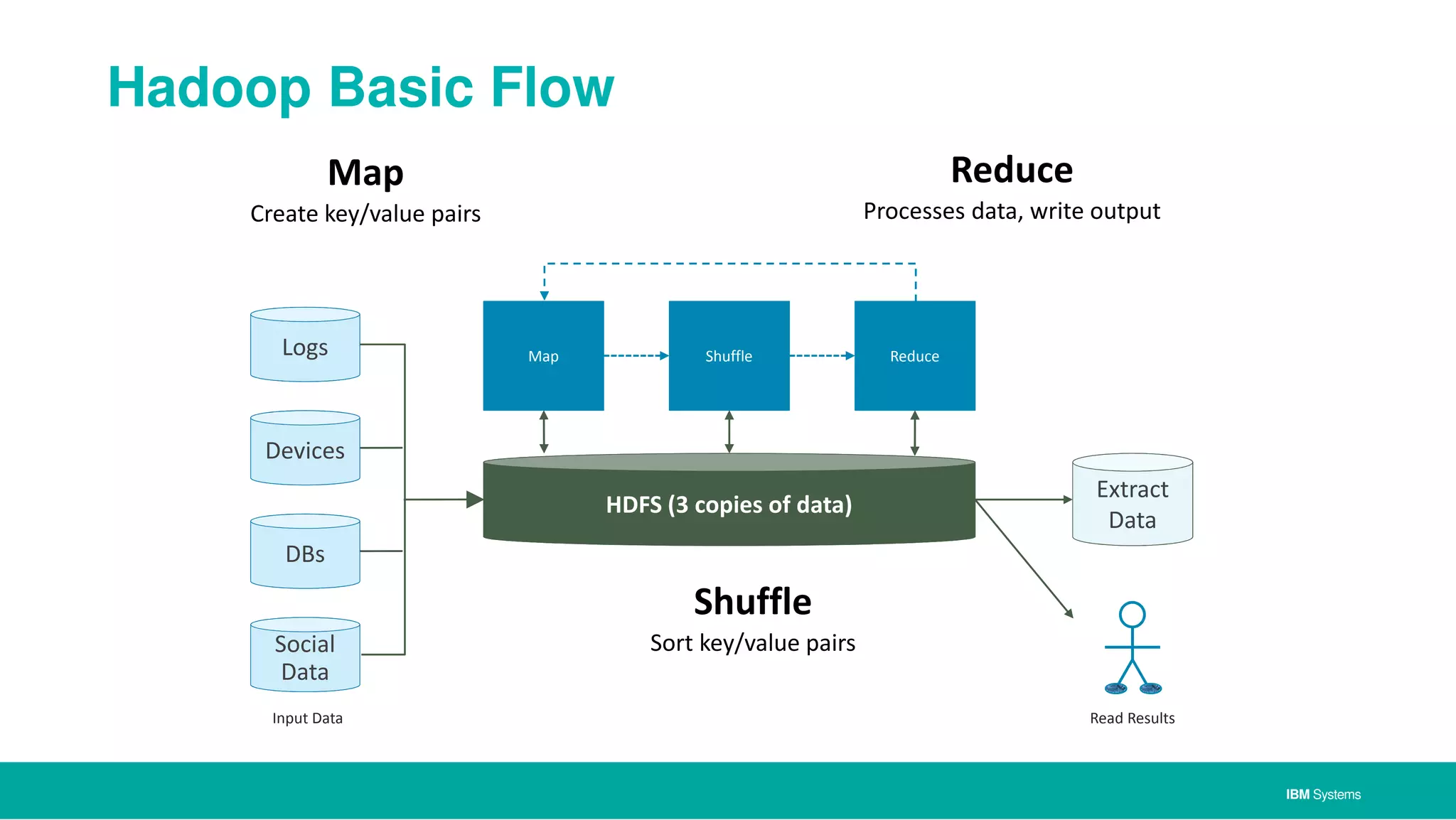
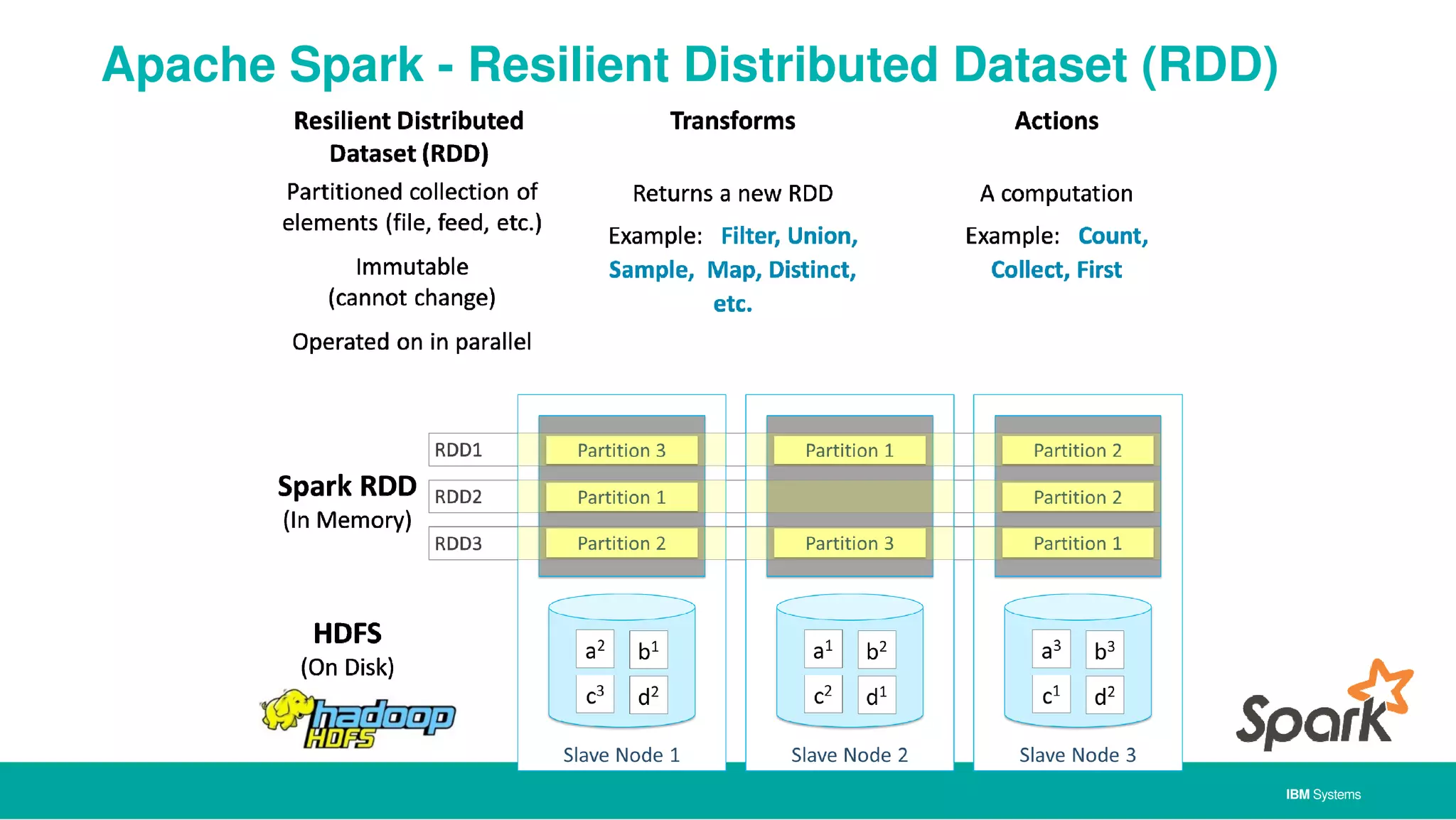
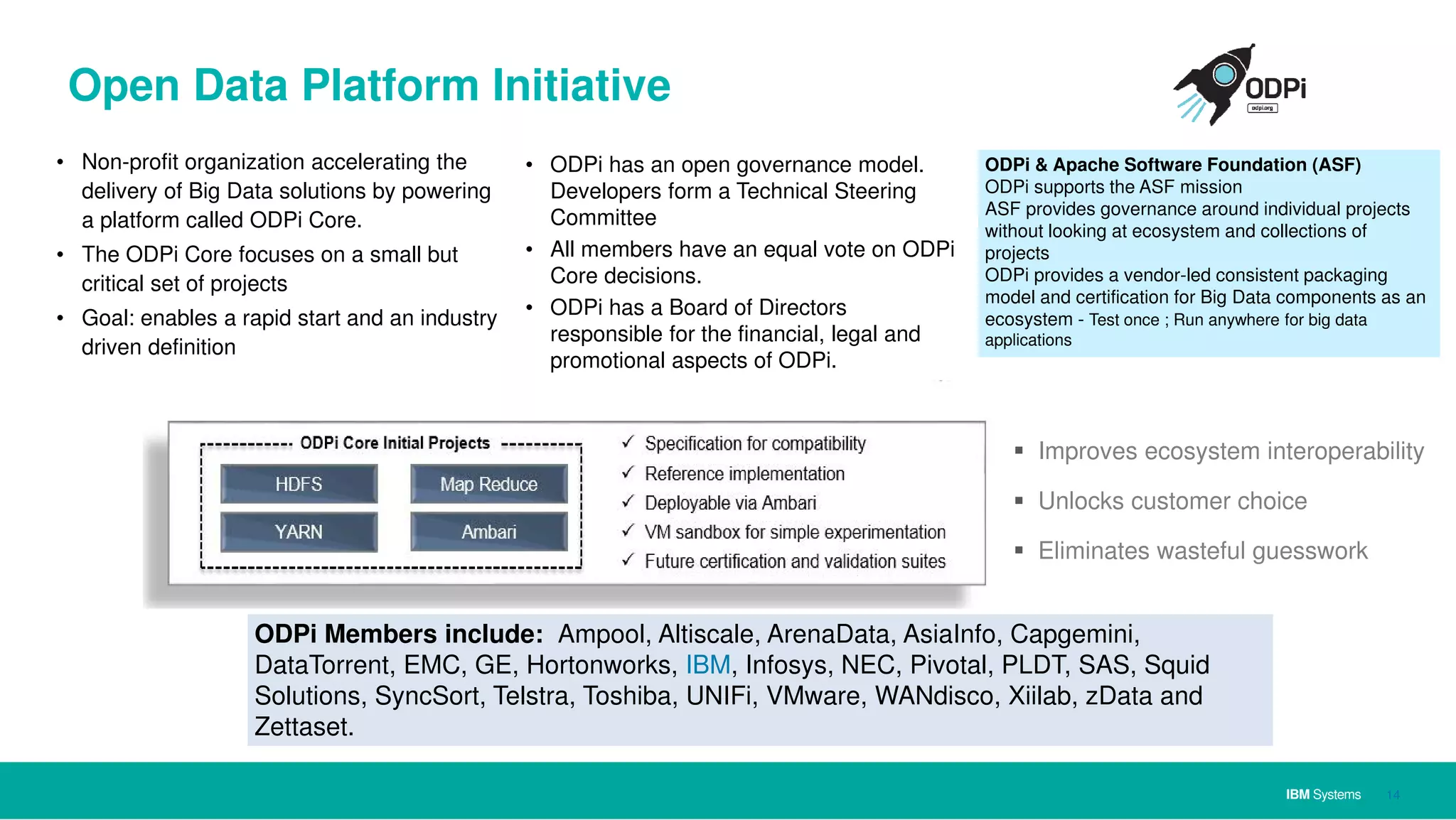
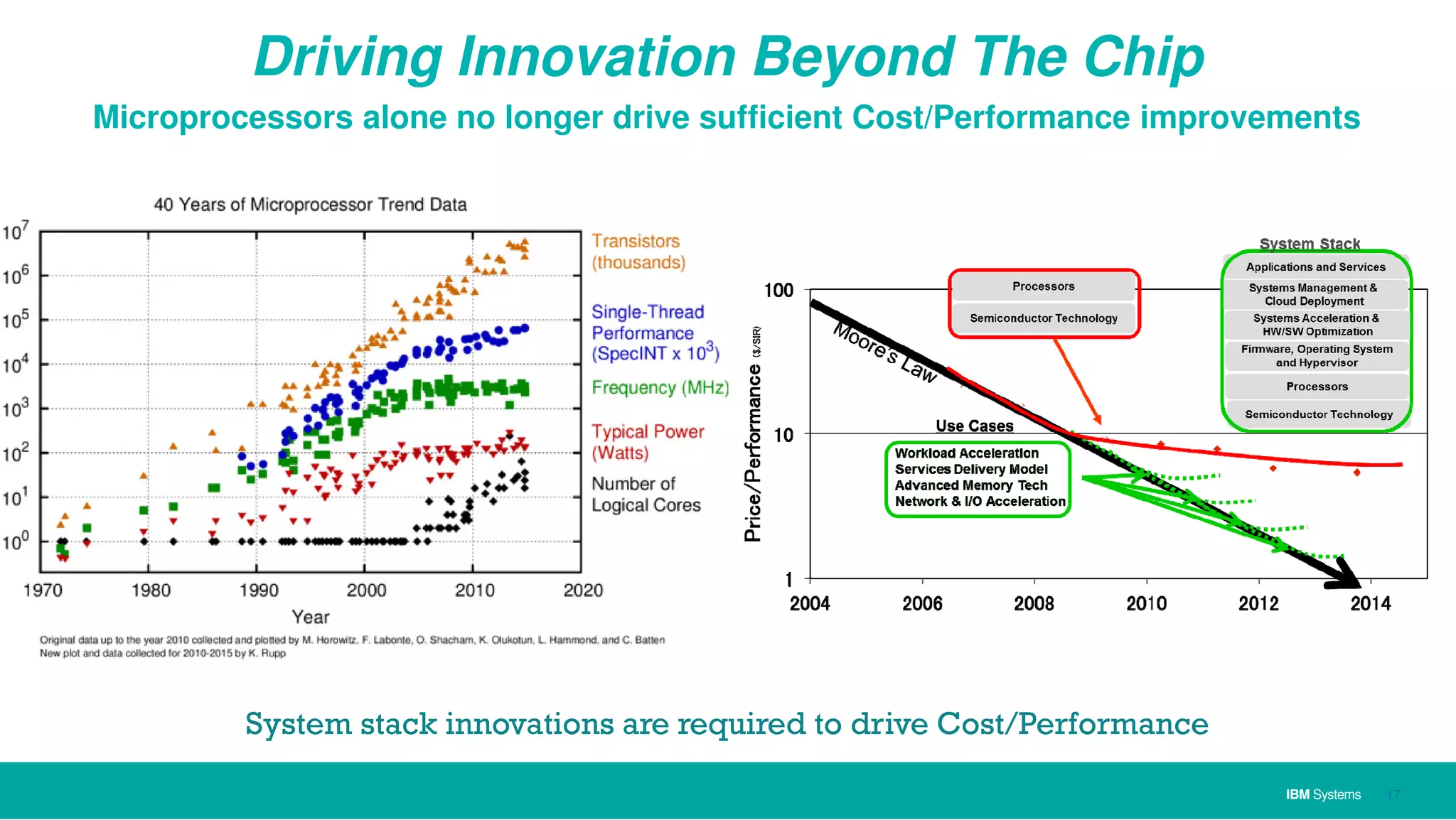
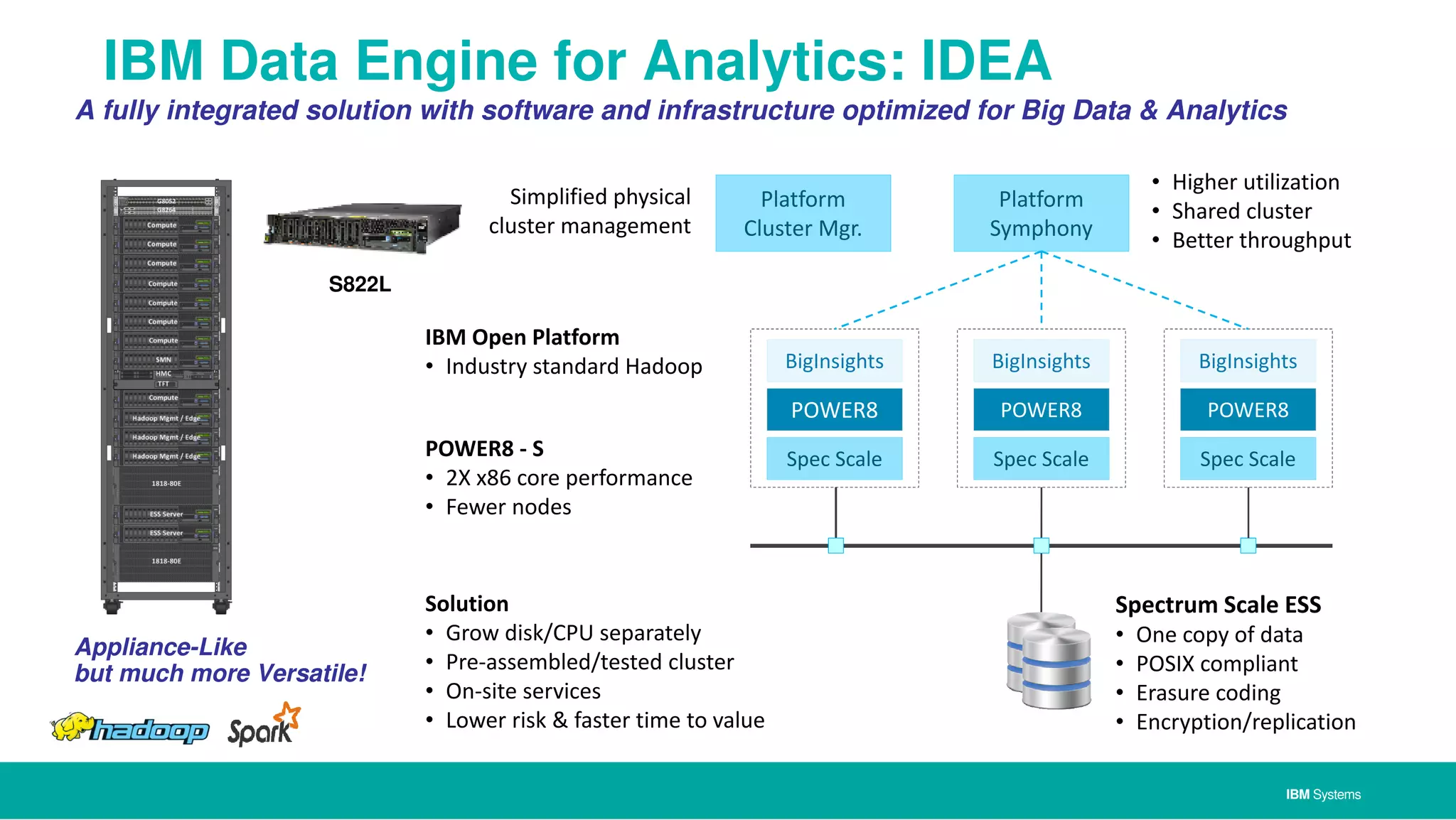
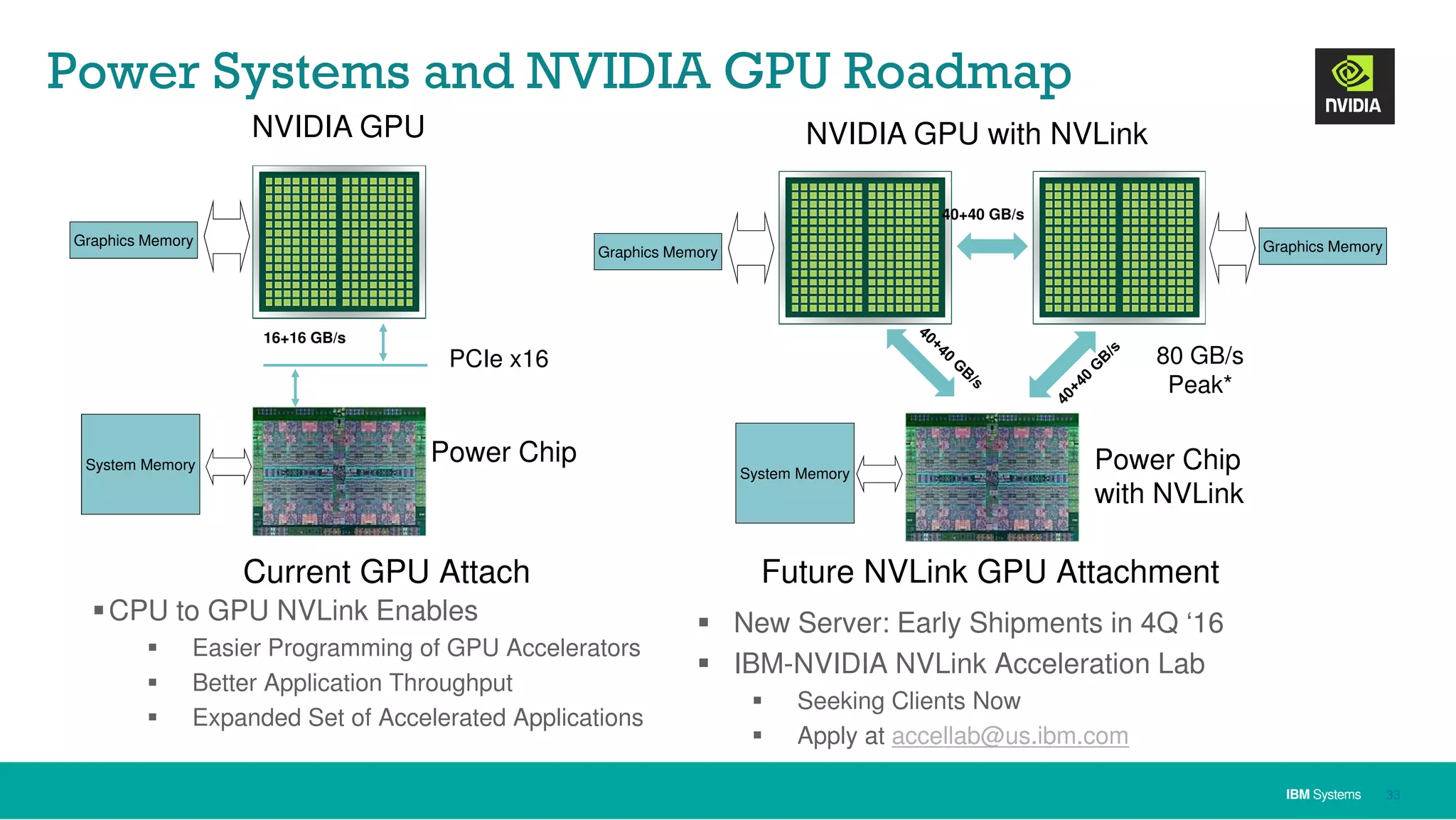
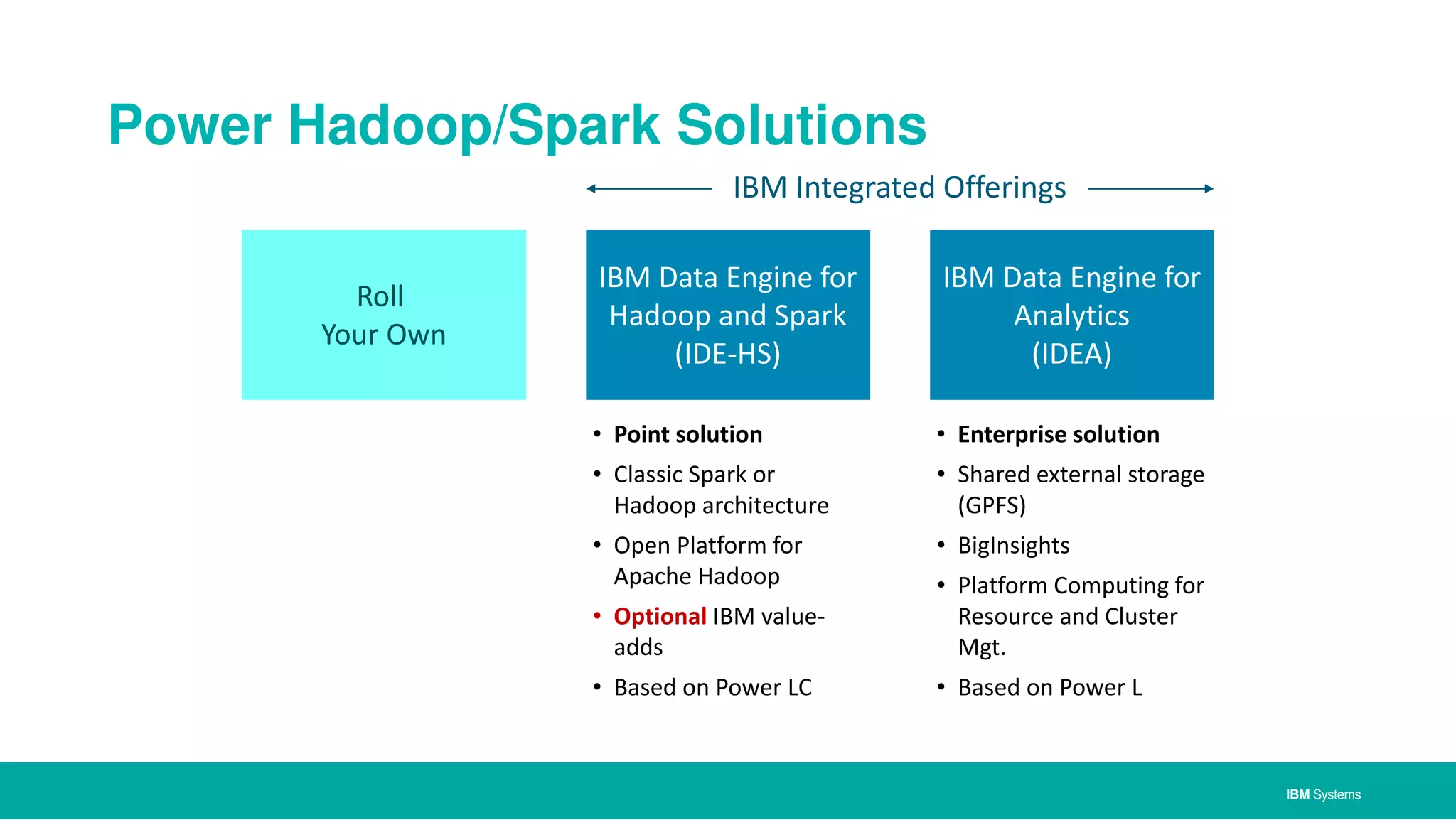
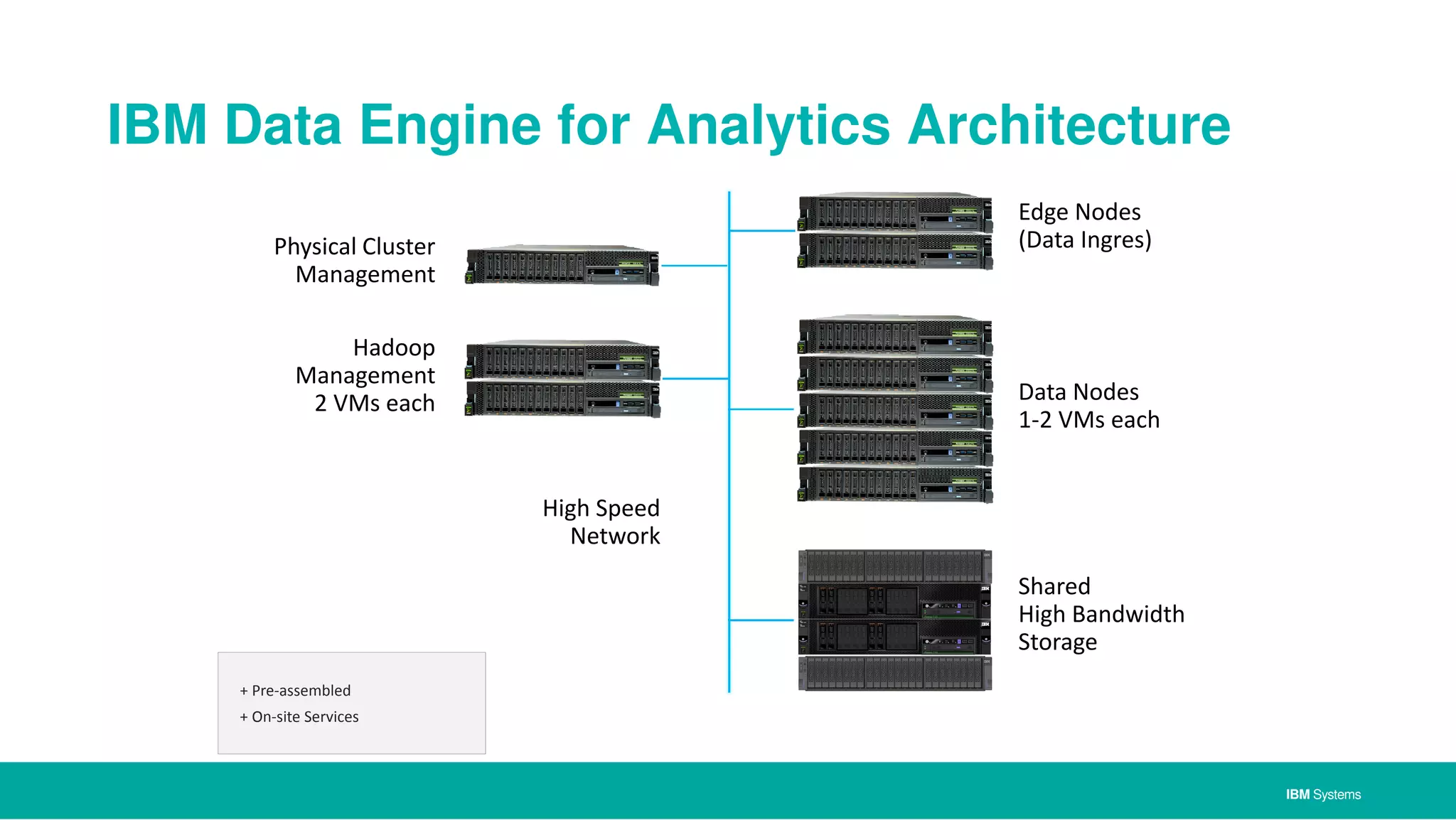
The document discusses IBM's approach to big data, highlighting key technologies like Hadoop and Spark, and the significance of IBM Power Systems in processing large-scale data efficiently. It emphasizes the transformative potential of big data and cognitive computing in leveraging rapid data insights for business value, while showcasing IBM's integrated hardware and software solutions designed for analytics. Furthermore, it outlines the role of the OpenPOWER Foundation in creating an open ecosystem for innovation in big data applications.