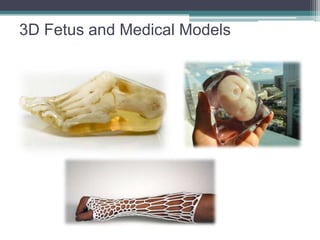
3D printing involves using an additive process to create objects by successively depositing layers of material based on a digital model. This document discusses how 3D printing can be used for bio-printing tissues and organs, as well as its applications in medicine, clothing, and other industries. Limitations include slow production speeds and limited materials, but advances may allow for printing of human organs, skin grafts, prosthetics, and tissues for drug testing. While this technology could help address organ shortages, issues around cost, rejection risks, and ethical concerns remain.