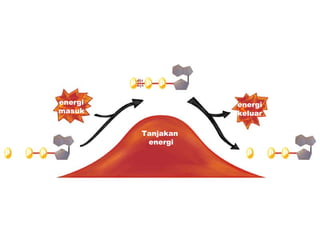
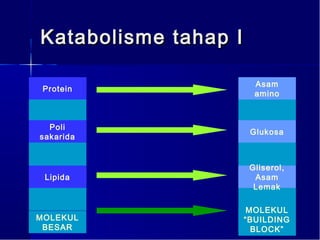
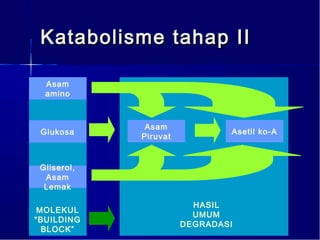
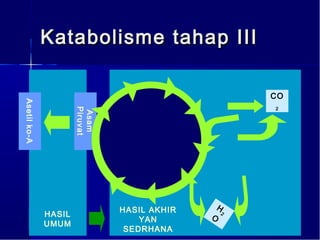
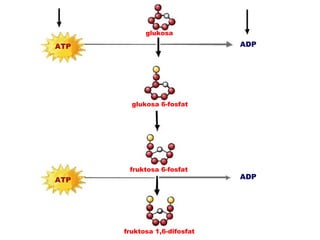
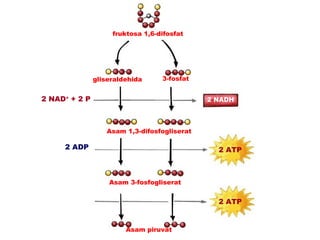
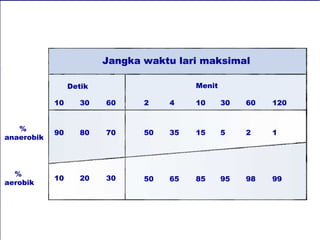
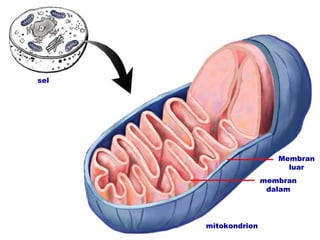
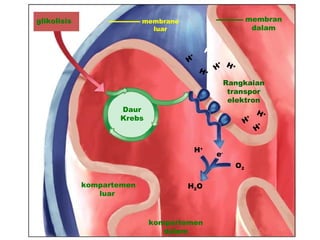
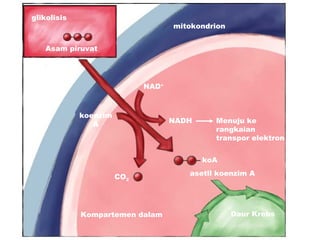
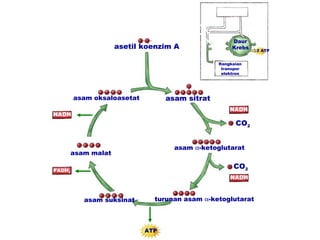
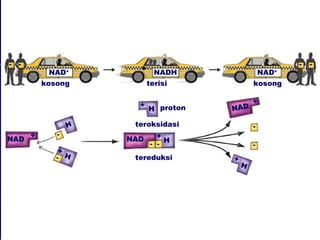
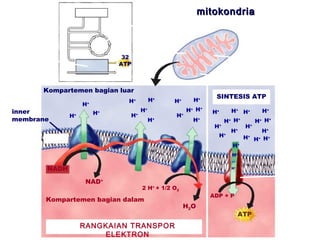
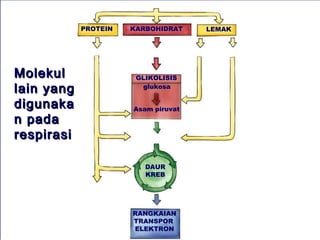
Dokumen ini membahas tentang proses pemanfaatan energi kimia dalam sel melalui respirasi seluler yang melibatkan glikolisis, daur Krebs, dan rangkaian transpor elektron. Selain itu, menjelaskan bagaimana nutrisi diubah menjadi energi dan peran ATP dalam menyediakan energi untuk berbagai proses kehidupan. Proses ini menentukan cara sel memperoleh dan menggunakan energi dari makanan, termasuk peran oksigen dalam metabolisme.