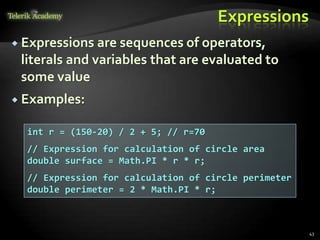
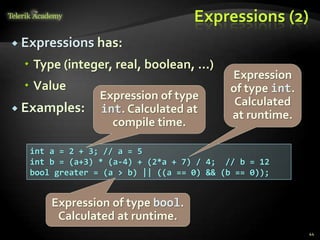
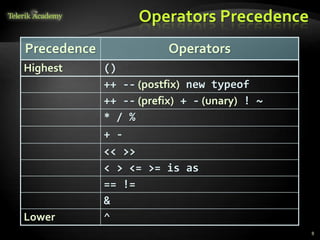
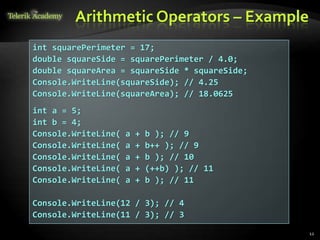
The document discusses operators and expressions in C#. It covers various categories of operators like arithmetic, logical, comparison, assignment, and other operators. It provides examples of using different operators and discusses operator precedence. It also covers implicit and explicit type conversions in C# expressions.





![Categories of Operators in C#
Category Operators
Arithmetic + - * / % ++ --
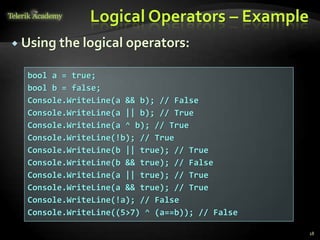
Logical && || ^ !
Binary & | ^ ~ << >>
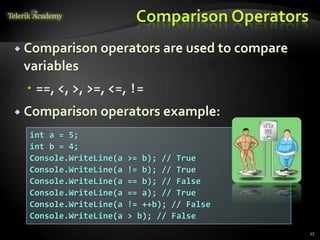
Comparison == != < > <= >=
Assignment
= += -= *= /= %= &= |=
^= <<= >>=
String concatenation +
Type conversion is as typeof
Other . [] () ?: new
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-operators-expressions-and-statements-120712073351-phpapp01-150420012000-conversion-gate01/85/3-operators-expressions-and-statements-120712073351-phpapp01-6-320.jpg)





















![Other Operators (2)
Member access operator . is used to access
object members
Square brackets [] are used with arrays
indexers and attributes
Parentheses ( ) are used to override the
default operator precedence
Class cast operator (type) is used to cast one
compatible type to another
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-operators-expressions-and-statements-120712073351-phpapp01-150420012000-conversion-gate01/85/3-operators-expressions-and-statements-120712073351-phpapp01-32-320.jpg)