Embed presentation
Download to read offline

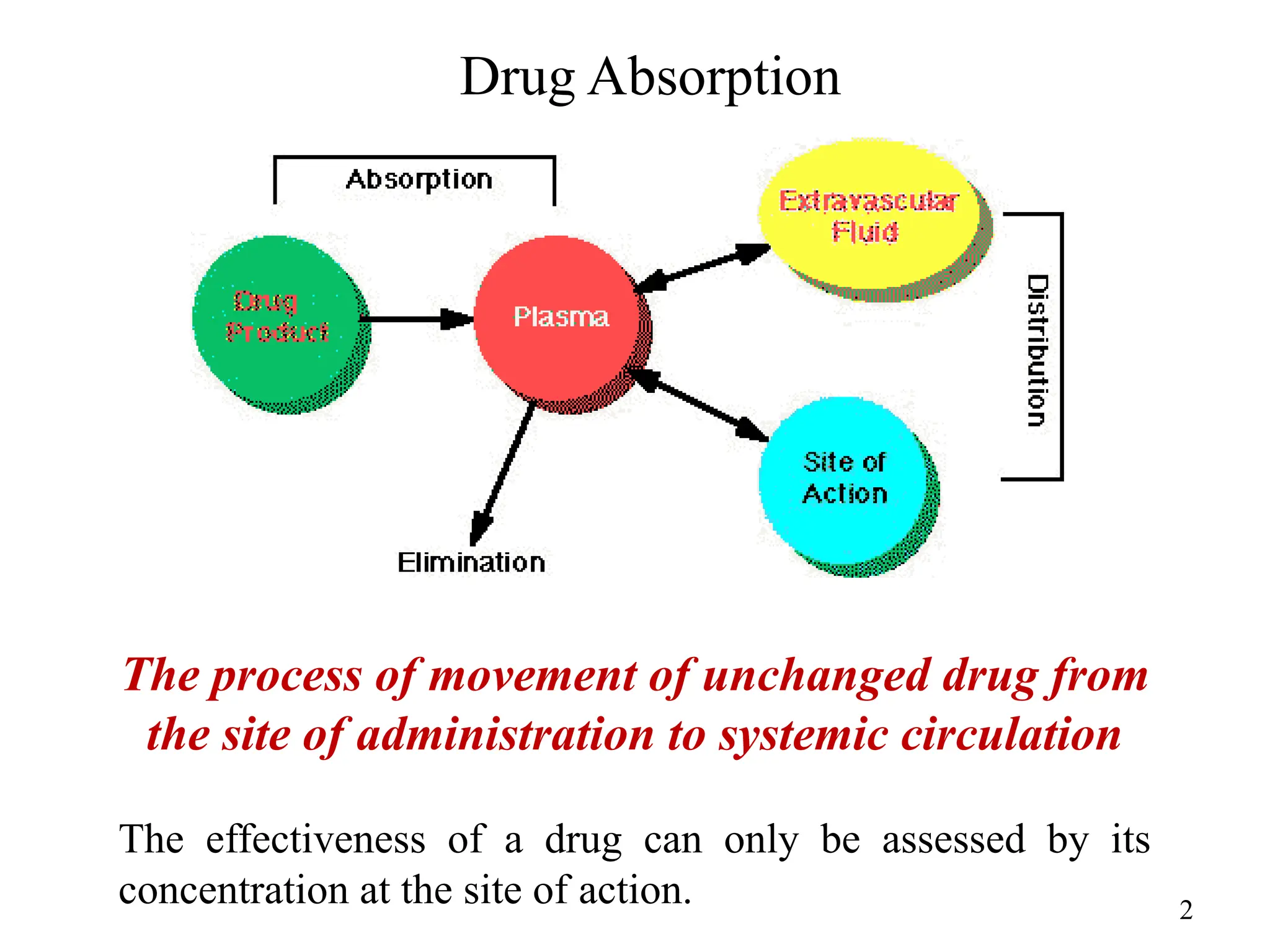
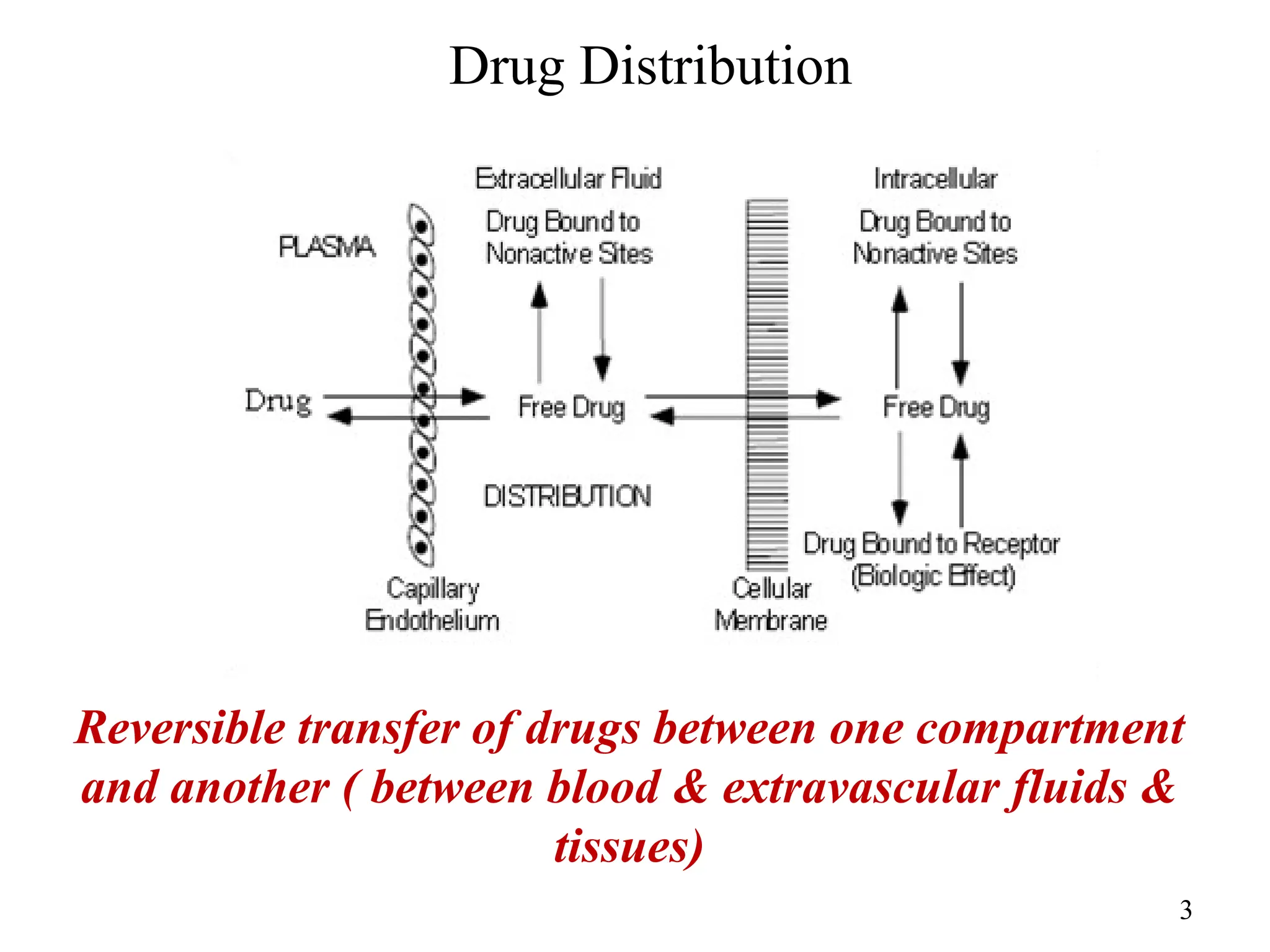
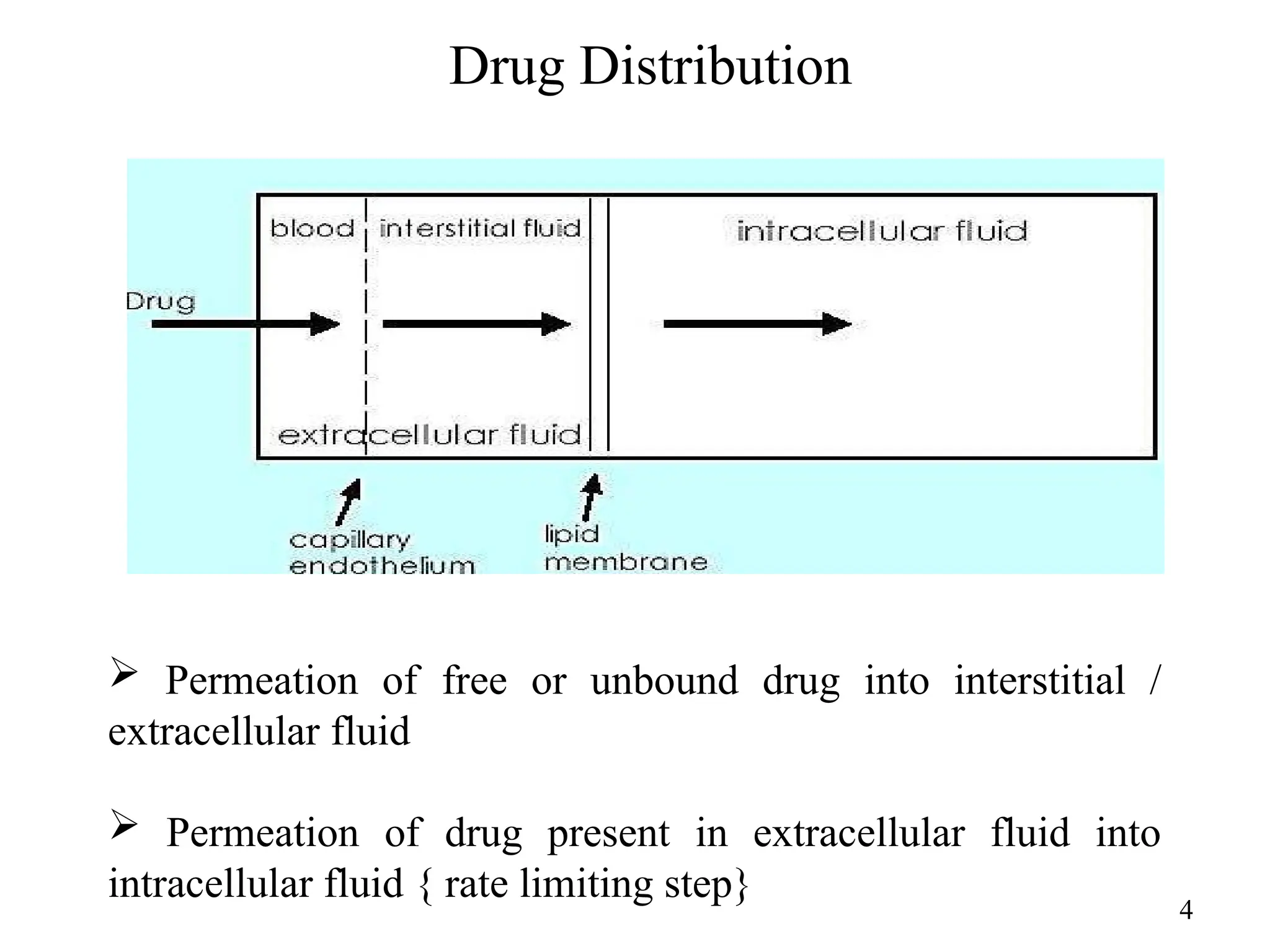
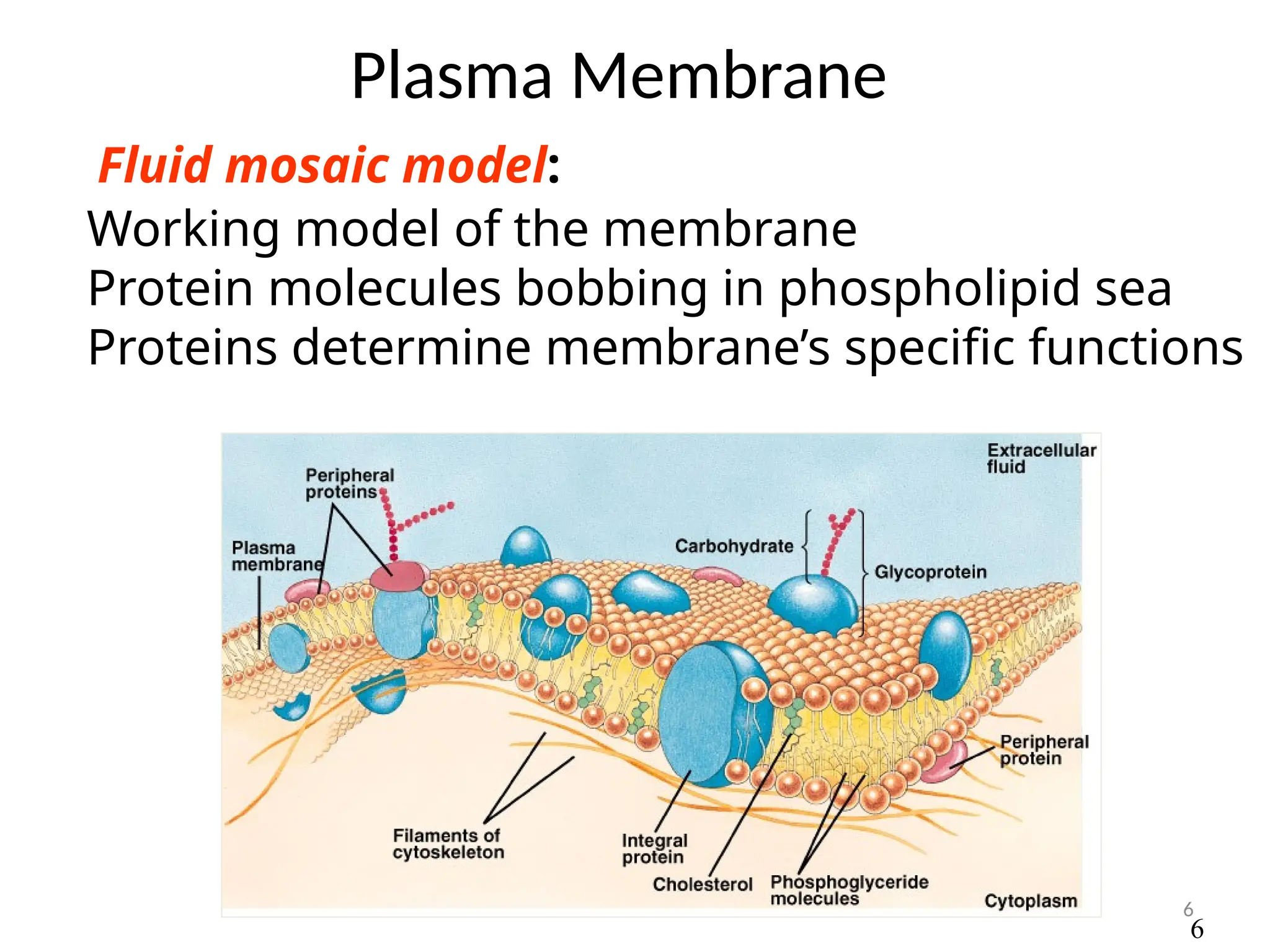

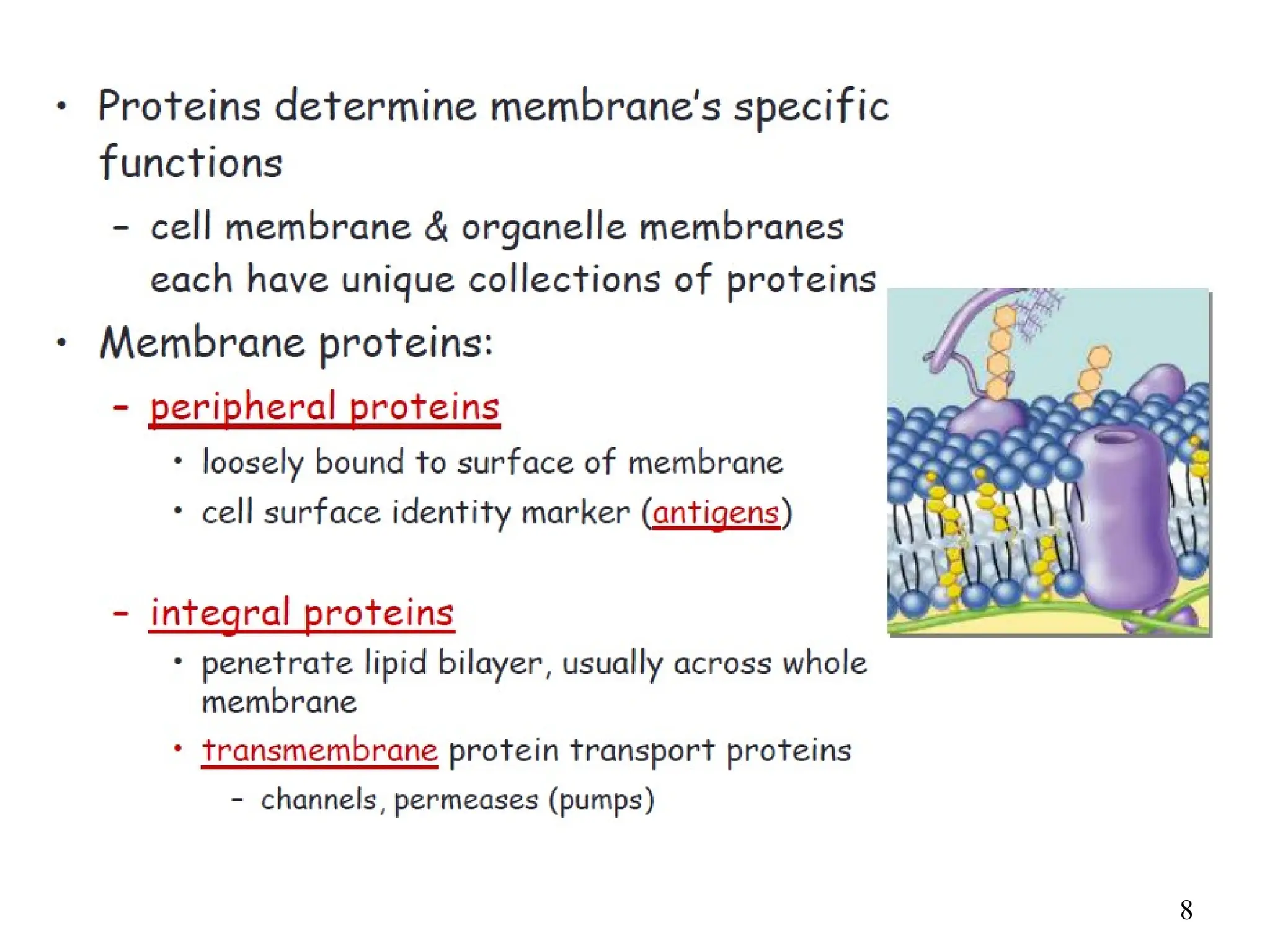
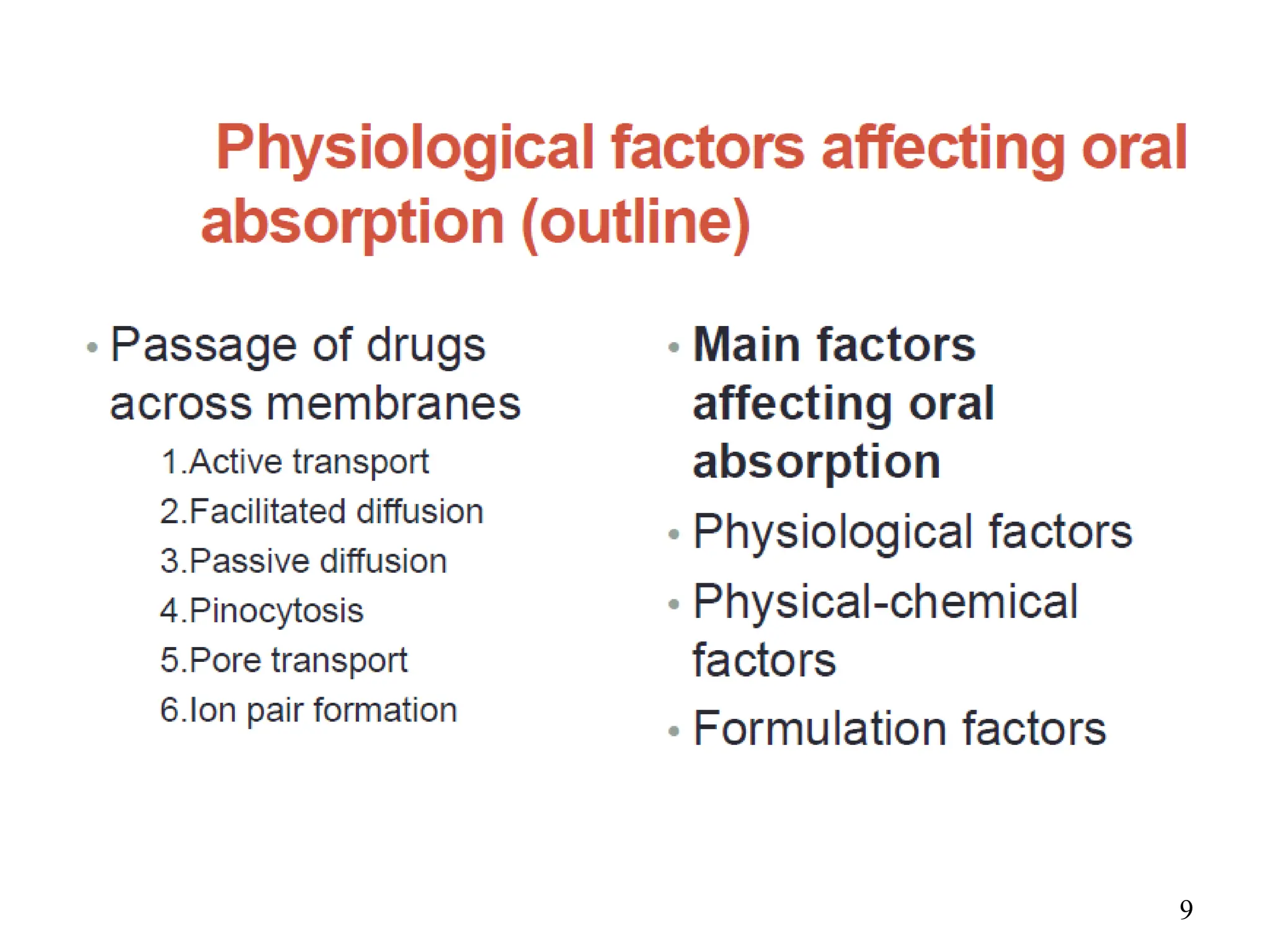
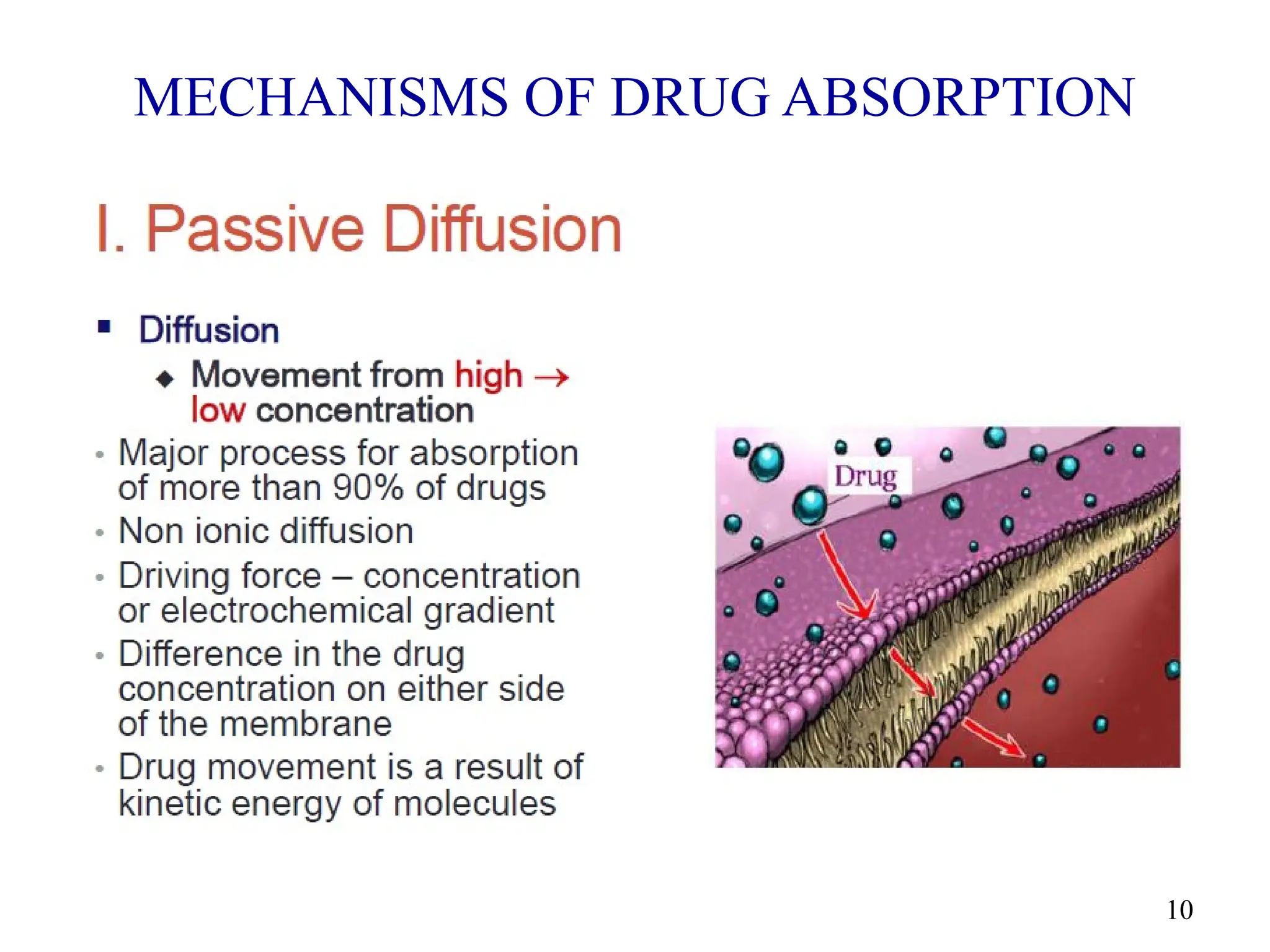
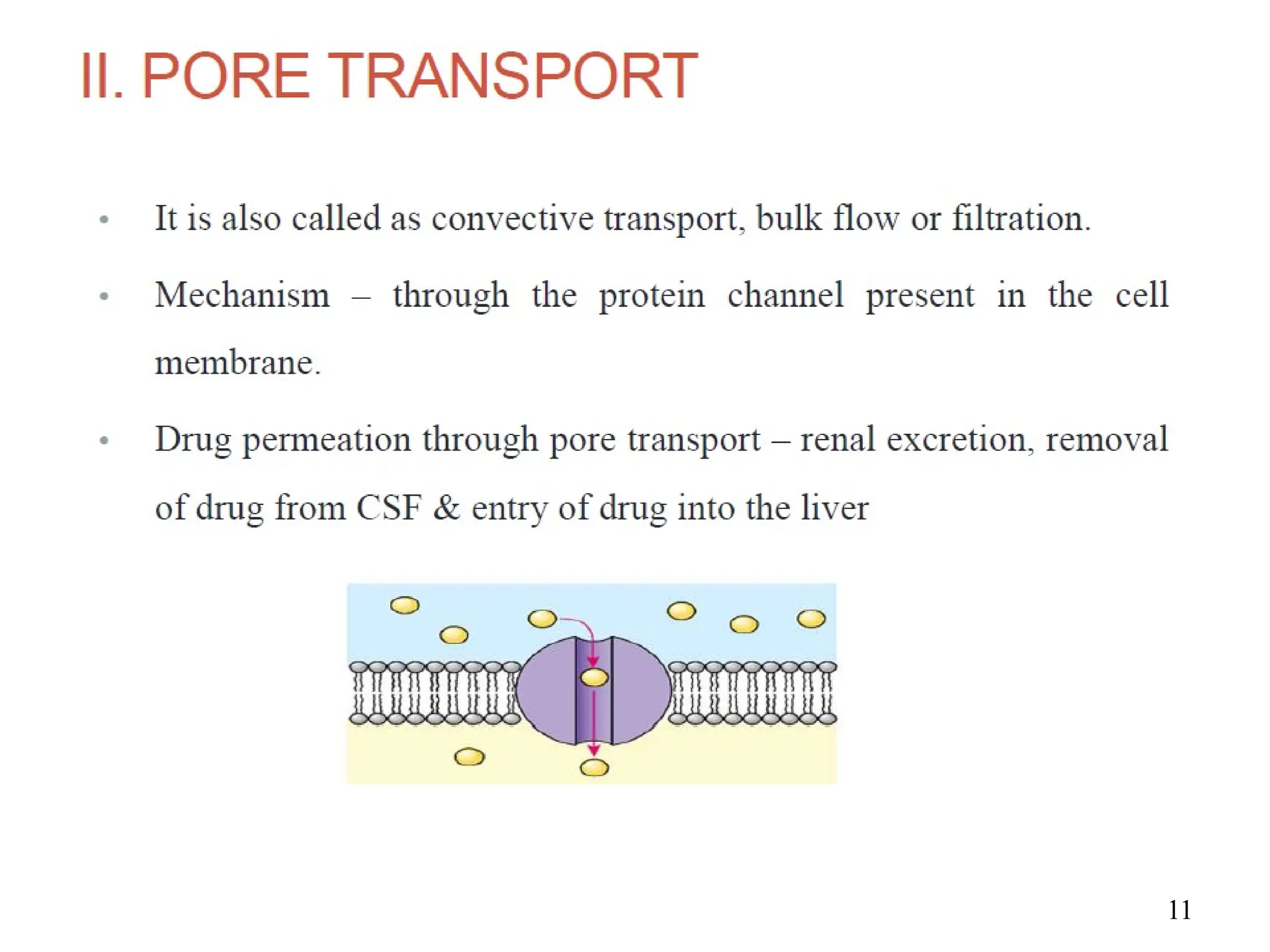

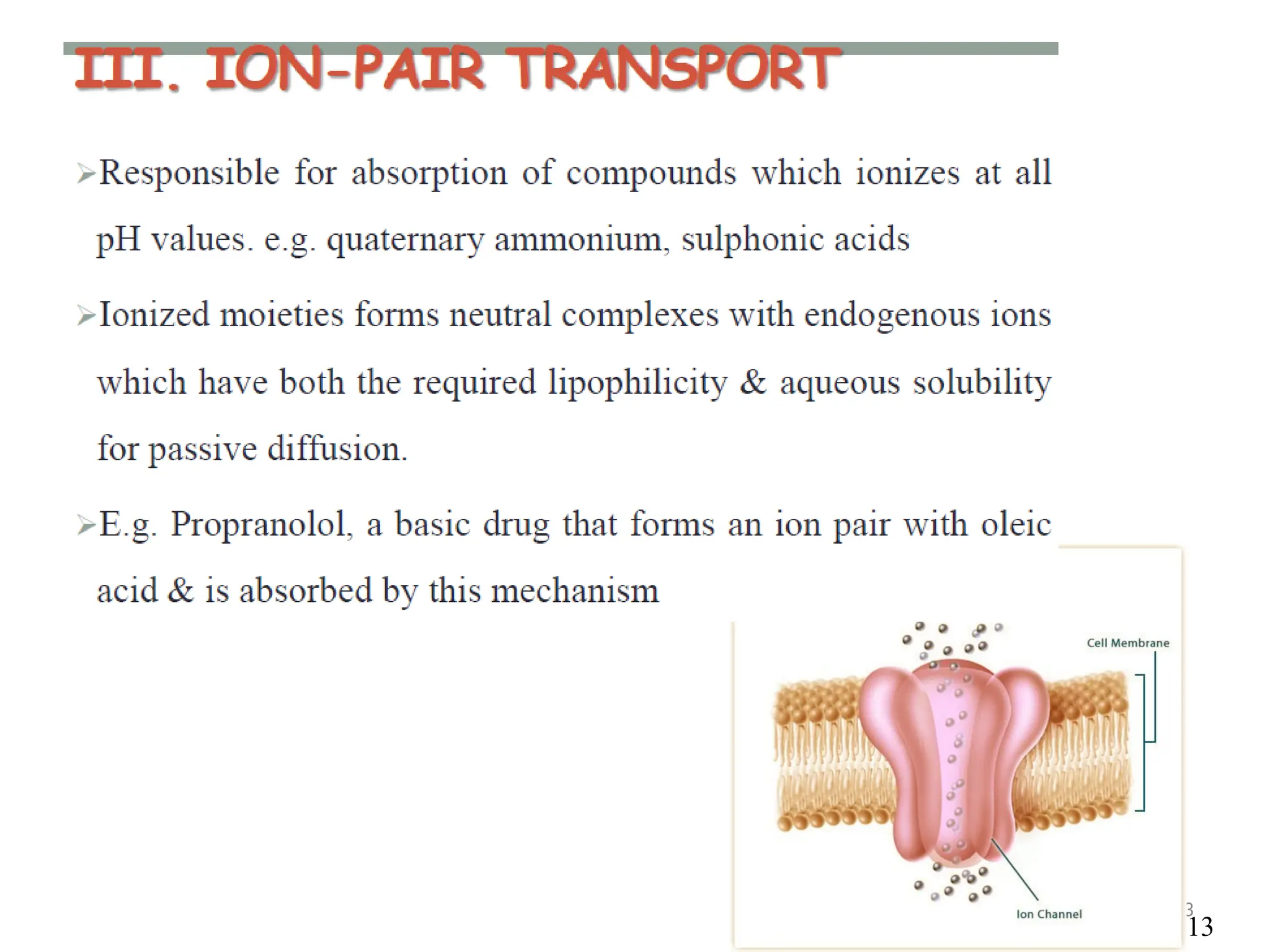
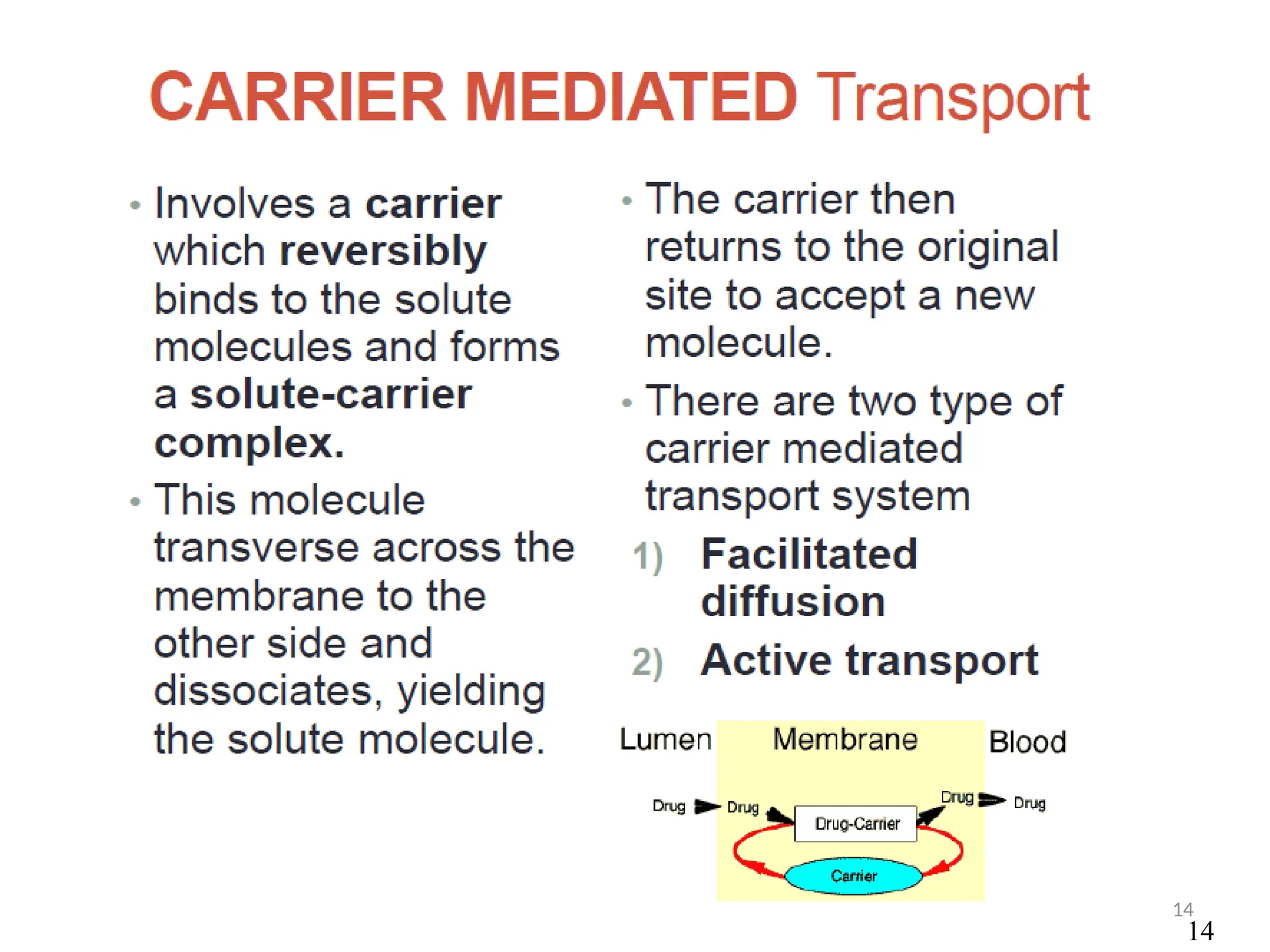
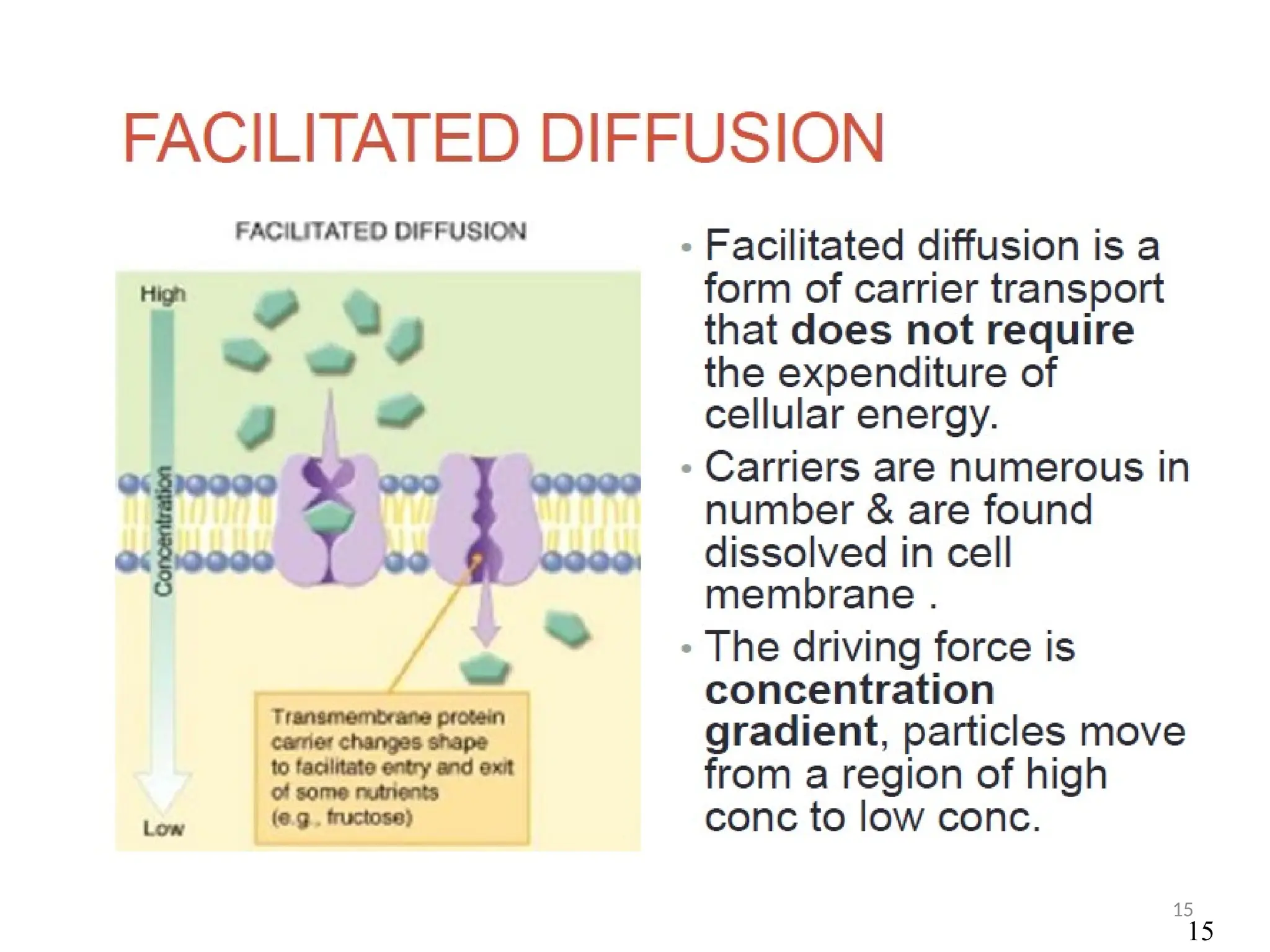
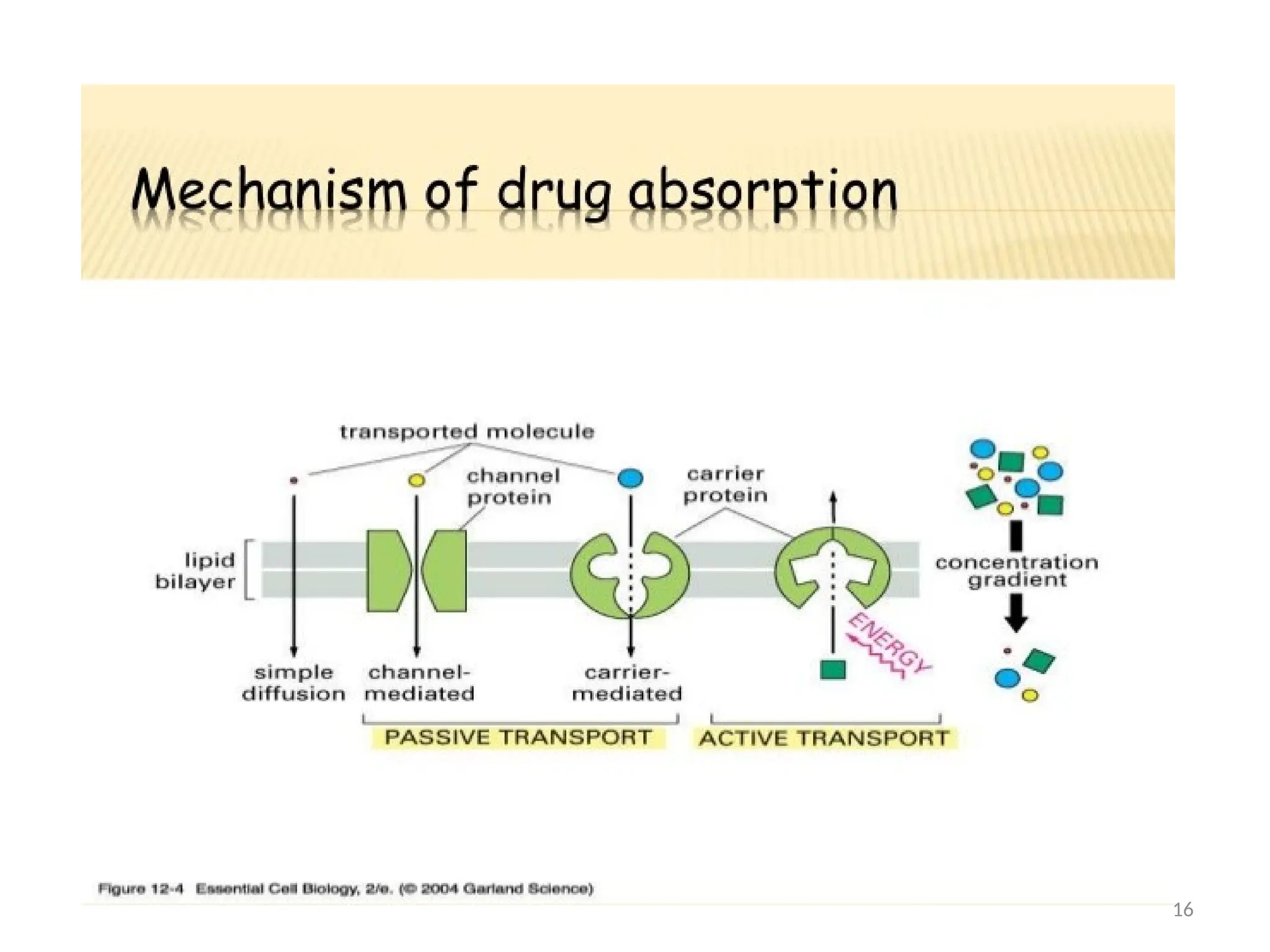
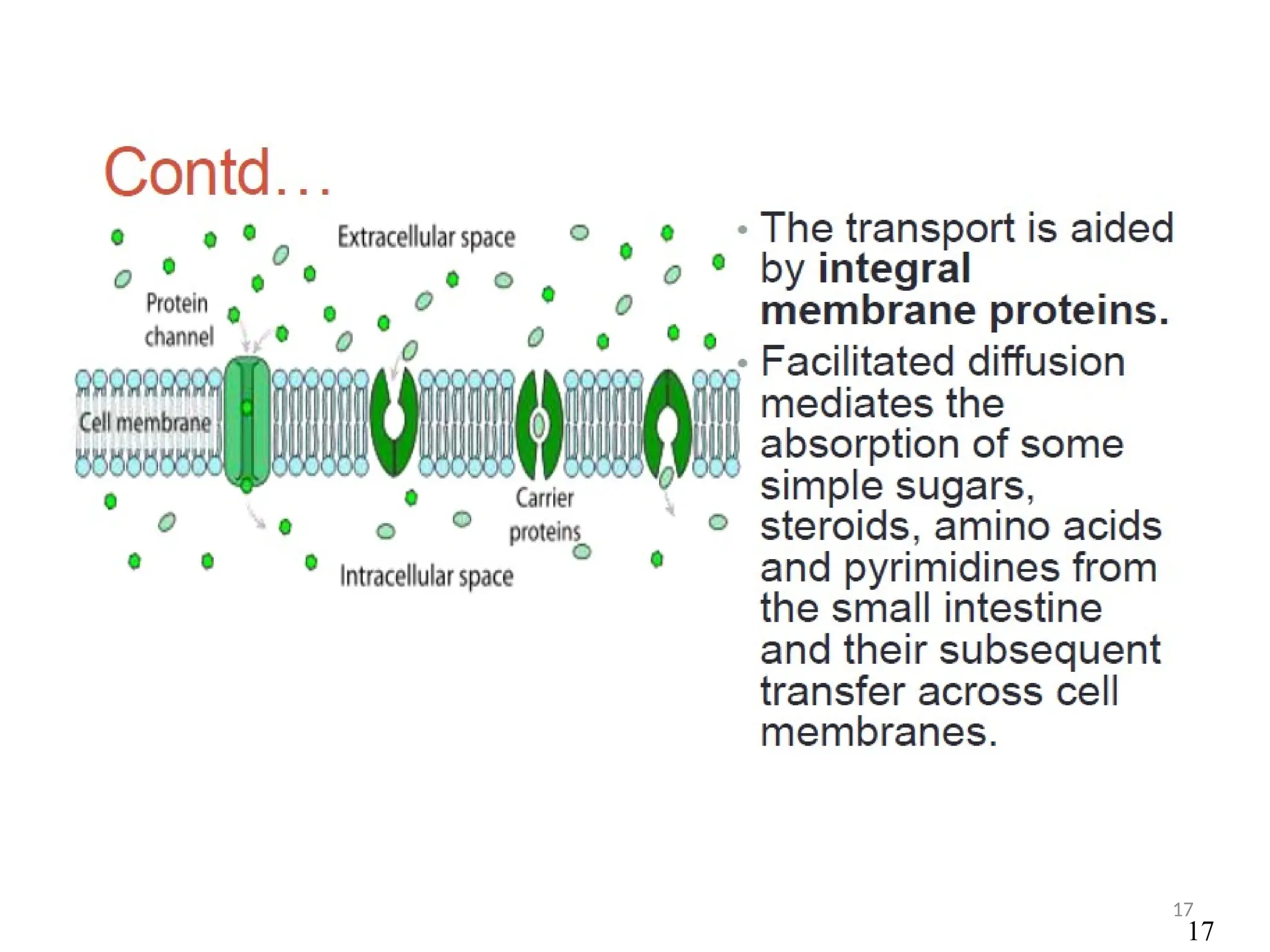
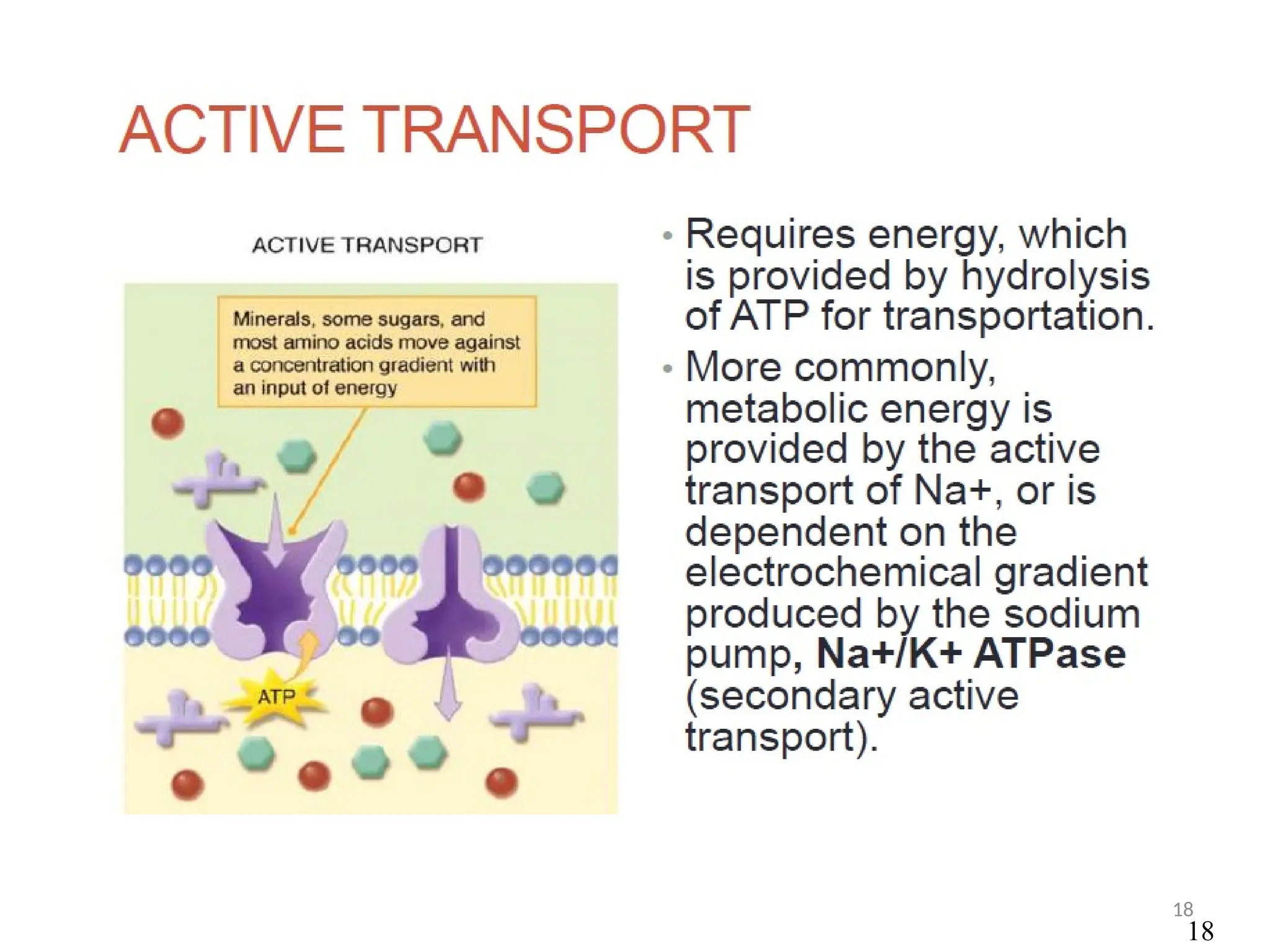
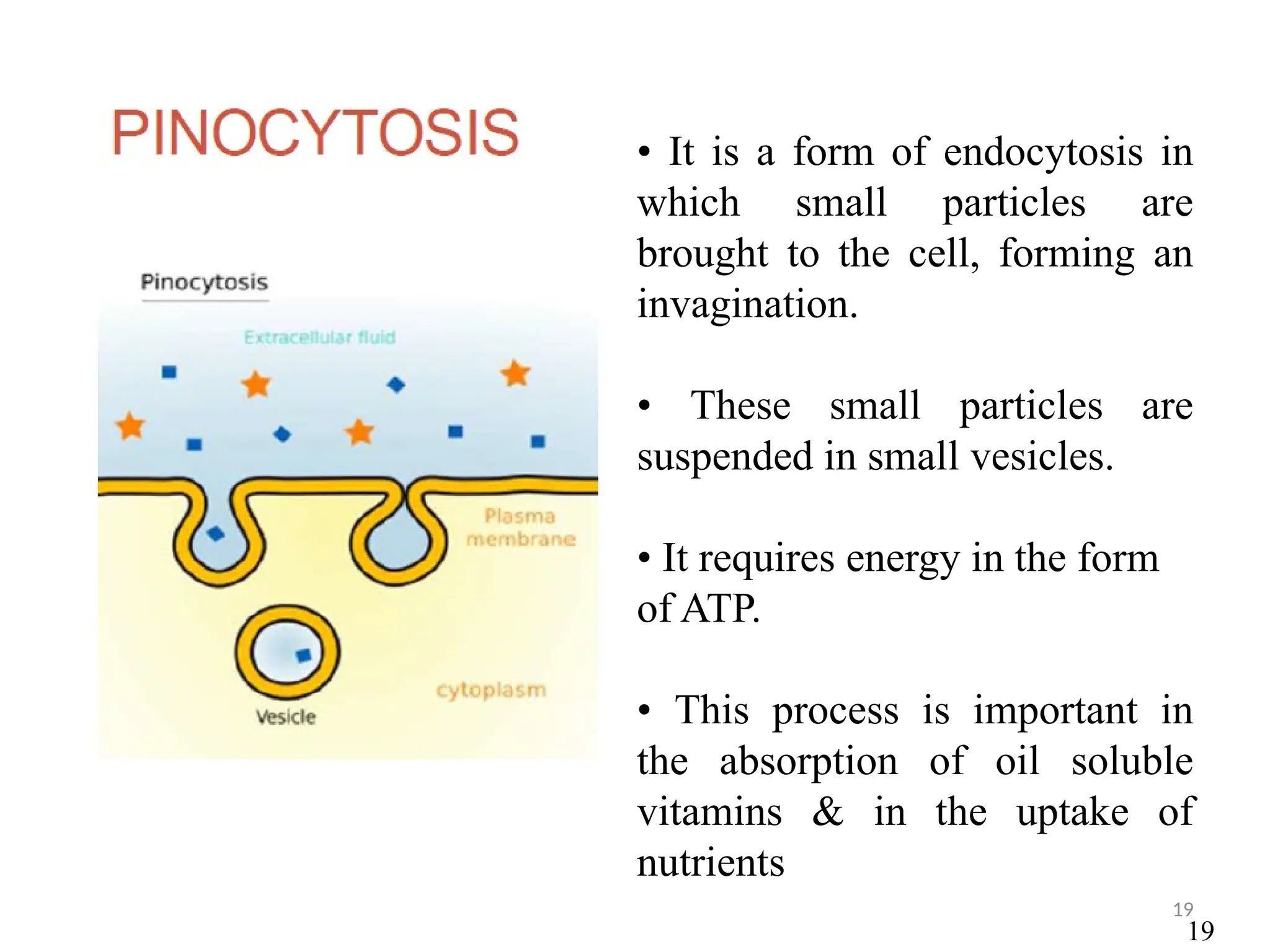
Drug absorption entails the movement of unchanged drugs to systemic circulation and their effectiveness is judged by the concentration at the site of action. Drug distribution involves the transfer of drugs between compartments, including blood and tissues, with specific mechanisms like endocytosis playing a key role in nutrient and vitamin uptake. The plasma membrane's fluid mosaic model describes the arrangement of proteins and phospholipids that facilitate these processes.


















