The document is a presentation from Percona Live London 2013 by Robert Hodges and Tim Callaghan about transitioning from MySQL to MongoDB. It details the differences in schema design, querying, data management, replication, sharding, and security between the two databases, along with practical coding examples. The session emphasizes understanding MongoDB's unique features and potential challenges for users familiar with MySQL.


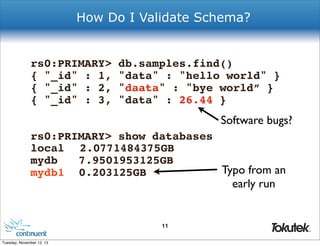
![One Bad Thing about MongoDB
MySQL
> select * from table1 where column1 > column2;
> ... 5 row(s) returned
MongoDB
> db.collection1.find({$field1: {gt: $field2}});
> ReferenceError: $field2 is not defined
[current] MongoDB query language is
<field> <operator> <literal>
®
Tuesday, November 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20131112-pluk-mysql-knowledge-to-mongodb-expert-6-131114140255-phpapp01/85/Use-Your-MySQL-Knowledge-to-Become-a-MongoDB-Guru-4-320.jpg)







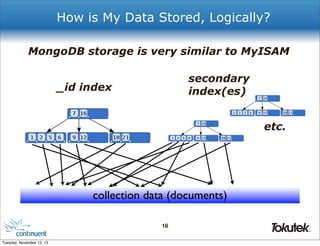






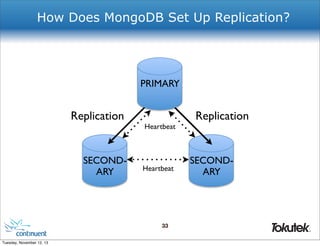
![Where Is The Replica Set Defined?
$ mongo localhost
...
# rs0:PRIMARY> rs.config()
{
!
"_id" : "rs0",
!
"version" : 8,
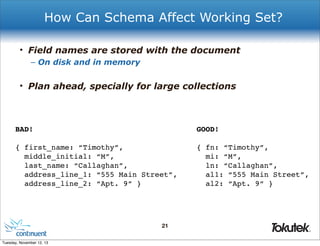
!
"members" : [
!
! {
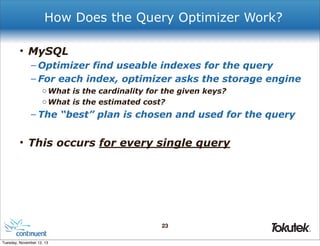
!
! ! "_id" : 0,
!
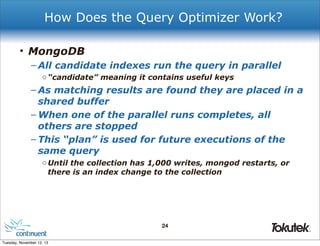
! ! "host" : "mongodb1:27017"
!
! },
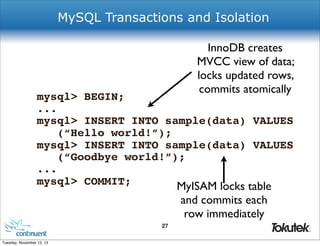
!
! {
!
! ! "_id" : 1,
!
! ! "host" : "mongodb2:27017"
!
! },
!
! {
!
! ! "_id" : 2,
!
! ! "host" : "mongodb3:27017”
!
! }
!
]
}
34
®
Tuesday, November 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20131112-pluk-mysql-knowledge-to-mongodb-expert-6-131114140255-phpapp01/85/Use-Your-MySQL-Knowledge-to-Become-a-MongoDB-Guru-34-320.jpg)
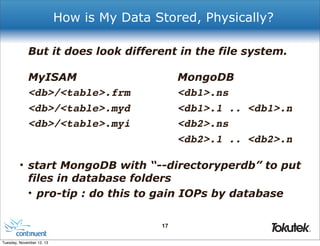
![How Do Applications Connect?
# Connect to MongoDB replica set.
client = MongoReplicaSetClient.new(
['mongodb1', 'mongodb2', 'mongodb3'])
# Access a collection and add data
db = client.db("xacts")
col = db.collection("data")
col.insert({"data" => "hello world"})
35
®
Tuesday, November 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20131112-pluk-mysql-knowledge-to-mongodb-expert-6-131114140255-phpapp01/85/Use-Your-MySQL-Knowledge-to-Become-a-MongoDB-Guru-35-320.jpg)
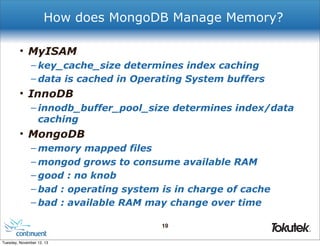
![How Do You Read From a Slave?
# Connect to MongoDB replica set.
client = MongoReplicaSetClient.new(
['mongodb1', 'mongodb2', 'mongodb3'],
:slave_ok => true)
# Access a collection and select documents.
db = client.db("xacts")
col = db.collection("data")
col.find()
36
®
Tuesday, November 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20131112-pluk-mysql-knowledge-to-mongodb-expert-6-131114140255-phpapp01/85/Use-Your-MySQL-Knowledge-to-Become-a-MongoDB-Guru-36-320.jpg)
![How Do You Fail Over?
• Planned failover: update rs.config and save:
rs0:SECONDARY>
rs0:SECONDARY>
rs0:SECONDARY>
rs0:SECONDARY>
rs0:SECONDARY>
cfg = rs.conf()
cfg.members[0].priority = 1
cfg.members[1].priority = 1
cfg.members[2].priority = 2
rs.reconfig(cfg)
• Unplanned failover: kill or stop mongod
39
®
Tuesday, November 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20131112-pluk-mysql-knowledge-to-mongodb-expert-6-131114140255-phpapp01/85/Use-Your-MySQL-Knowledge-to-Become-a-MongoDB-Guru-39-320.jpg)







![What Else is There to Learn?
• Tools - mongostat, mongo[export/
•
•
import], mongo[dump/restore]
Aggregation Framework
• Think SQL aggregate functionality
Map/Reduce
®
Tuesday, November 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20131112-pluk-mysql-knowledge-to-mongodb-expert-6-131114140255-phpapp01/85/Use-Your-MySQL-Knowledge-to-Become-a-MongoDB-Guru-50-320.jpg)
![Summary
We liked...
• Ease of install
• Ability to just “jump in”
Look [out] for...
• Query language (Tim says hang in there!)
• You have to think about storage and queries in advance
Highly Recommended Reading
• Karl Seguin’s “The Little MongoDB Book”
• http://openmymind.net/mongodb.pdf
• MongoDB’s “SQL to MongoDB Mapping Chart”
• http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/sql-comparison/
®
Tuesday, November 12, 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20131112-pluk-mysql-knowledge-to-mongodb-expert-6-131114140255-phpapp01/85/Use-Your-MySQL-Knowledge-to-Become-a-MongoDB-Guru-52-320.jpg)
