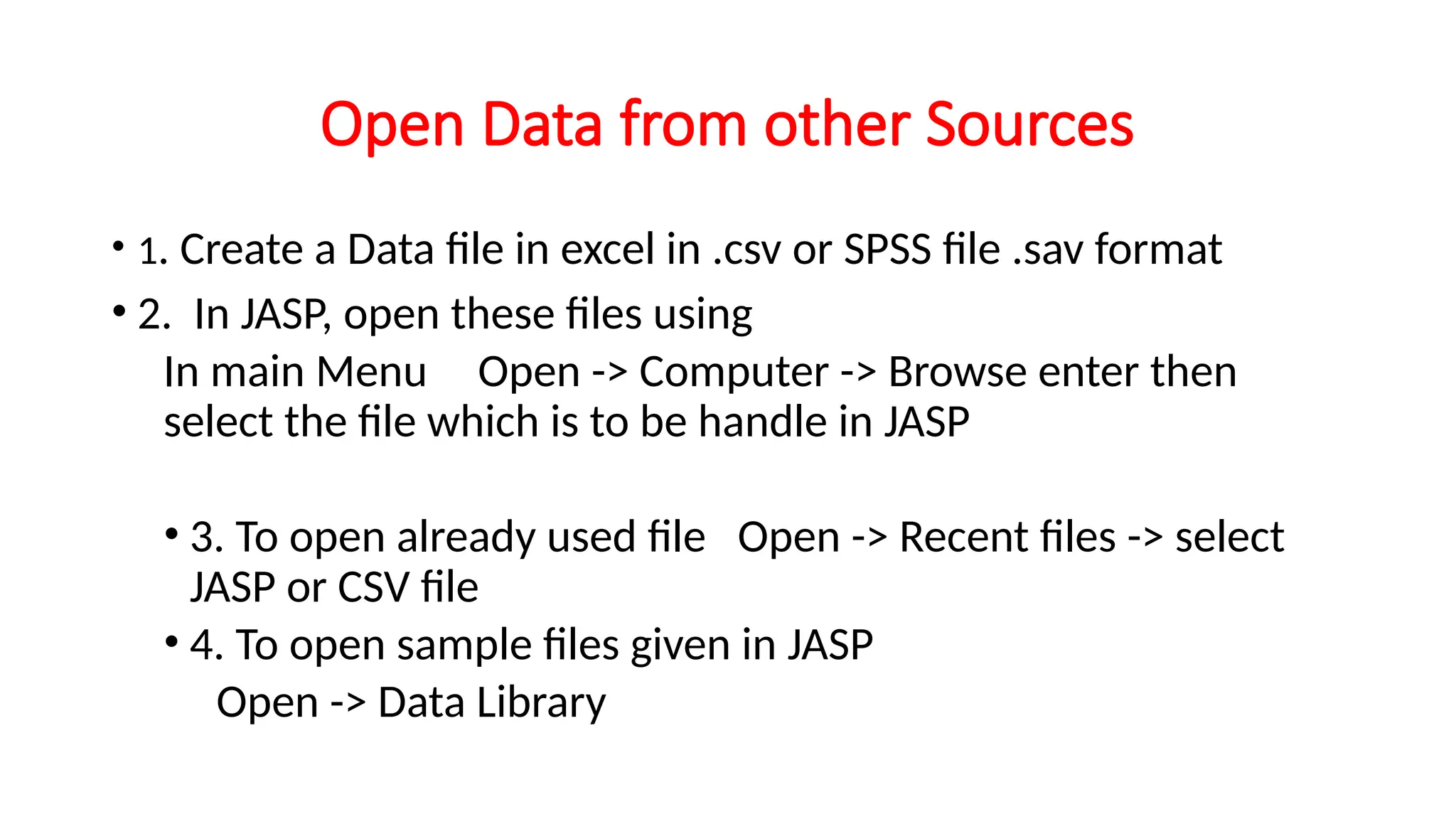
JASP, or Jeffrey's Amazing Statistics Program, is a free, multi-platform open-source statistics software developed by researchers at the University of Amsterdam, emphasizing usability and intuitive interfaces for both standard and Bayesian analyses. The program allows easy data manipulation with features like drag-and-drop, real-time computations, and exporting options in various formats, adhering to APA style for tables and plots. Users can customize their experience through preferences, including updating data synchronization, output formatting, and interface themes.