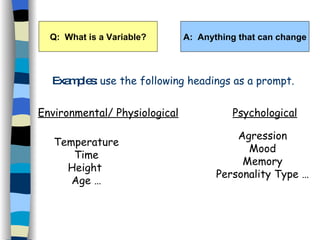
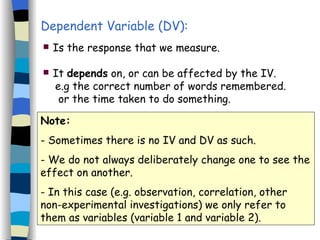
The document defines key terms used in psychological research, including independent variable (IV), dependent variable (DV), conditions, extraneous variables, and confounding variables. It provides examples of how these variables could be manipulated and measured in experiments investigating factors that influence memory, concentration, and conformity. Operational definitions precisely defining the IVs and DVs are important to allow accurate replication of studies. The key study on eyewitness testimony by Loftus et al. (1978) is given as an example to write the IV, DV, and their operational definitions.