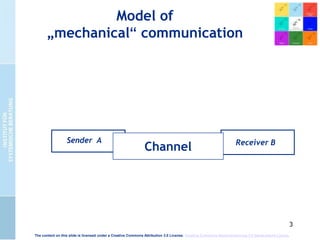
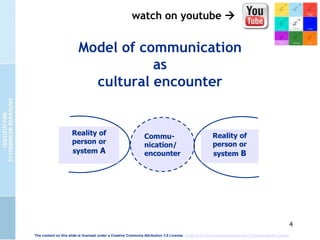
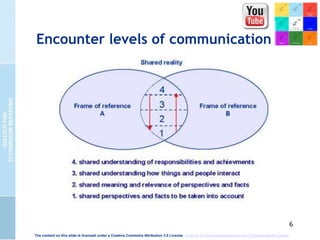
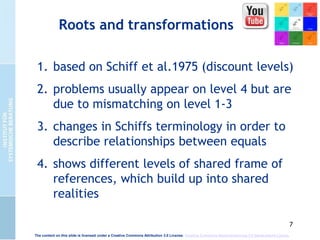
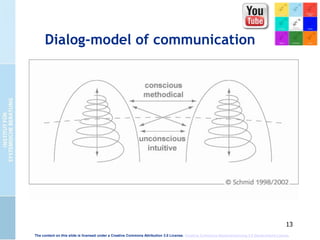
The document presents the cultural encounter model of communication, emphasizing that communication involves the interaction of different cultural realities. It suggests that mutual understanding is not assumed and highlights the need for creating shared realities through conscious effort. Additionally, it discusses the dialog-model of communication, which integrates methodical and intuitive elements to enhance communicative competence and organizational culture.