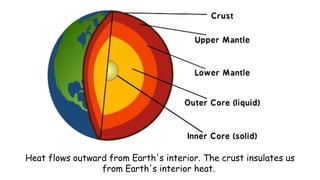
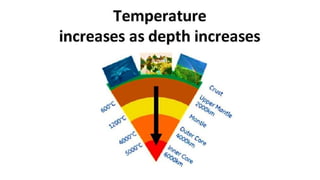
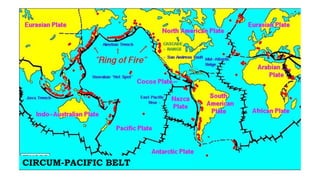
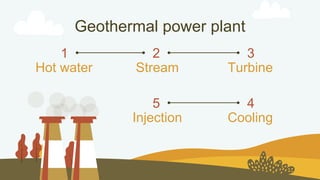
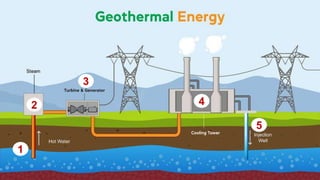
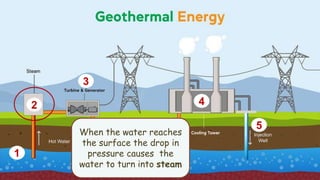
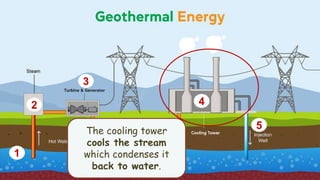
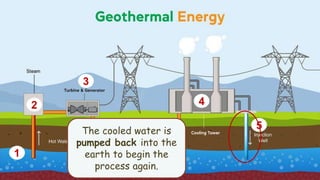
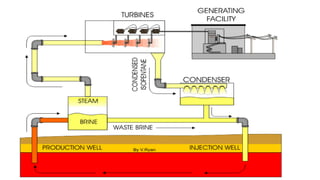
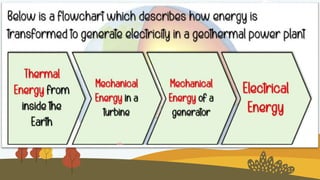
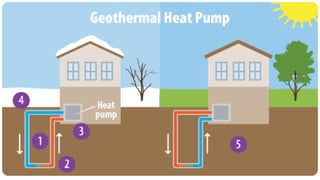
This document discusses geothermal energy and how it can be used as a renewable energy source. It explains that geothermal energy harnesses heat from within the Earth and can be used to generate electricity through geothermal power plants. The document also describes how geothermal power plants work by drilling wells into the Earth to extract hot water that is used to power steam turbines and generators. Additionally, the advantages of geothermal energy being renewable and more environmentally friendly than fossil fuels are balanced with the disadvantages of high initial costs and potential to trigger earthquakes.