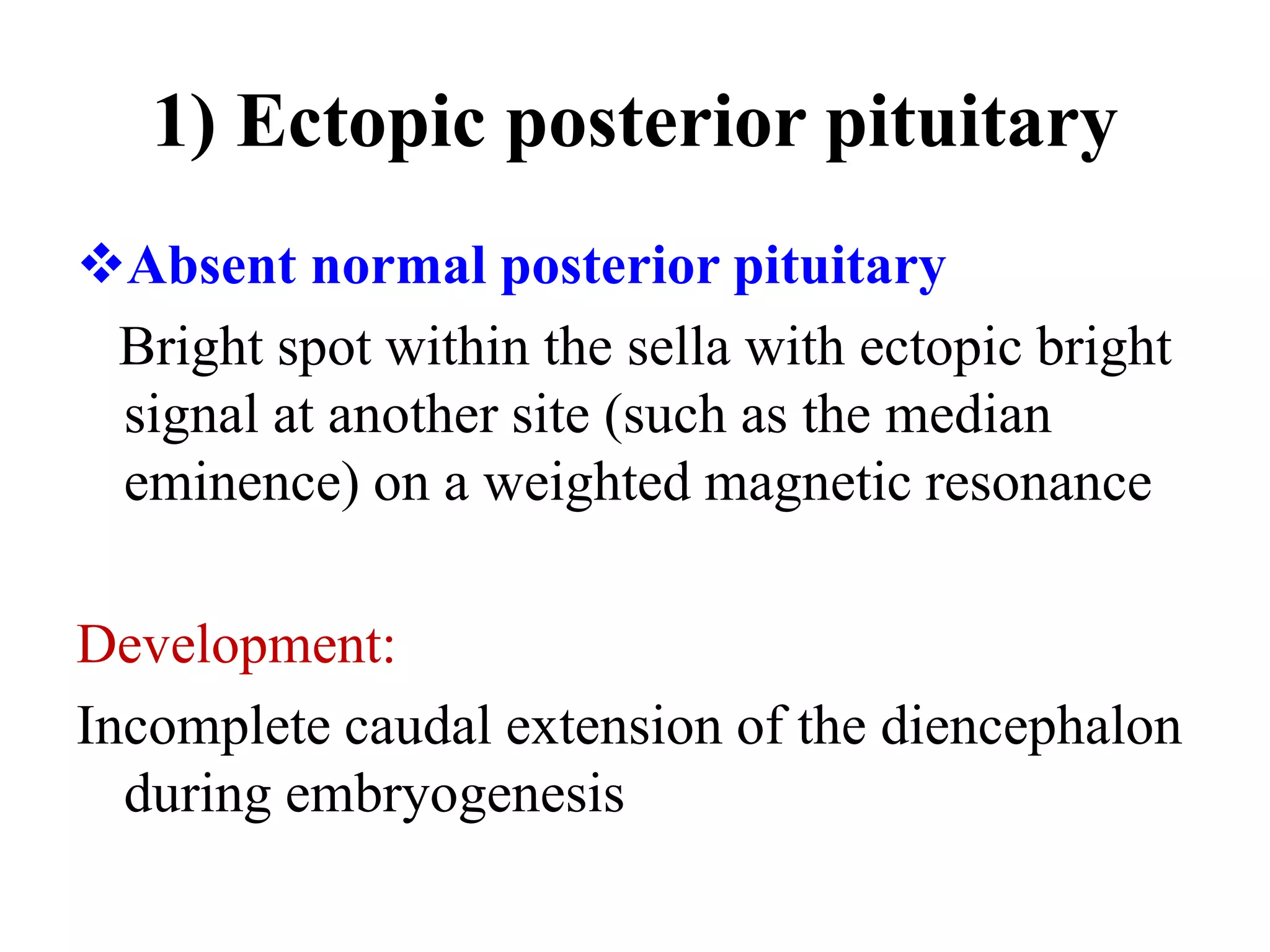
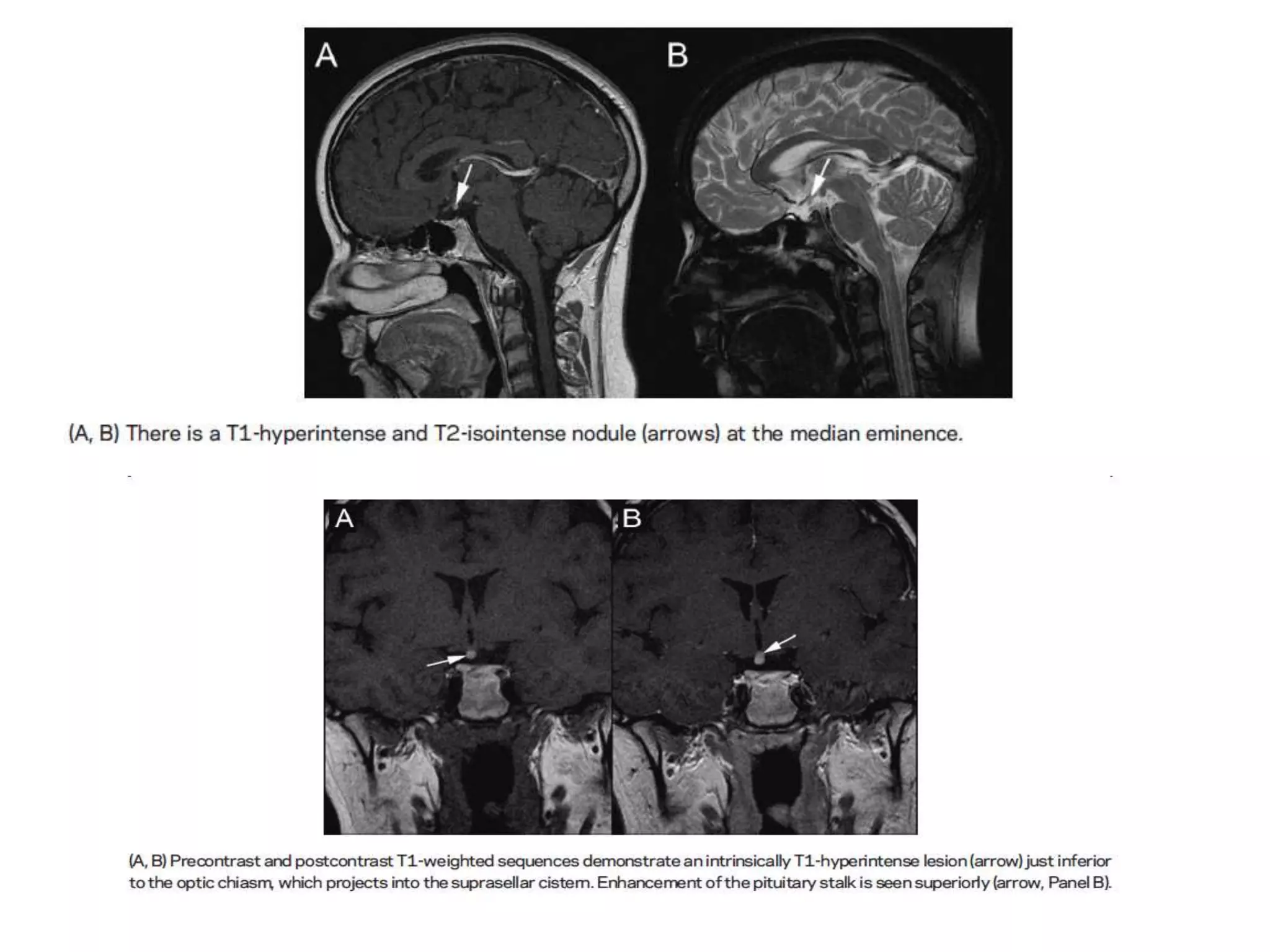
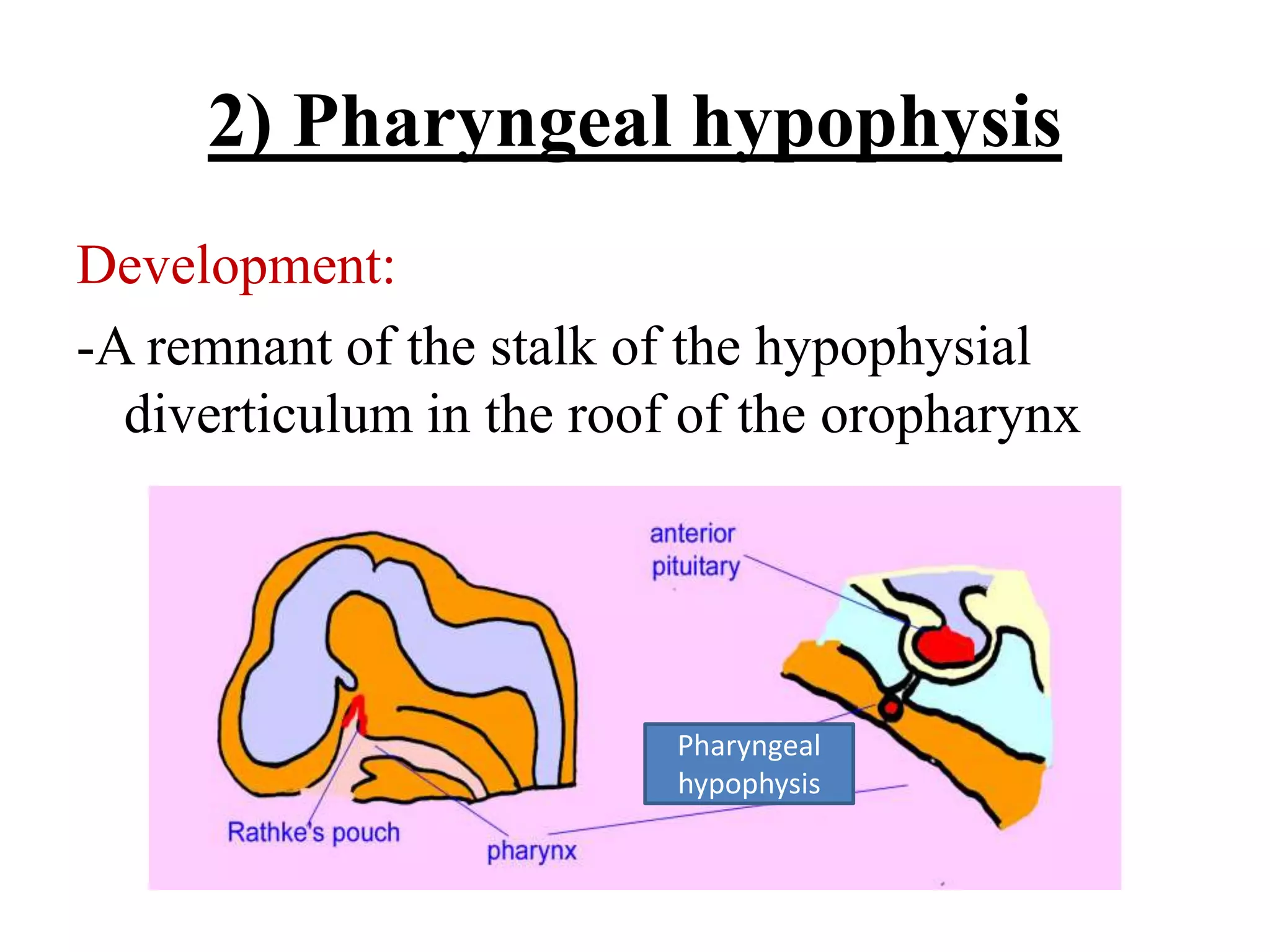
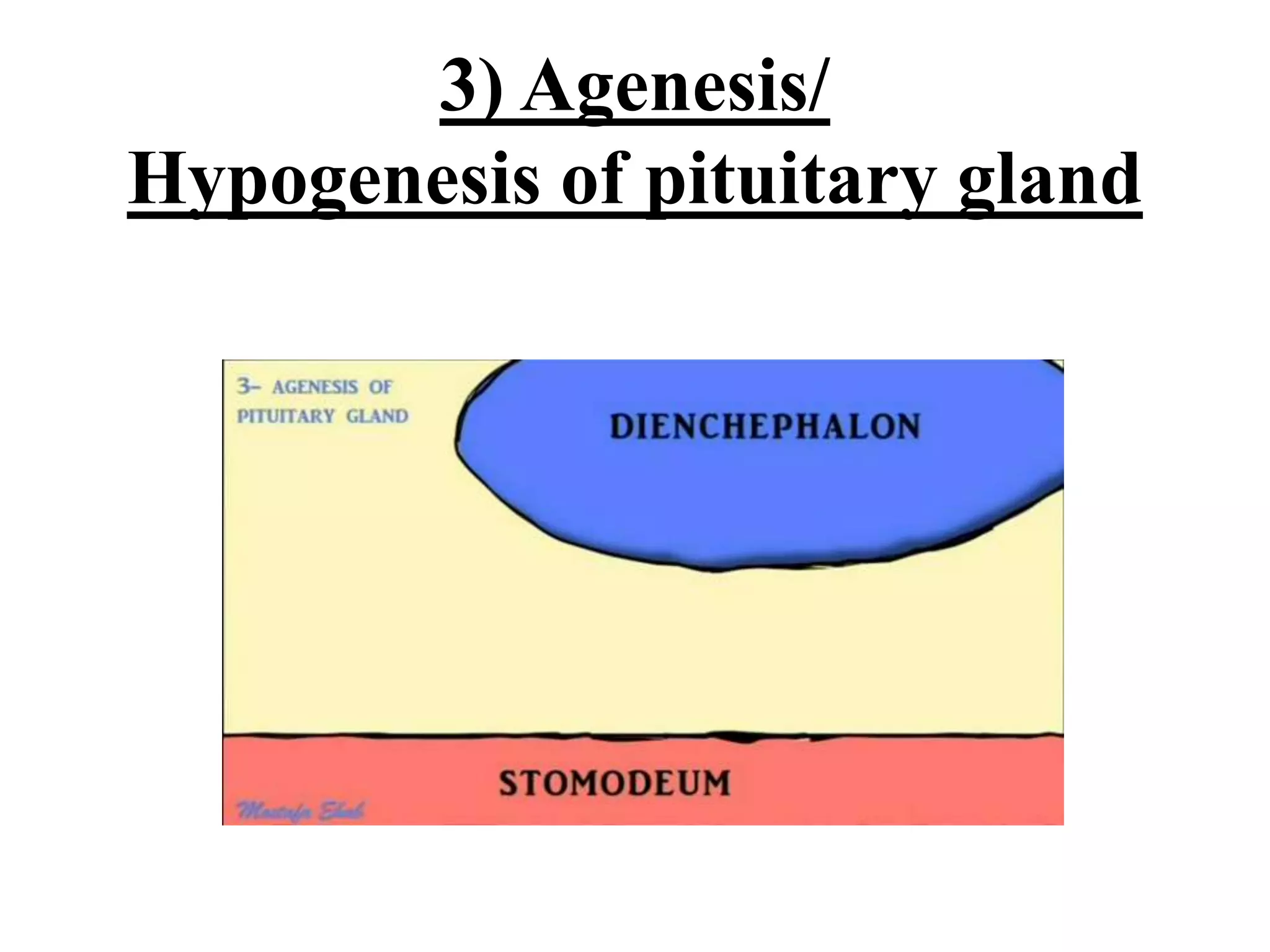
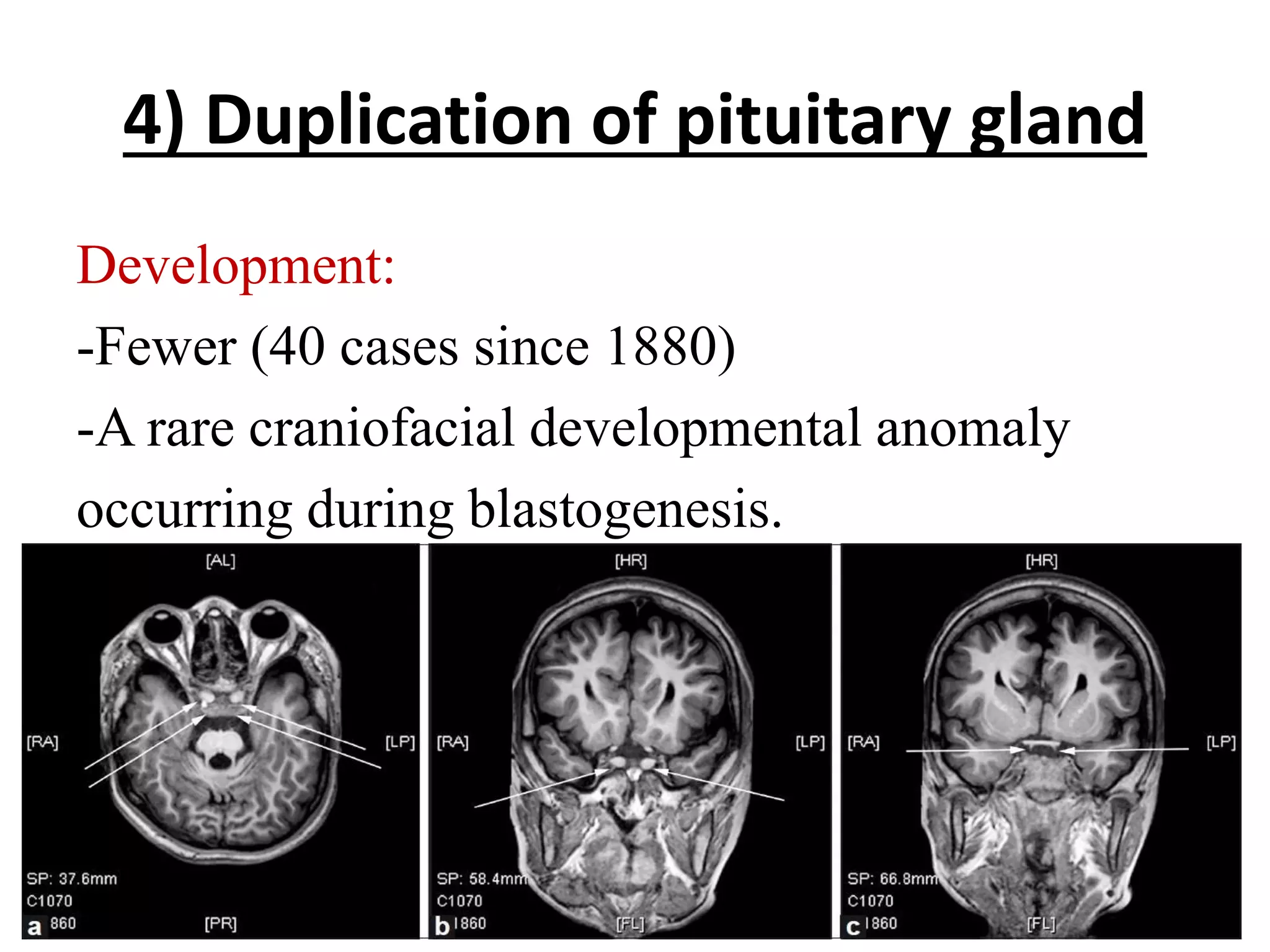
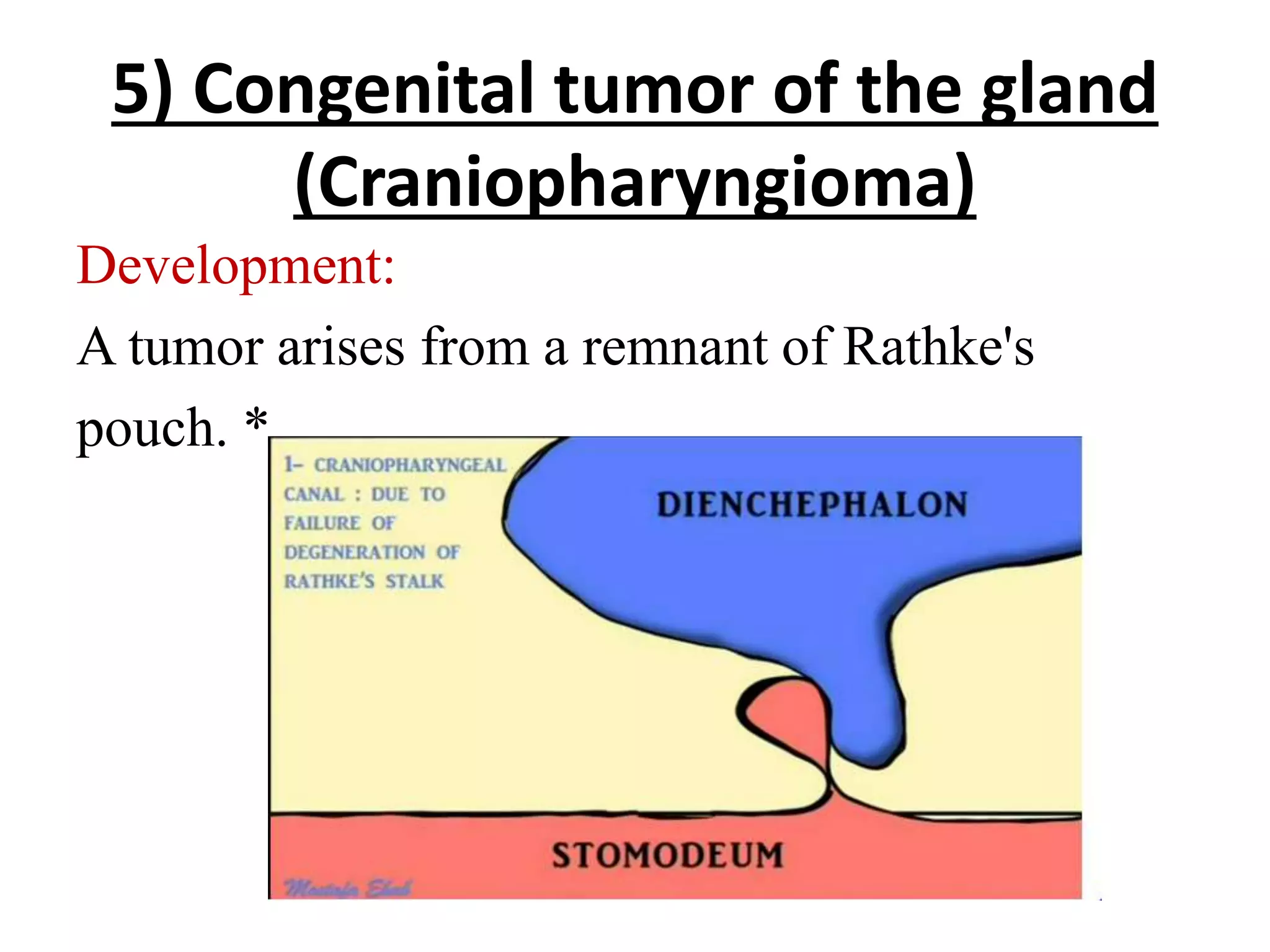
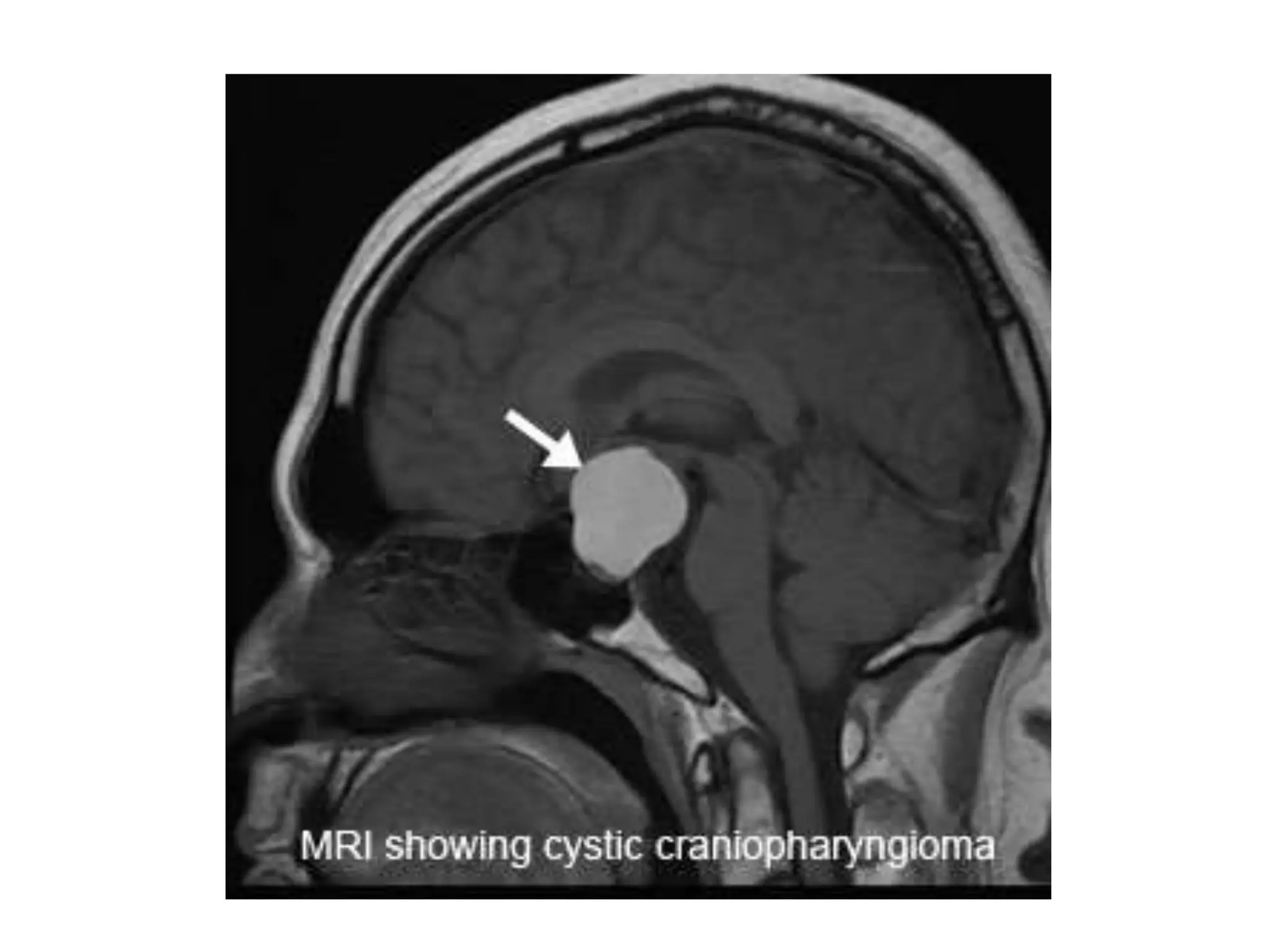
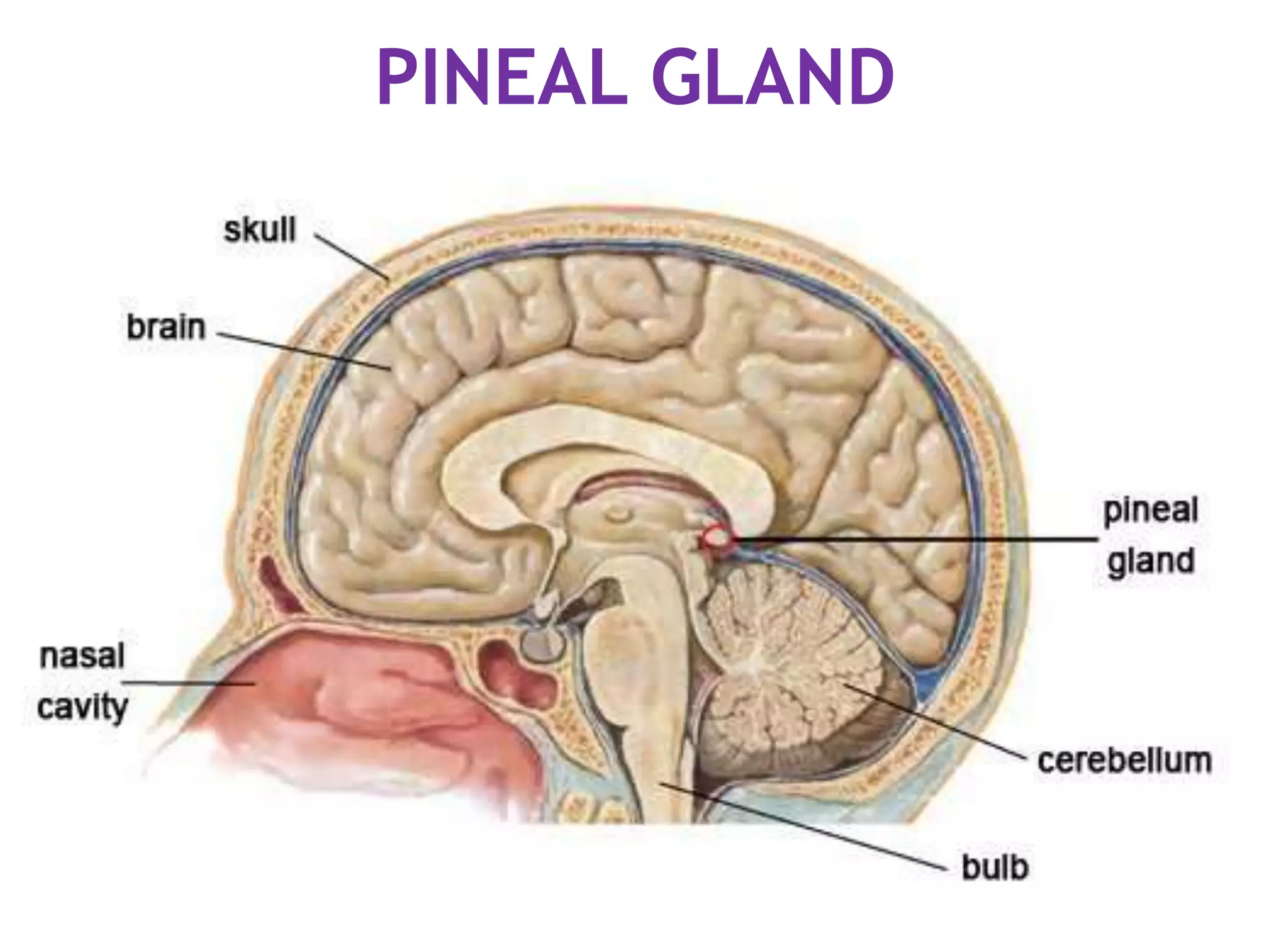
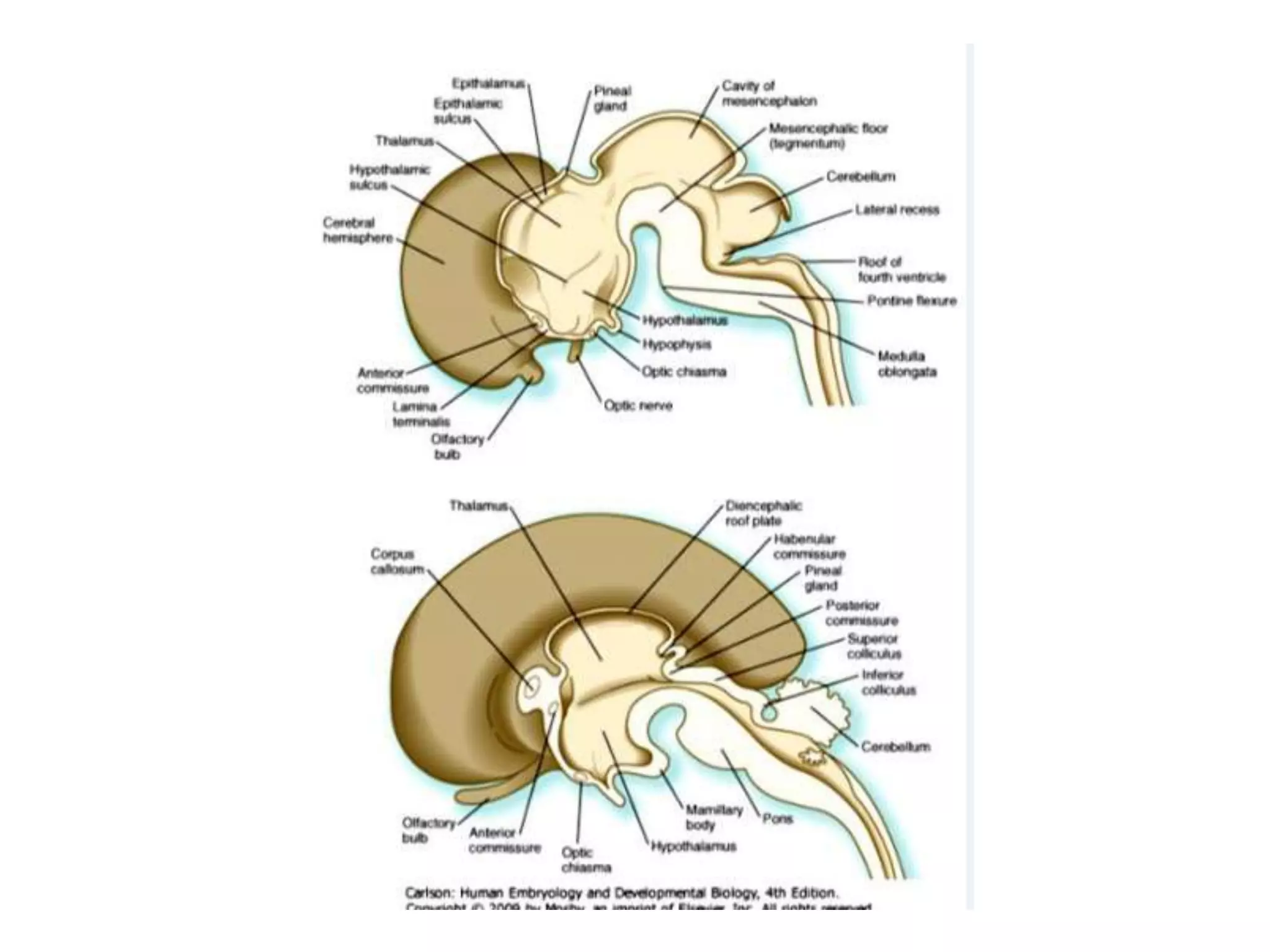
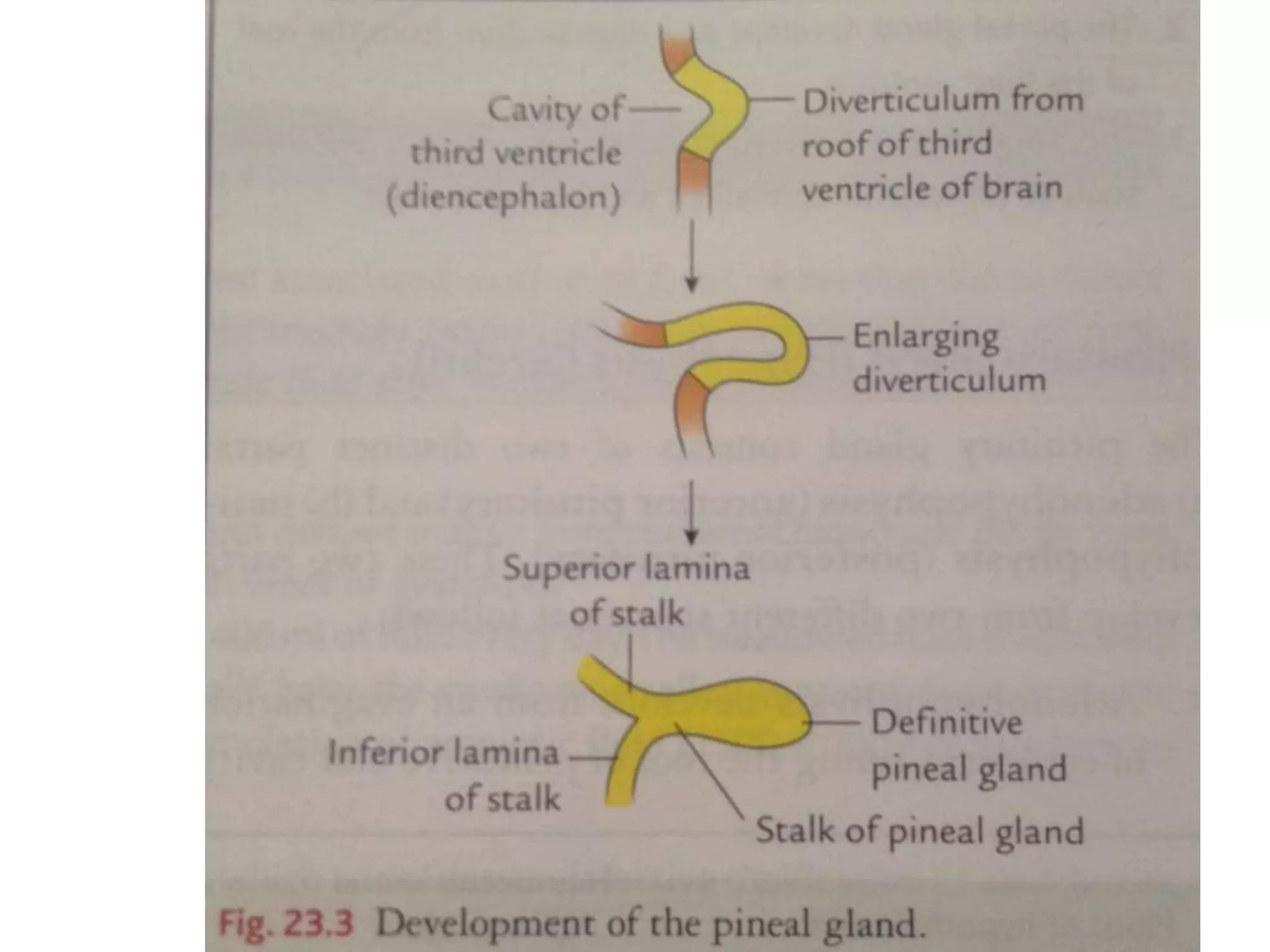
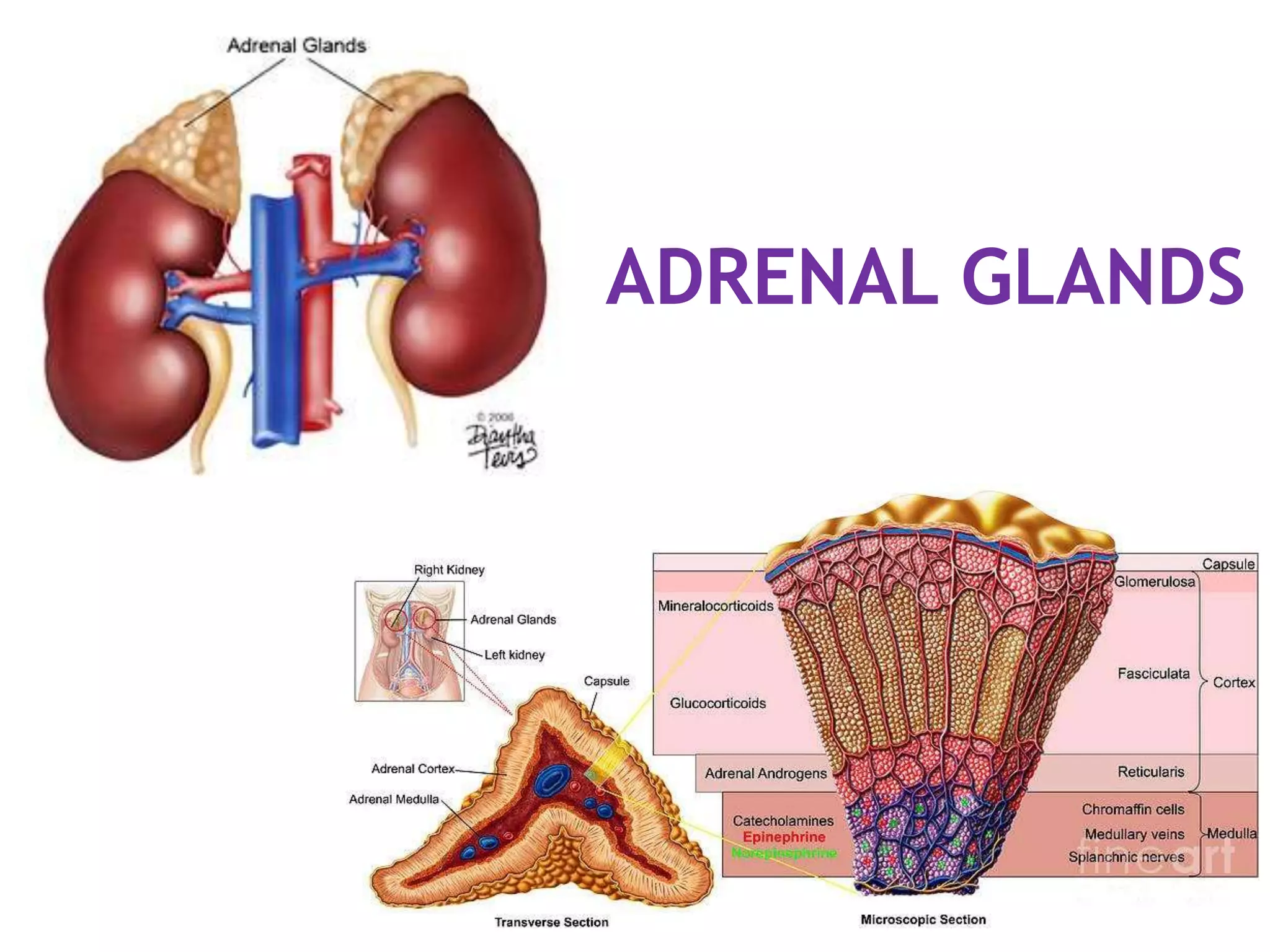
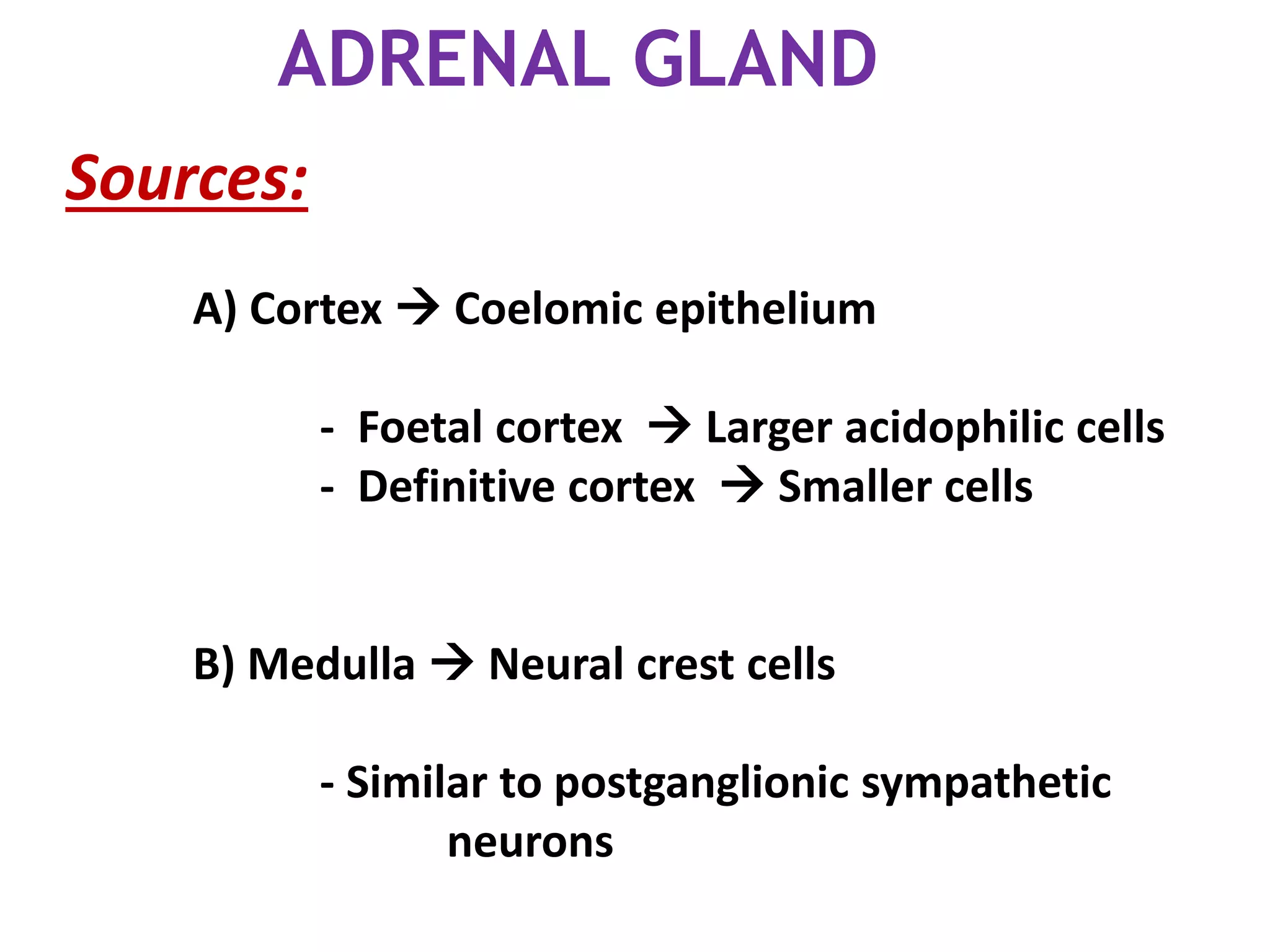
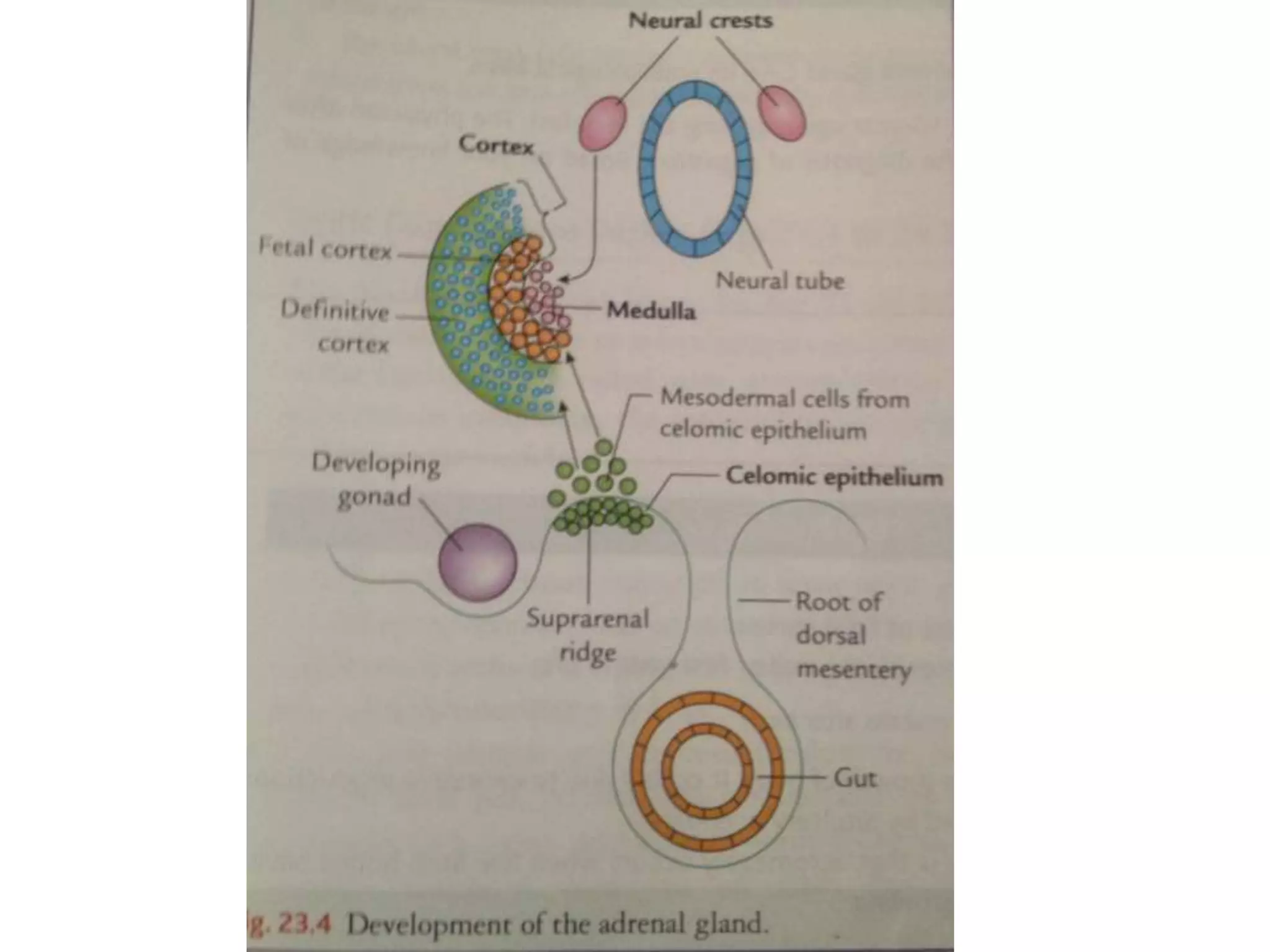
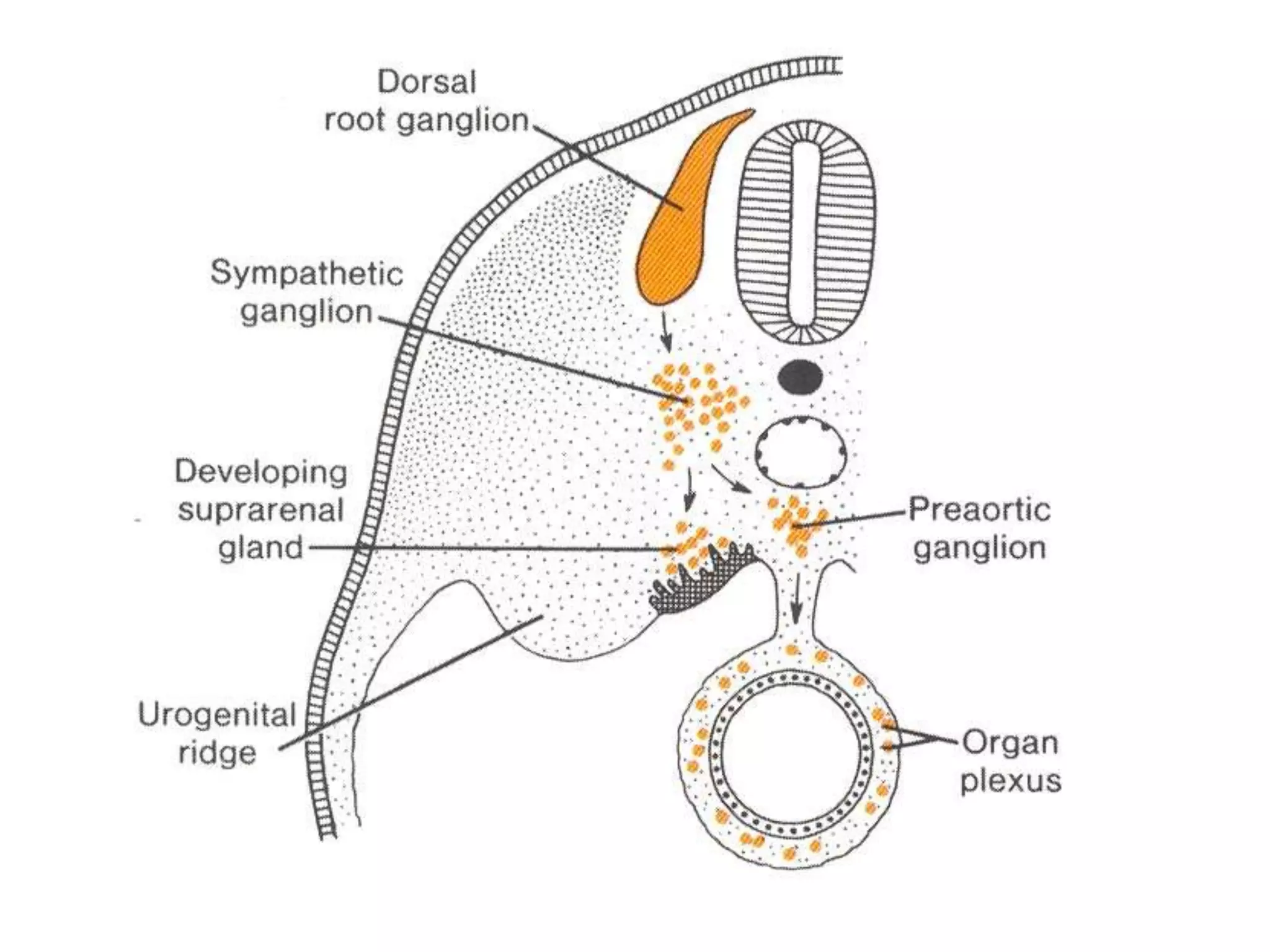
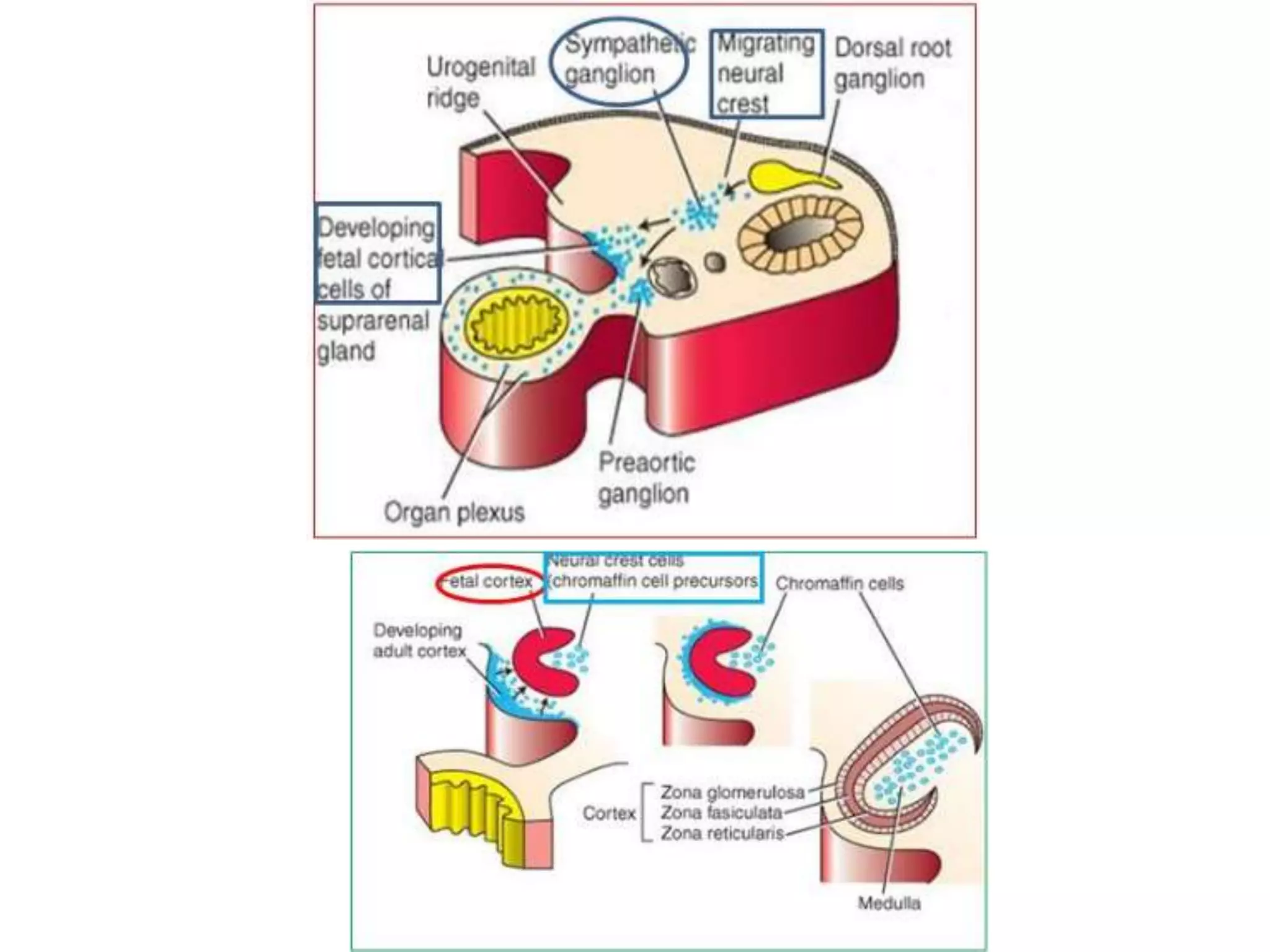
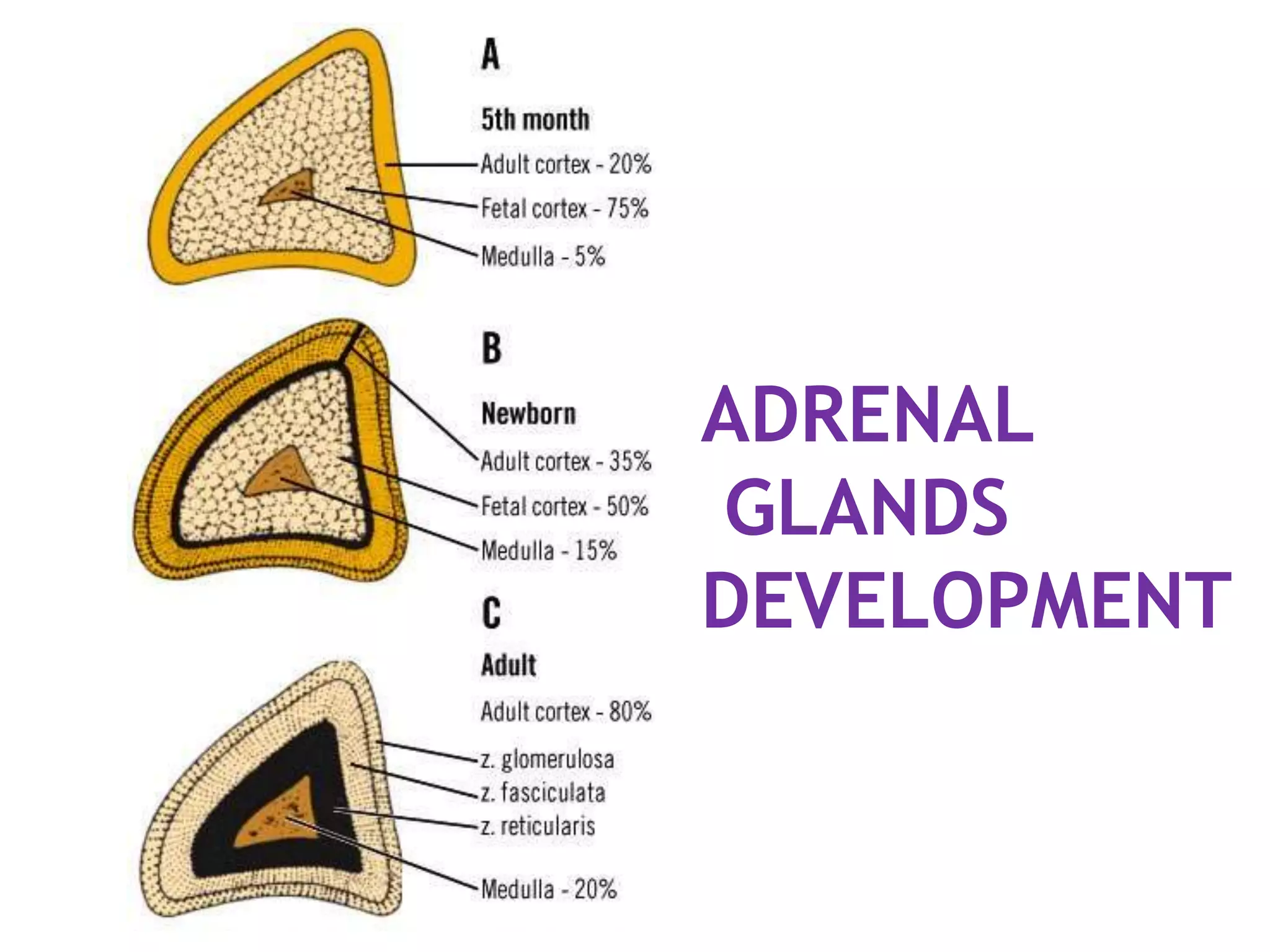
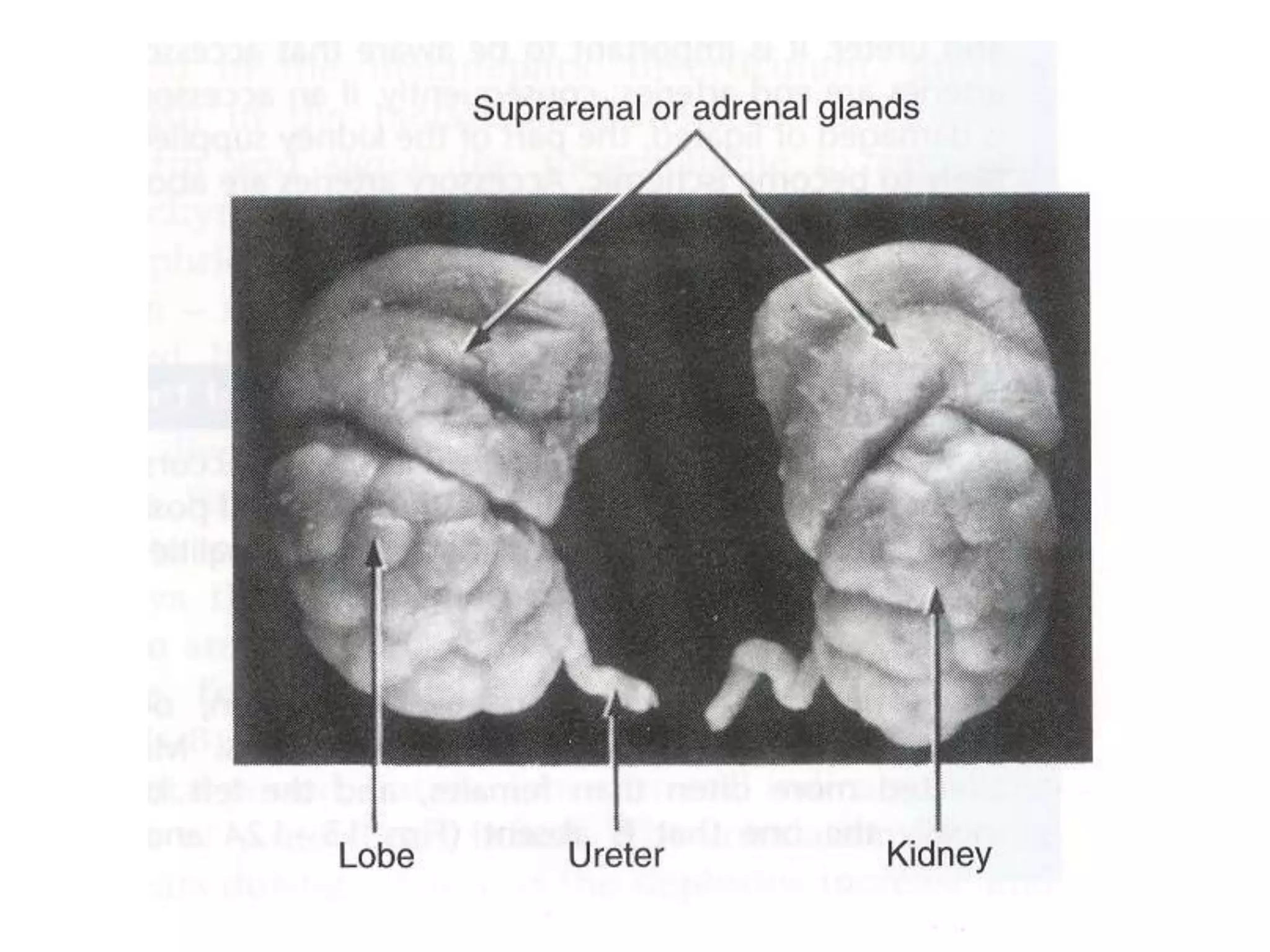
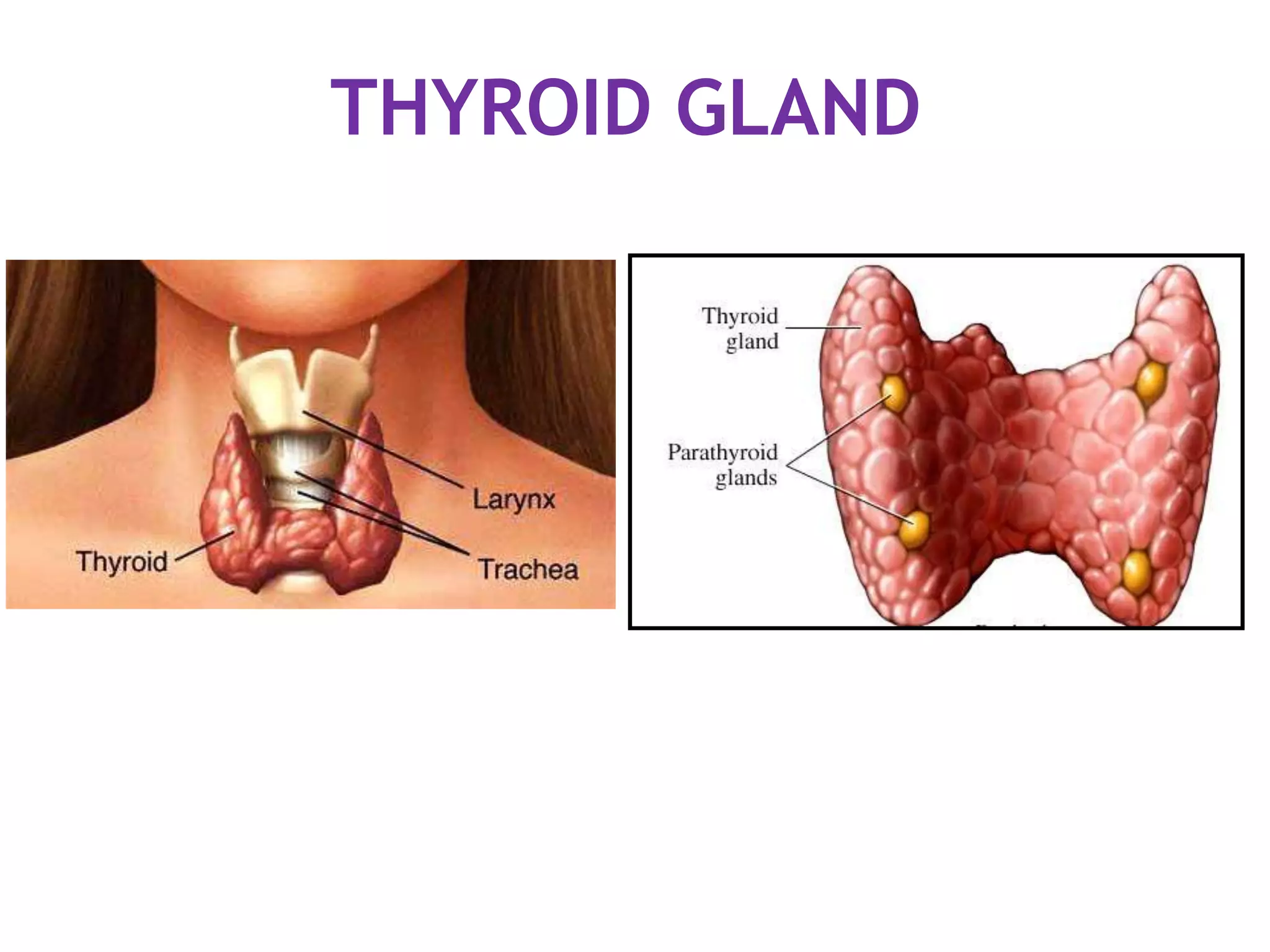
The pituitary gland develops from an evagination of ectoderm called Rathke's pouch and a neuroectodermal diverticulum from the hypothalamus. The anterior pituitary develops from Rathke's pouch while the posterior pituitary develops from the diverticulum. Possible anomalies include ectopic posterior pituitary, pharyngeal hypophysis, agenesis of the pituitary gland, duplication, and craniopharyngioma tumor. The pineal gland develops from a diverticulum of the diencephalon. The adrenal glands develop from coelomic epithelium for the cortex and neural crest cells for the medulla. The thyroid gland is the first endocrine gland to develop









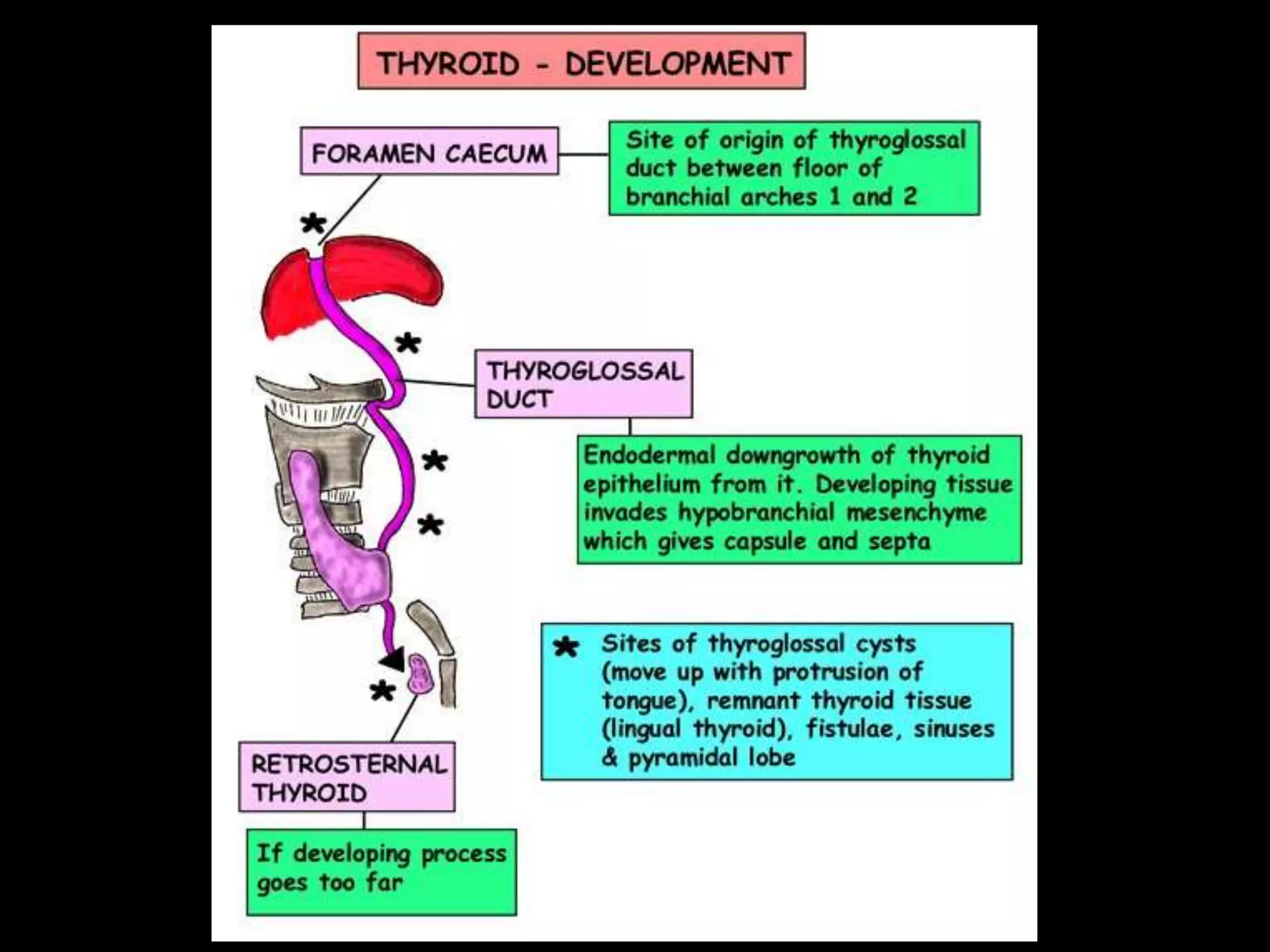
![THYROID GLAND
Chronological age:
3th week of IUL (1st endocrine organ to develop)
Germ layer:
Endodermal diverticulum (Thyroglossal duct)
Site:
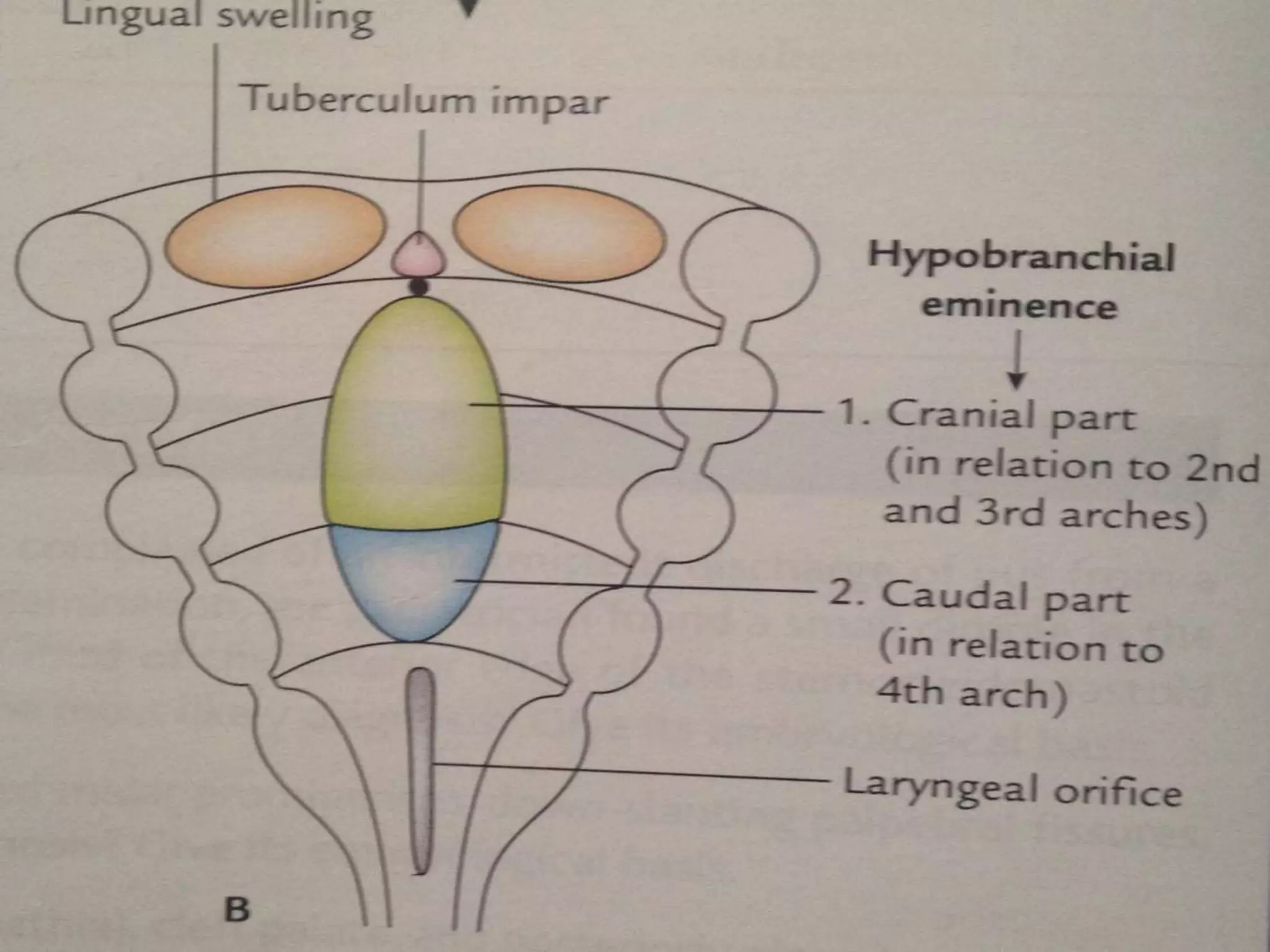
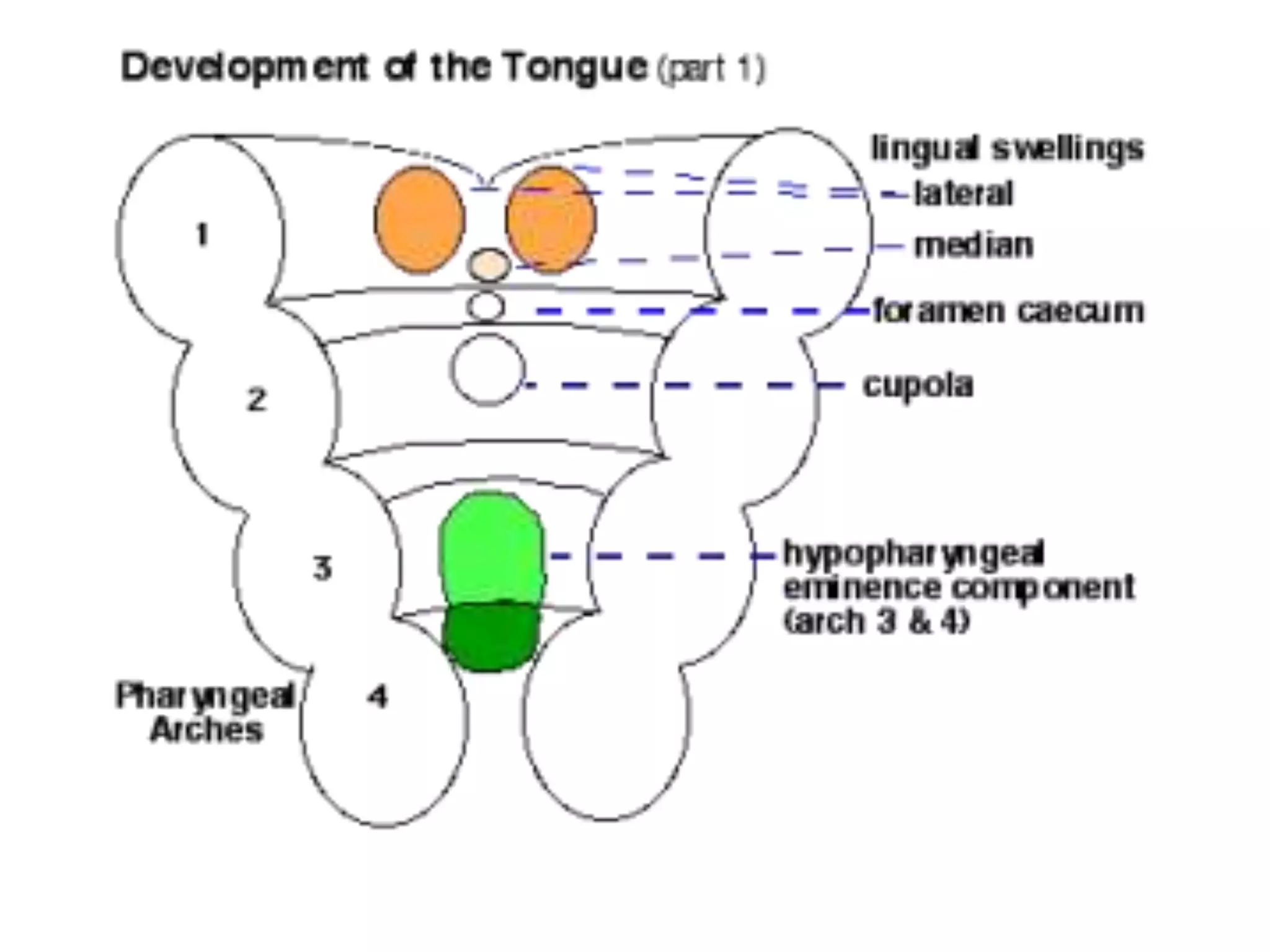
Floor of the pharynx [below & behind the
tuberculum impar of developing tongue]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developmentofendocrinesystem-170529044346/75/Development-of-endocrine-system-43-2048.jpg)