20.dentin.pptx
- 1. DENTIN
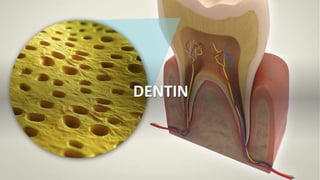
- 2. Introduction • Dentin is the mineralised tissue that forms the bulk of the tooth • It is present in the crown and in the root portion of the tooth. • It is covered by enamel in the crown portion and cementum in the root portion. • It consists of mineralized collagen matrix consisting of closely packed dentinal tubules which extends the entire thickness of the dentin.
- 3. Physical properties of dentin • Dentin is pale yellow contributes the color of the tooth • Dentin is harder than the bone and cementum but softer than the enamel. • Even though the dentin is rigid ,it is an elastic in nature ,which permits slight deformation. • The tubular structure of dentin makes it permeable ;this permeability , however decreases with increasing age.
- 4. Chemical properties of dentin • 70% of inorganic material and 20% of organic material and 10% water • Inorganic portion –calcium hydroxy apetite crystal • Organic portion – collagen fibres mainly type I collagen. • Ground substance- non collagenous matrix protein.
- 5. Histology of dentin 1. DENTINAL TUBULES Odontoblast forms the dentin matrix and move towards the pulp. shape of dentinal tubules
- 6. • The thickness of dentin ranges from 3 to 10 mm. • Buccal and lingual surfaces are bigger than the mesial and distal surfaces. • The tubules are closely packed towards pulp and widely packed dentinoenamel junction. • Dentinal tubules contains terminal branches and lateral branches
- 8. Predentin • Predentin is the newly laid ,yet to be mineralized dentin matrix. • It is the innermost layer of the dentin clos to the pulp. • Width is 6 to 10micrometer. • It becomes a part of mineralized dentin when it starts undergoing mineralization.
- 9. Peritubular dentin • The dentin that present immediately next to the dentinal tubules is the peritubular dentin. • The minerals are deposited in the inner wall of tubule for the formation of peritubular dentin so it is called as INTRATUBULAR DENTIN. • The thickness of peritubular dentin is 0.75micrometer in outer dentin and 0.4micrometer. • The thick organic matter rich in glycosaminoglycans called lamina lamitants is seen in peri tubular dentin
- 10. Intertubular dentin • The dentin situated between the dentinal tubules is the intertubular dentin which forms the major bulk of the dentin • It is made up of type I collagen fibres.
- 11. Odontoblastic process • Odontoblastic process are the cytoplasmic extensions of the odontoblast which extend into the dentinal tubules • The process has a diameter of 3- 4 micrometer when it enters the dentinal tubules and tapers to 1micrometer as it extends further into the tubule.
- 13. Primary dentin • MANTLE DENTIN Mantle dentin is a first formed dentin in the crown. It is less mineralised It is composed of larger collagen fibre It shows branching of dentinal tubules.
- 14. Circumpulpal dentin • Circumpulpal dentin constitutes the remaining primary dentin • When compared to mantle dentin , circumpulpal dentin is more mineralised and has collagen fibres
- 15. Interglobular dentin • During the mineralisation of dentin matrix the minerals are deposited as globules • In most areas these globules fuse to form a uniformly calcified tissue . • When some of the globules fails to fuse into a homogenous mass hypomineralised area will form, called as interglobular dentin.
- 16. Age and functional changes • Secondary dentin • Transluscent dentin • Tertiary dentin • Sclerotic dentin • Dead tracts
- 17. Secondary Dentin • Dentin formed after root completion • Borders the pulp • Formed by continuous , slow deposition of dentin by odontoblasts • Fewer dentinal tubules • Function : Continuous deposition leads to smaller pulp chamber and narrow root canals in old patients • Protects the pulp from exposure
- 18. Translucent dentin • As a result of physiologic ageing, dentinal tubules become completely occluded with apatite crystals • Common in the root • Same refractive index as intertubular dentin • Occluded dentinal tubules appear translucent in ground section • Formation starts apically, proceeds cervically with age. • Function: Used in Forensic dentistry for age estimation
- 19. Tertiary dentin • Dentin formed in response to various stimuli like attrition, caries or restorative dental procedure • Types • Reactionary dentin • Reparative dentin/Osteodentin
- 20. Reactionary dentin • Formed by existing odontoblasts which have survived severe damage cause to them by stimulus. • Irregular appearance with fewer tubules
- 21. Reparative dentin • Formed by newly differentiated odontoblast-like cells that replace the original odontoblasts that have been destroyed by stimulus • Newly differentiated odontoblast like cells arise from deeper regions of the pulp • Irregular with fewer , more twisted tubules • Newly differentiated odontoblast like cells get entrapped in the matrix they form to produce osteodentin.
- 22. Possible origin of newly differentiated odontoblast like cells • Dormant odontoblast cells formed as a result of epithelial- mesenchymal interaction during tooth development • Odontoblast like cells that arise from stem cell population,without epithelial-mesenchymal interaction, under the influence of cytokines and growth factors
- 23. Sclerotic dentin • Filling up of dentinal tubules with calcified material in response to caries, attrition, erosion • Defensive reaction • Keeps the pulp vital for a longer time • Fine meshwork of apatite crystals • Transparent • Appears light in transmitted light and dark in reflected light. • Mineral concentration is higher, crystal size is smaller • Harder
- 24. Dead tracts • Empty dentinal tubules due to retraction of odontoblastic process or death of odontoblast. • Occurs as a result of caries, attrition, erosion • In ground sections, appear dark in transmitted light and white in reflected light • Commonly seen in narrow pulp horns • Common in older teeth
- 25. DENTIN SENSITIVITY • DIRECT NEURAL STIMULATION THEORY • FLUID OR HYDRODYNAMIC THEORY • TRANSDUCTION THEORY
- 26. DENTINOGENESIS • Dentin formation begins when the tooth germs has reached the bell stage of development.