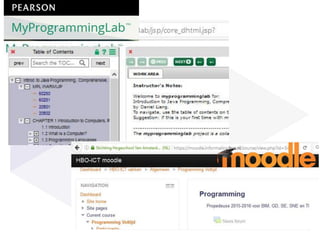
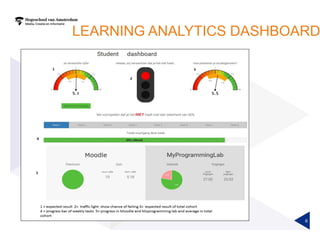
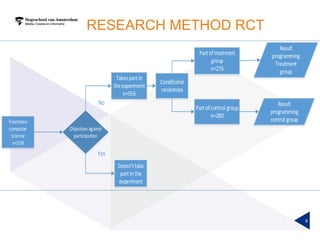
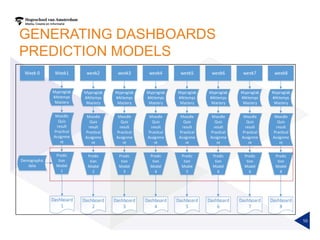
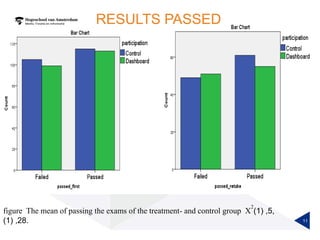
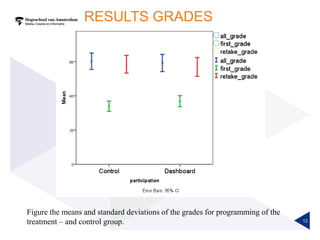
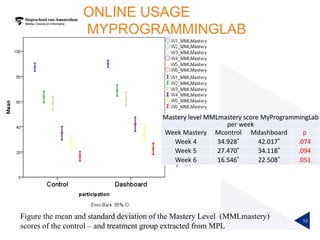
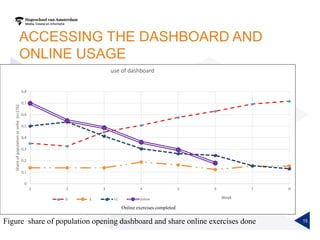
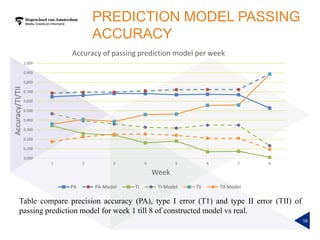
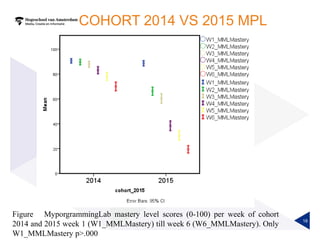
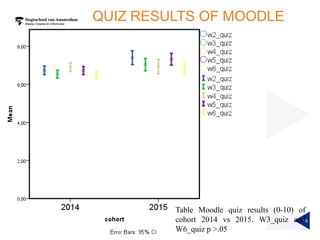
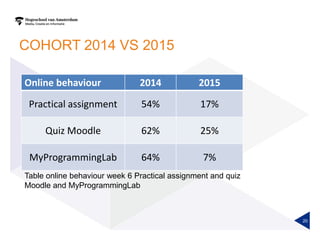
(1) A randomized controlled experiment was conducted to evaluate the effect of a learning analytics dashboard on student performance in a Java programming course with 558 freshman students. (2) The students were randomly assigned to a treatment group that received weekly dashboard updates or a control group. (3) While the dashboard had a small positive effect on online activity, it did not significantly improve pass rates, grades, or the accuracy of predictive models compared to literature benchmarks.