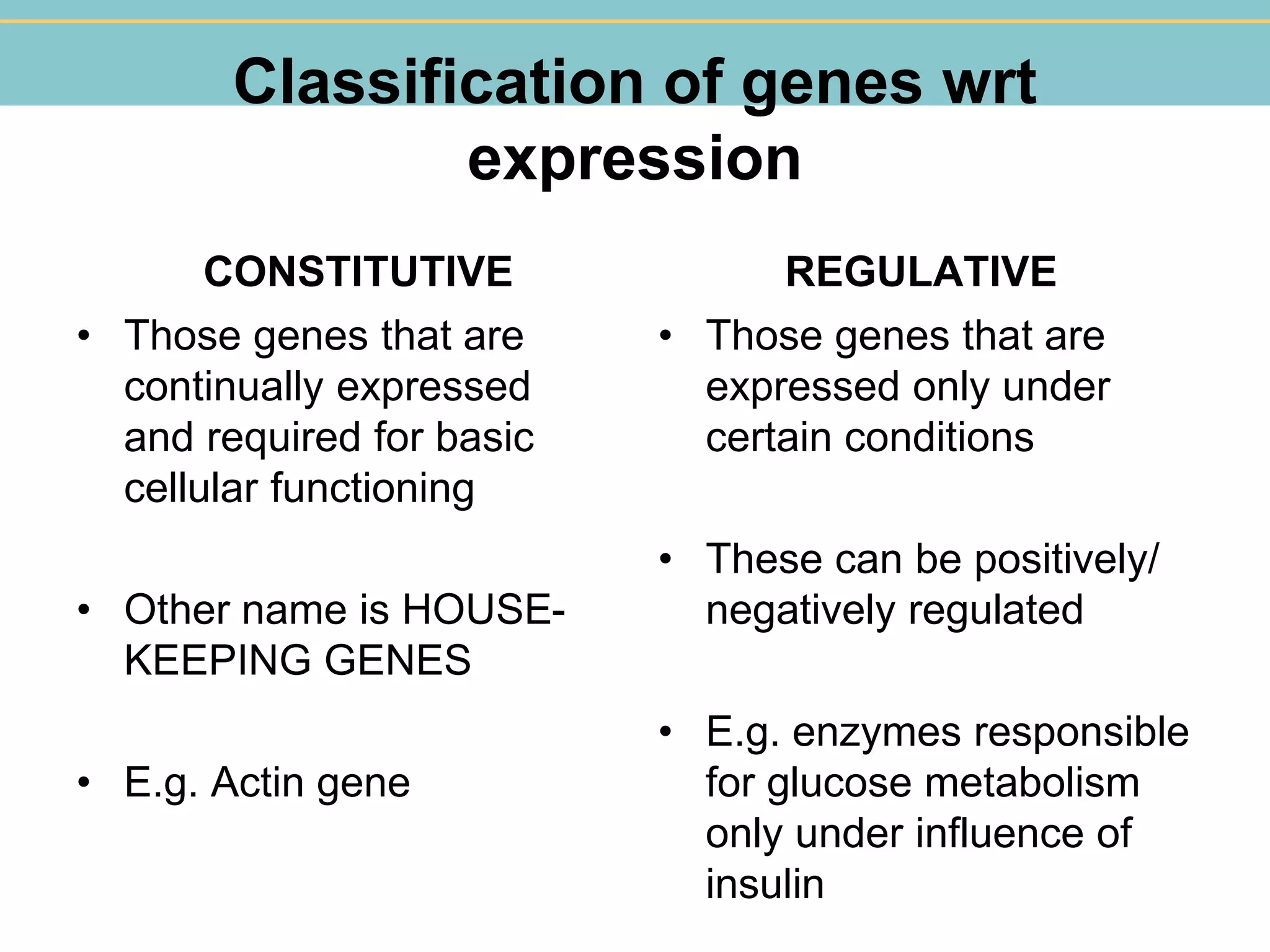
The document discusses molecular biology focusing on gene expression regulation, including the processes of transcription, translation, and replication. It categorizes genes into constitutive and regulative types, with examples and details on prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene control mechanisms. Eukaryotic gene structure is highlighted, noting the presence of introns and exons.