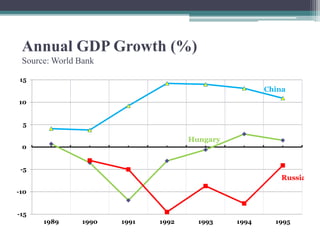
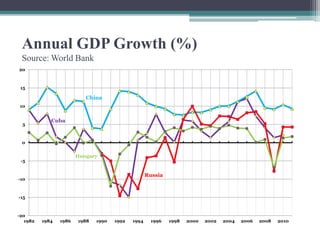
The document summarizes the transition of economies in Central and Eastern Europe from centrally planned socialist systems to market economies. It describes the features of state socialism, including one-party states, public ownership, and centrally planned economies. It then outlines reforms in places like Hungary in the 1960s-1980s that decentralized control and allowed more market mechanisms and private business. However, rapid economic liberalization in the 1990s weakened these "socialist entrepreneurs" and state capacity was limited, allowing political elites to dominate. Overall it questions the "social engineering" approach promoted by the West.