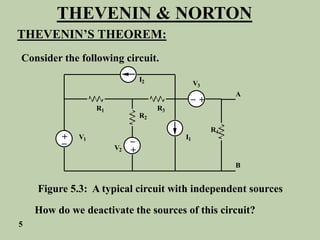
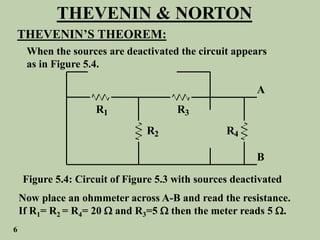
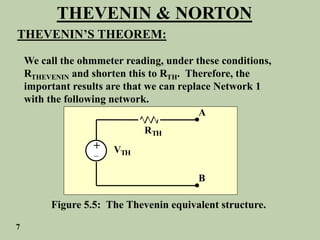
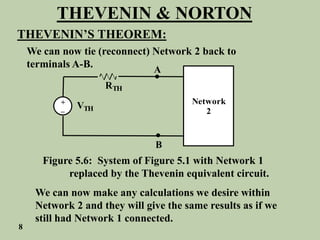
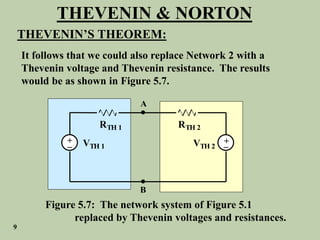
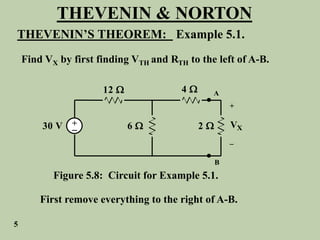
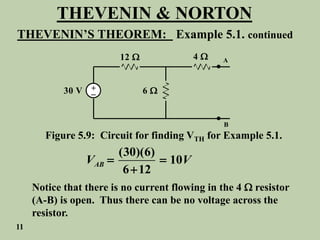
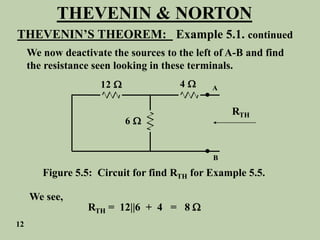
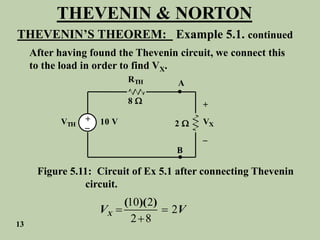
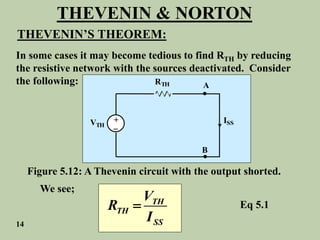
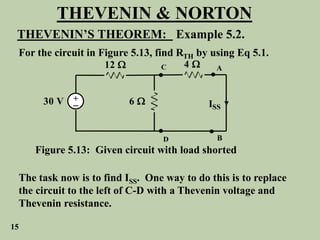
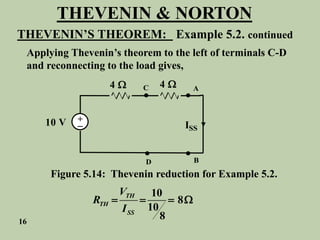
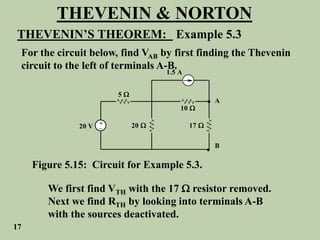
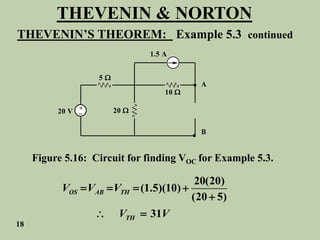
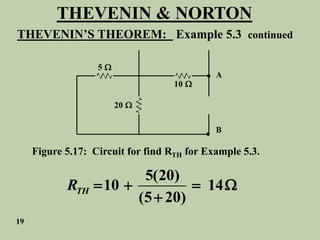
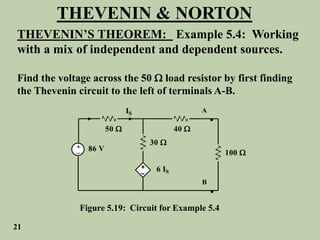
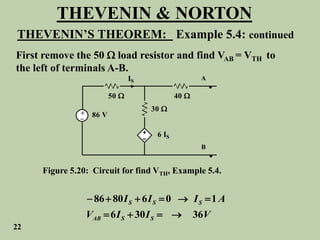
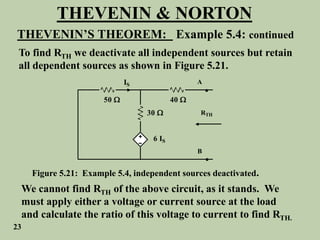
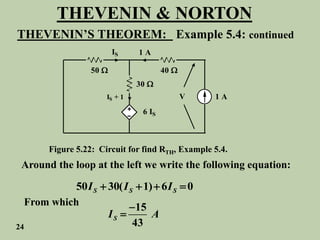
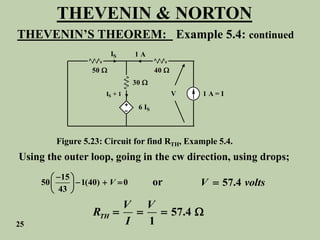
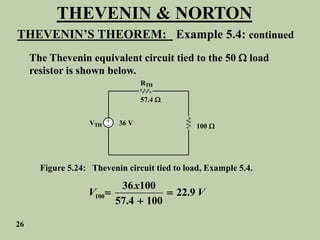
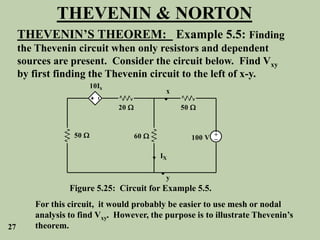
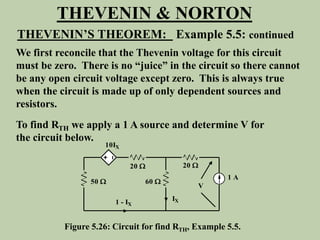
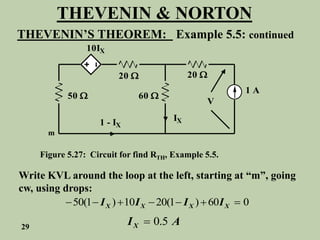
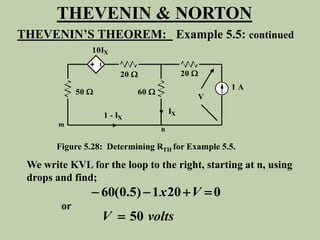
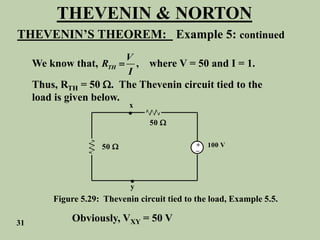
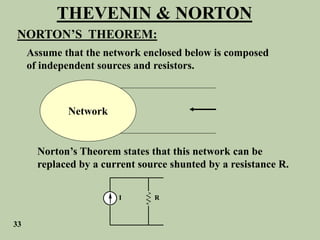
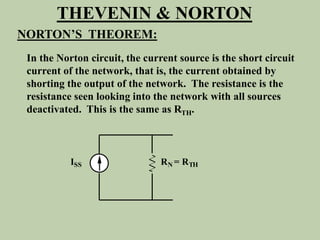
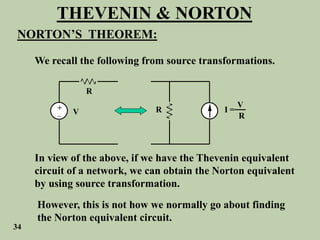
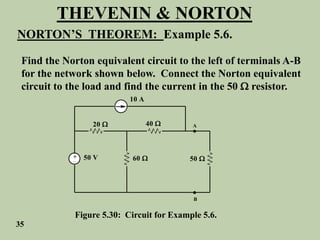
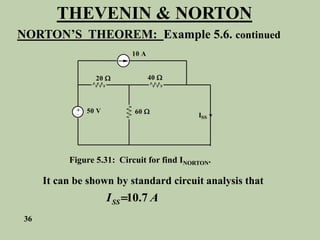
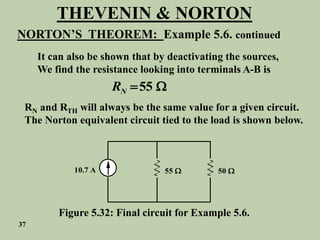
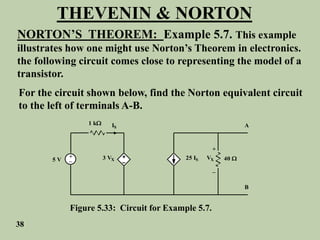
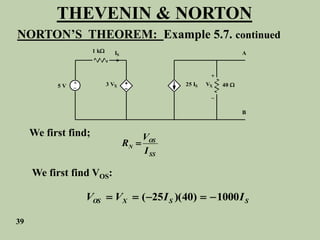
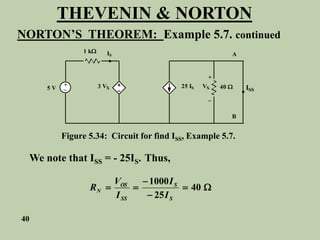
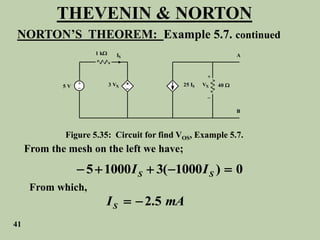
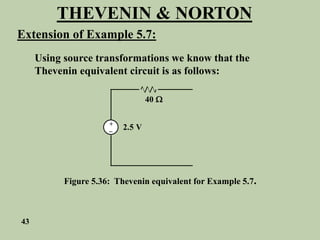
The document explains Thevenin's theorem, which states that any linear electrical network can be reduced to an equivalent circuit consisting of a voltage source in series with a resistor. The voltage source is equal to the open-circuit voltage of the network, and the resistor is equal to the resistance measured across the terminals when all independent sources are deactivated. Several examples are provided to demonstrate how to use Thevenin's theorem to find equivalent circuits and calculate voltages in more complex networks.