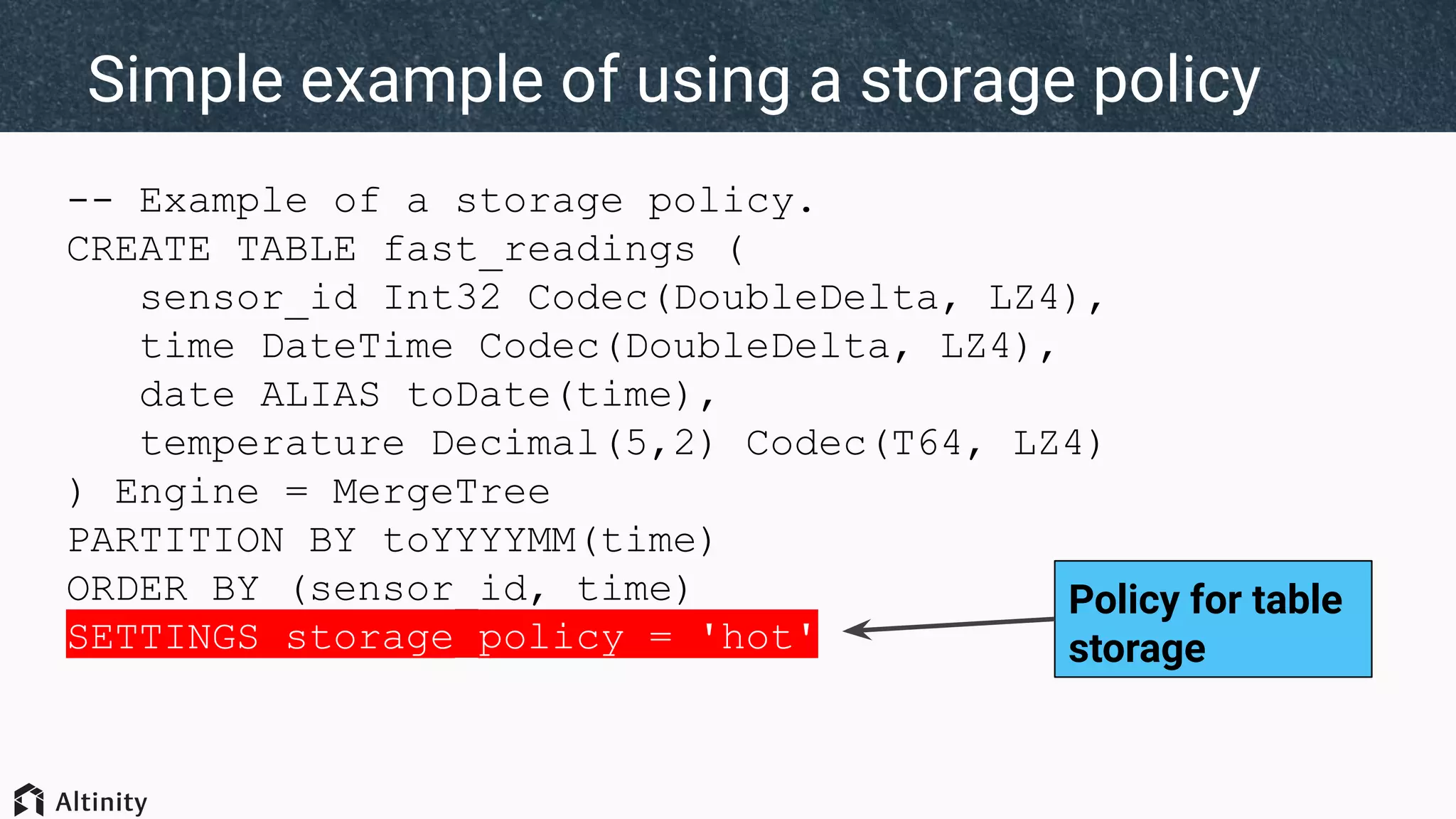
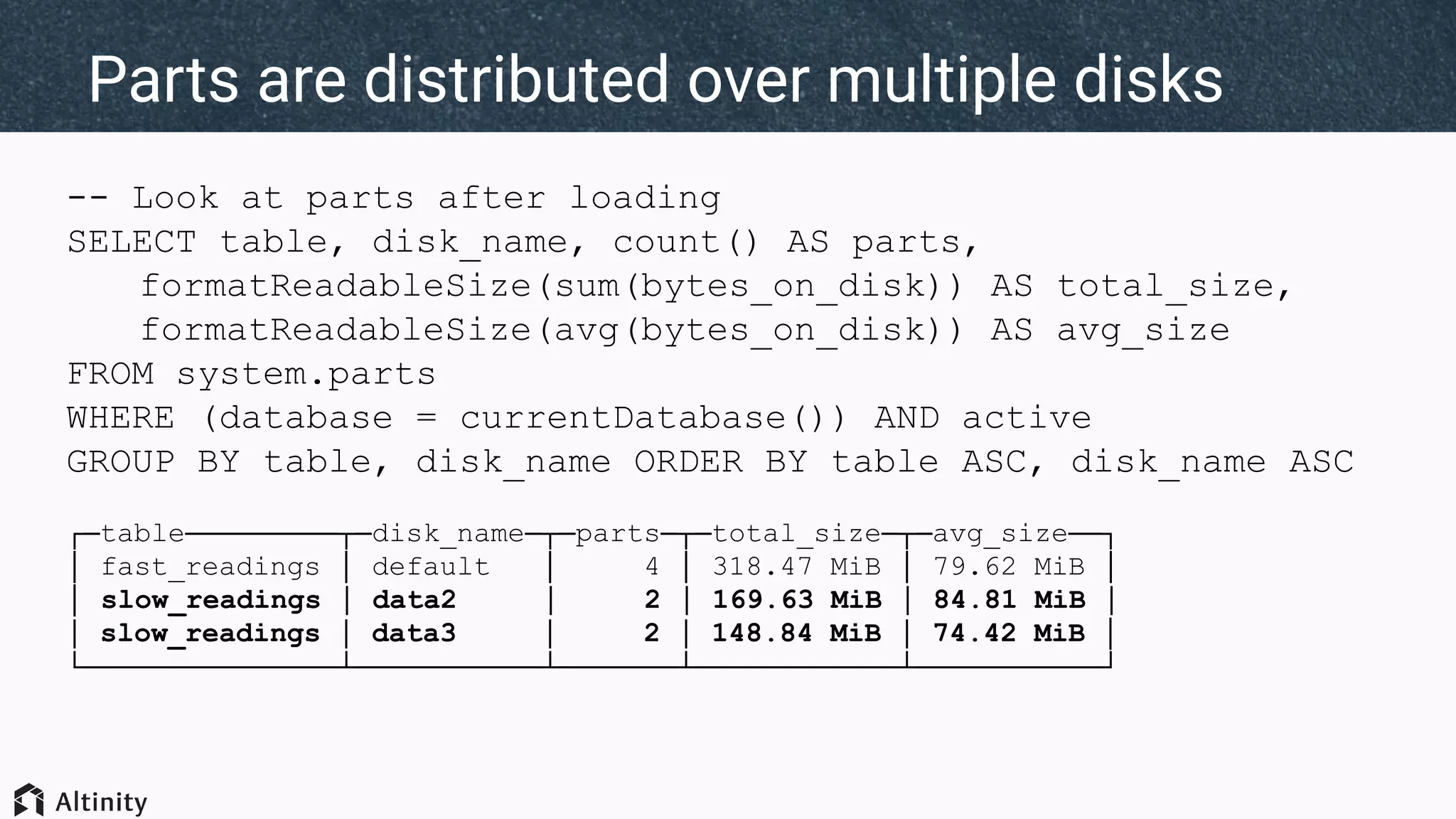
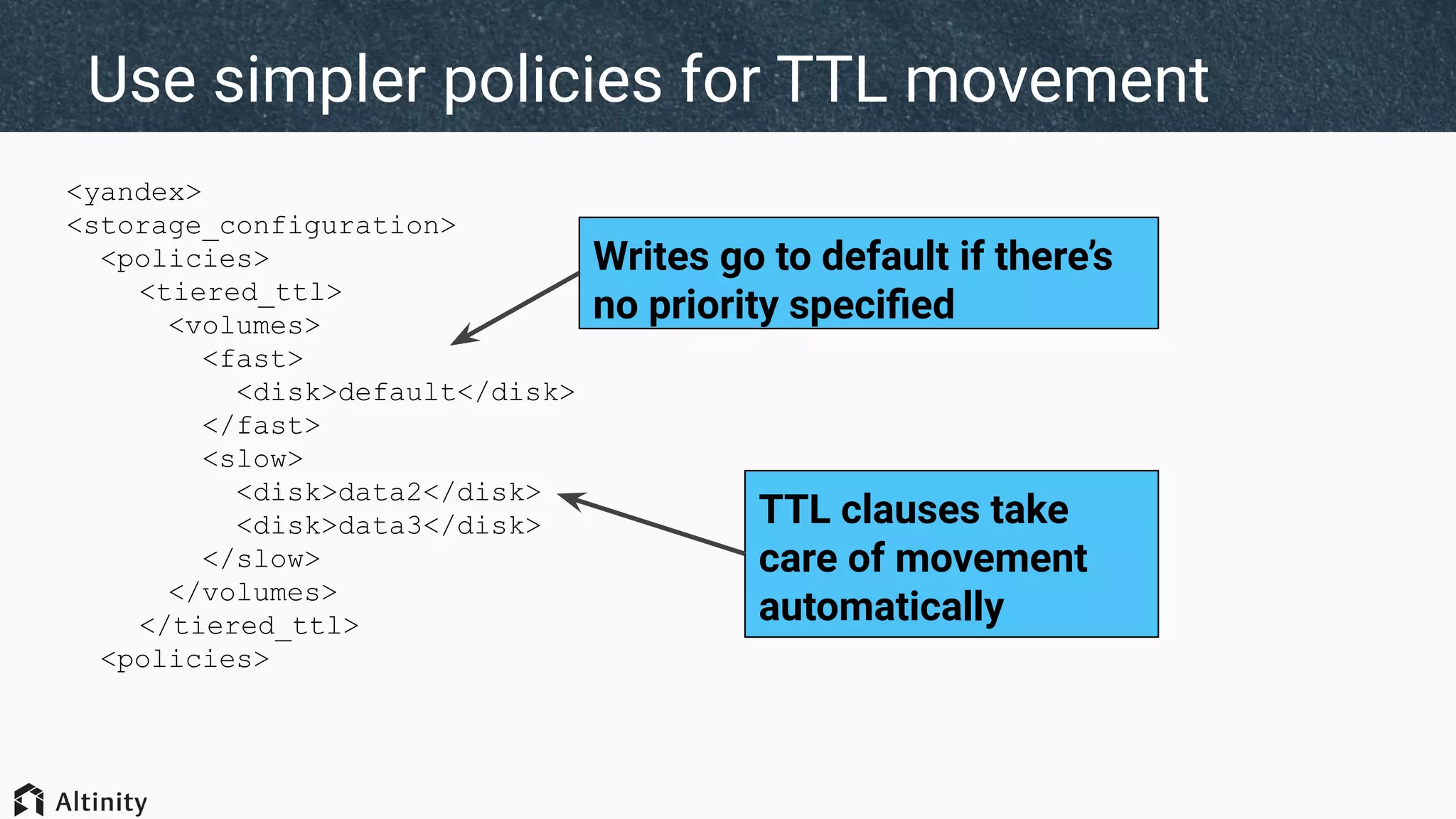
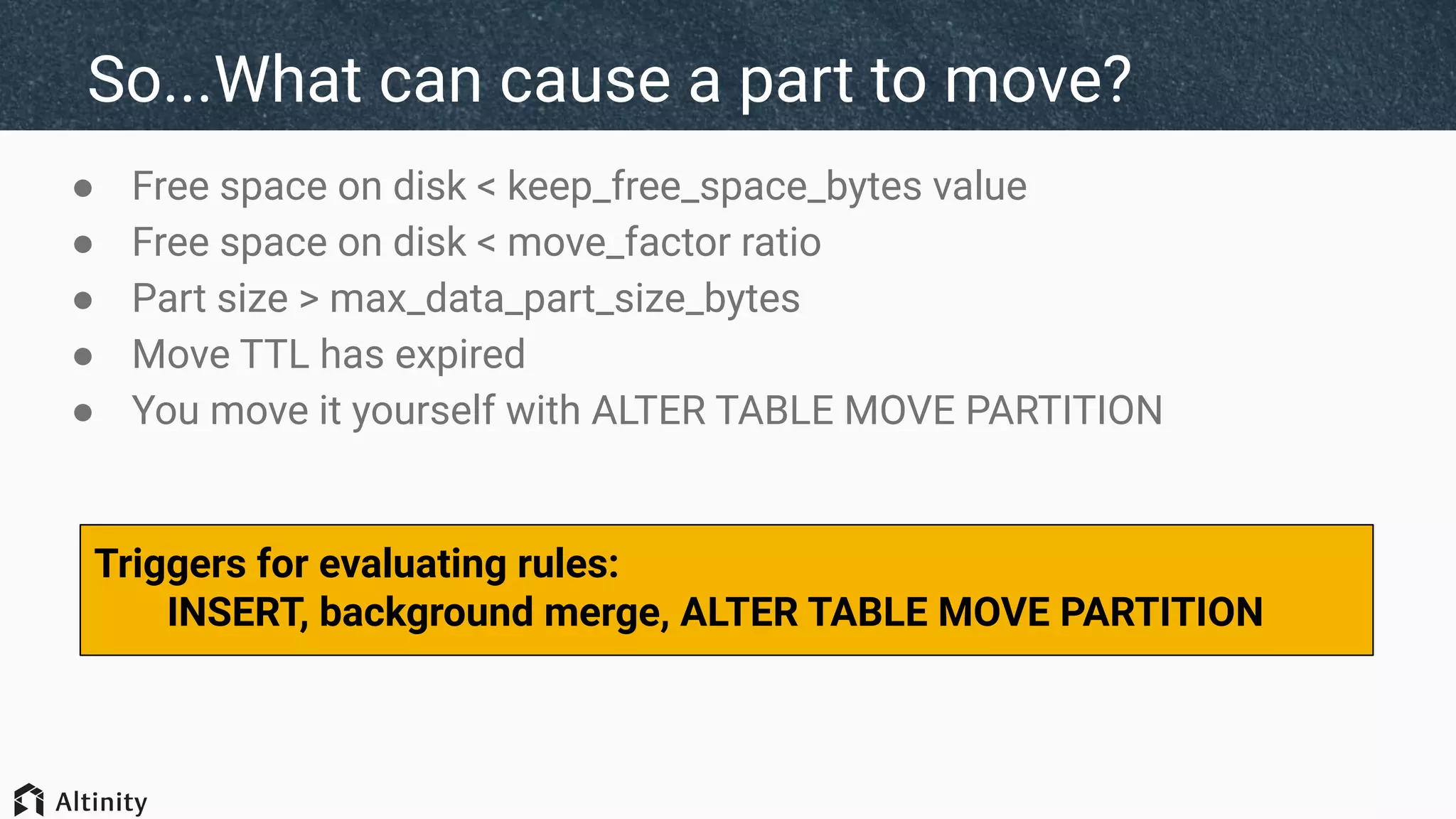
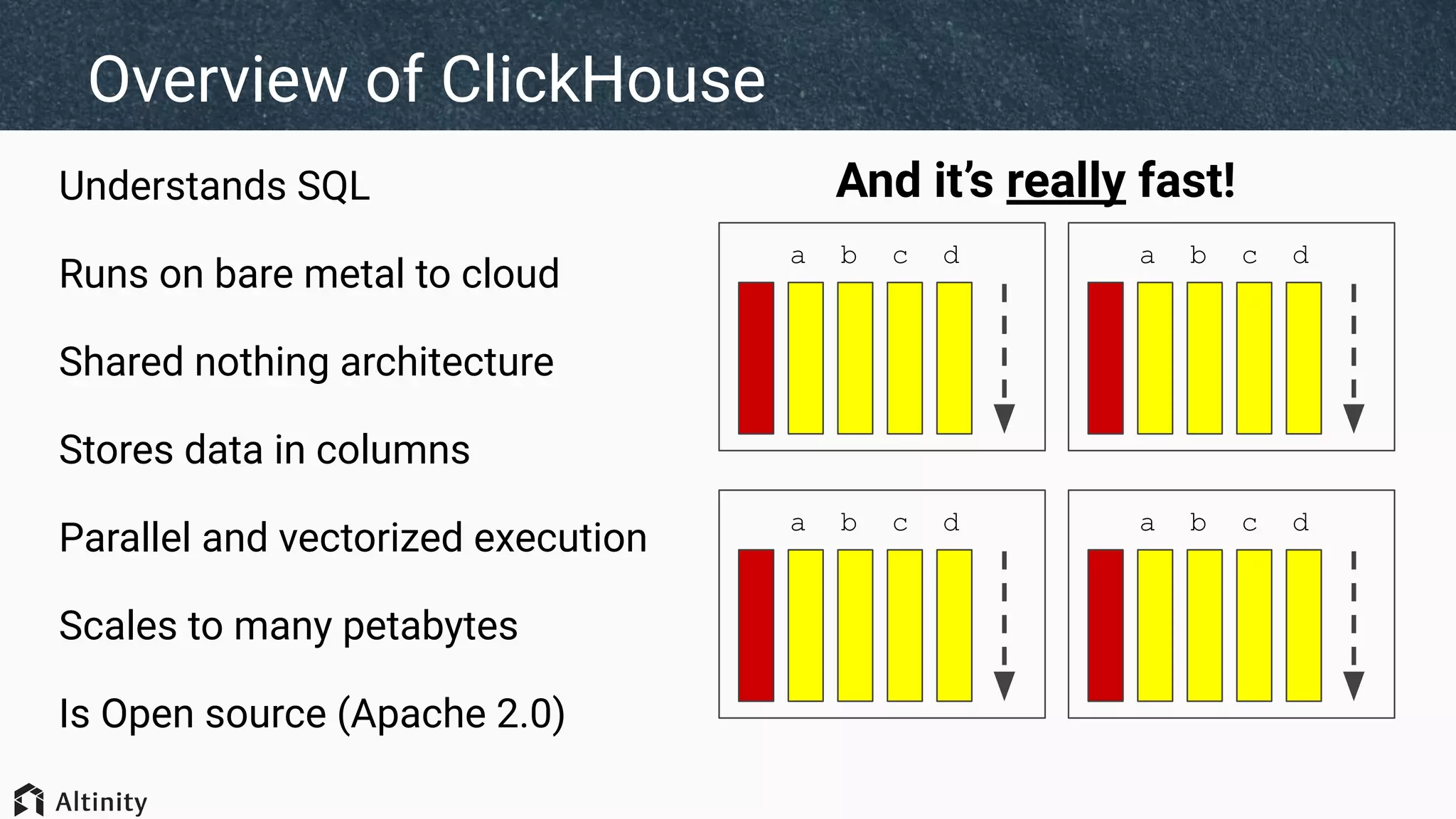
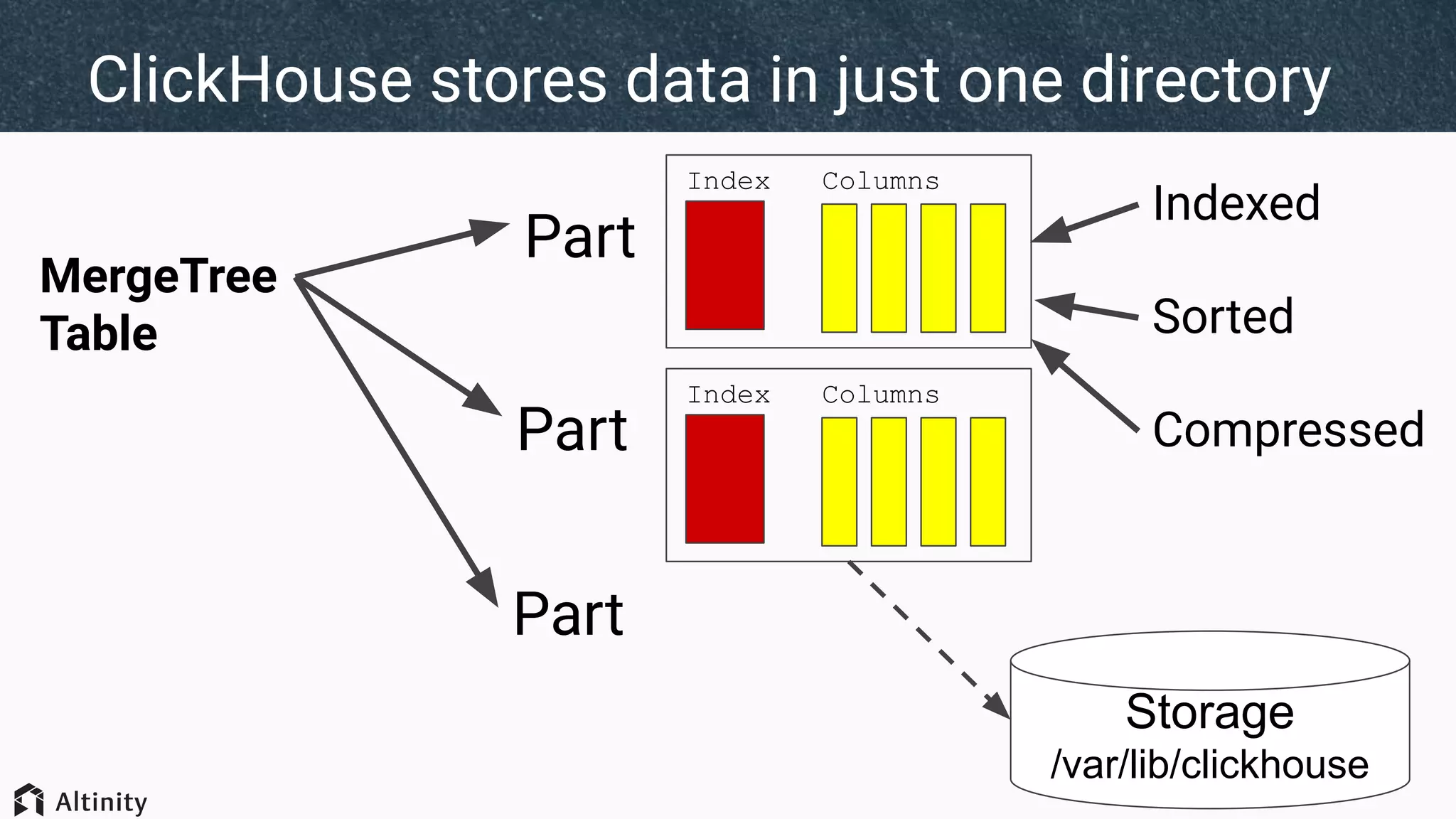
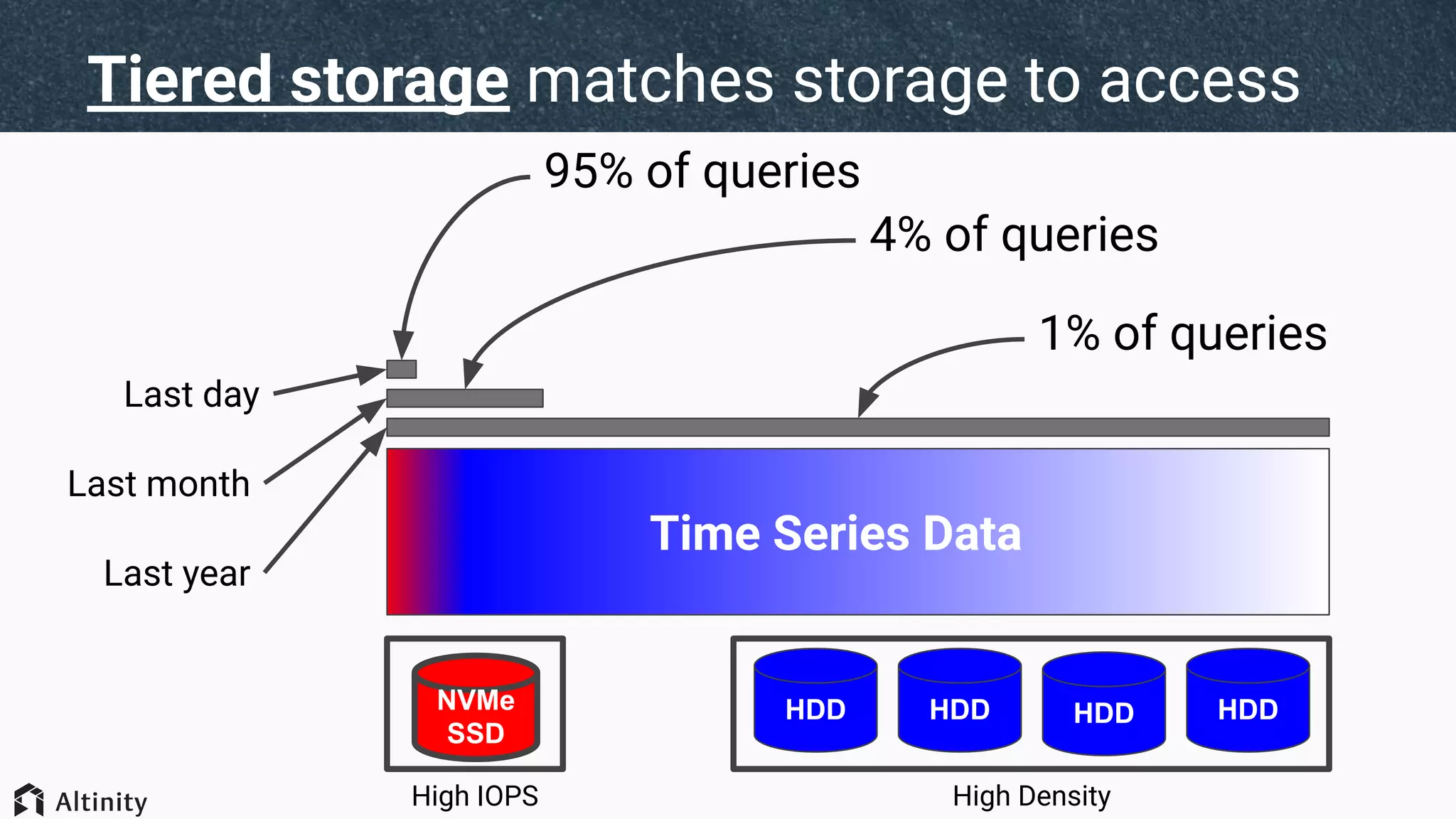
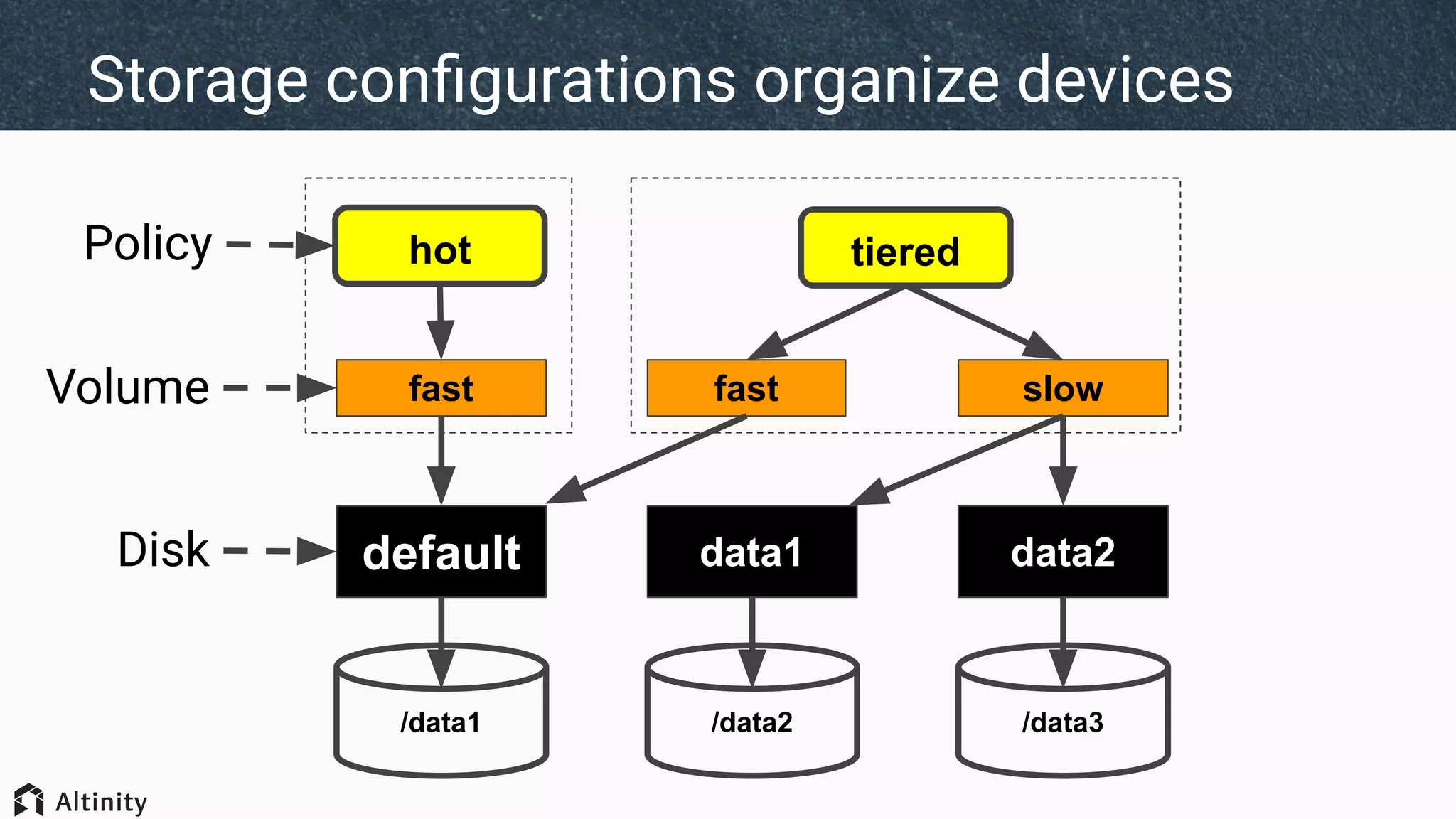
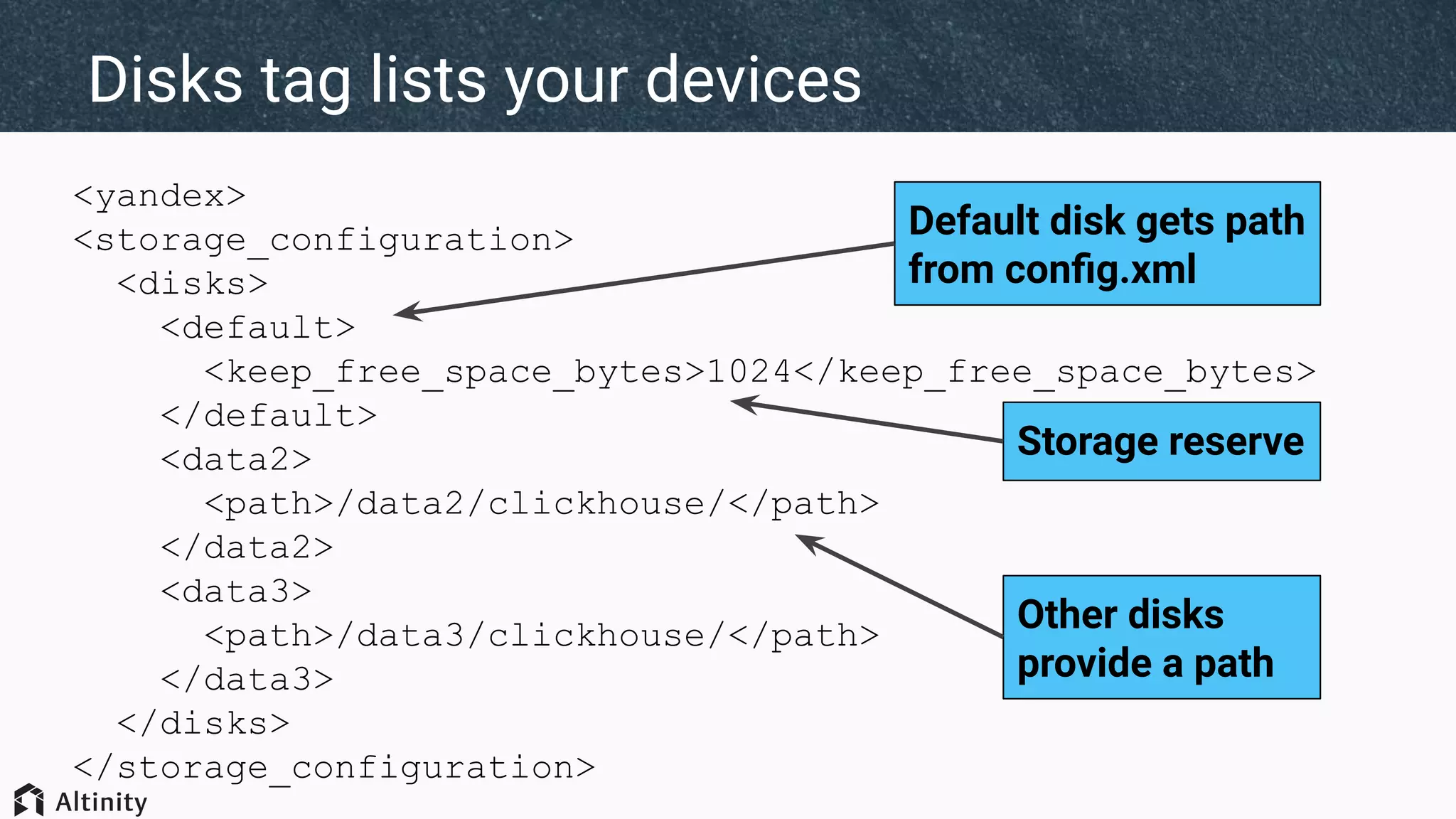
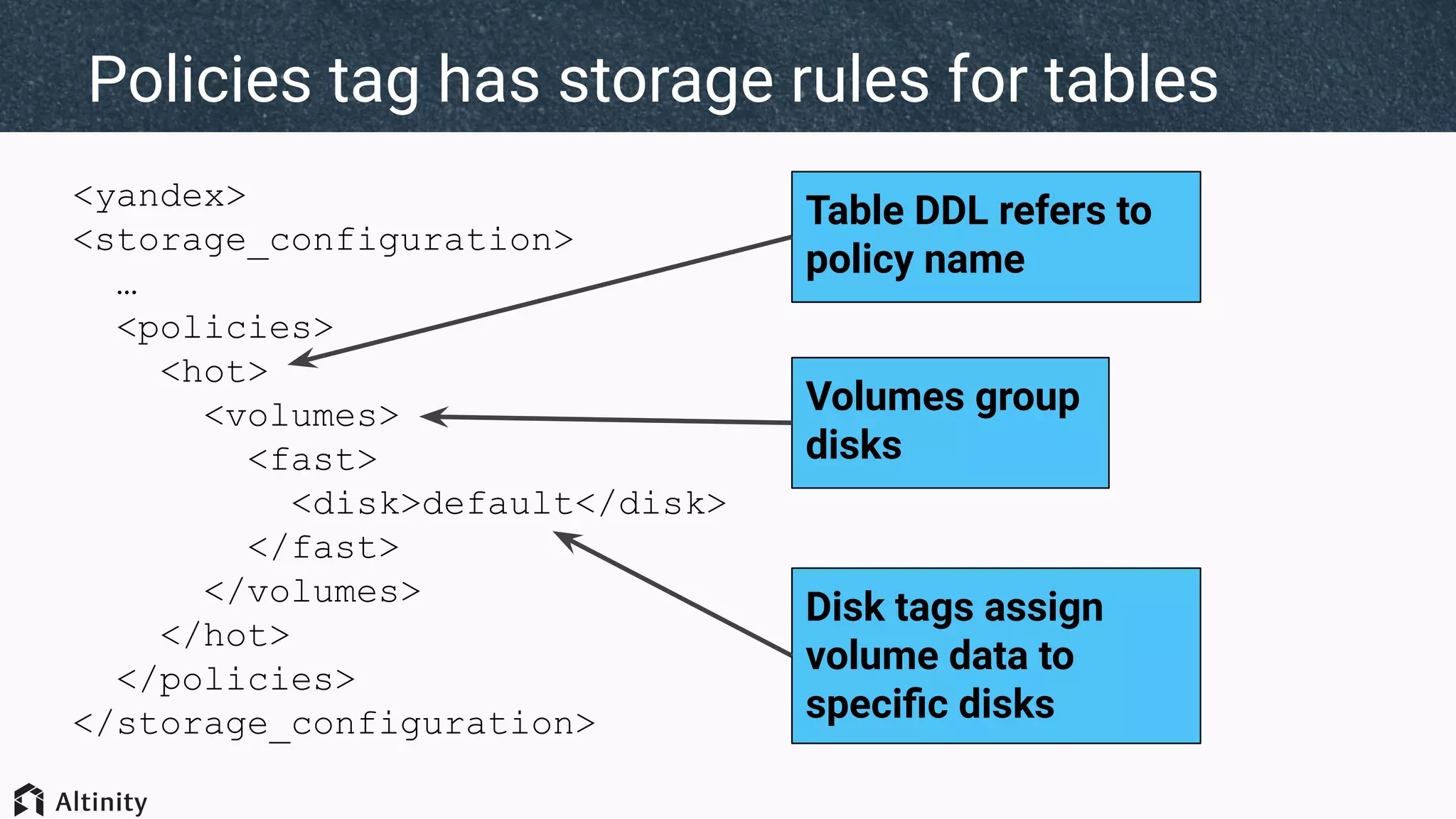
The document discusses ClickHouse's tiered storage feature, which allows data to be stored across multiple storage devices based on access patterns and policies. It provides an overview of ClickHouse's storage architecture and how data is normally stored in a single directory. It then introduces storage configurations that define policies and mappings to different disks/volumes. Examples are given of using policies to control where newly inserted or optimized data is stored. This allows fast and less frequently accessed data to be tiered across storage with different performance characteristics.






![SELECT
policy_name,
volume_name,
volume_priority,
disks
FROM system.storage_policies
┌─policy_name─┬─volume_name─┬─volume_priority─┬─disks─────────────┐
│ cold │ slow │ 1 │ ['data2','data3'] │
│ default │ default │ 1 │ ['default'] │
│ hot │ fast │ 1 │ ['default'] │
│ tiered_auto │ fast │ 1 │ ['default'] │
│ tiered_auto │ slow │ 2 │ ['data2','data3'] │
│ tiered_ttl │ fast │ 1 │ ['default'] │
│ tiered_ttl │ slow │ 2 │ ['data2','data3'] │
└─────────────┴─────────────┴─────────────────┴───────────────────┘
...And another to see storage policies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whattheheckisclickhousetieredstorage-200217144733/75/Tiered-storage-intro-By-Robert-Hodges-Altinity-CEO-13-2048.jpg)