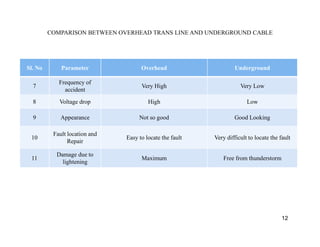
Electrical power can be transmitted through overhead power lines or underground cables. Each method has benefits and drawbacks. Overhead lines are cheaper and easier to install but less safe, while underground cables are more expensive but safer. The choice depends on factors like voltage, cost, safety, and the application. Overhead lines are generally used for their lower cost and ability to transmit higher voltages, while underground cables are used where overhead lines present safety issues or cannot be implemented.