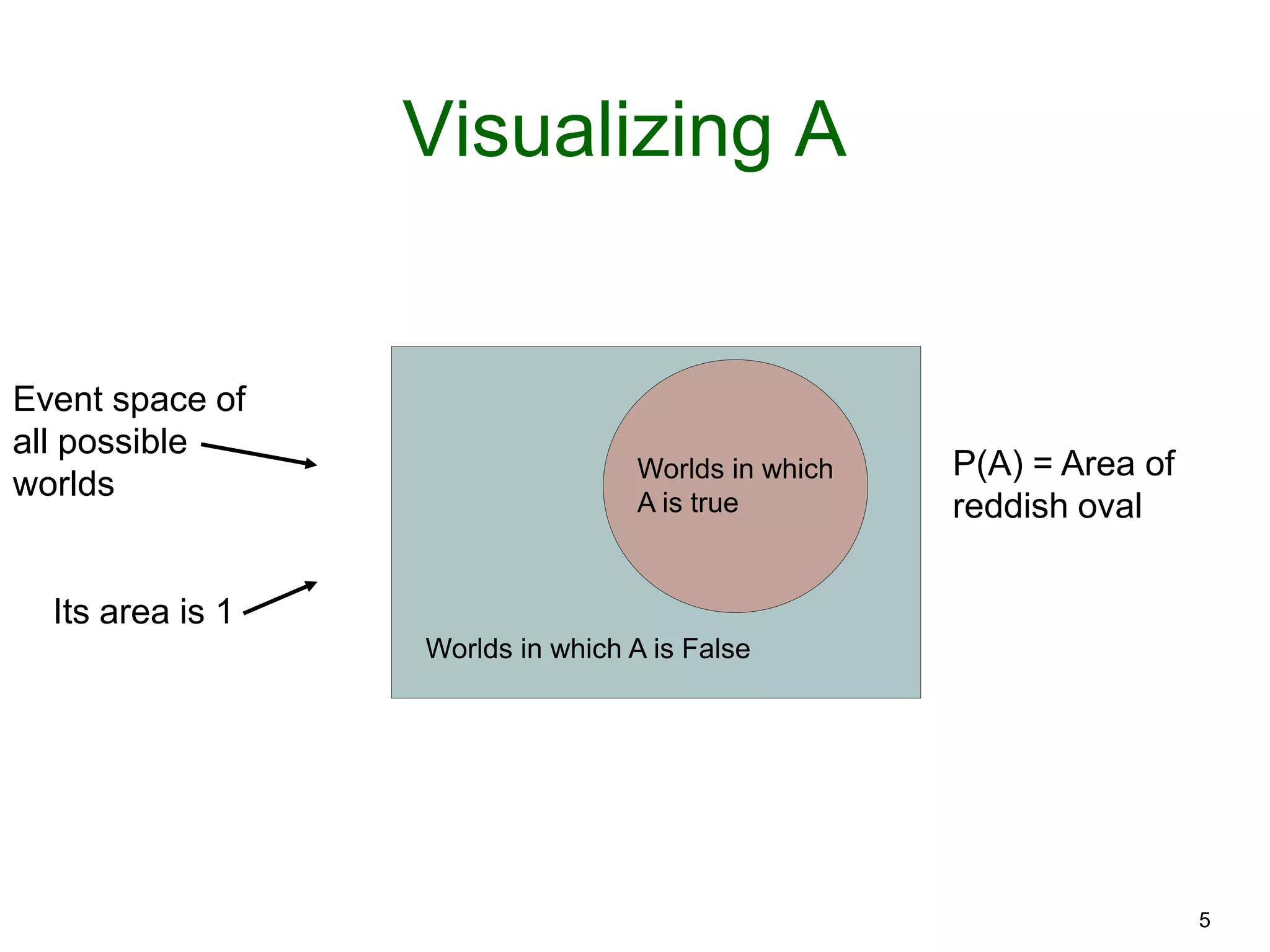
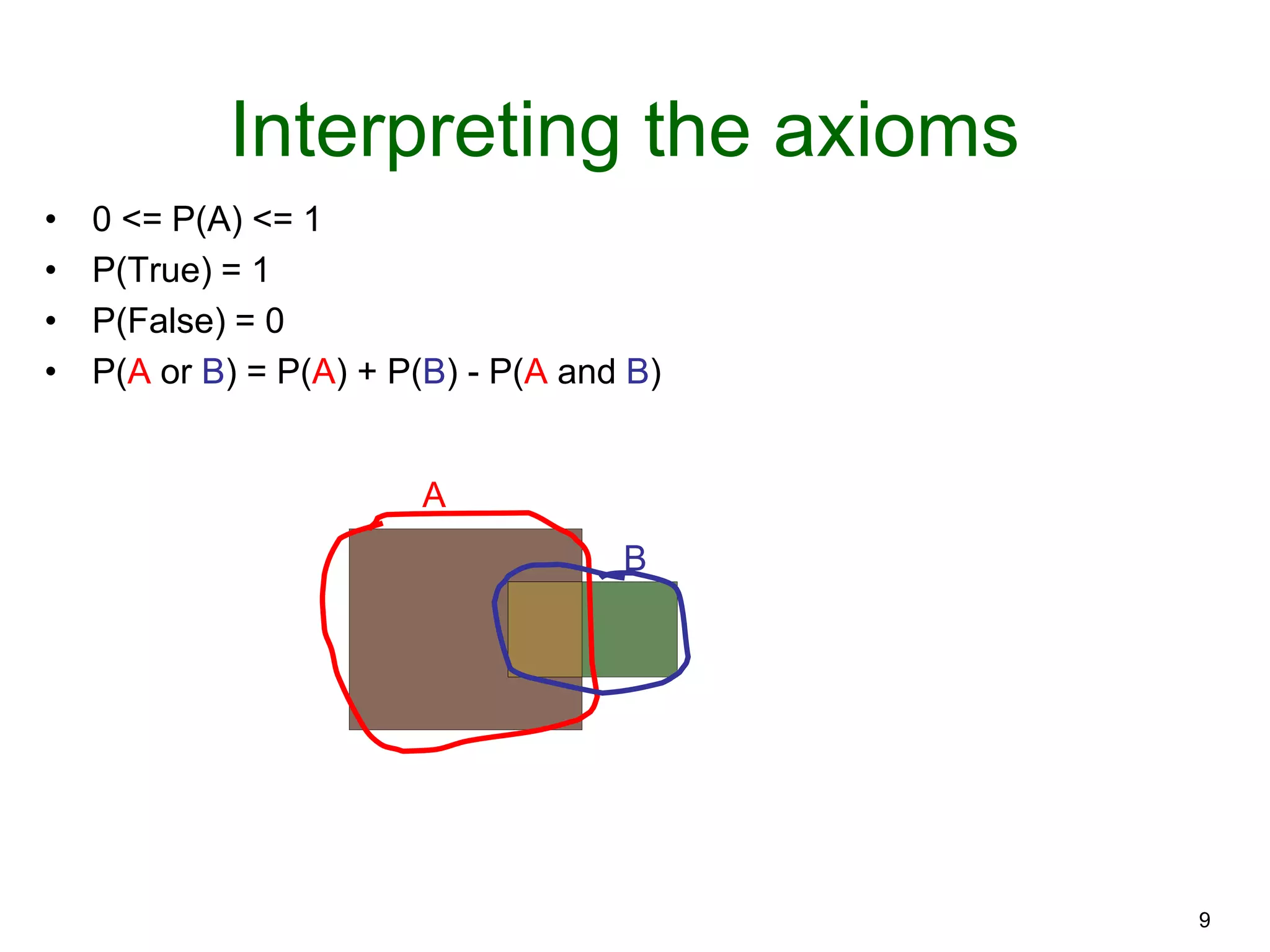
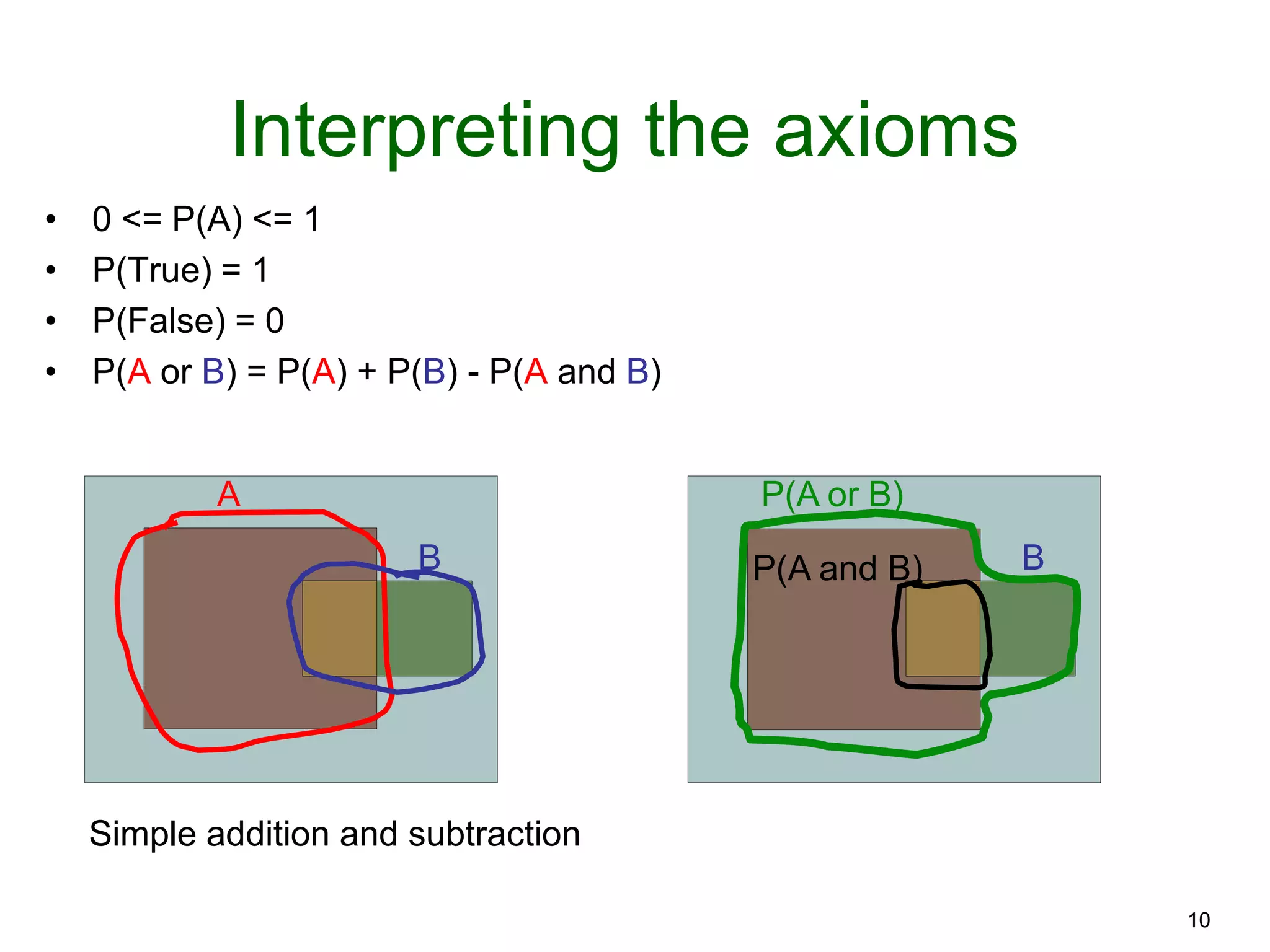
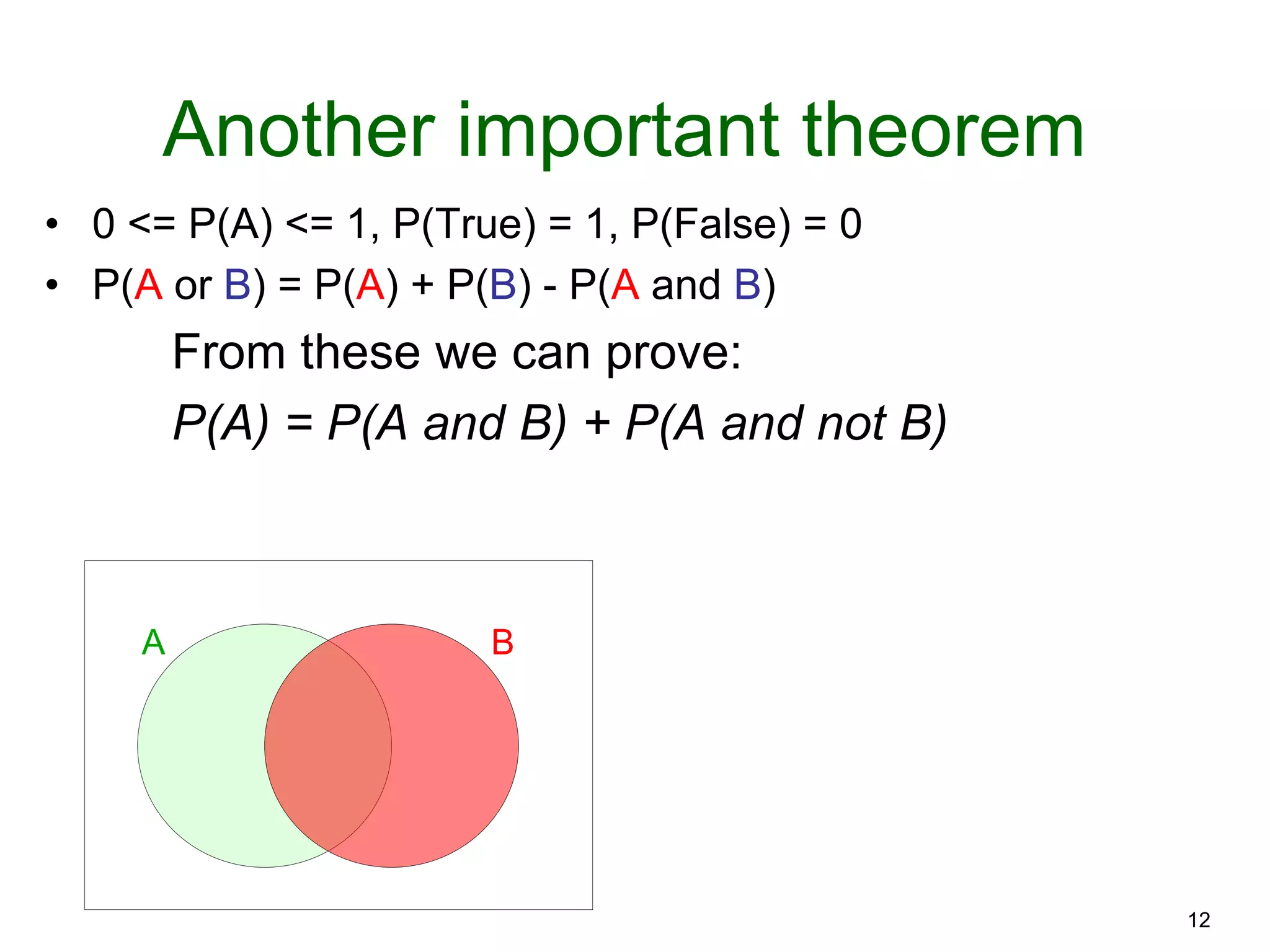
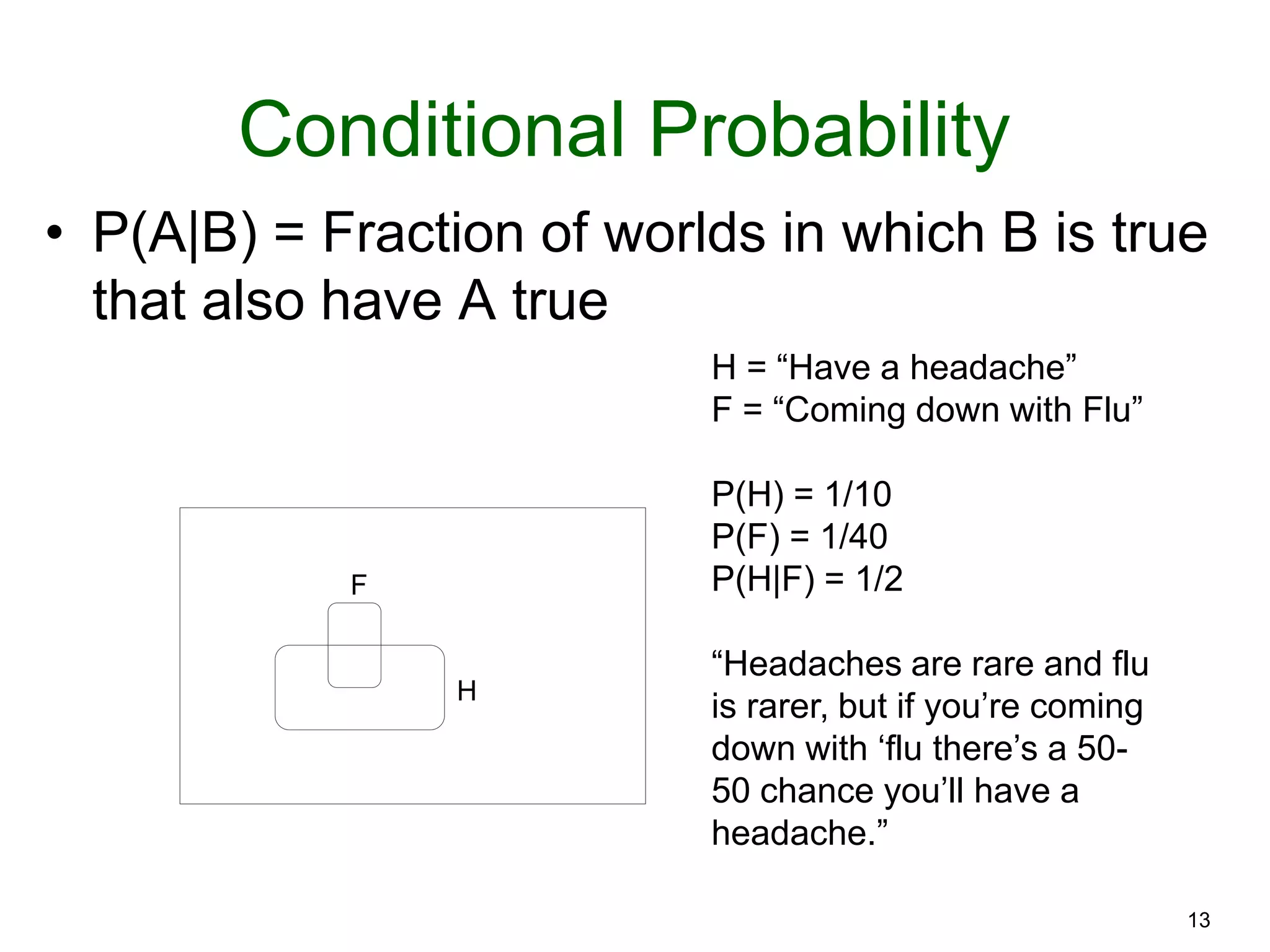
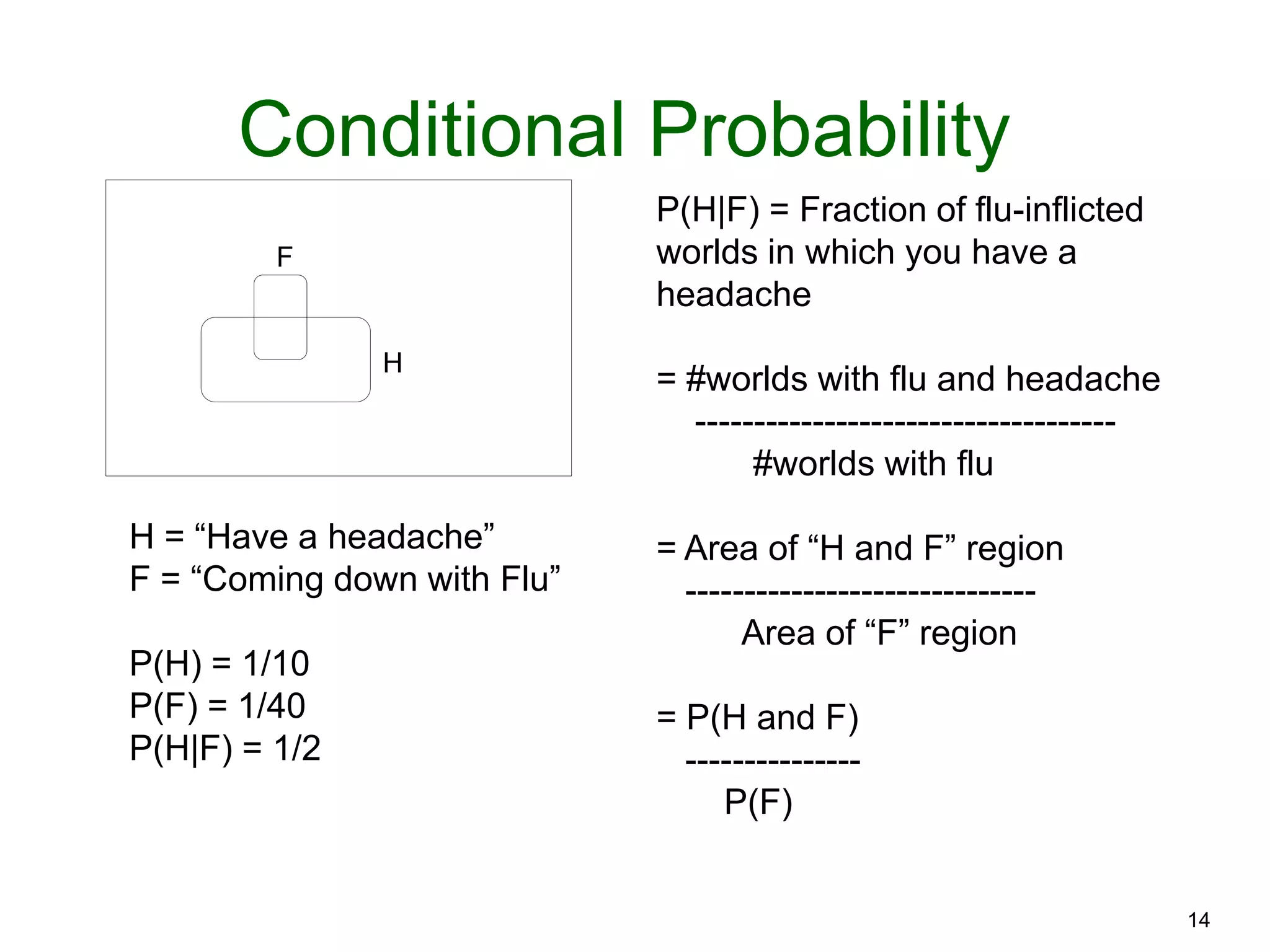
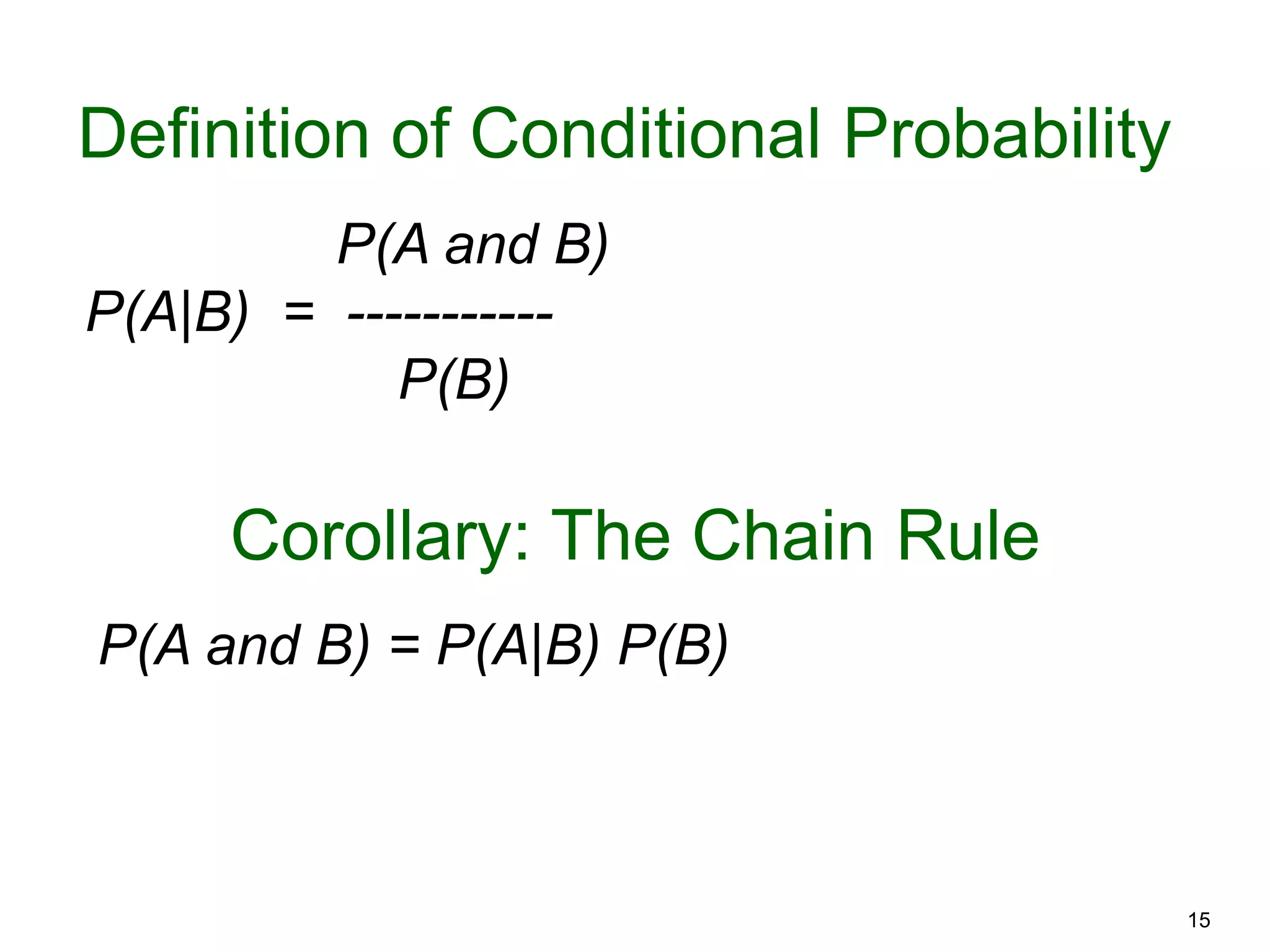
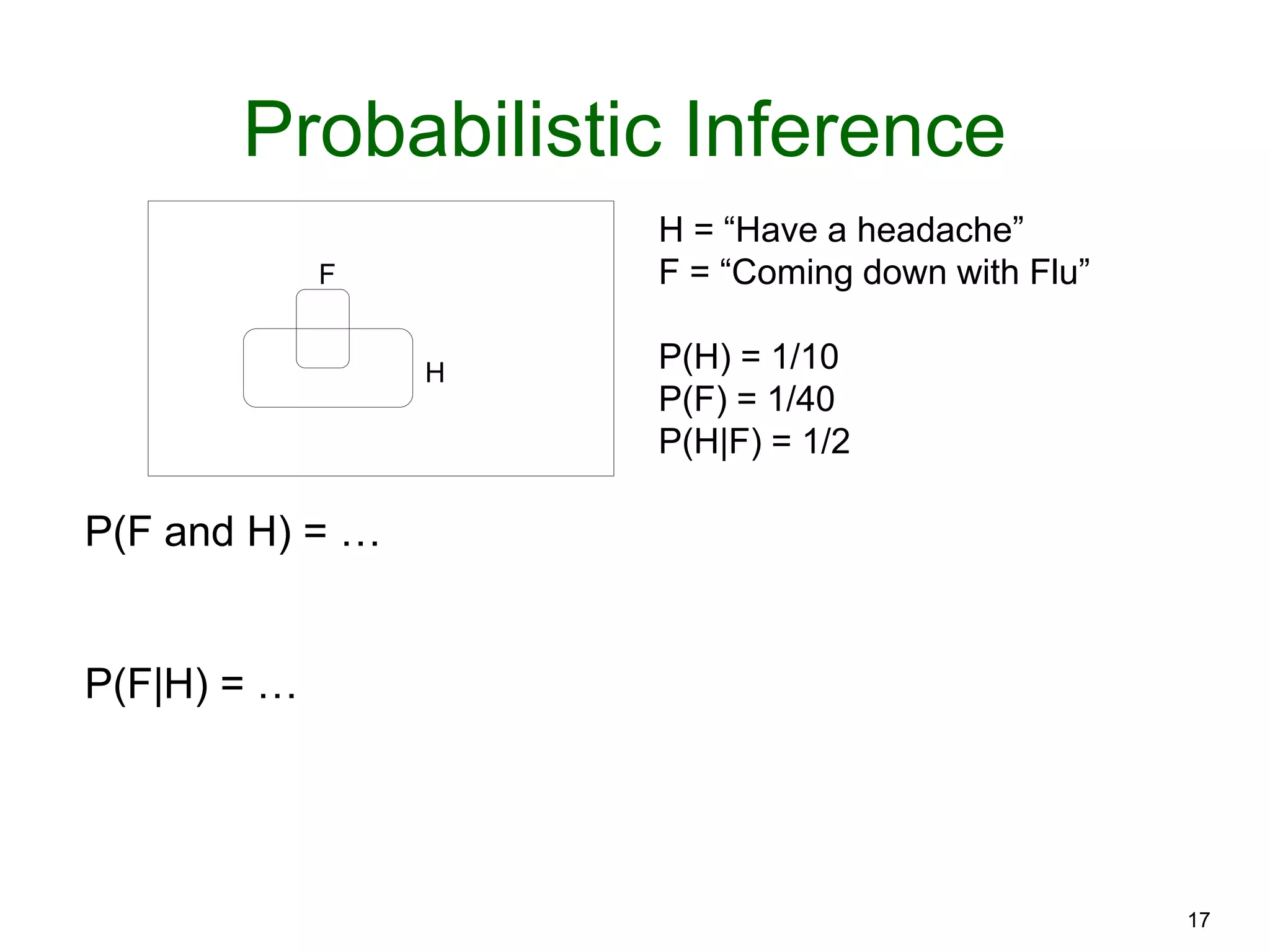
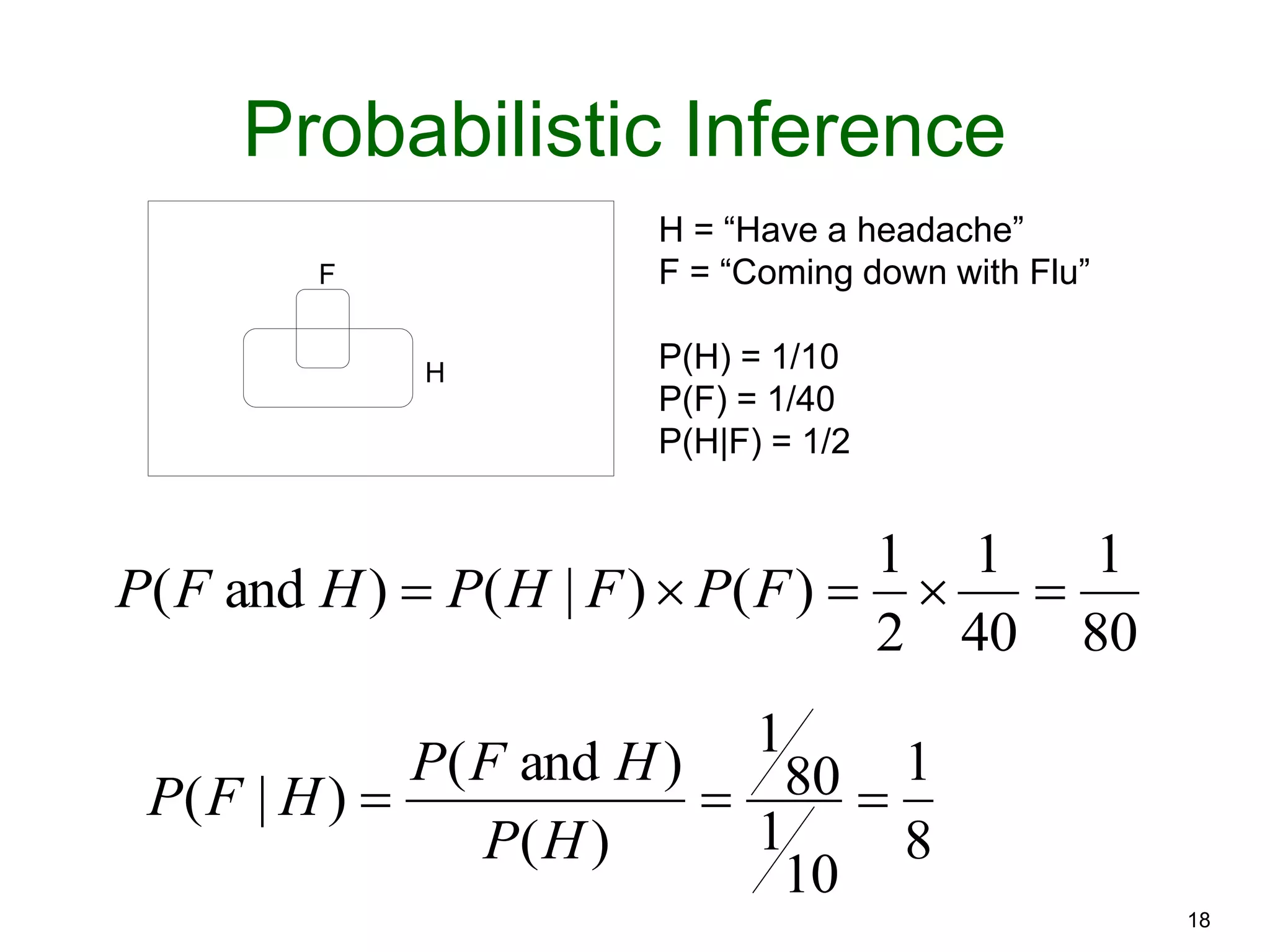
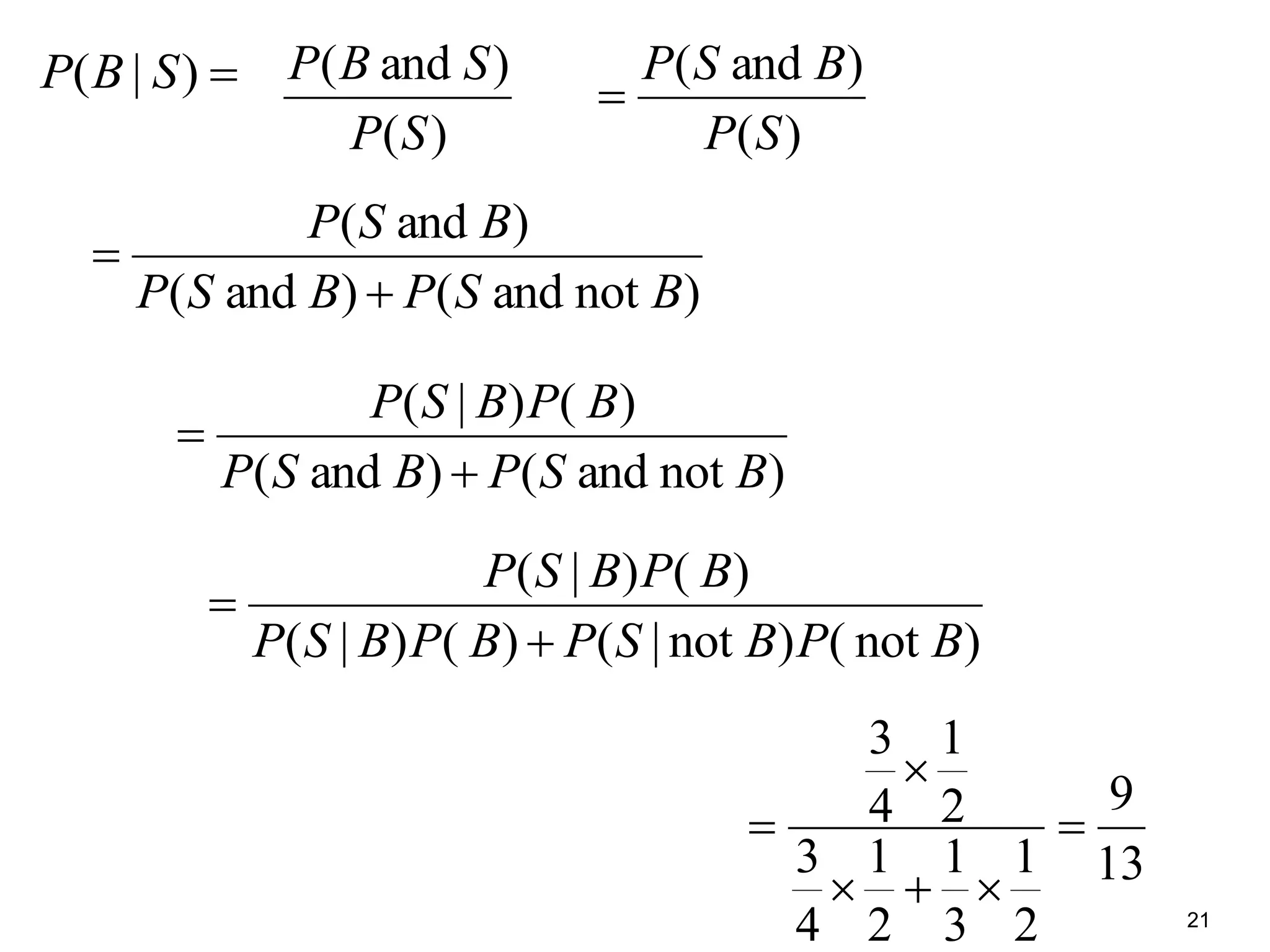
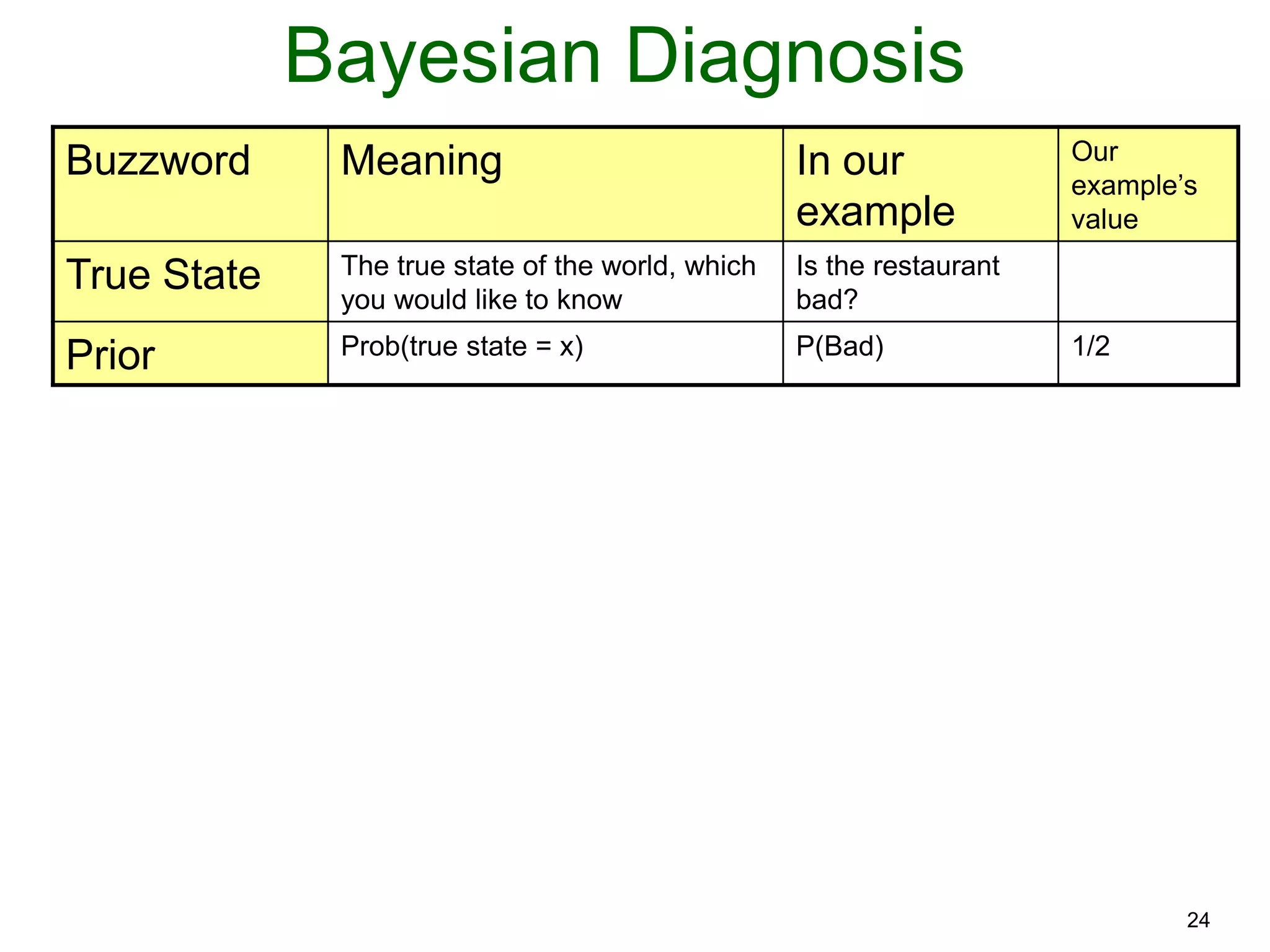
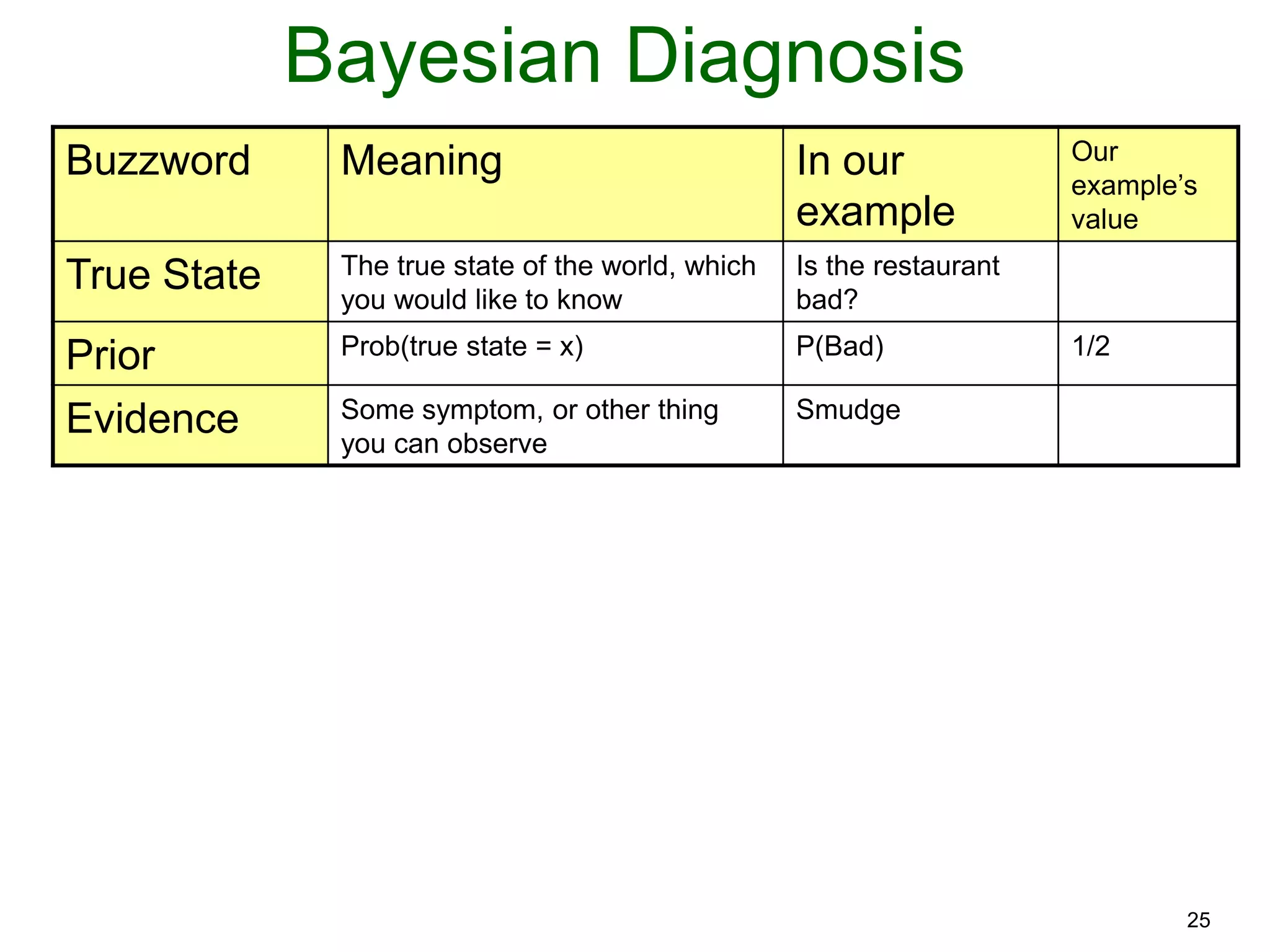
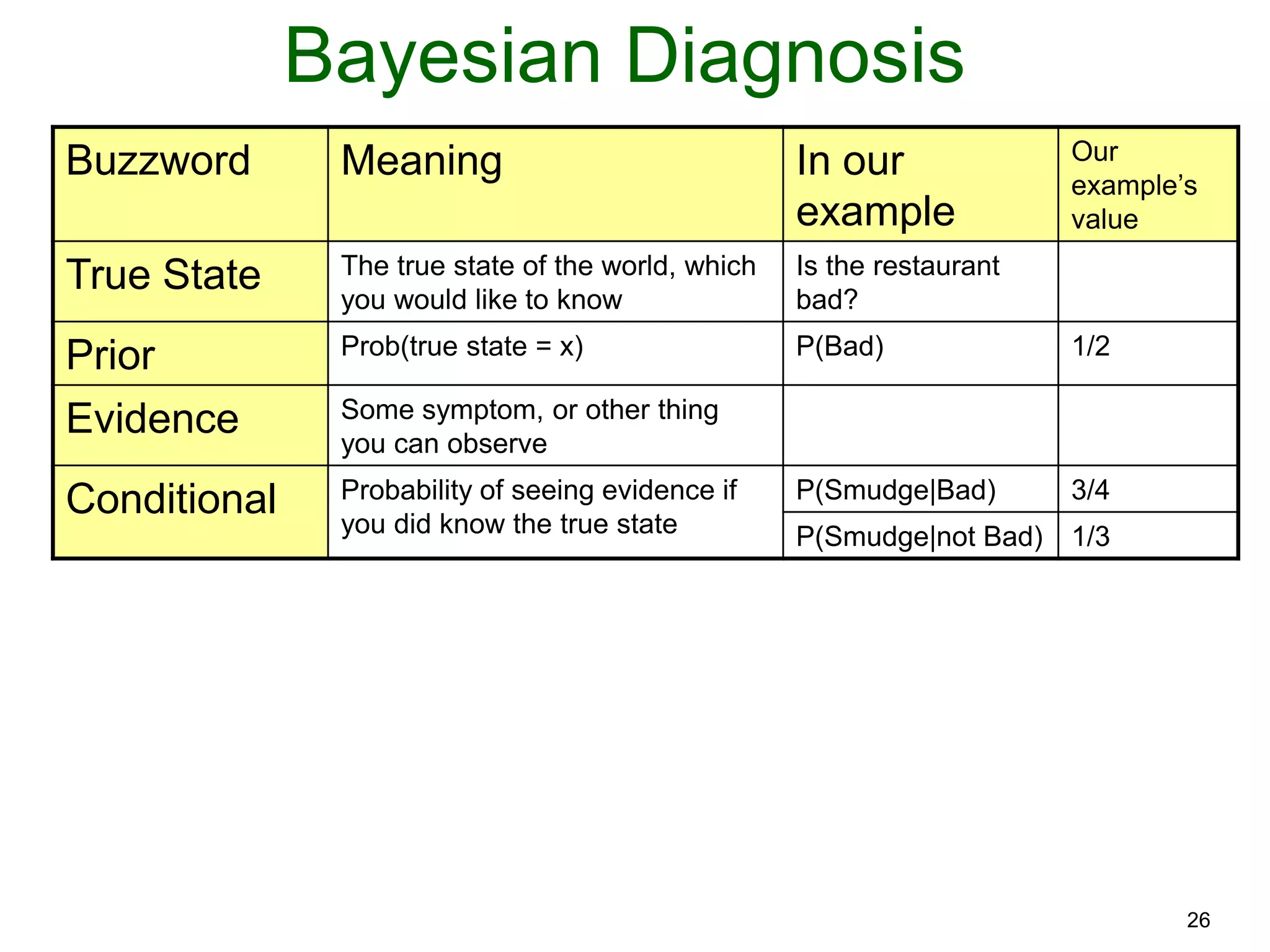
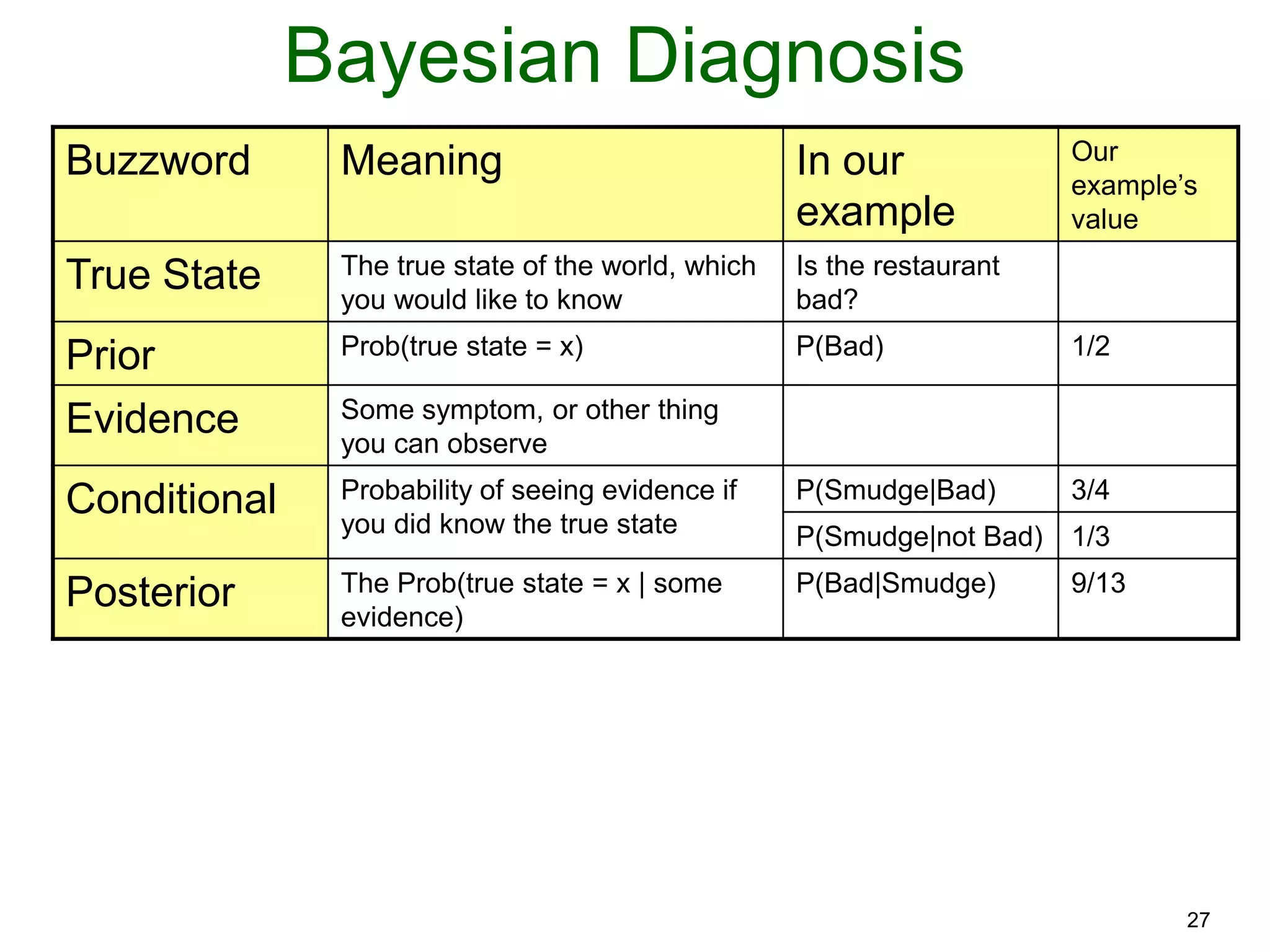
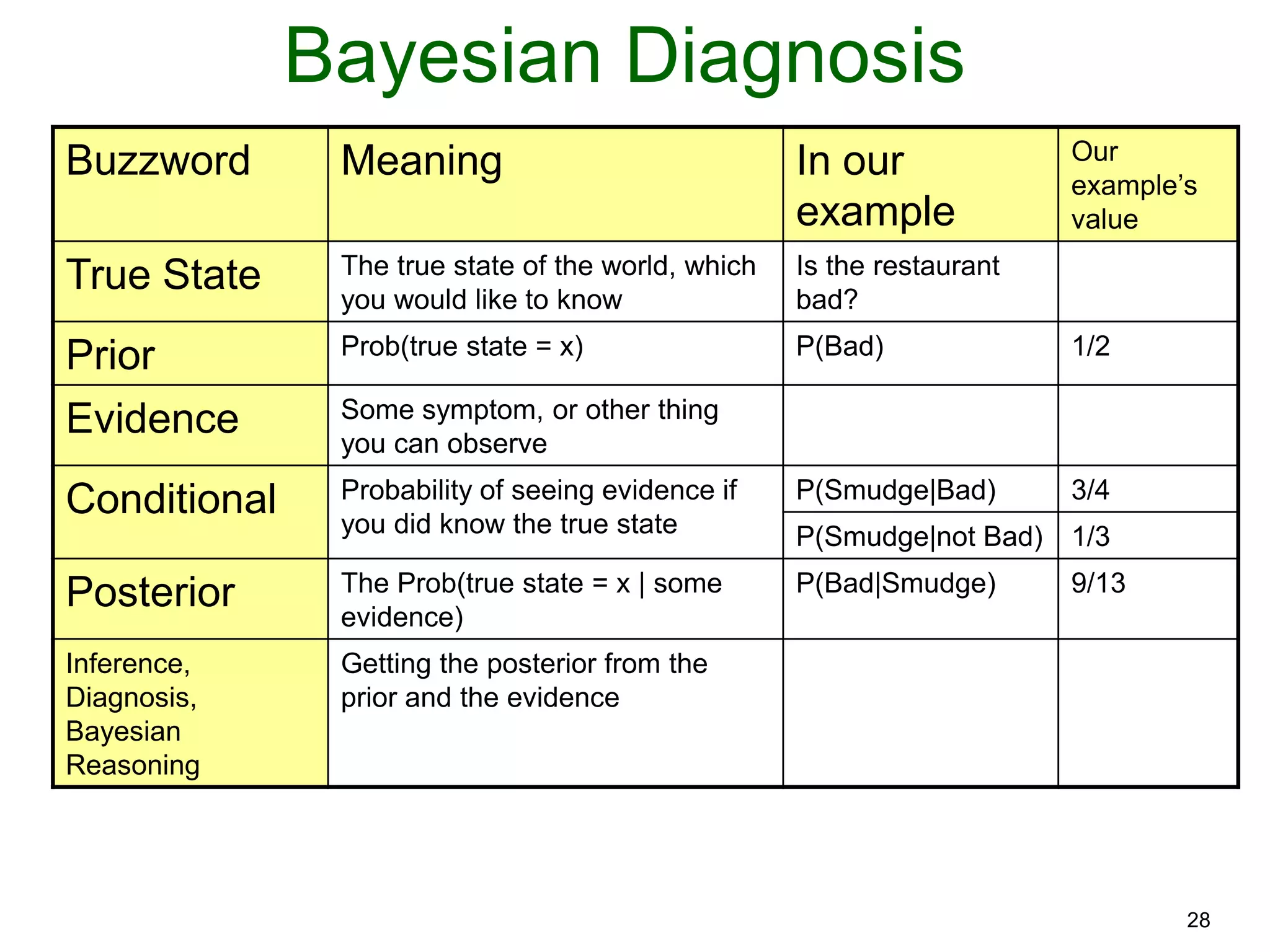
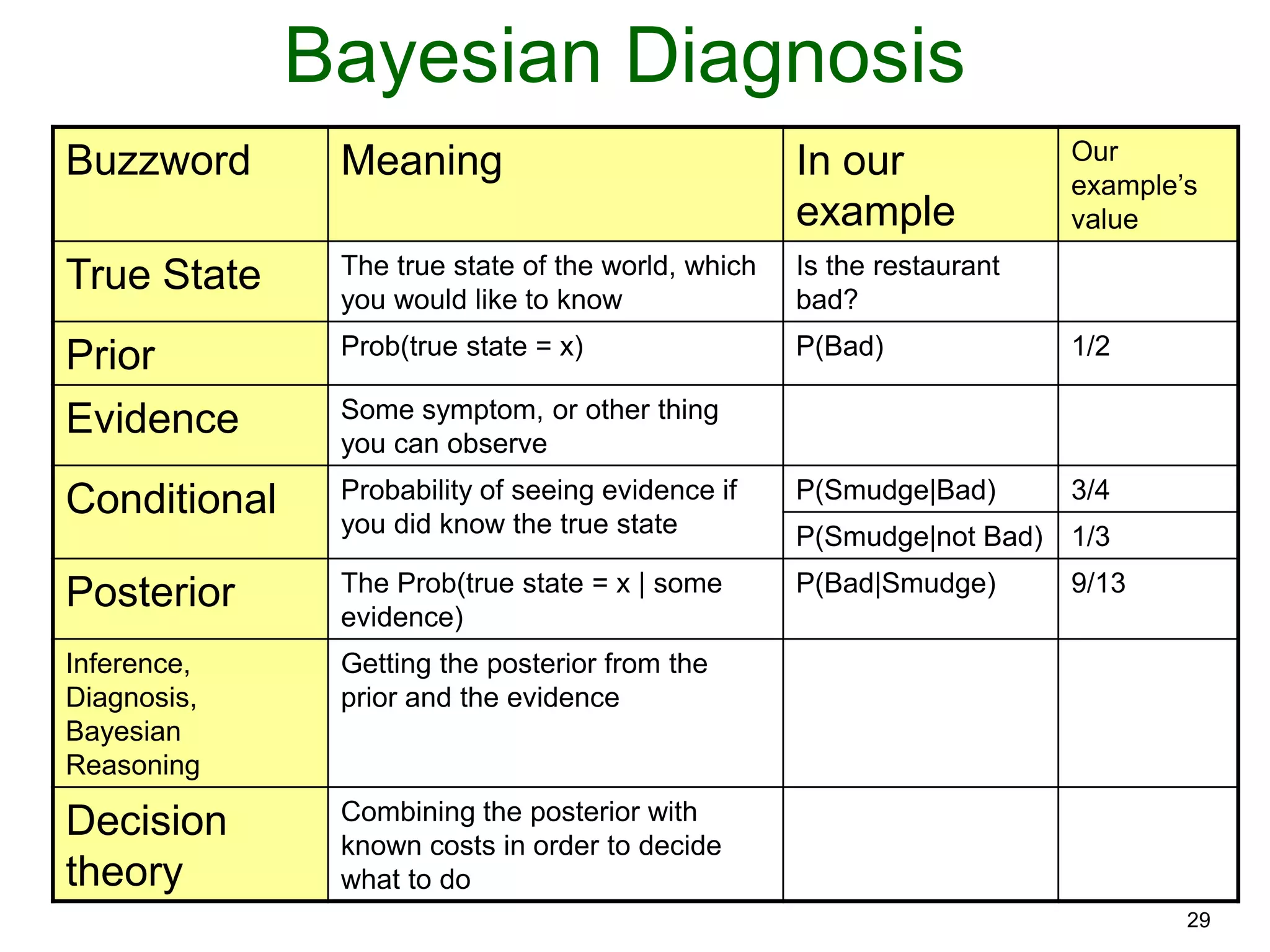
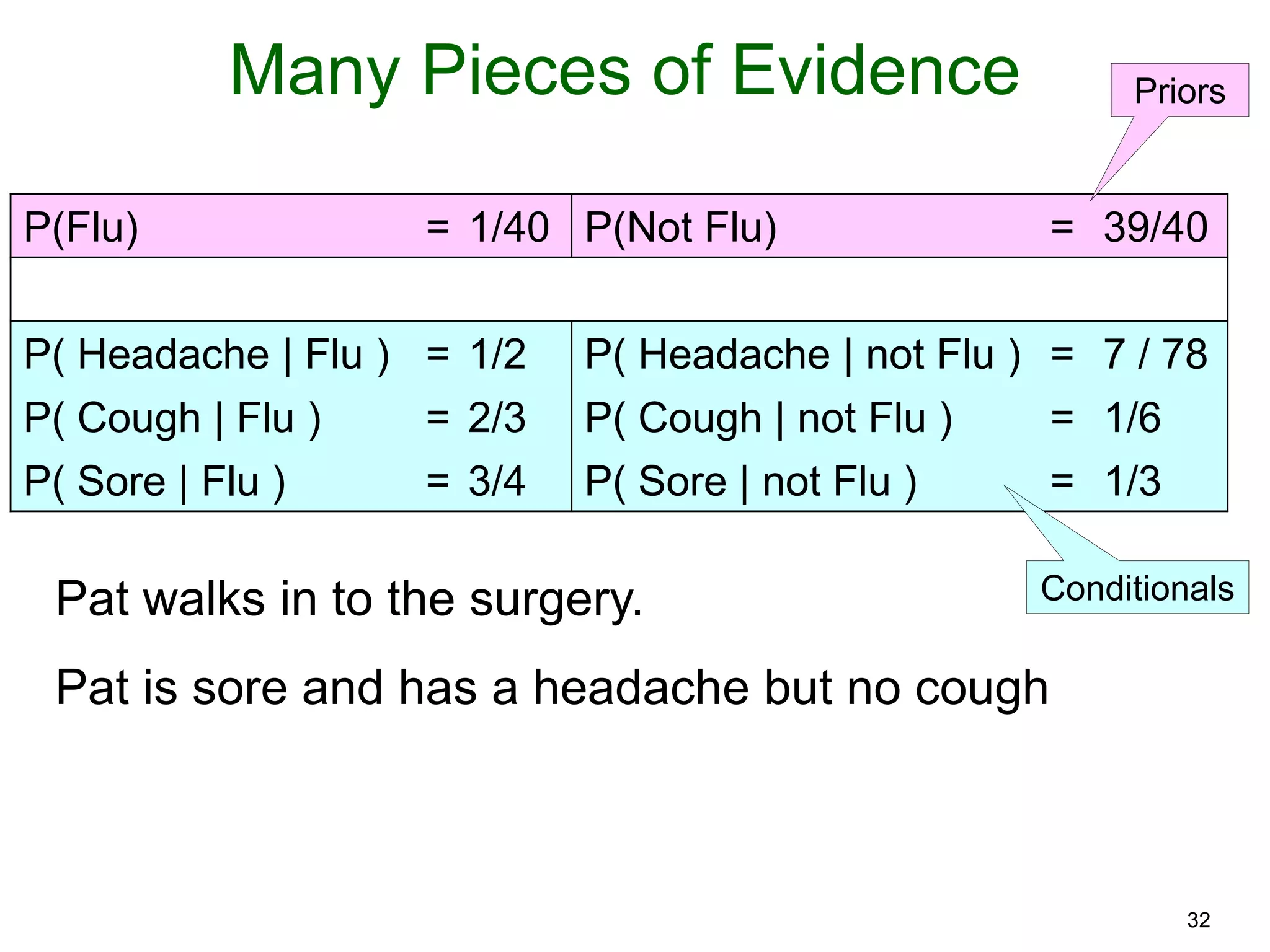
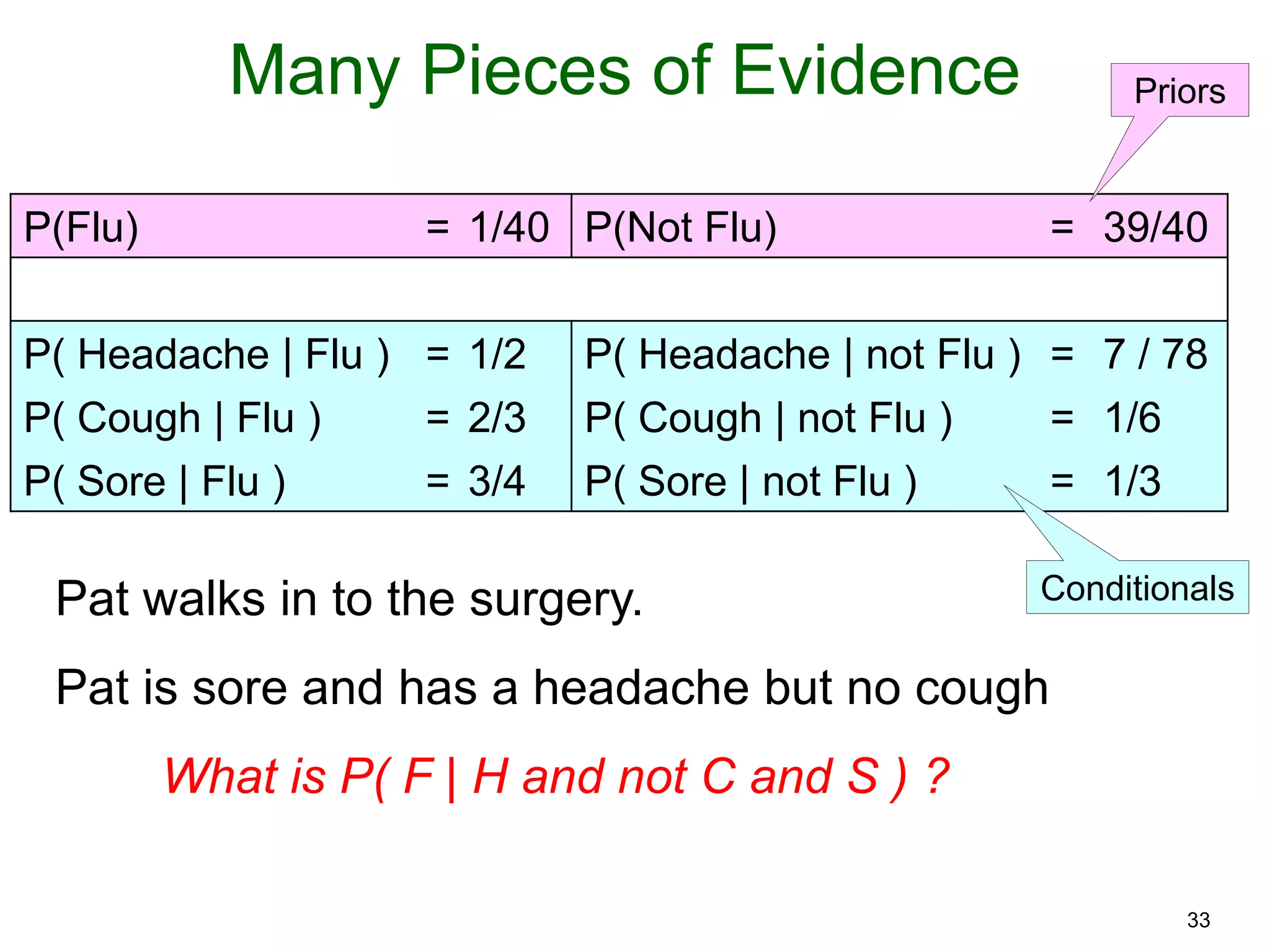
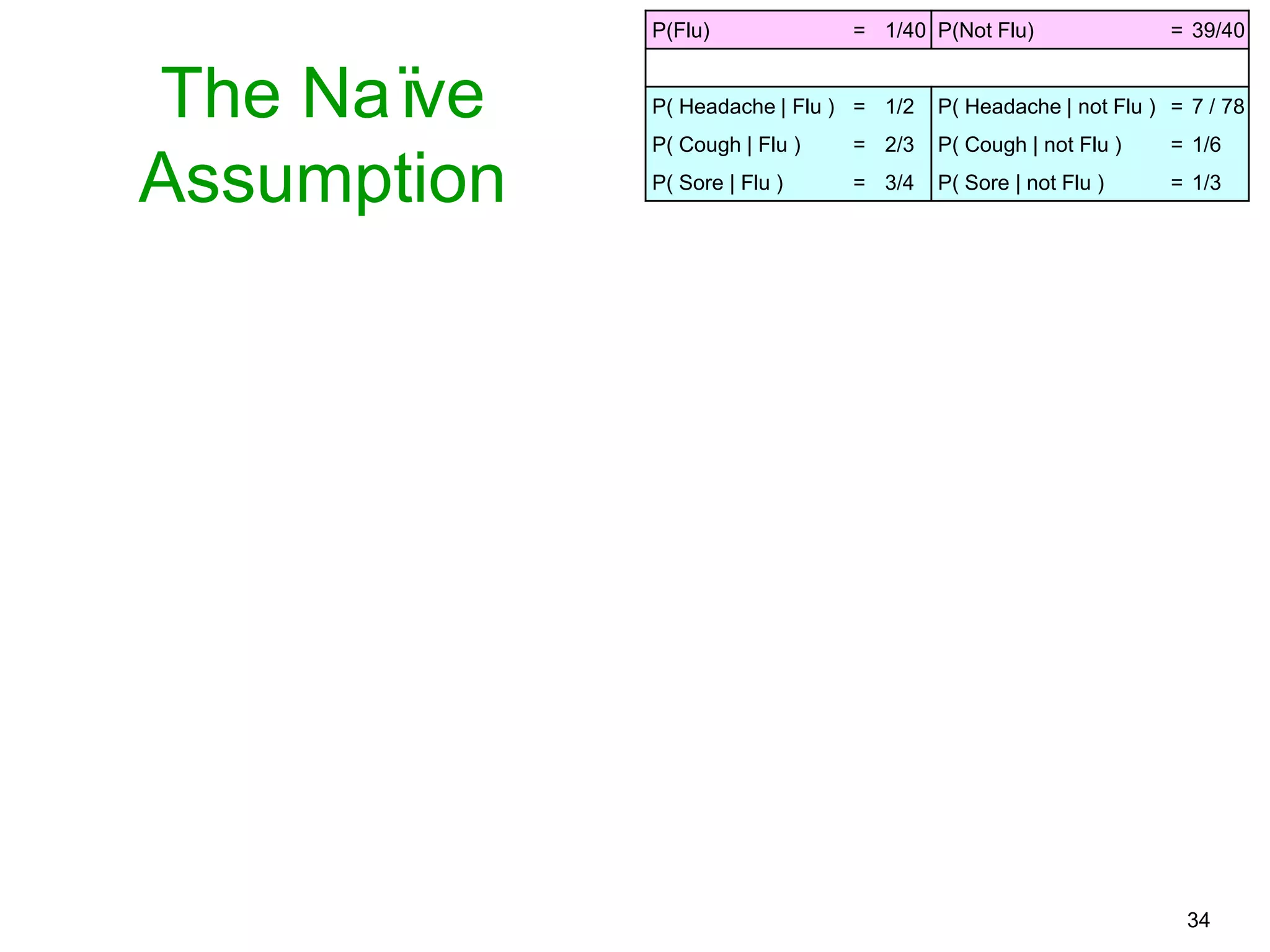
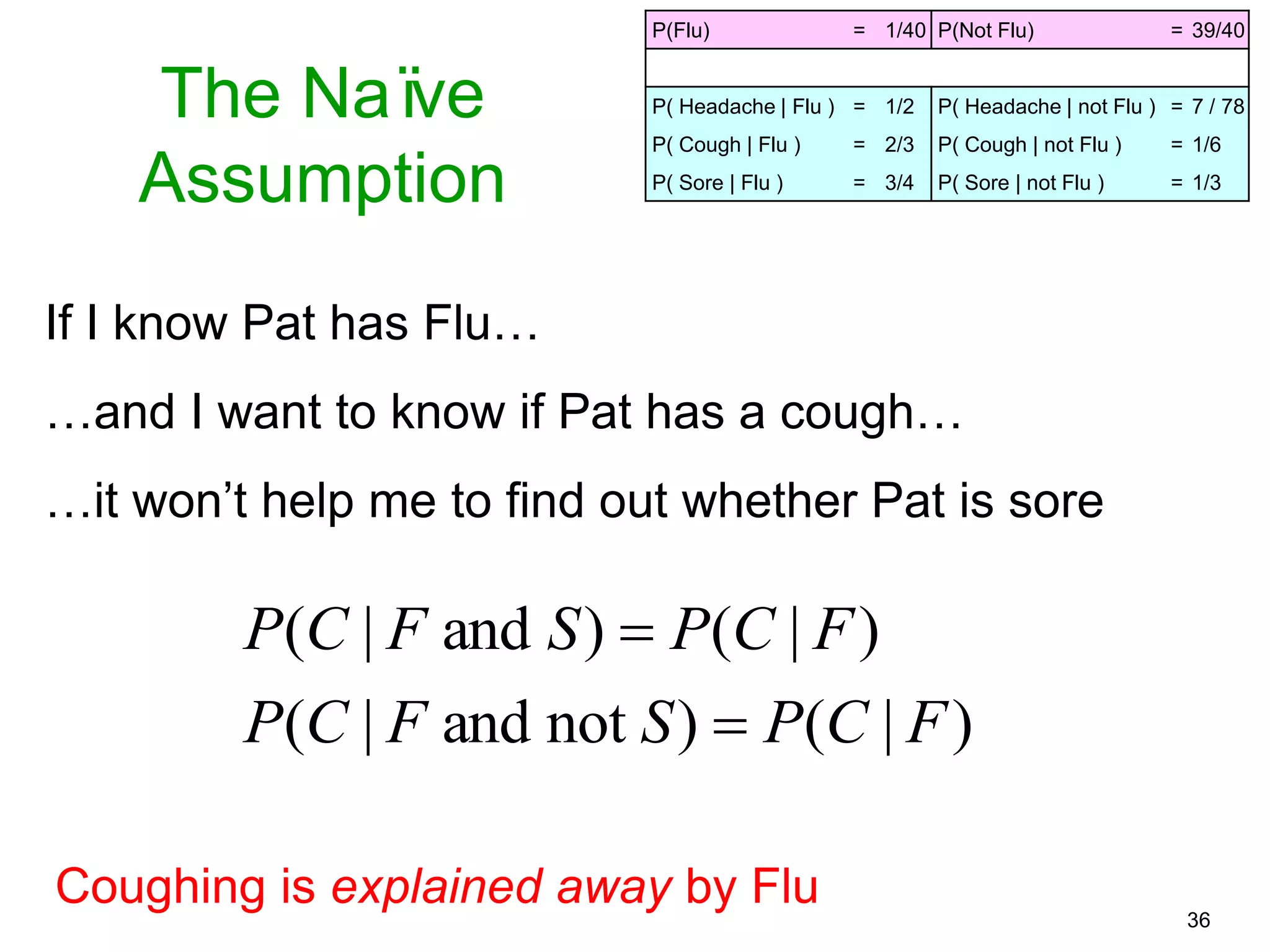
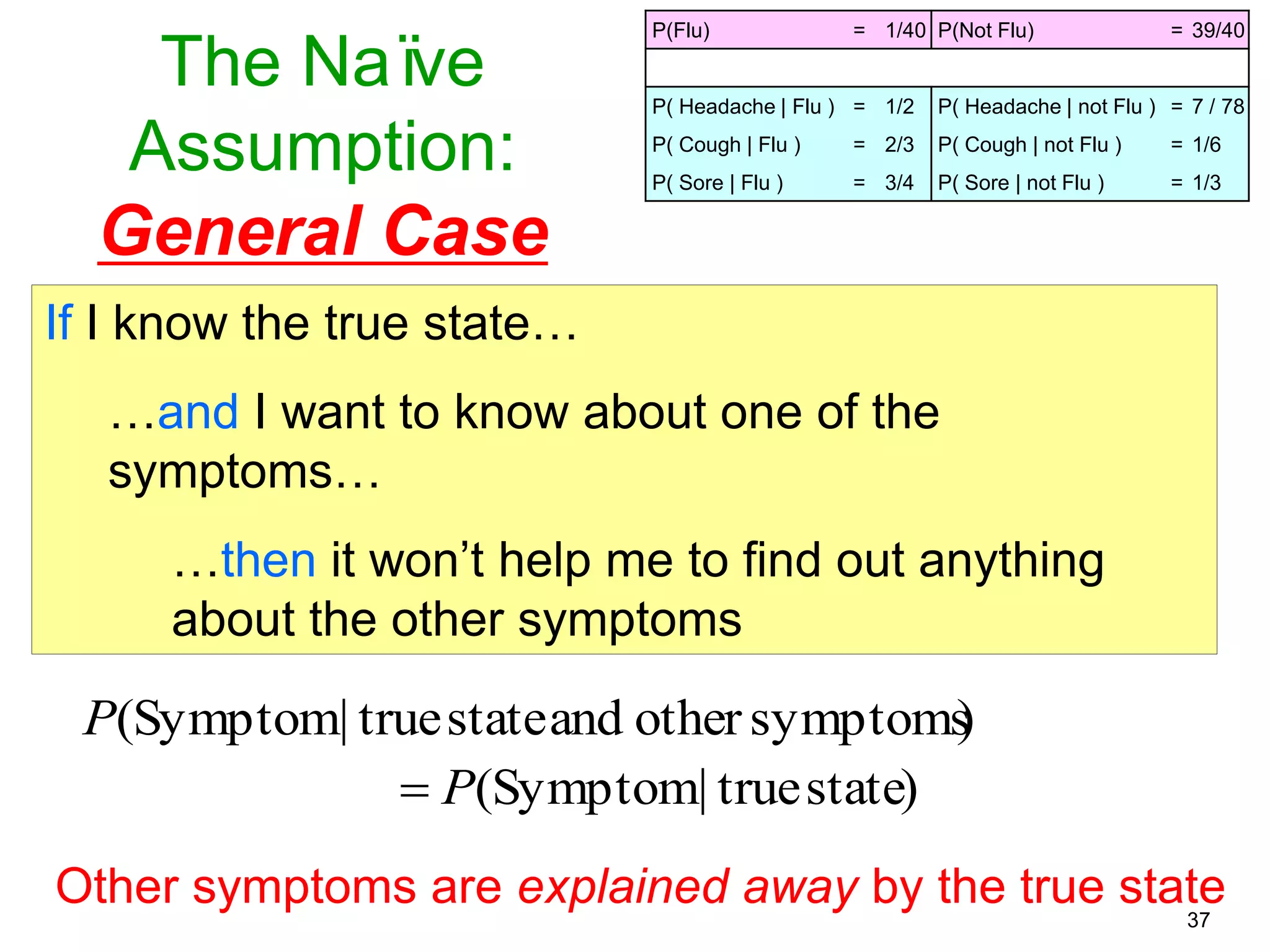
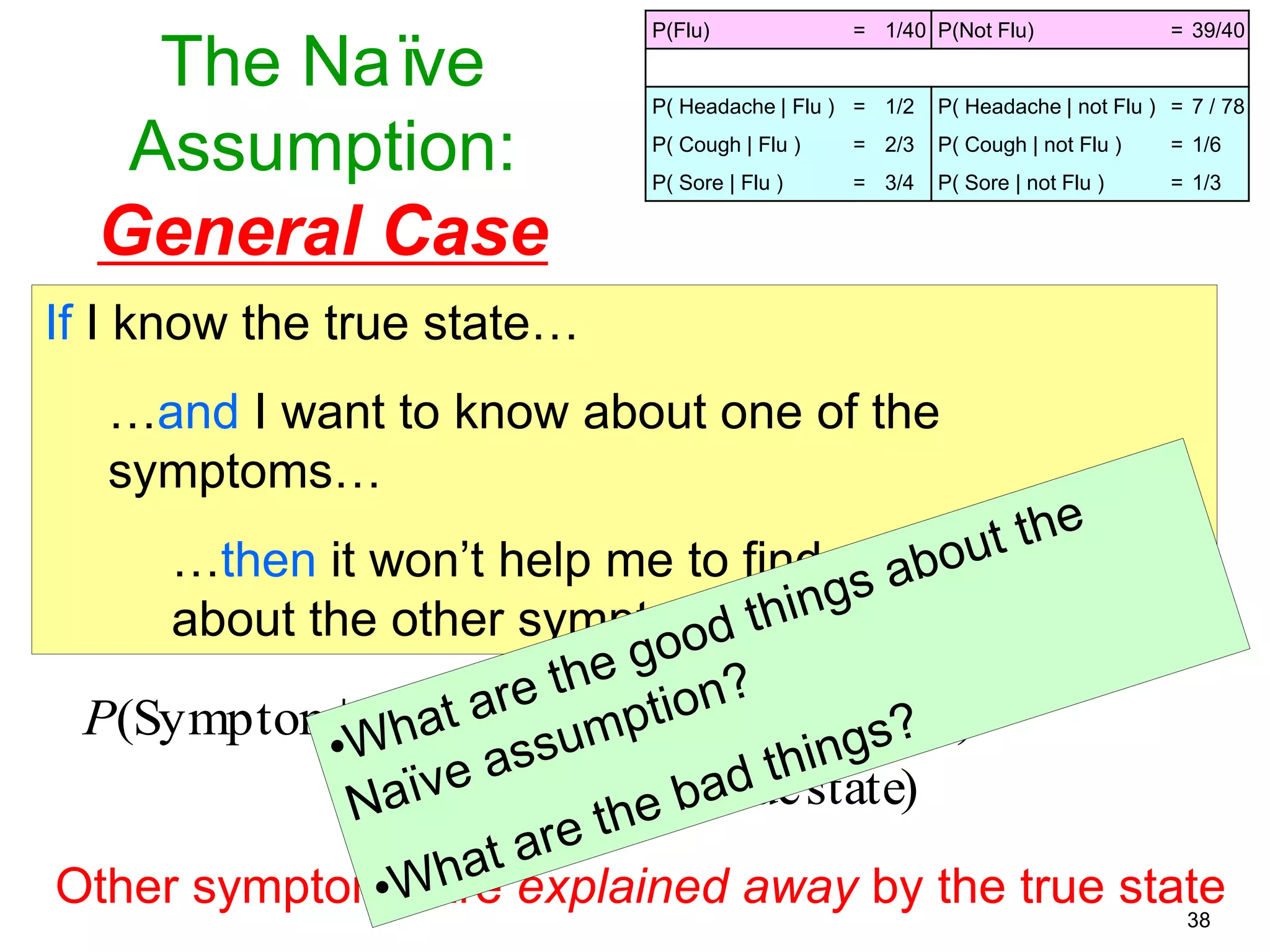
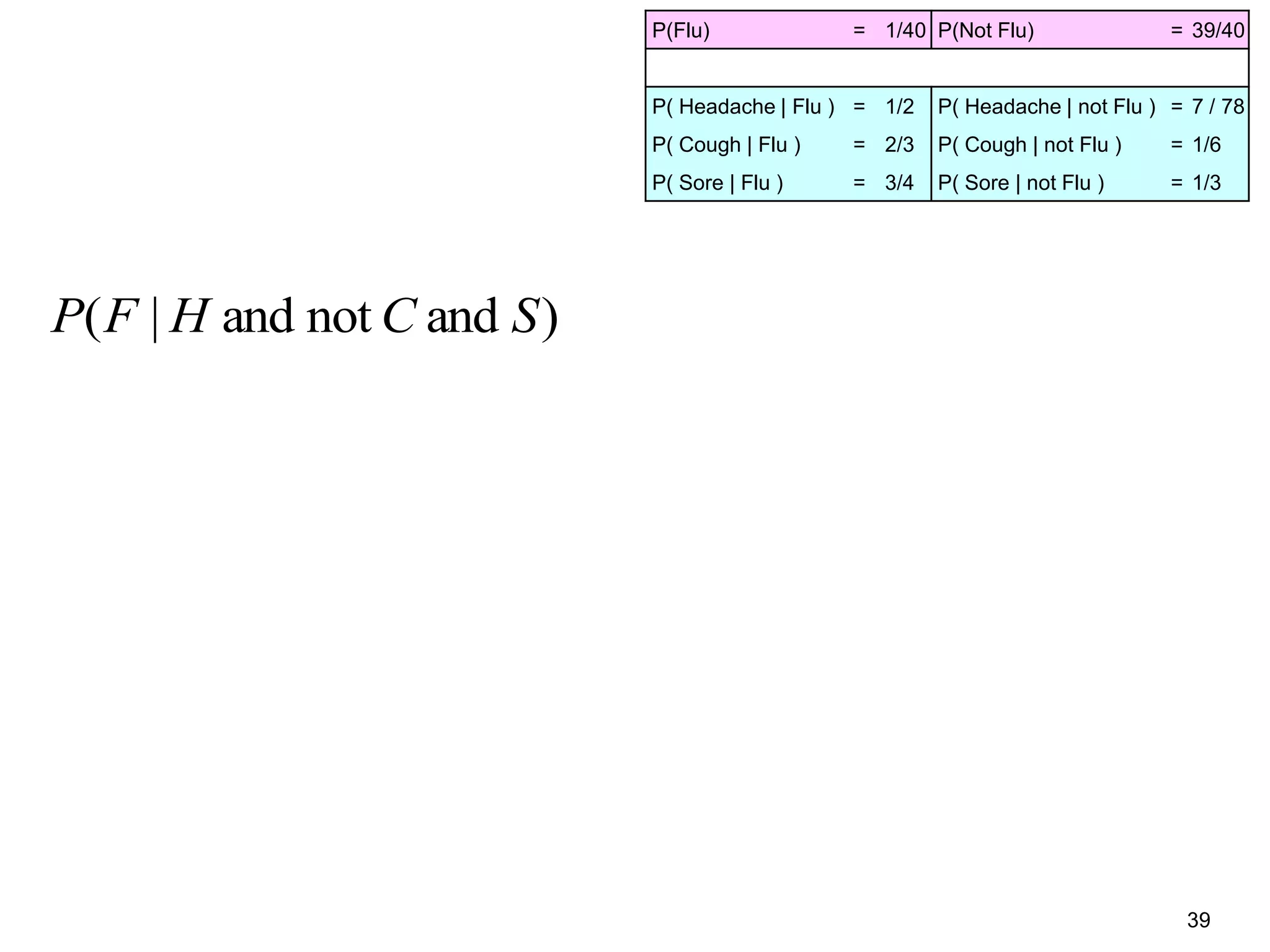
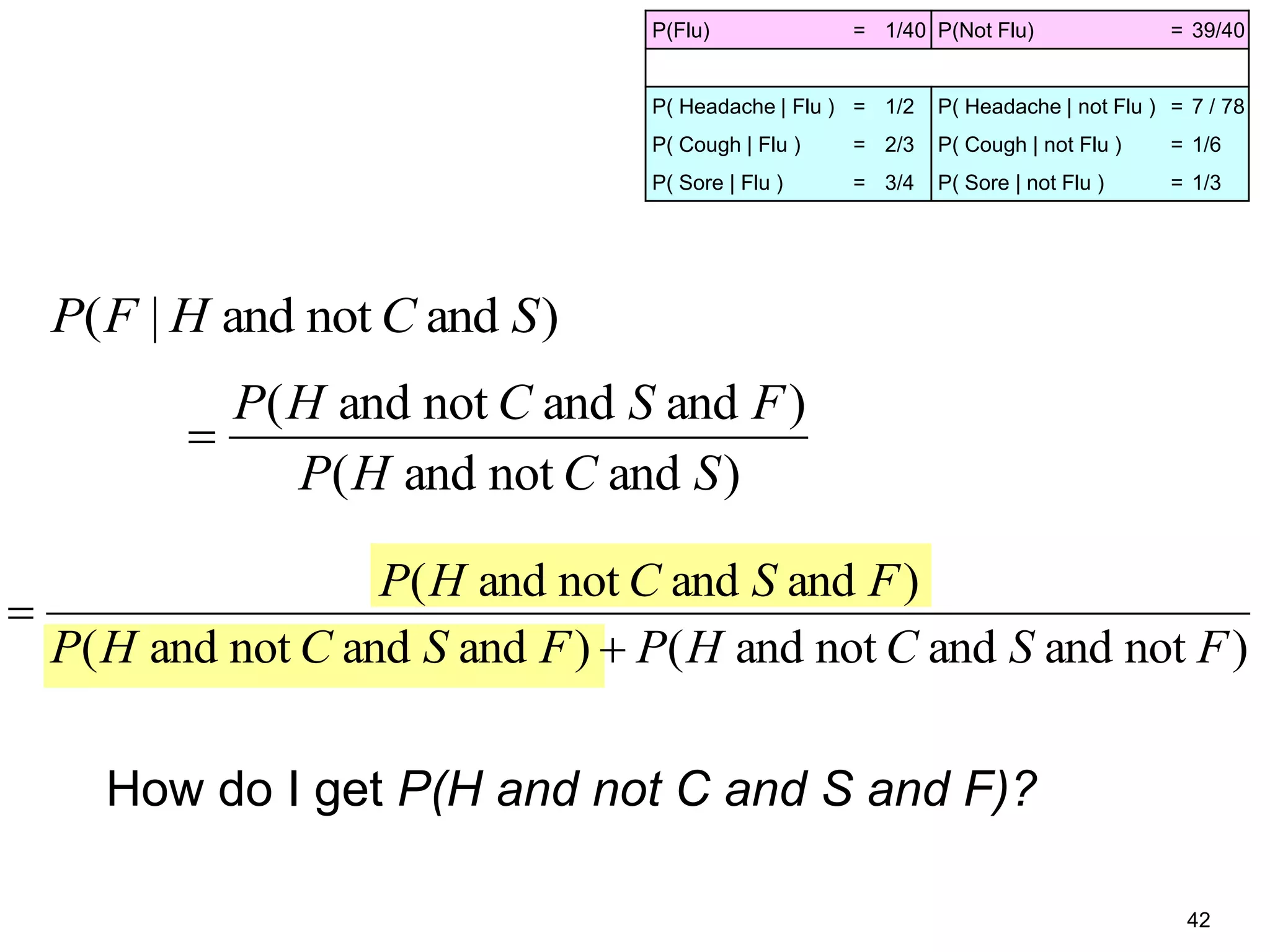
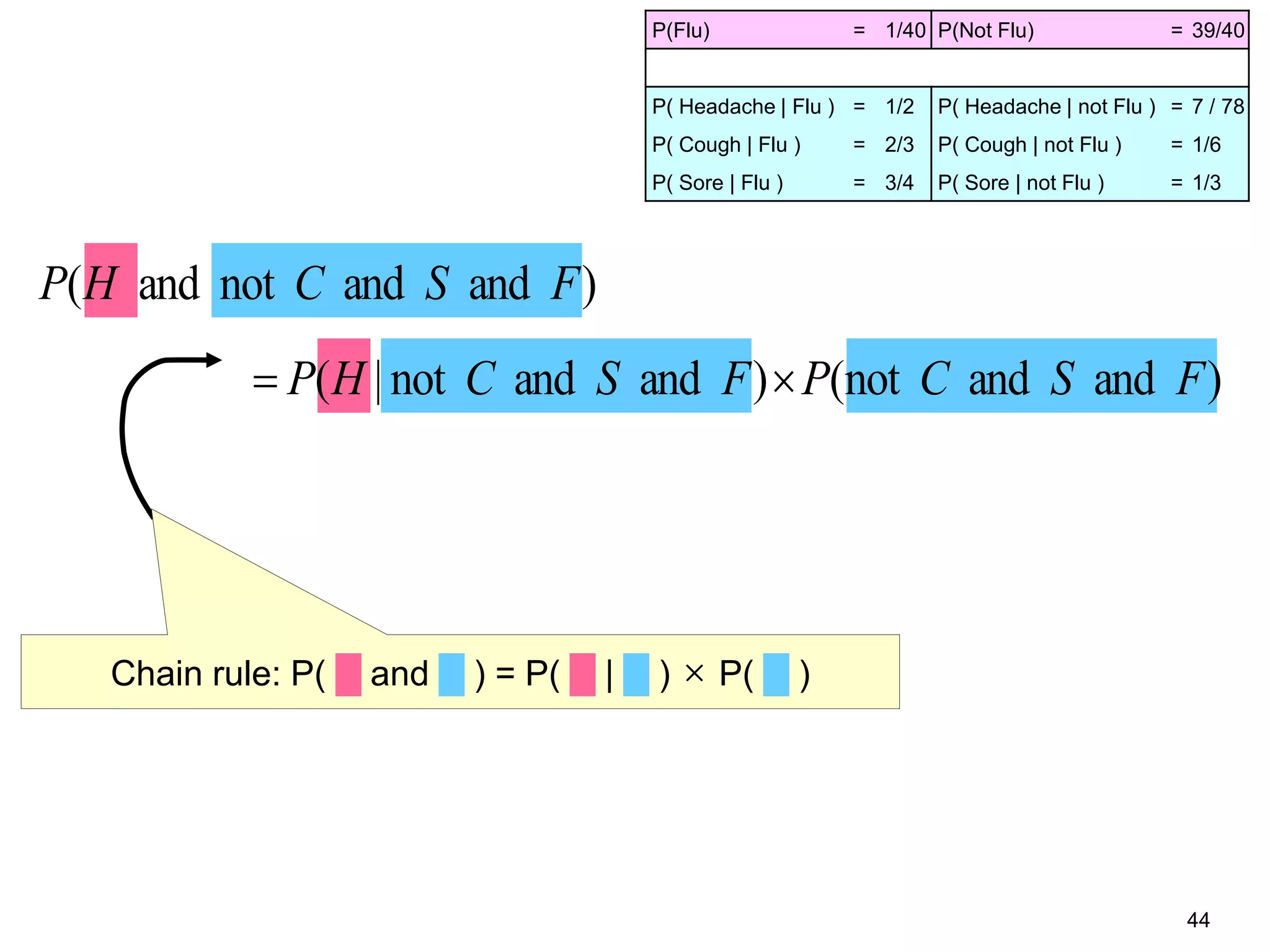
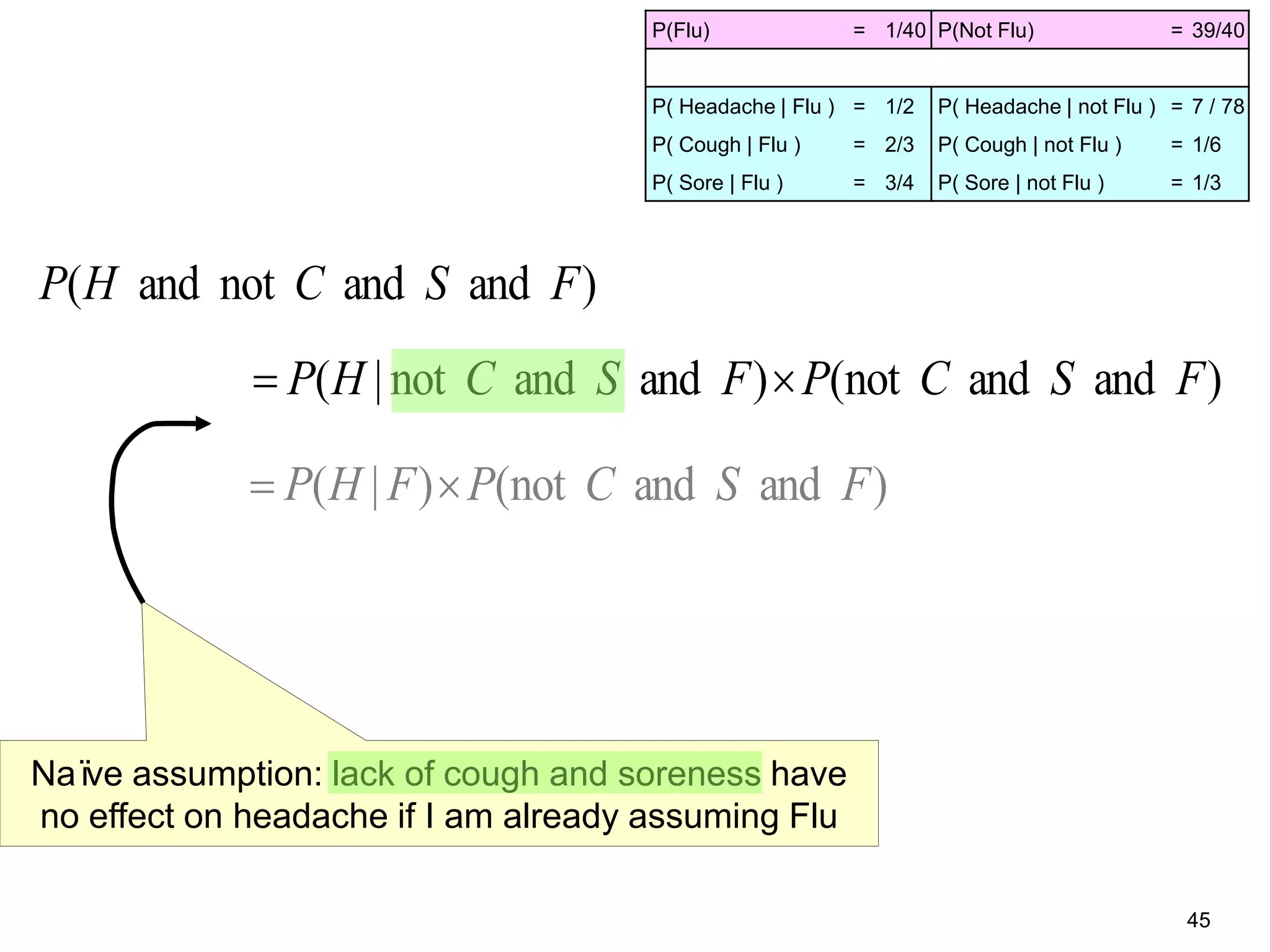
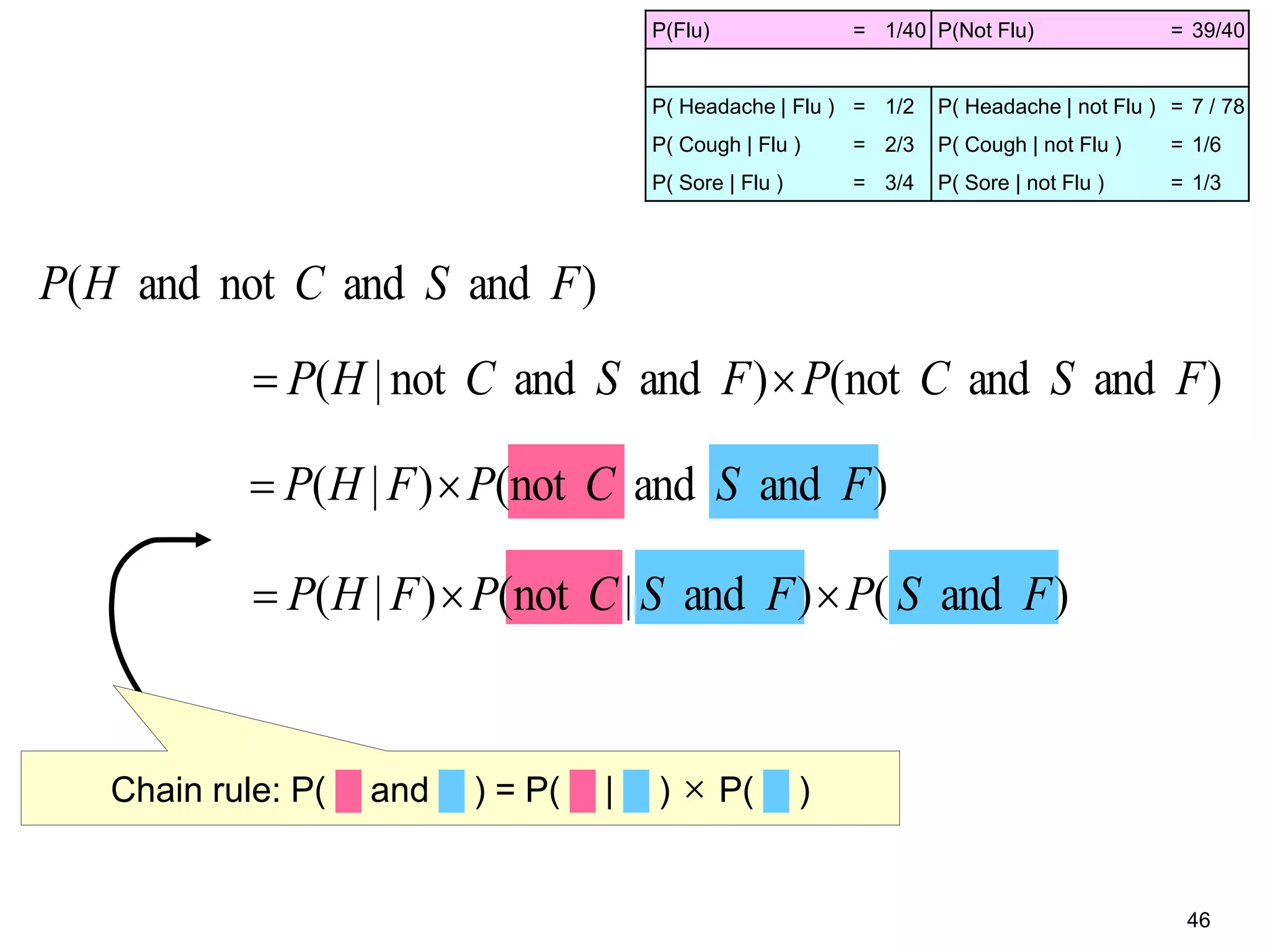
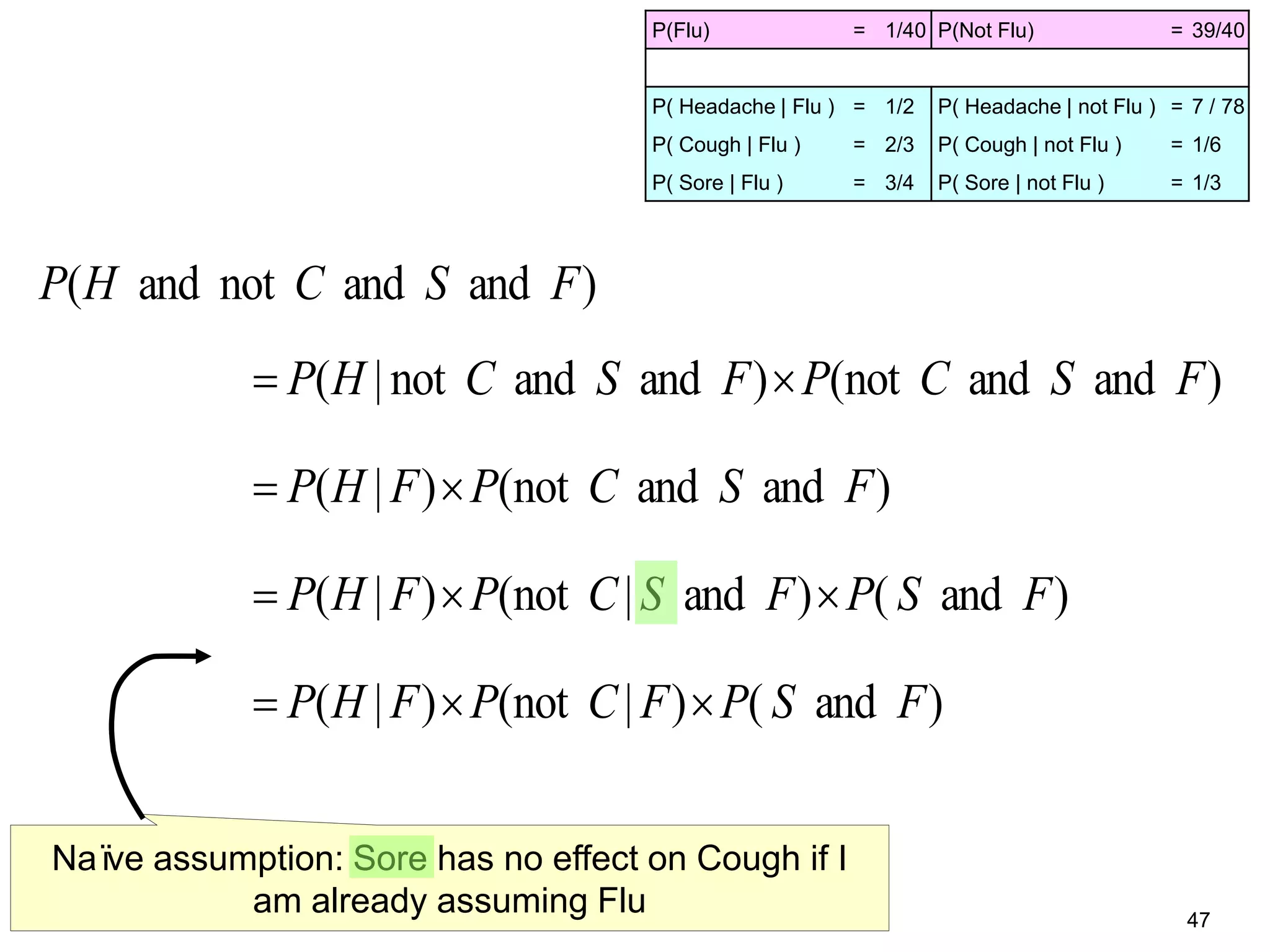
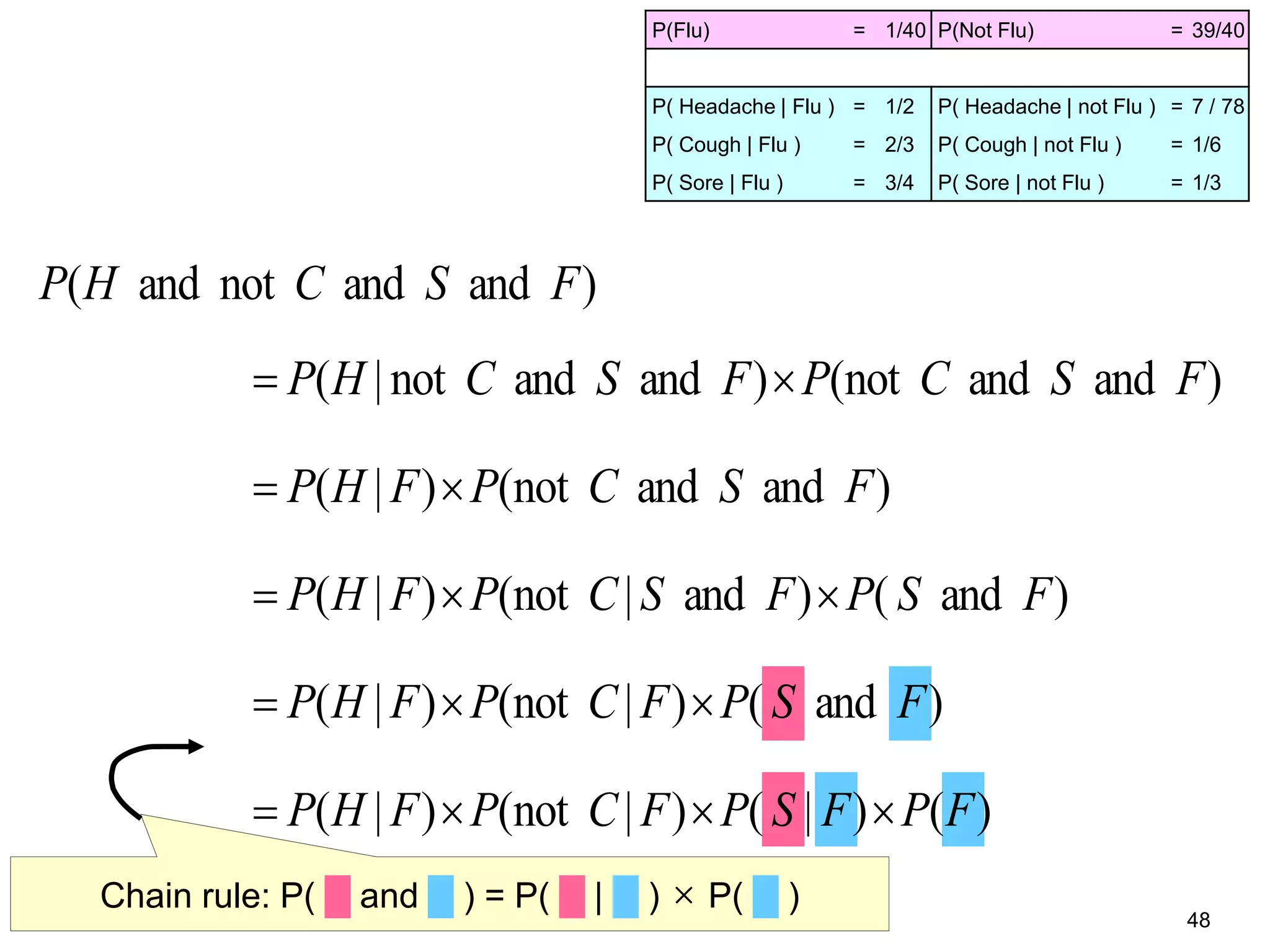
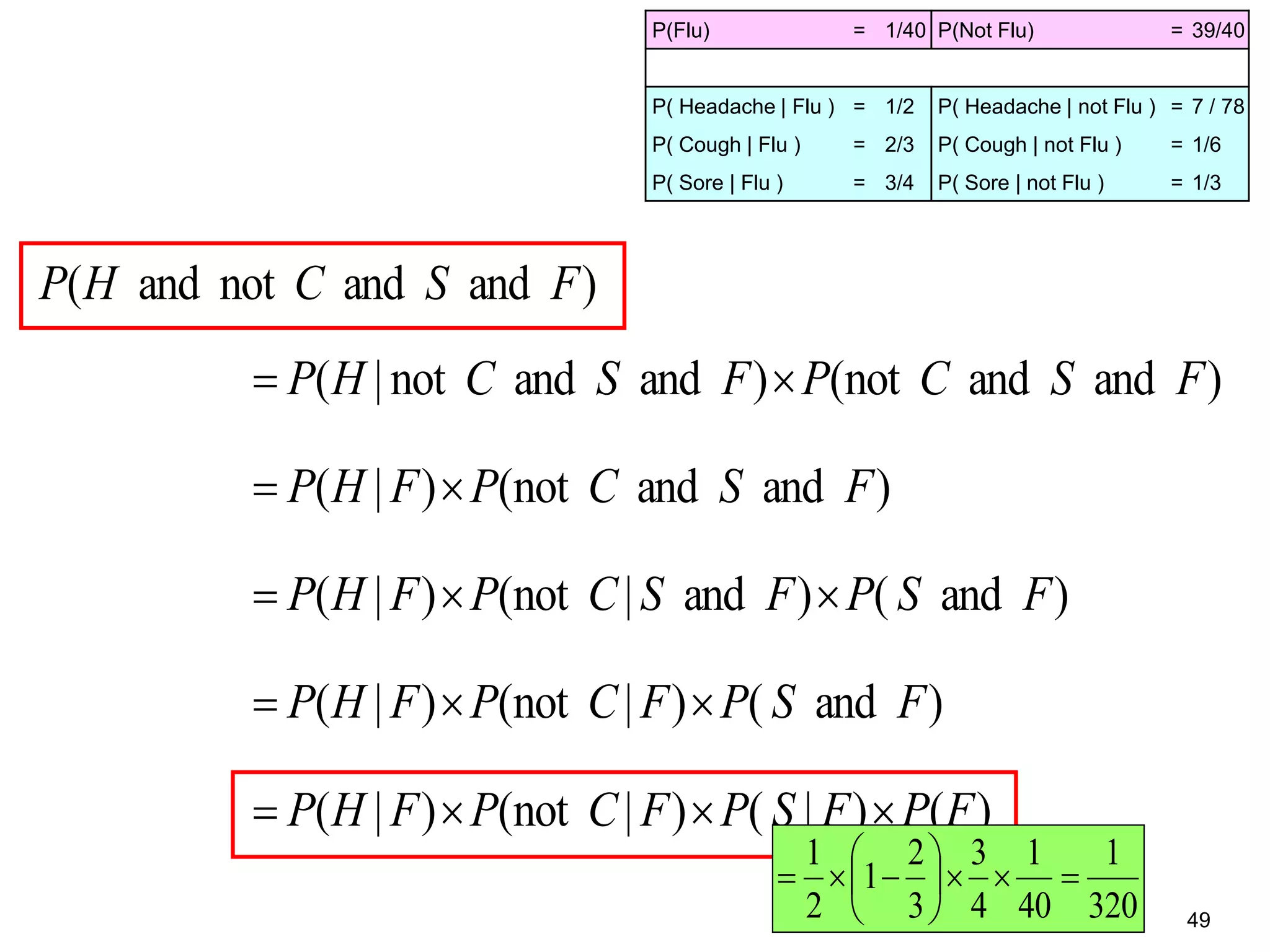
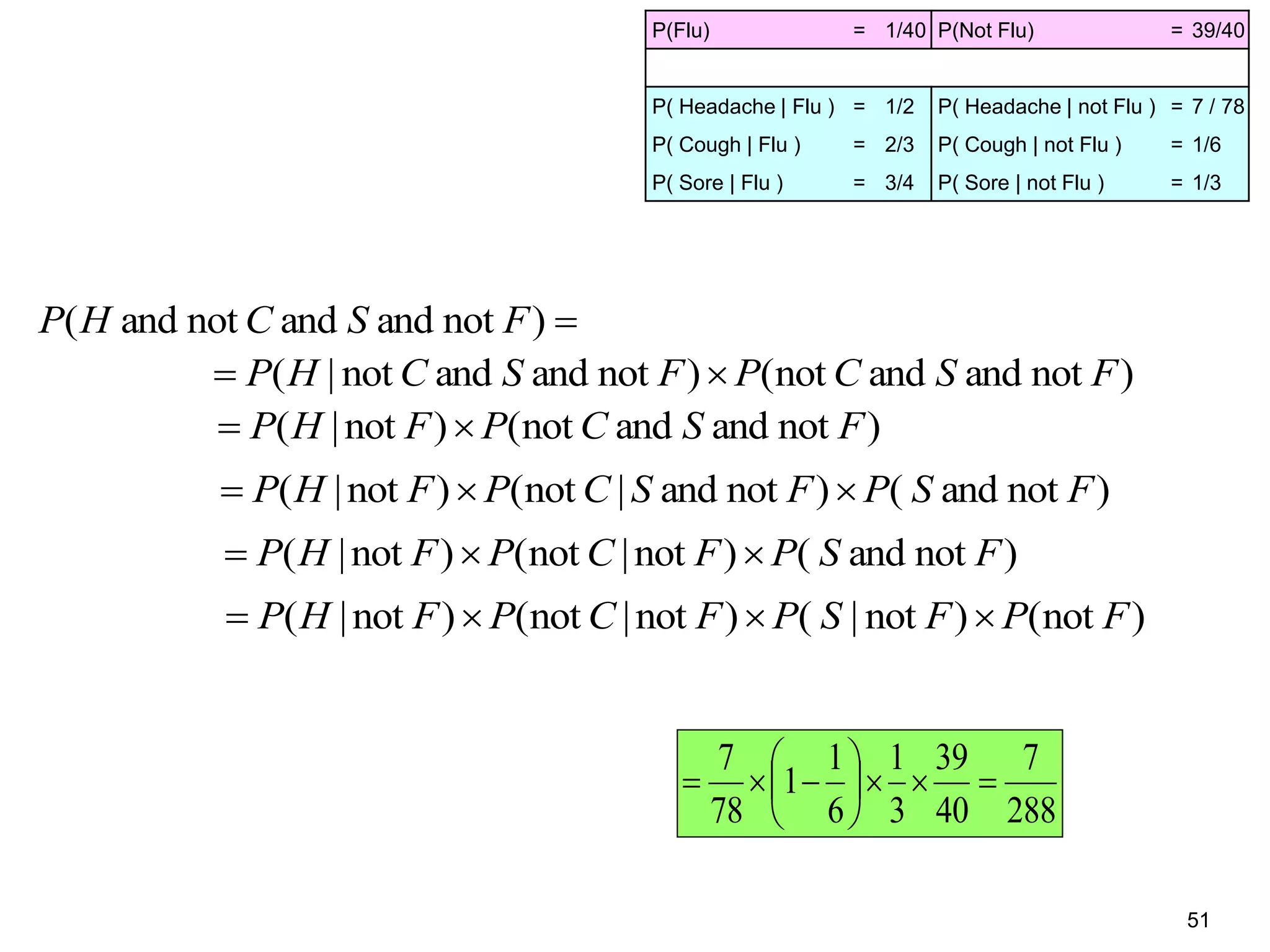
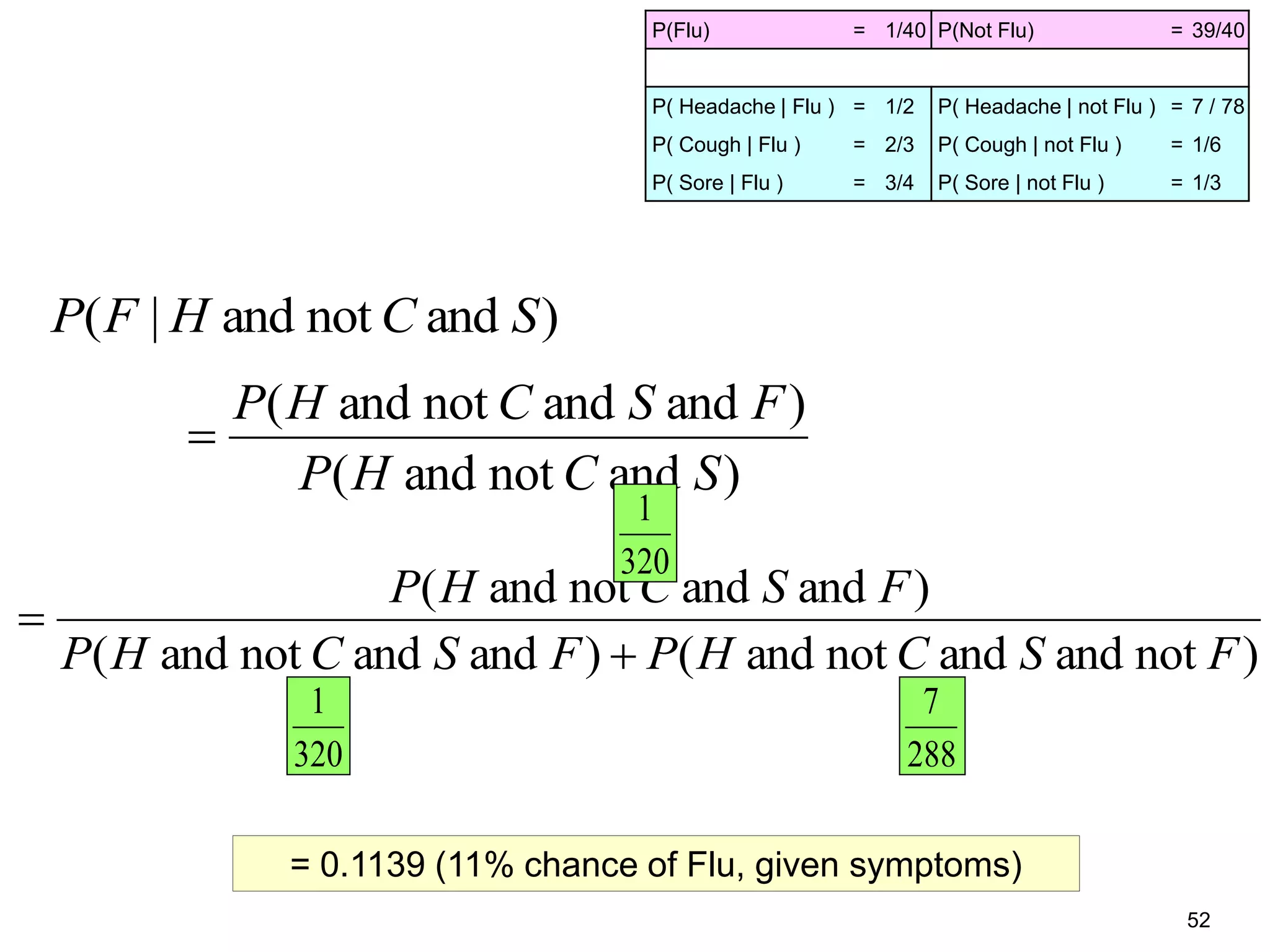
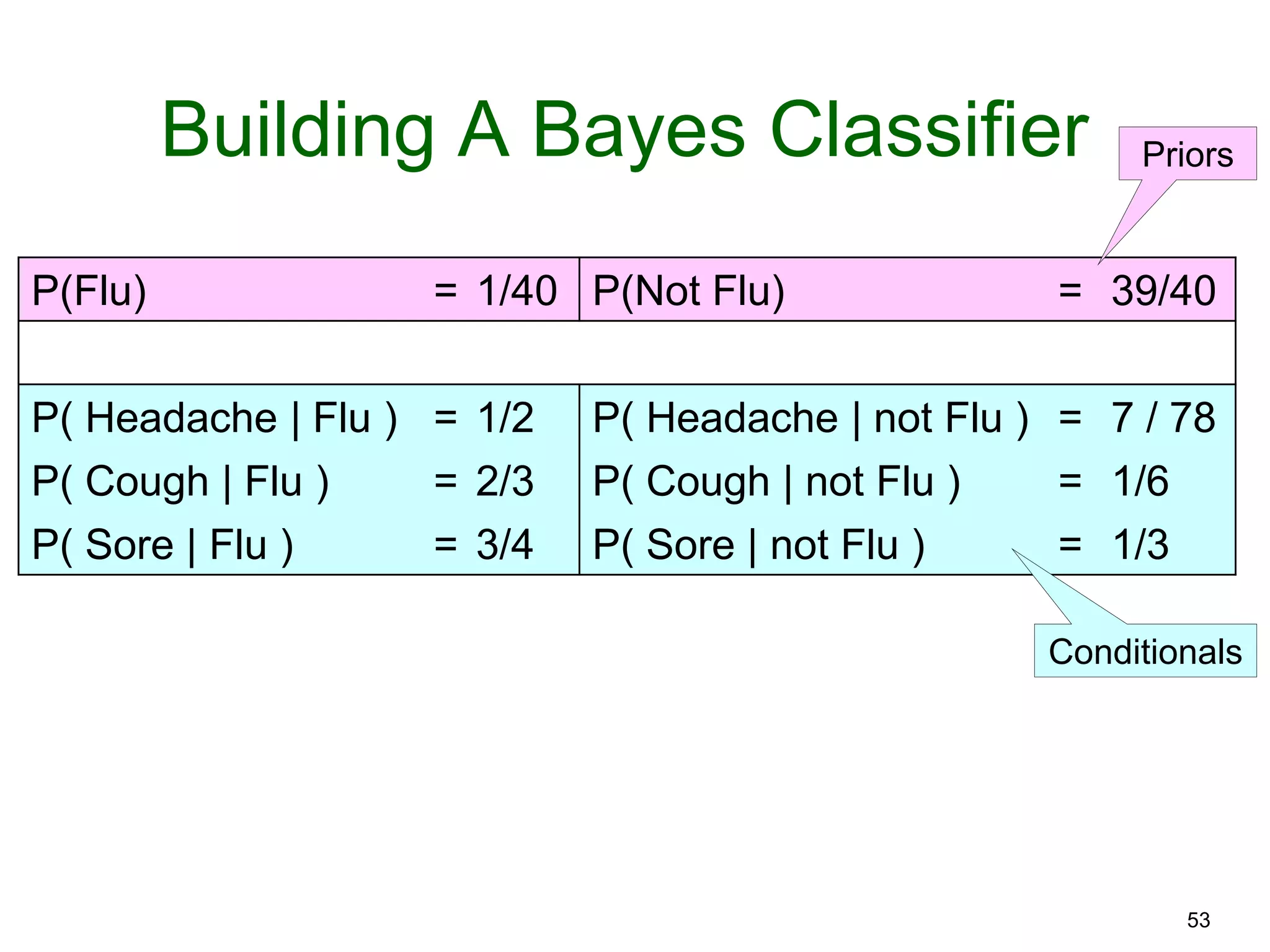
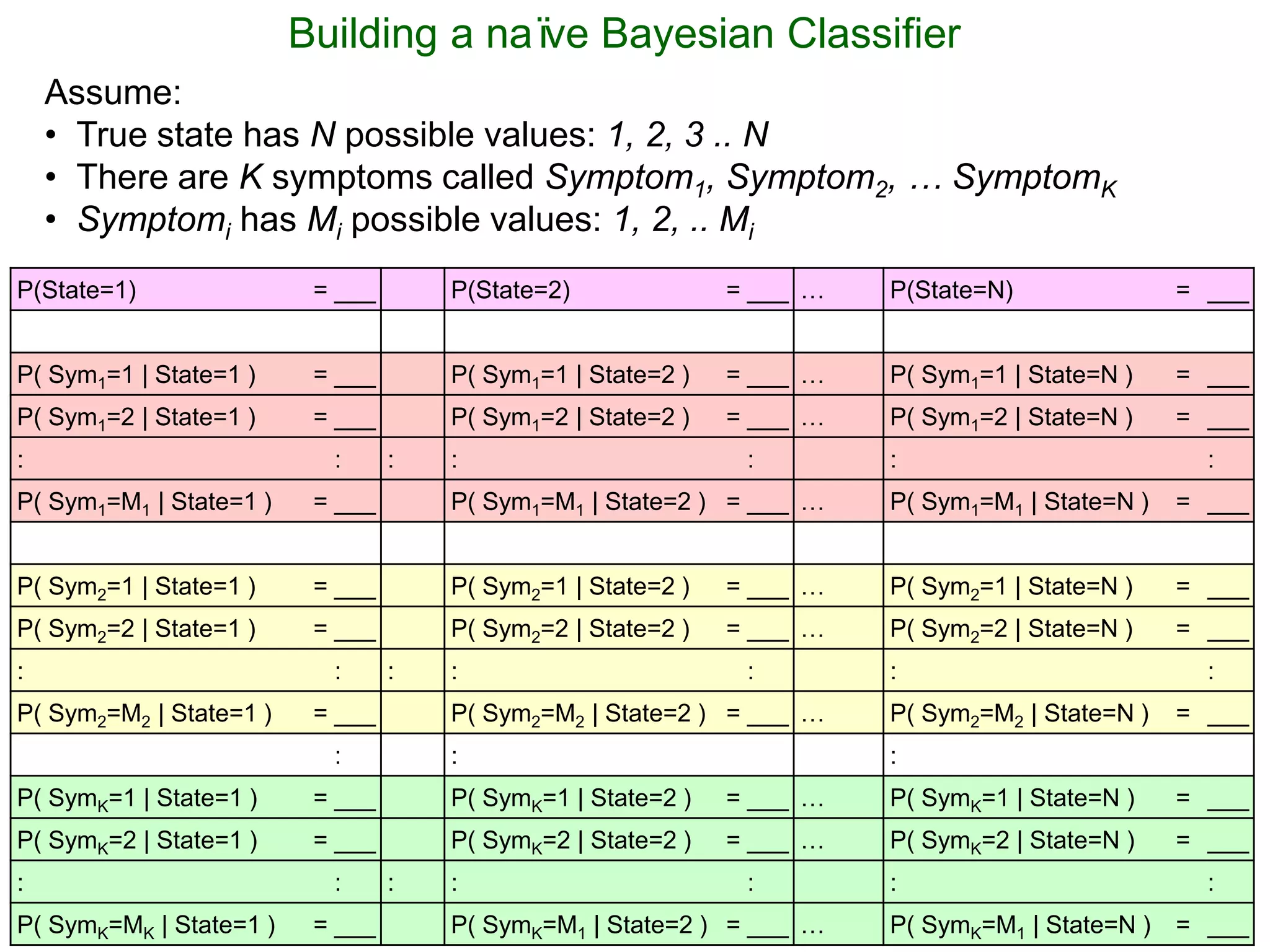
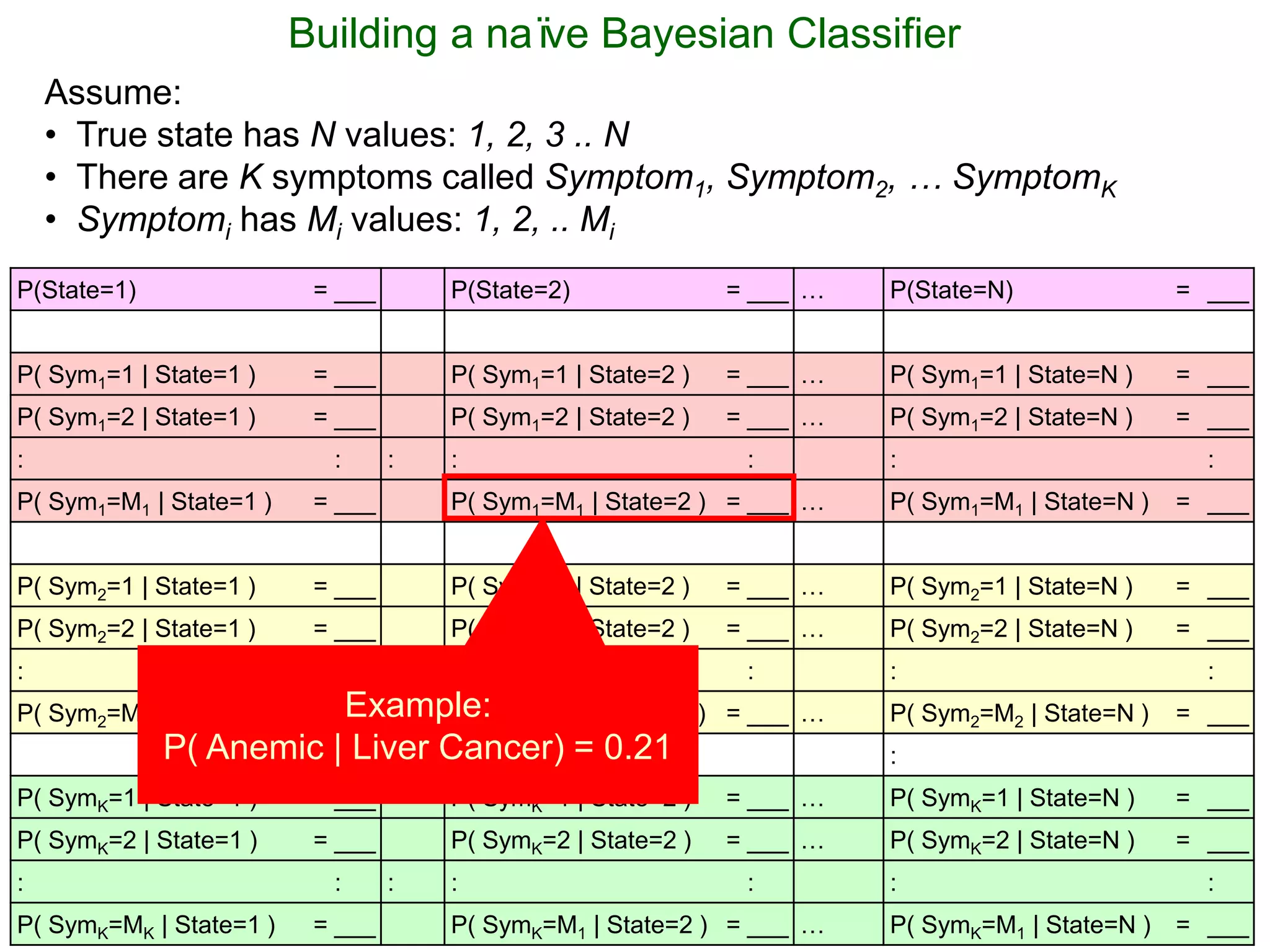
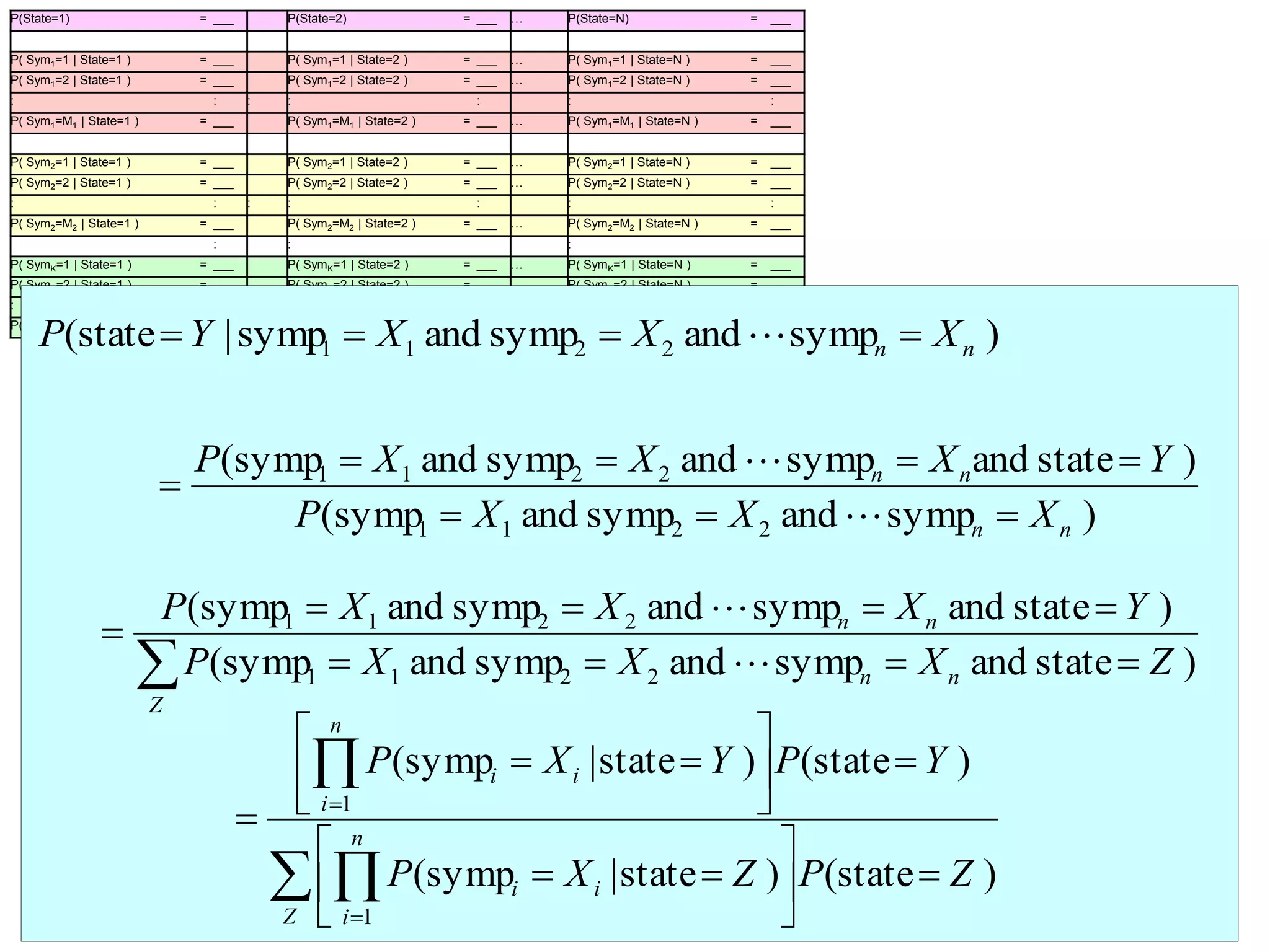
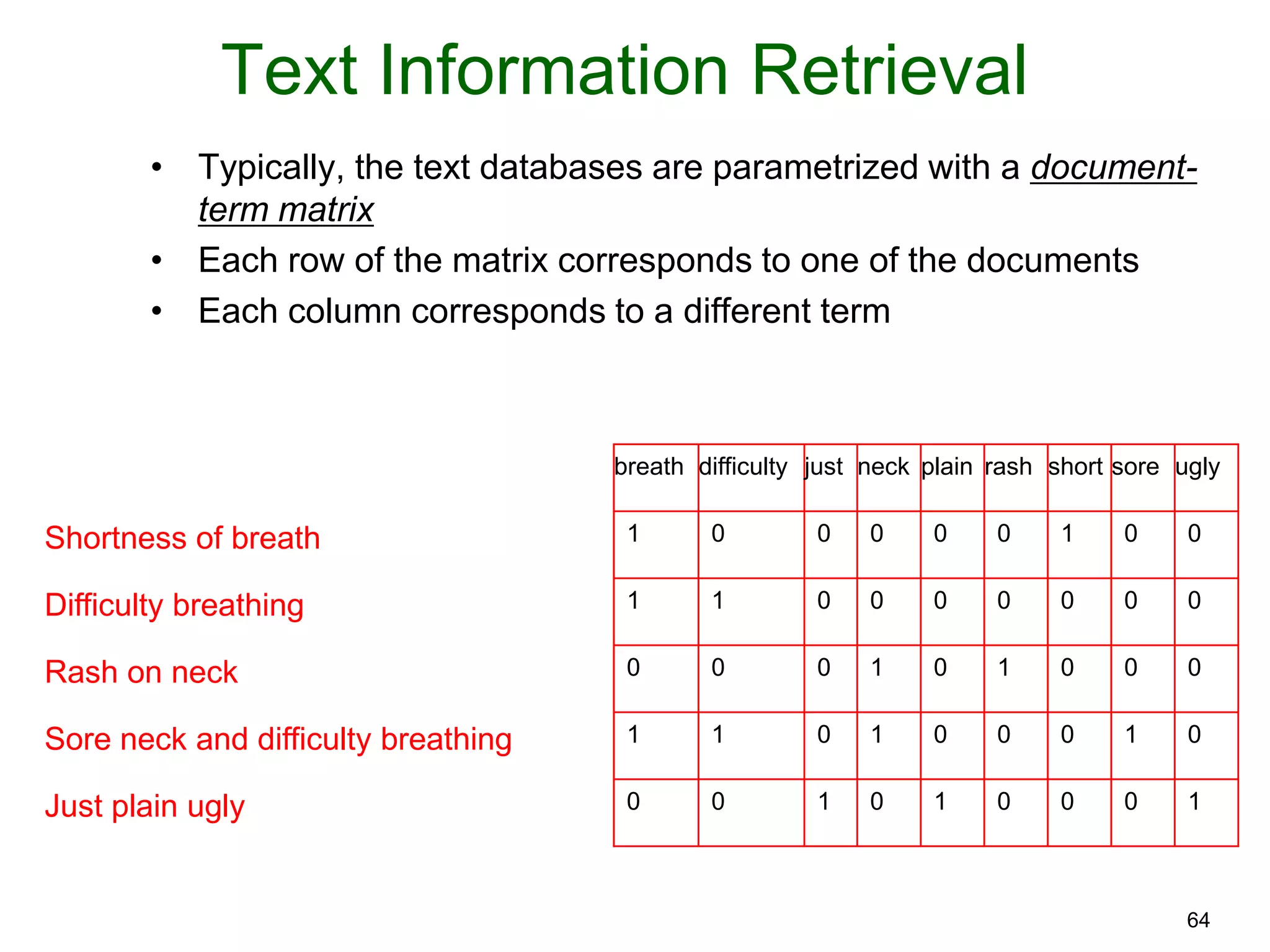
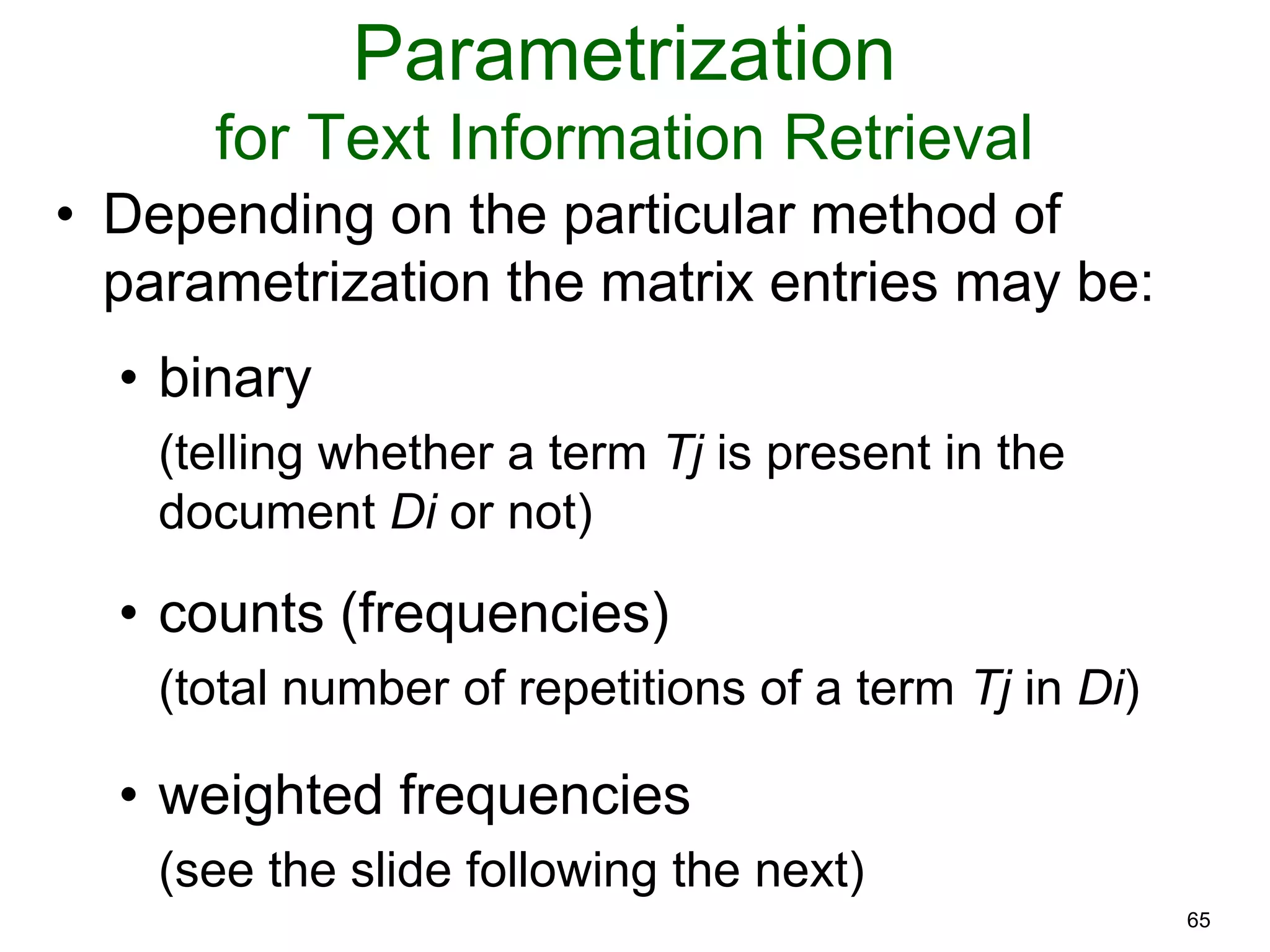
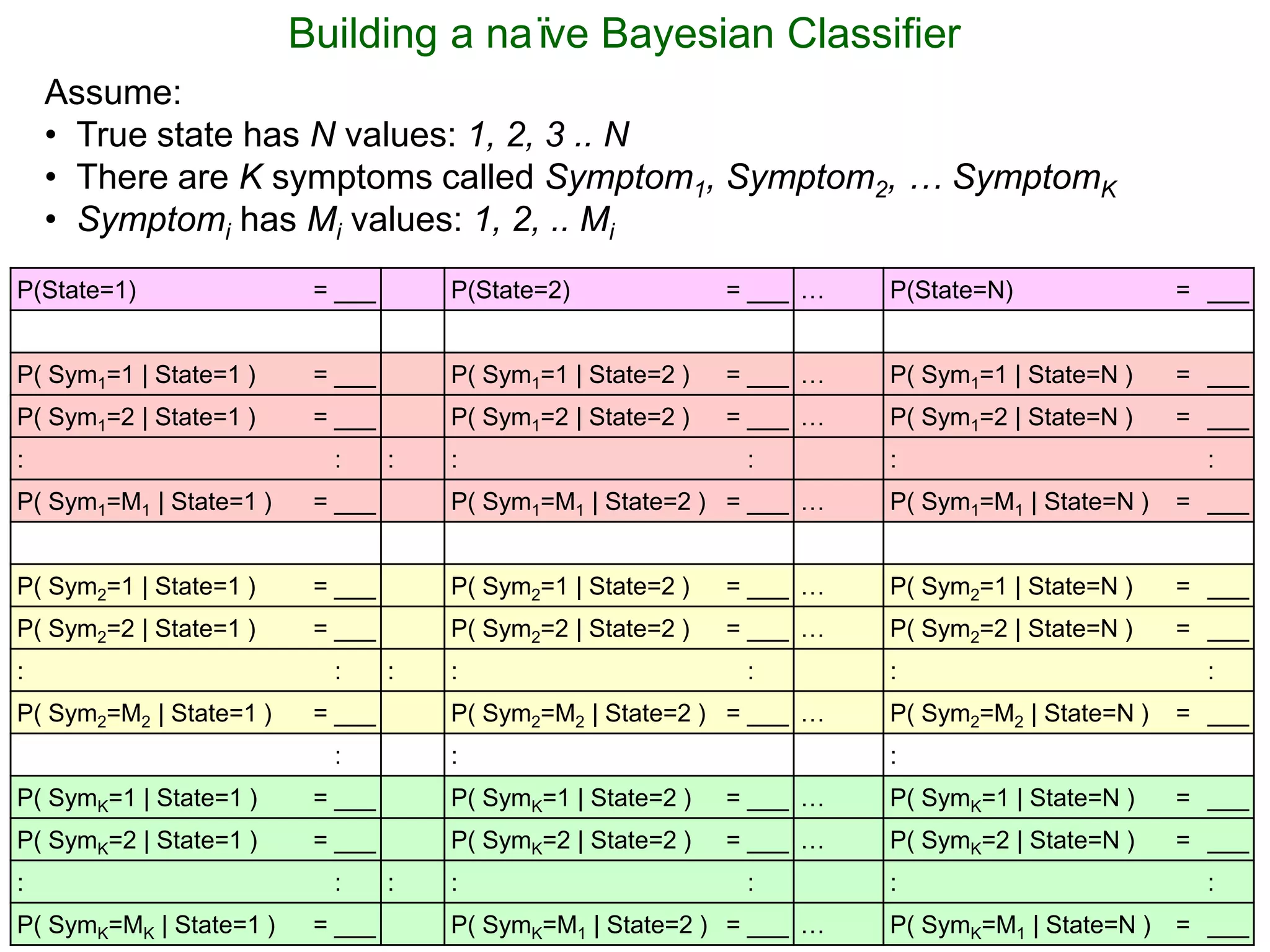
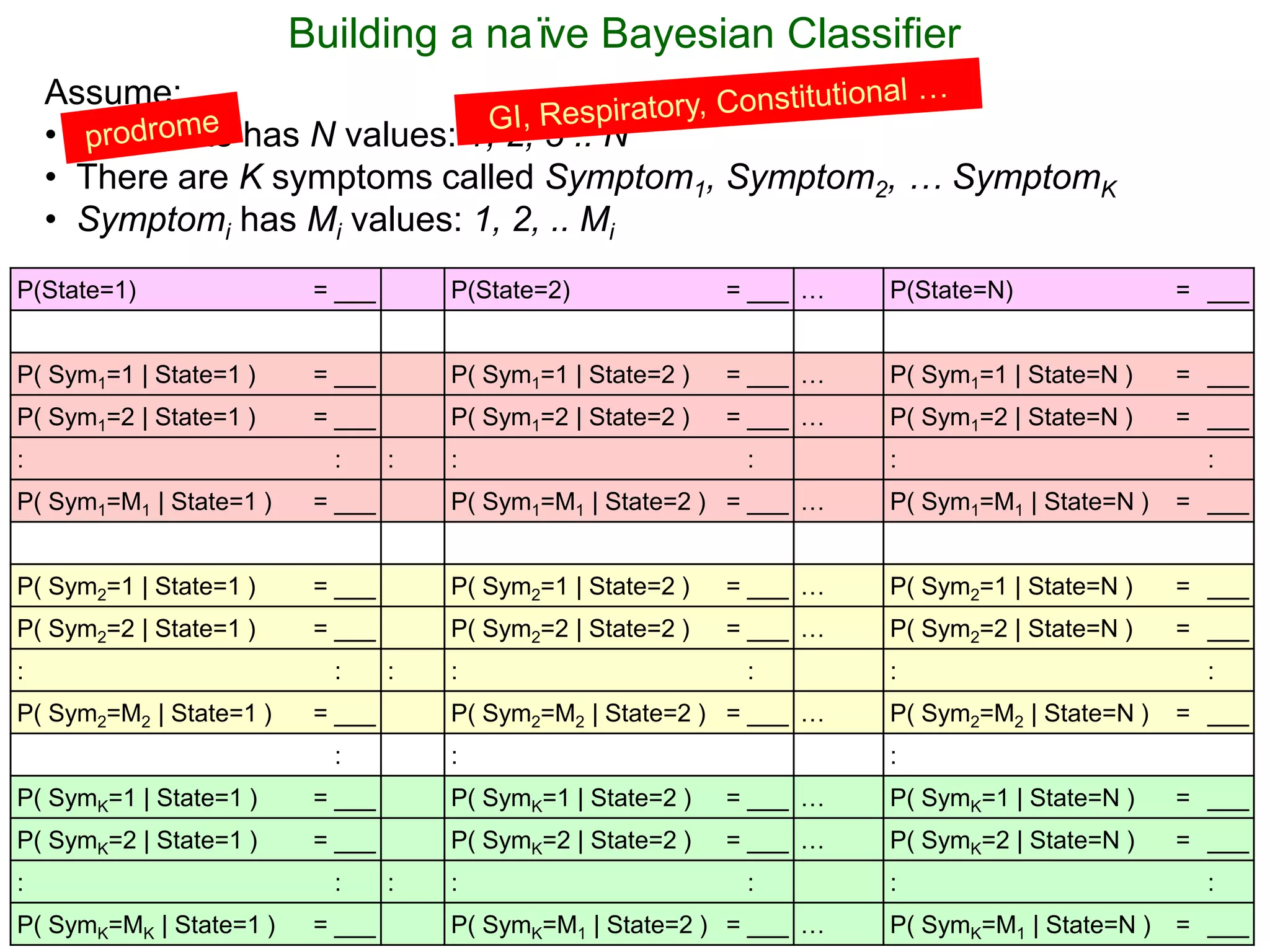
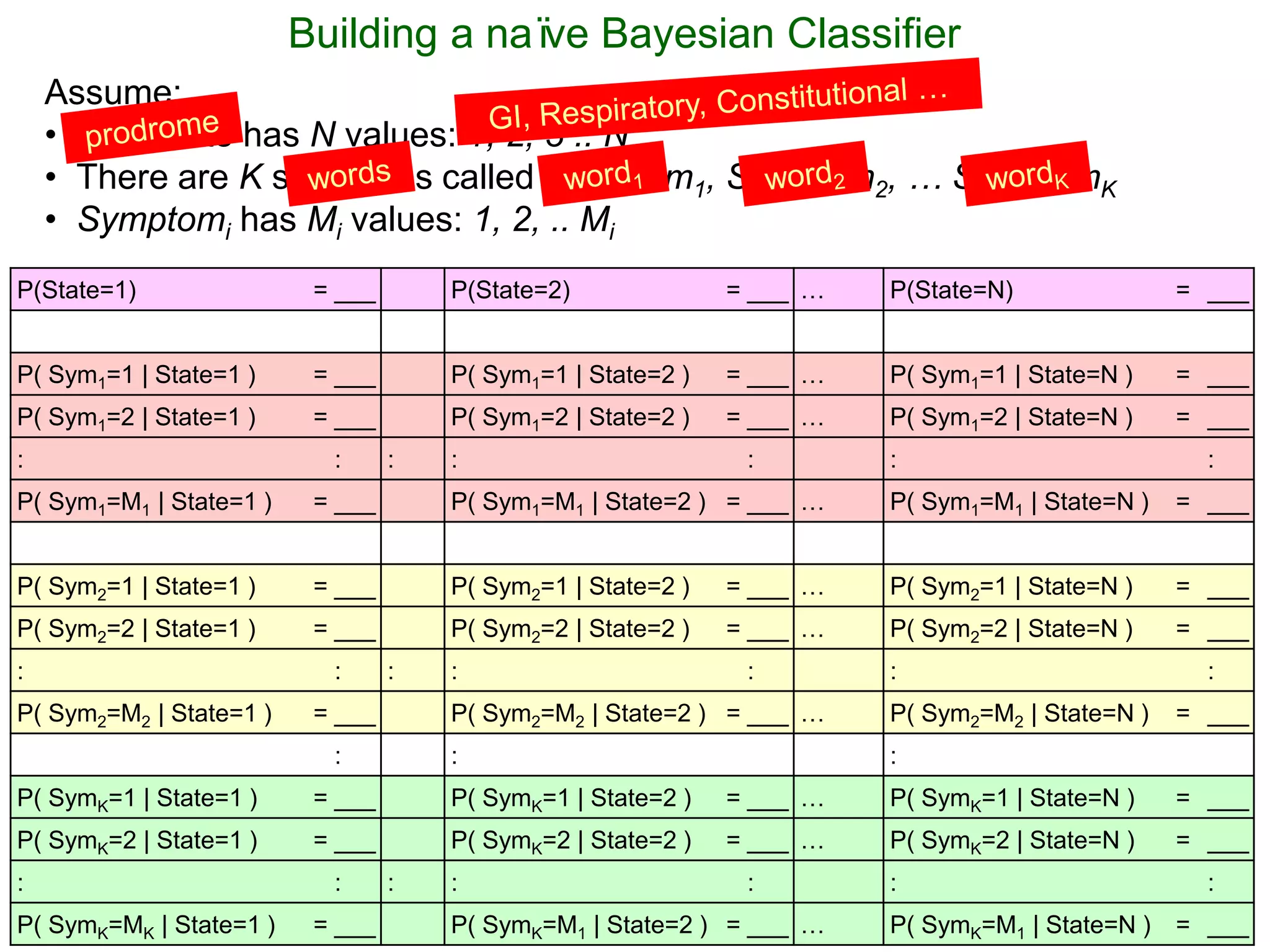
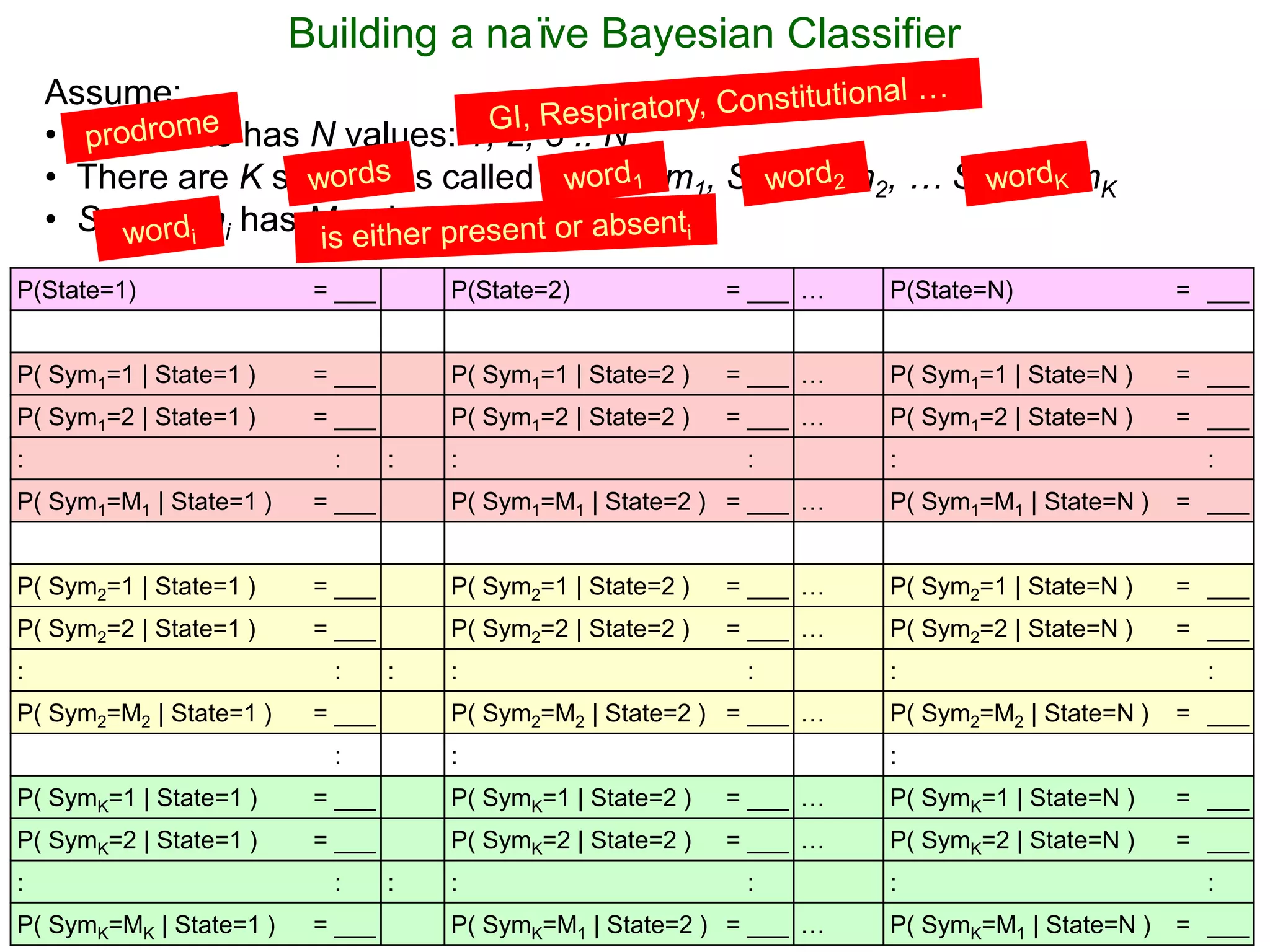
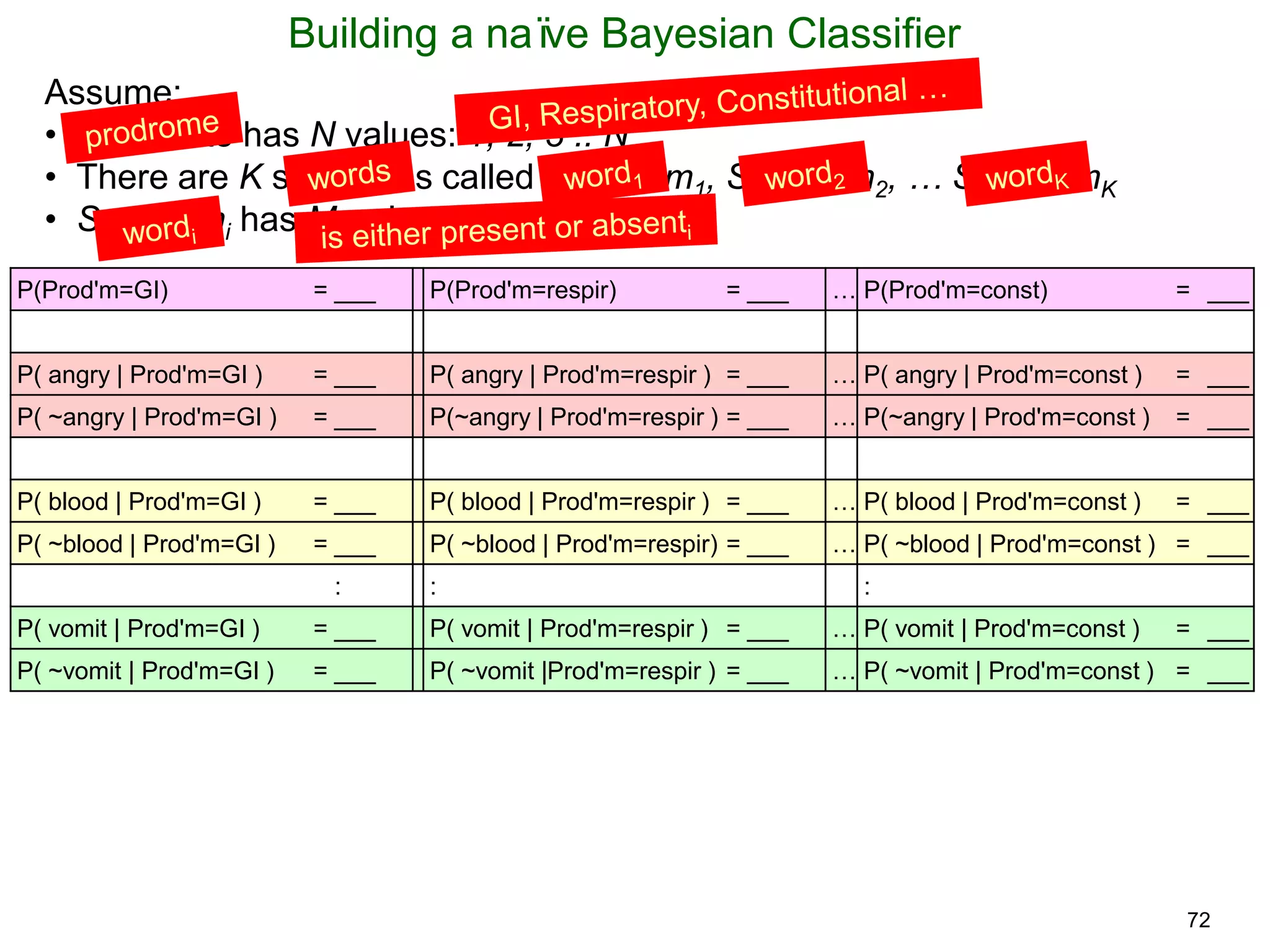
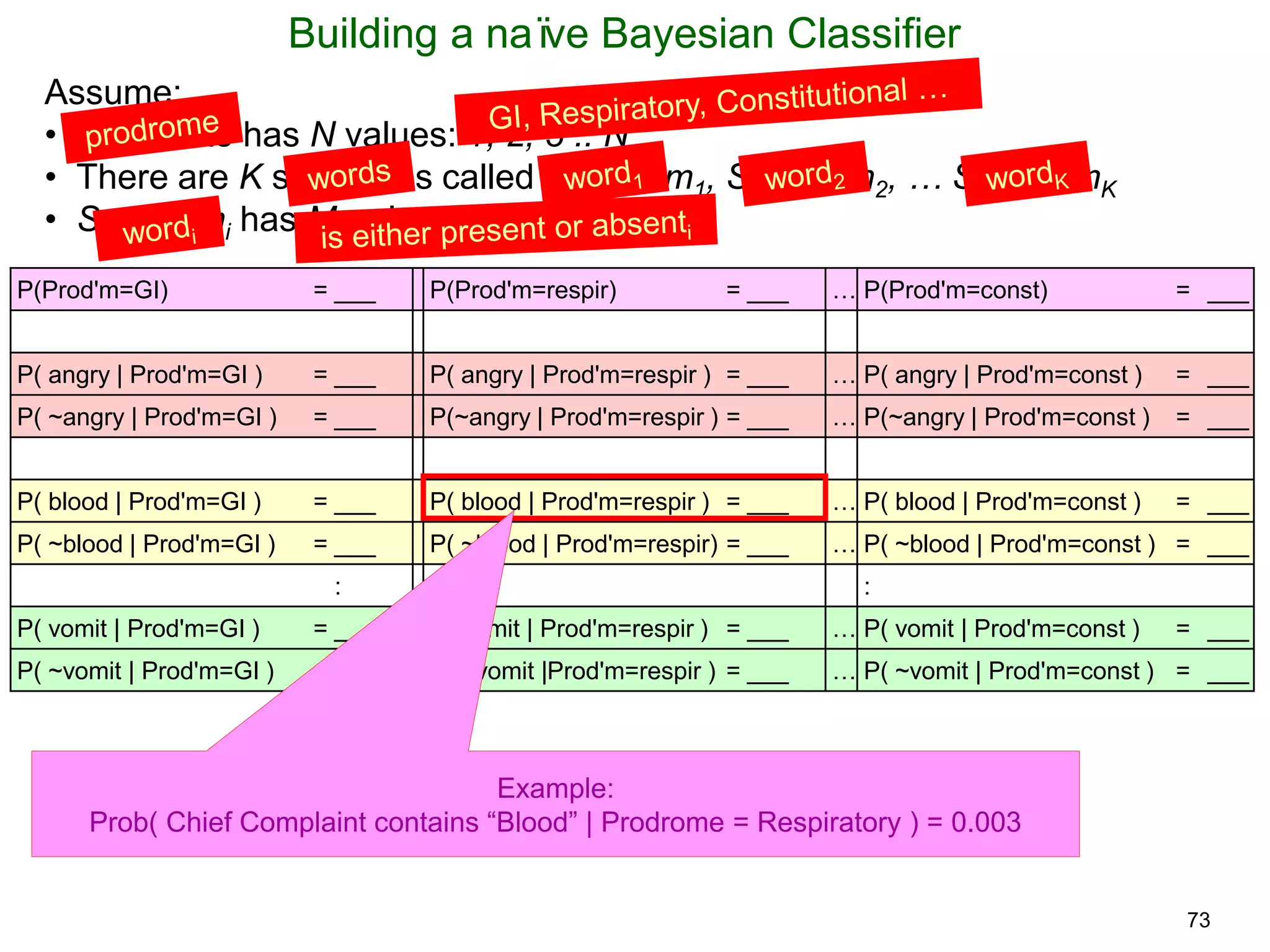
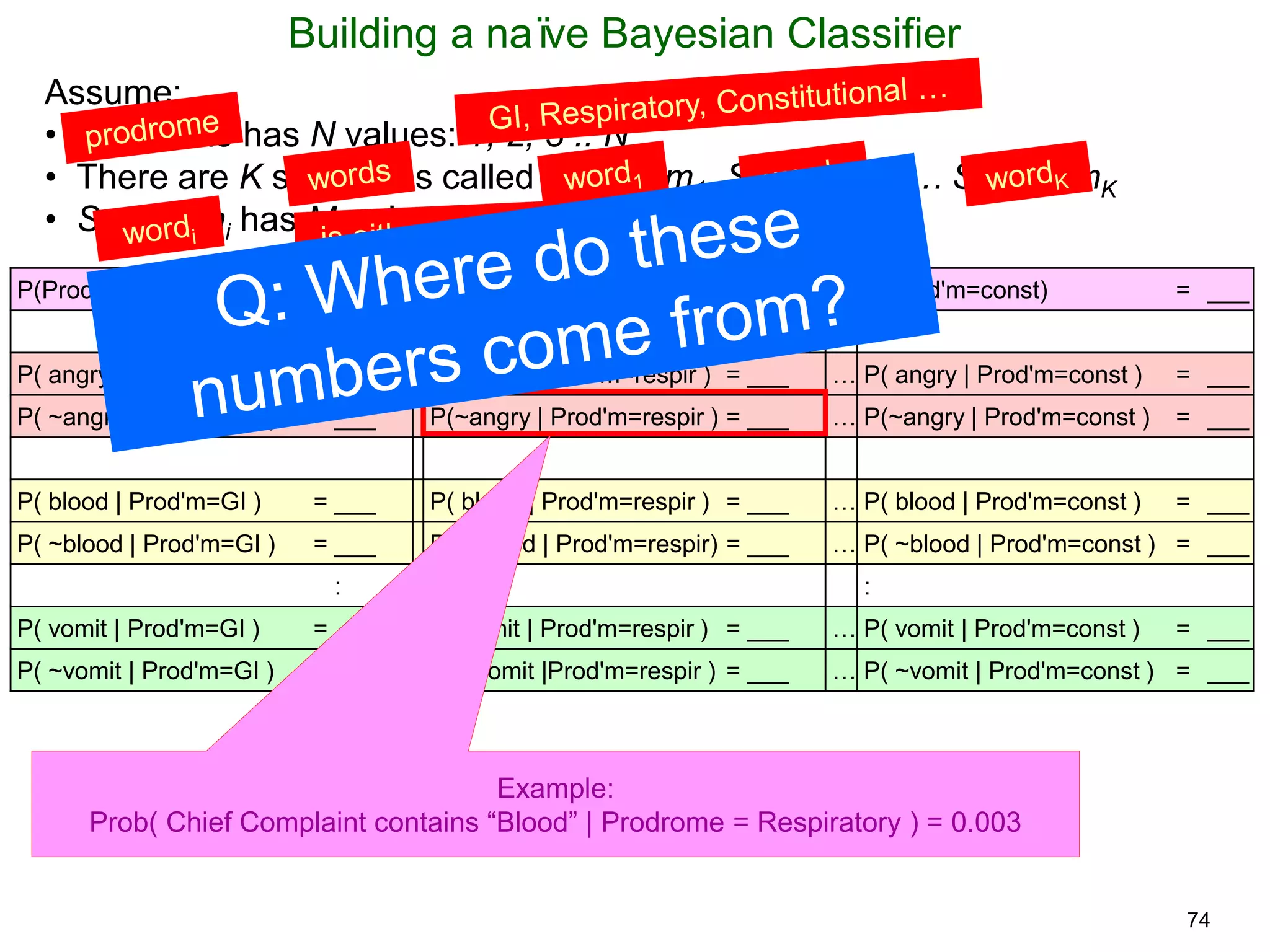
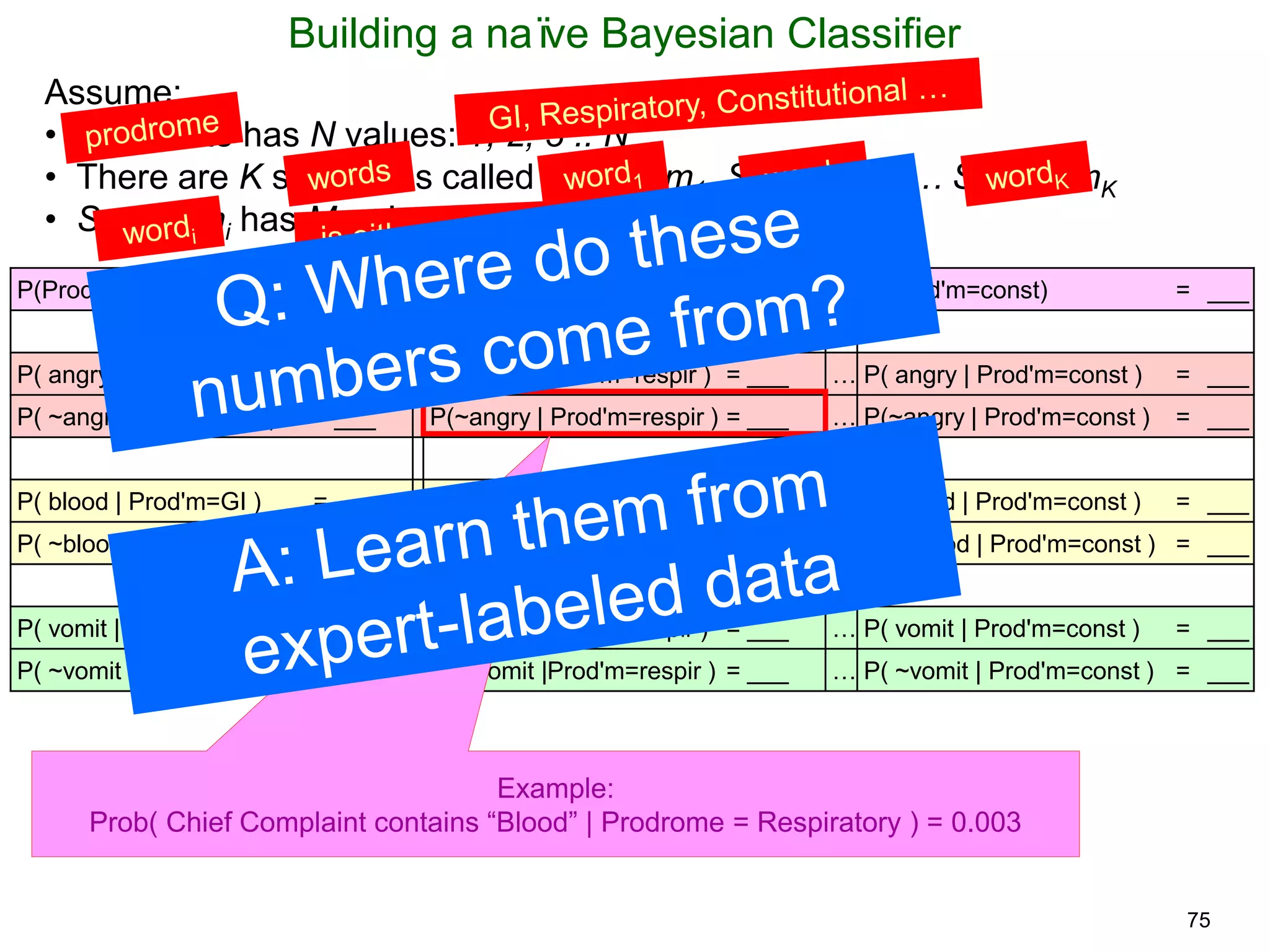
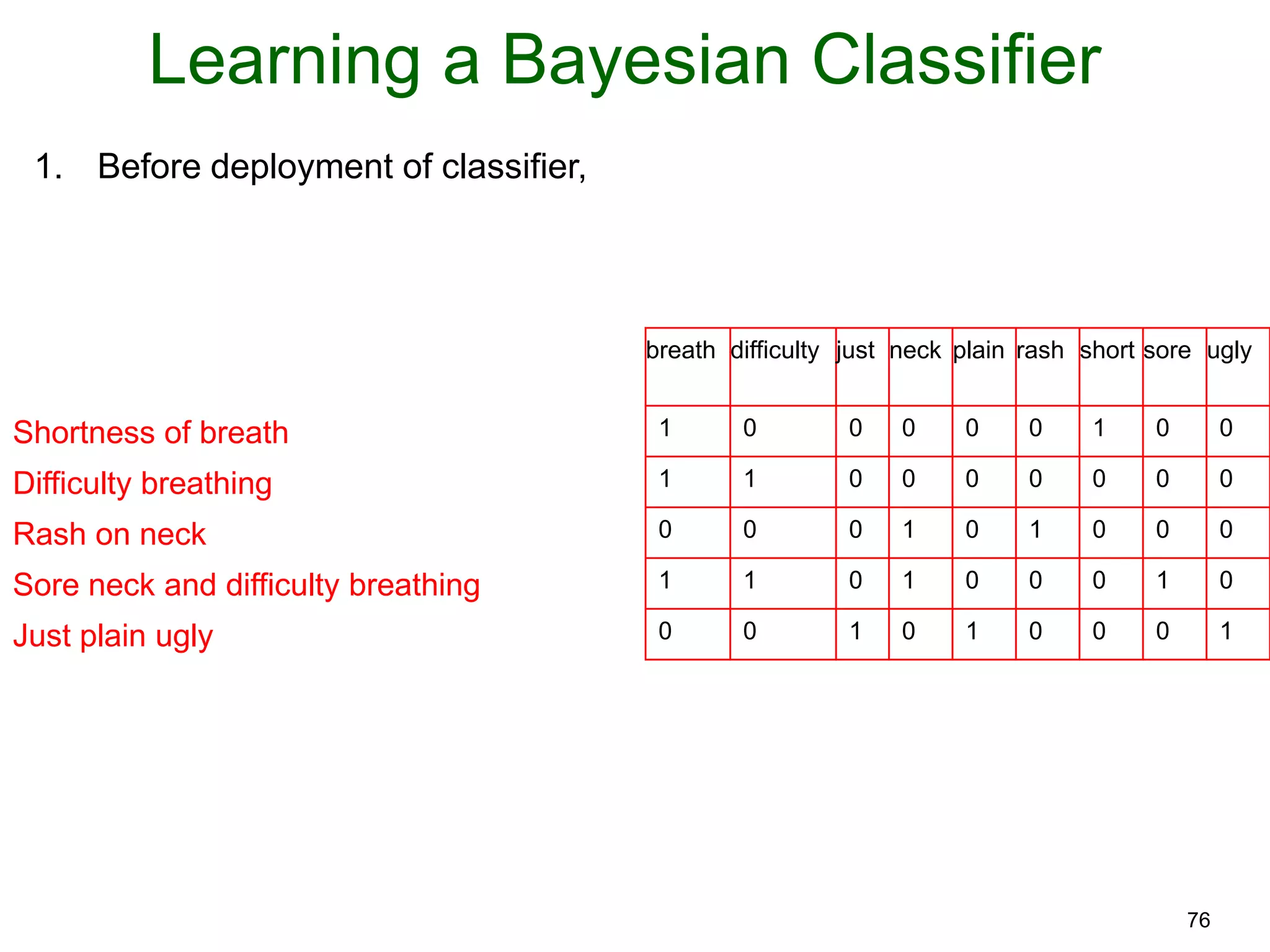
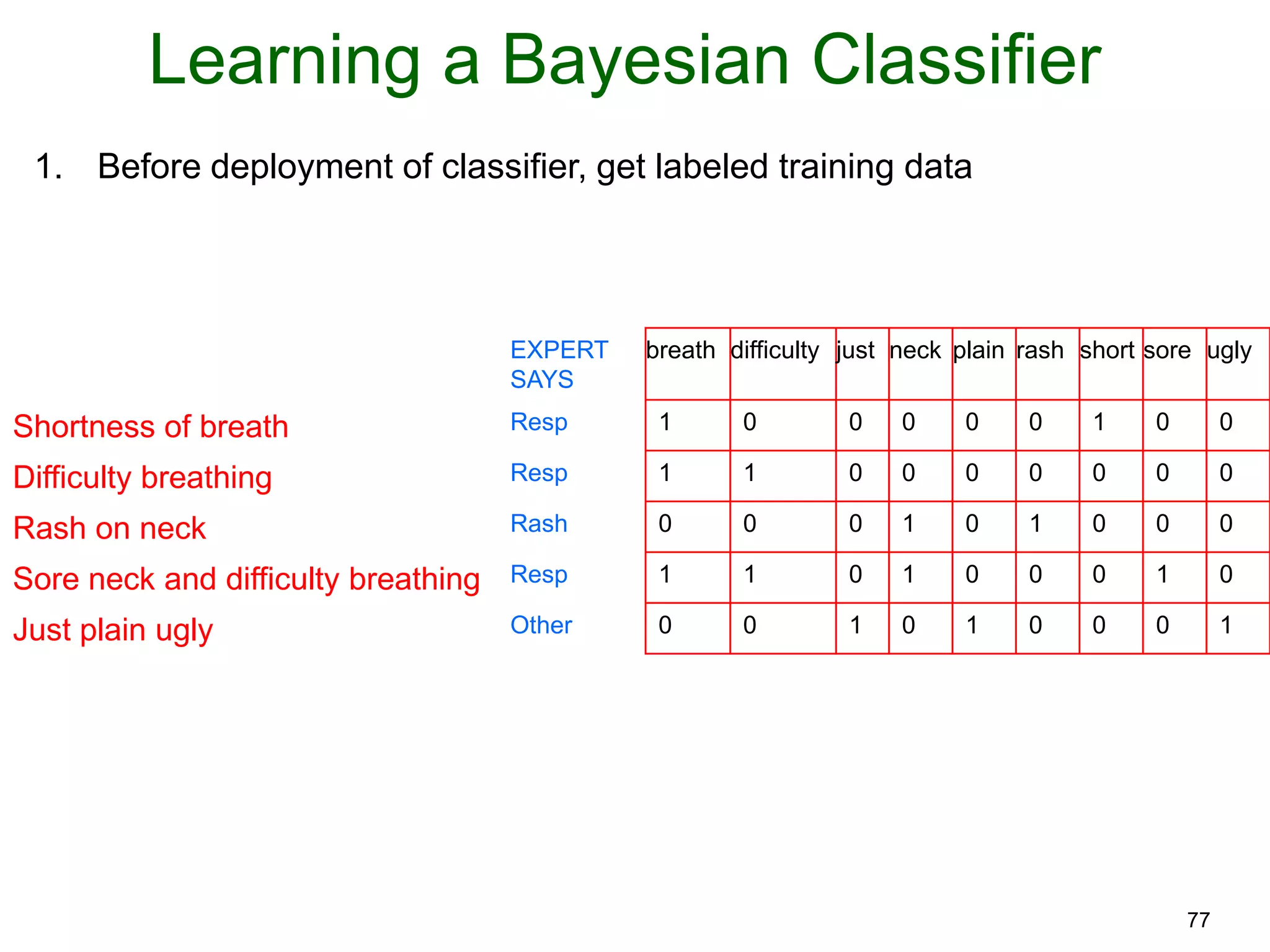
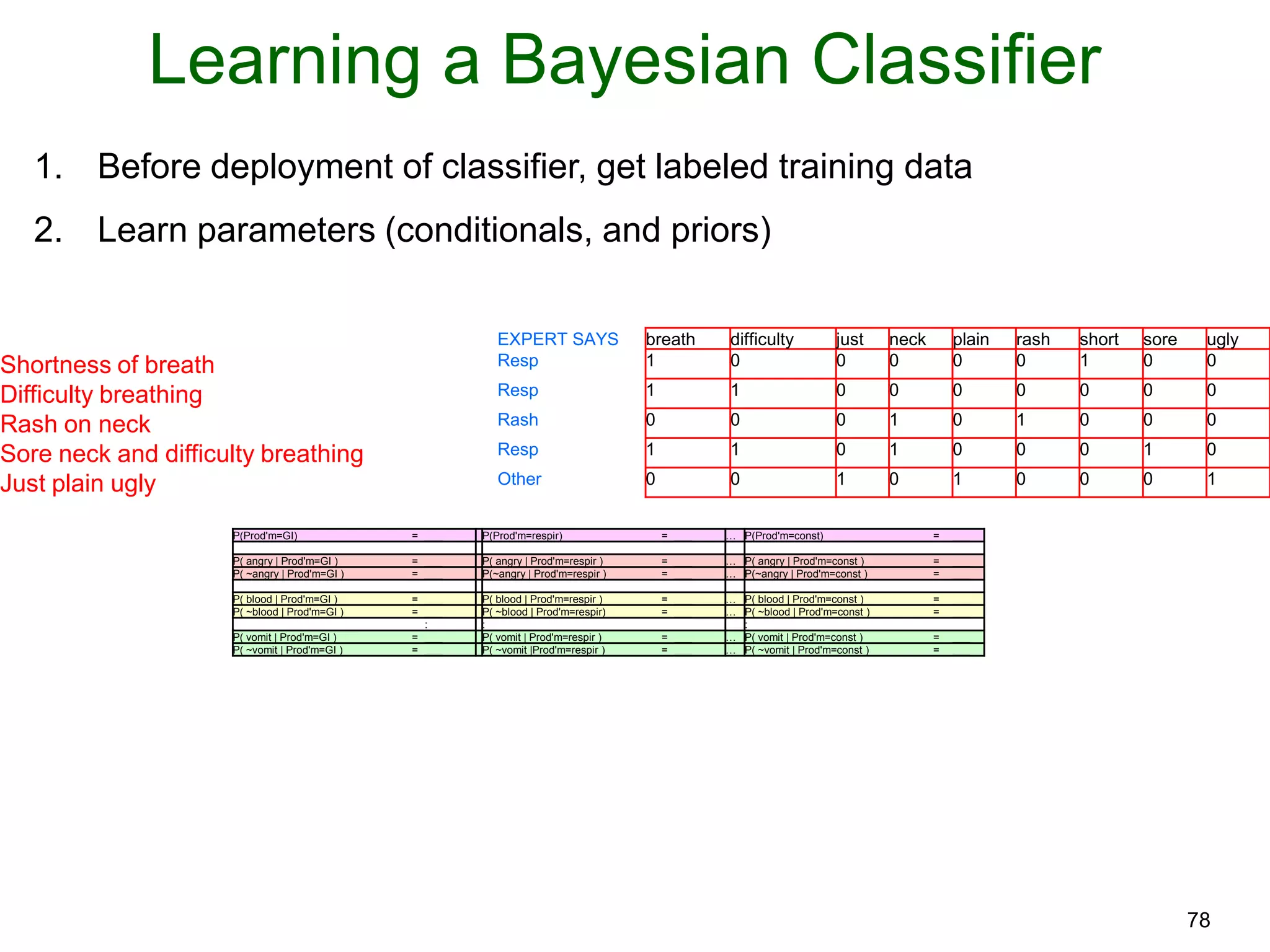
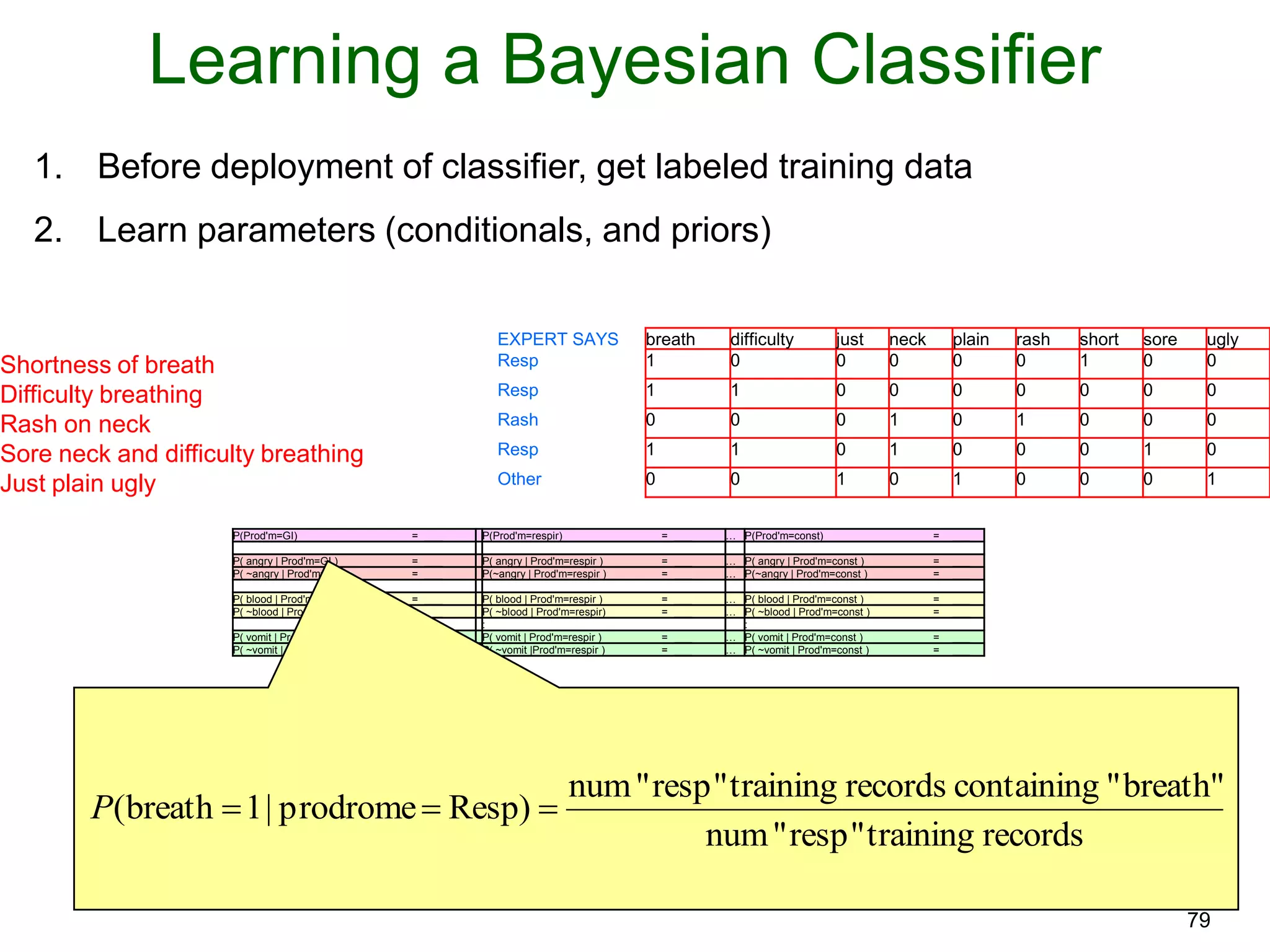
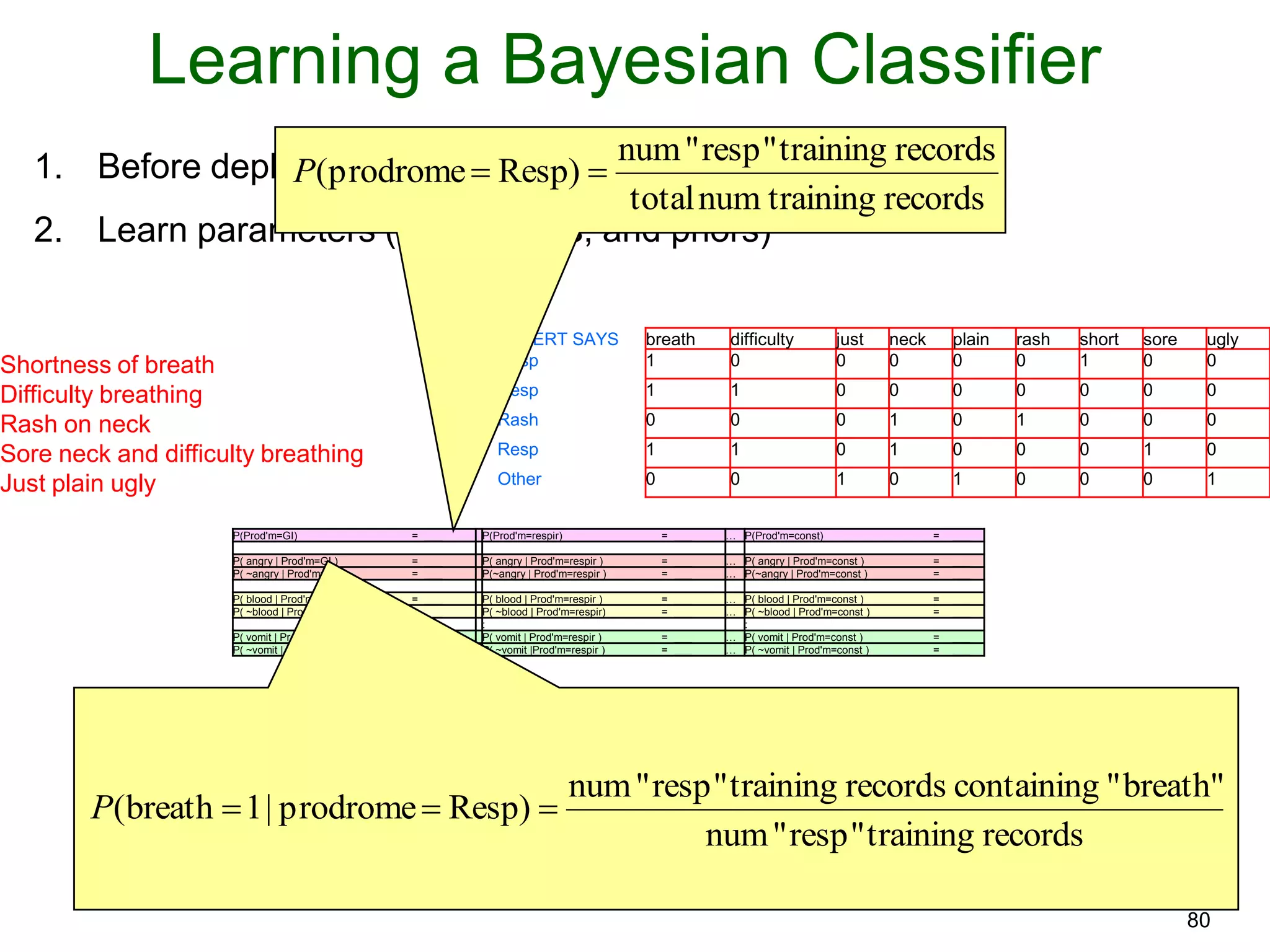
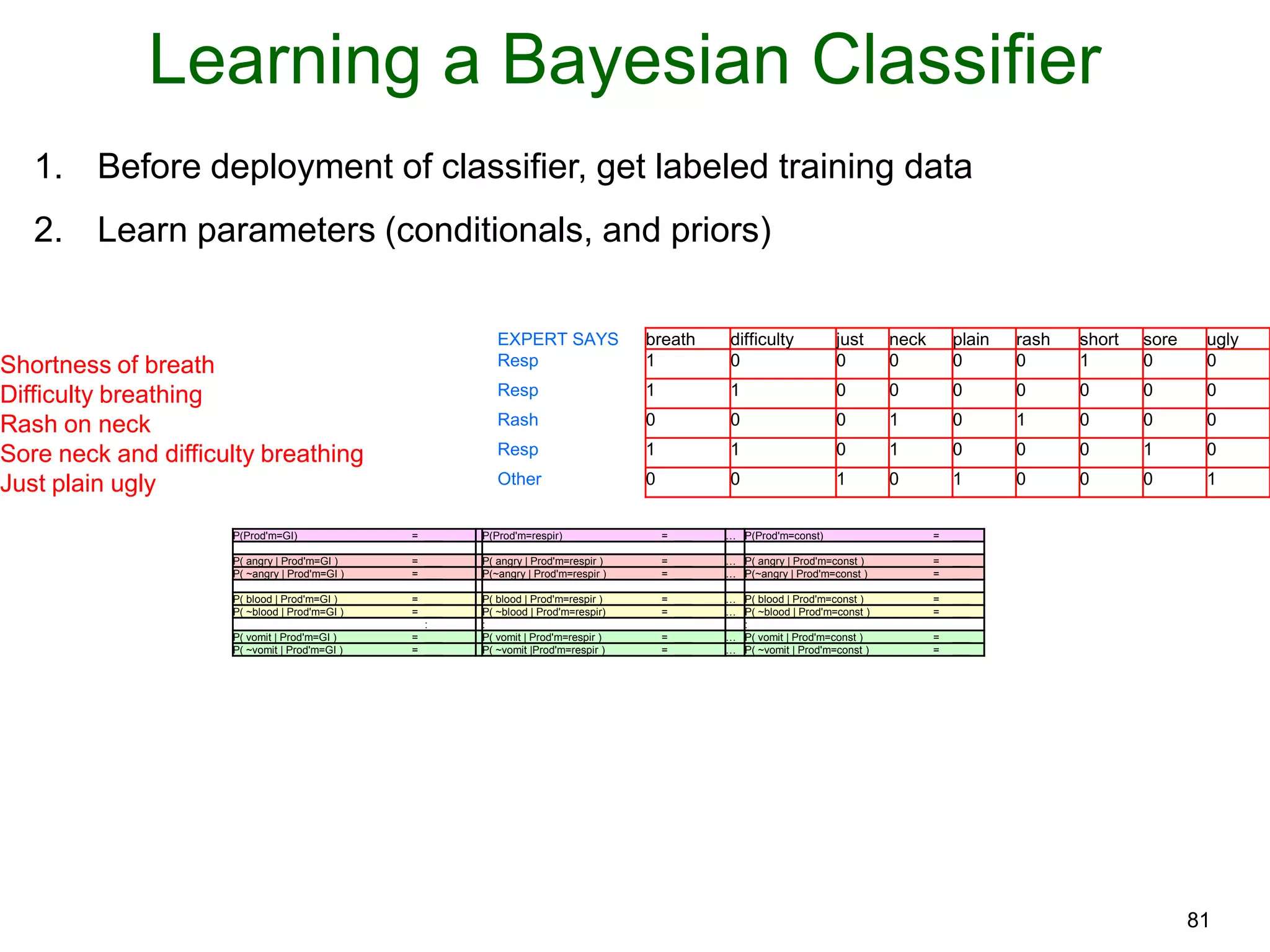
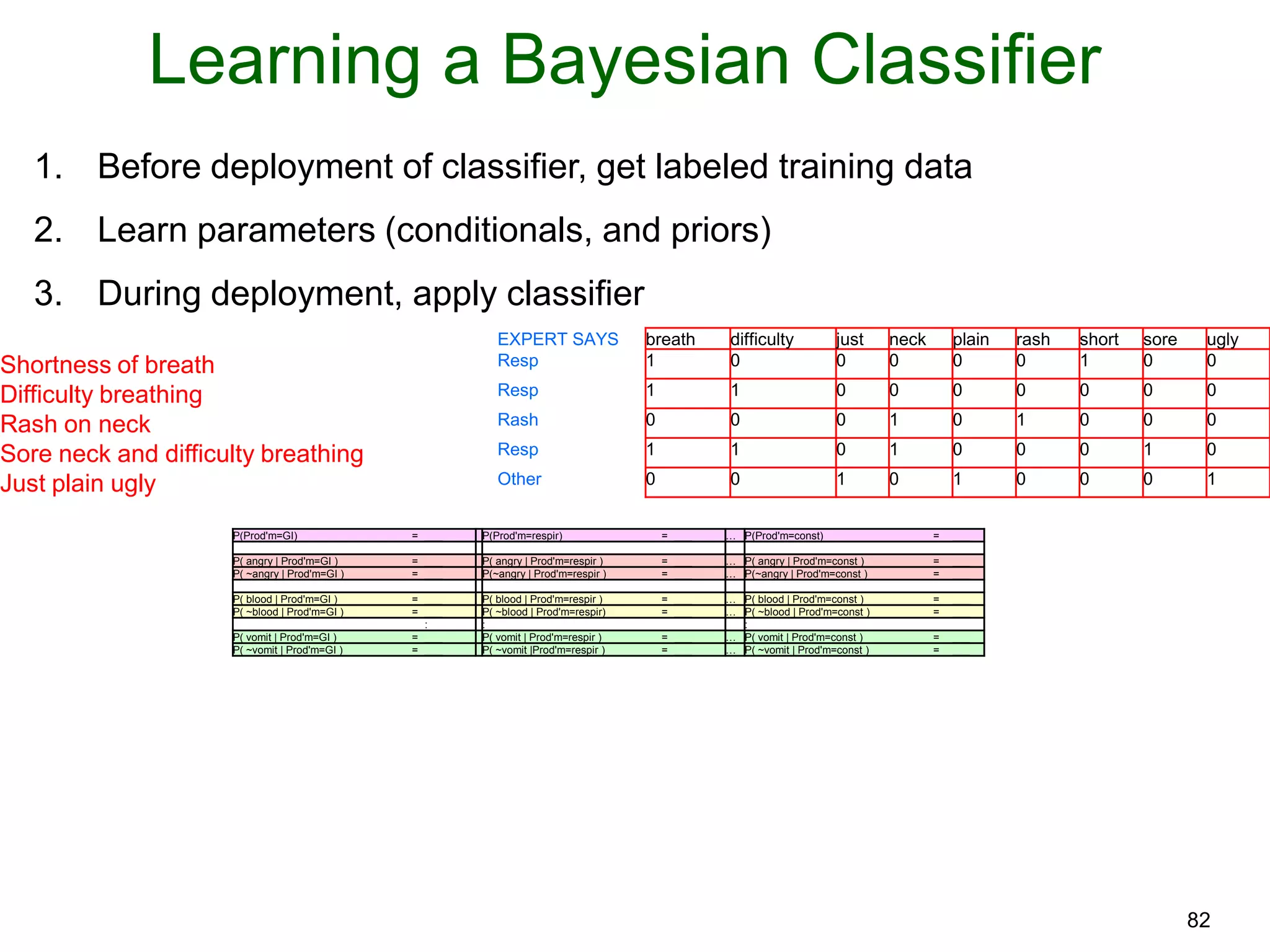
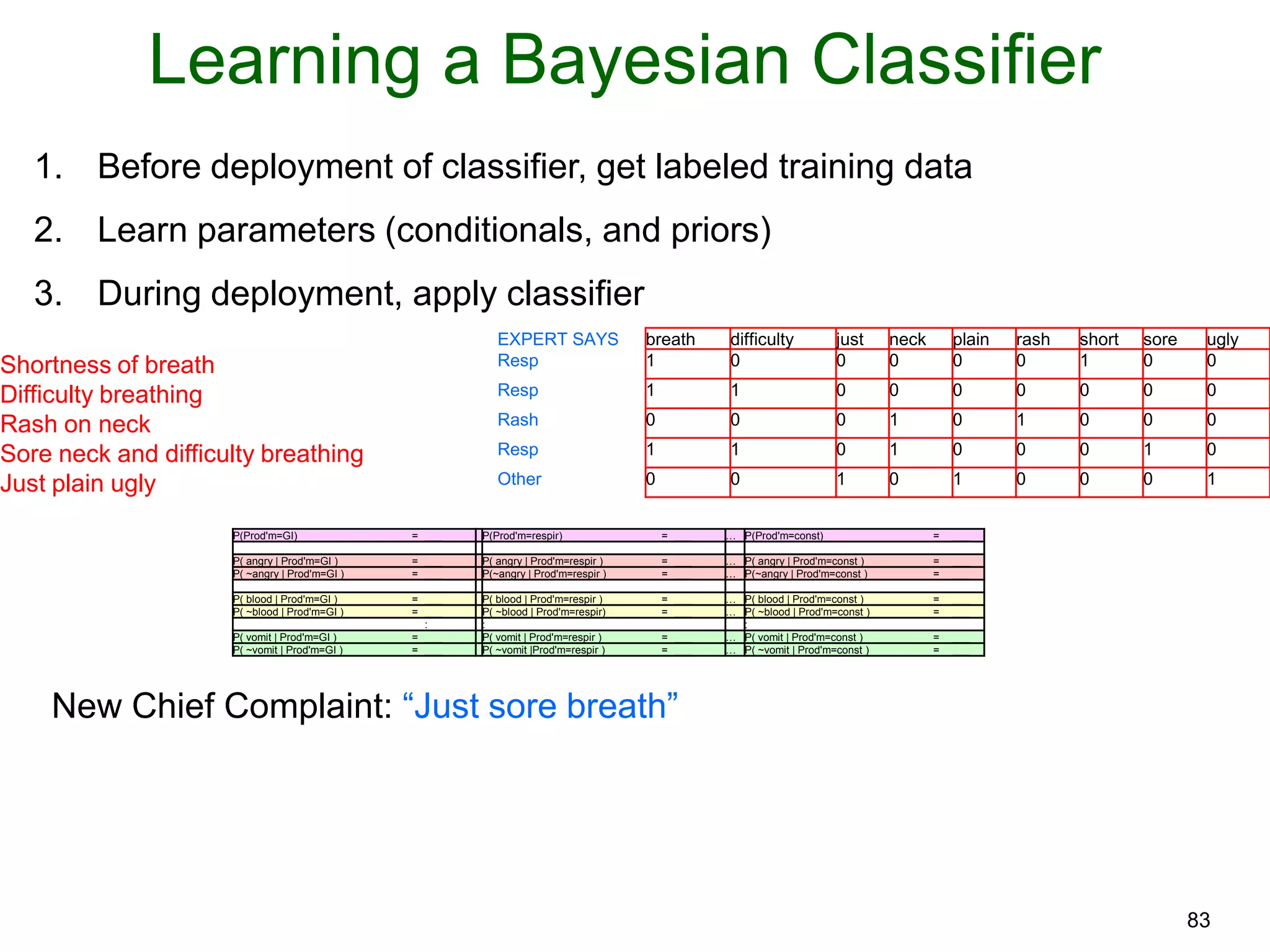
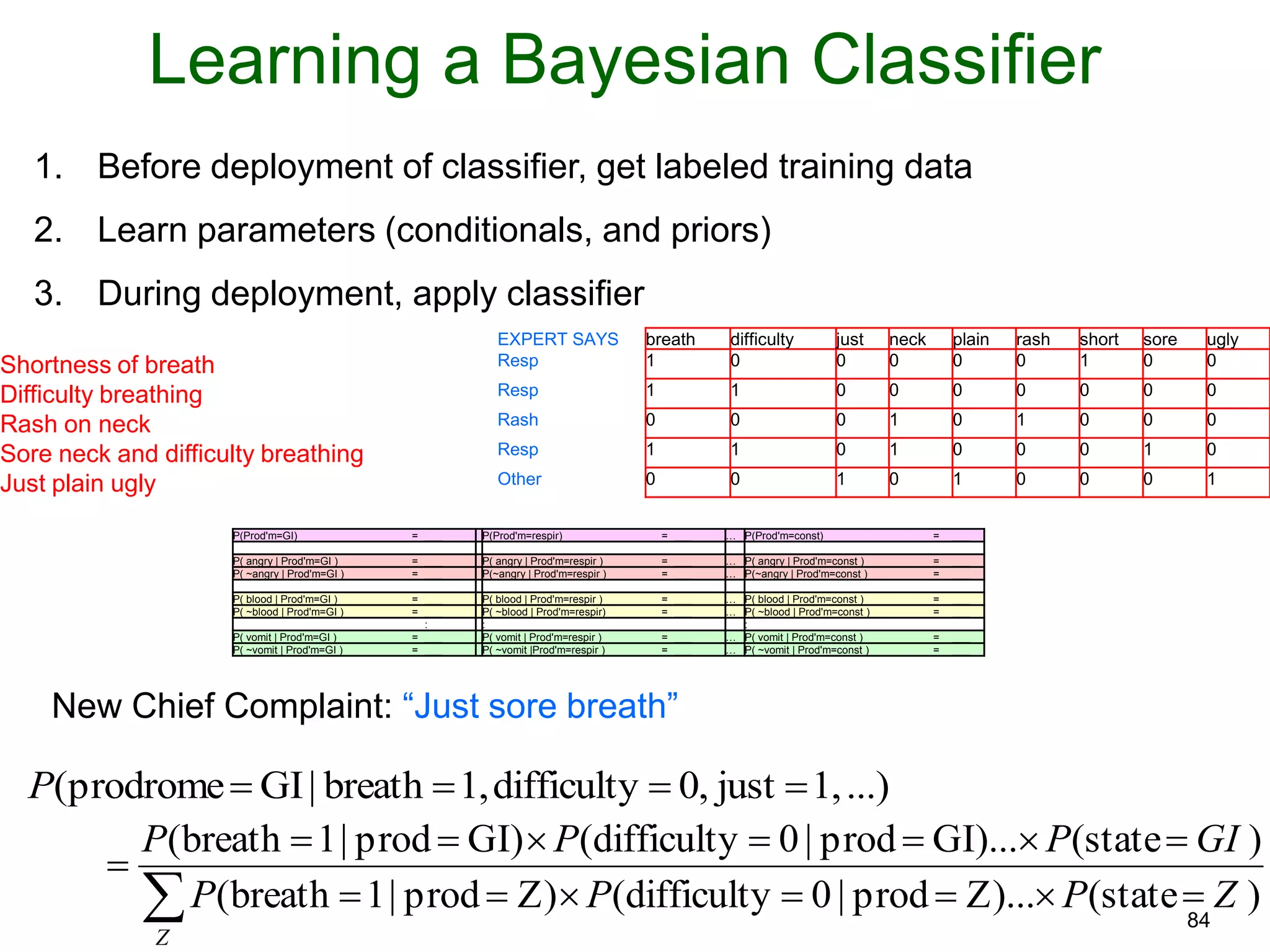
The document provides an introduction to Bayesian reasoning and probabilistic inference using conditional probabilities. It explains key concepts like prior probabilities, evidence, conditionals, and how to calculate posterior probabilities using Bayes' rule. As an example, it walks through a scenario where a health official must decide whether to investigate a restaurant based on observing a smudged menu, calculating the conditional probabilities of seeing a smudge given the restaurant is good or bad.