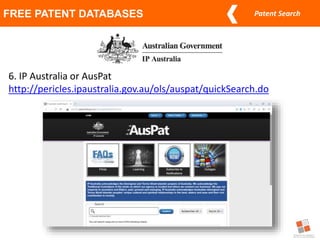
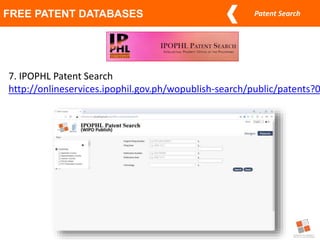
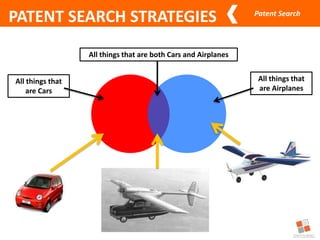
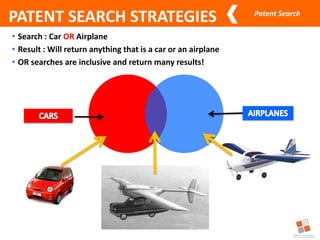
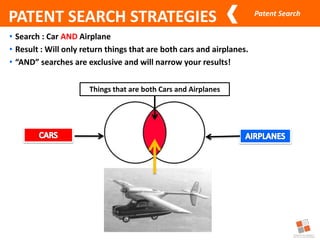
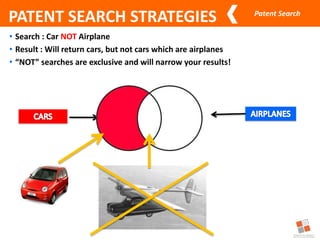
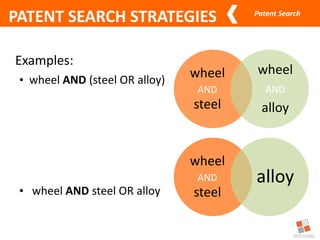
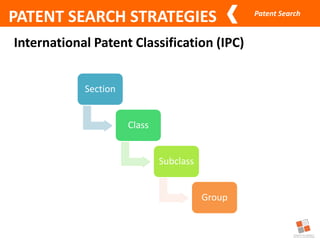
This document discusses different types of patent searches and strategies for conducting patent searches. It identifies seven main types of patent searches: state of the art, novelty, validity, name, freedom to operate, non-infringement opinion, and family/legal status. It also outlines eight strategies for searching patent databases, including using keywords, Boolean operators, nesting, phrases, truncation, classification searches, citation searches, and assignee/inventor searches. Finally, it identifies some free patent databases and concludes with key points about the coverage of patent documents.