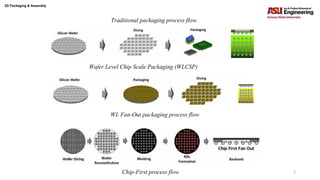
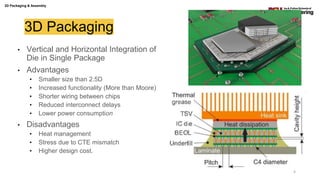
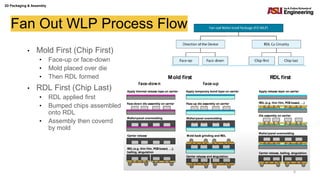
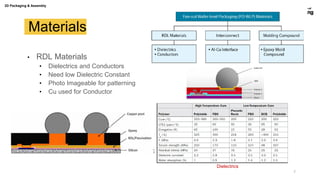
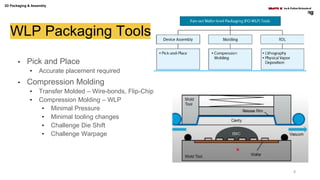
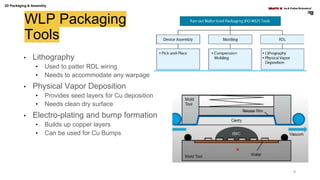
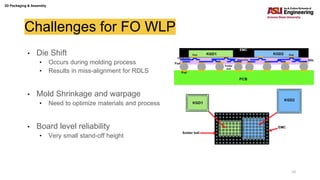
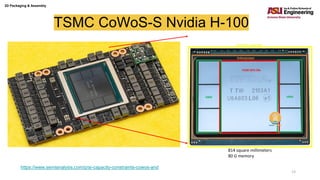
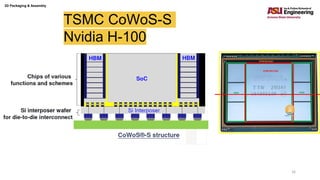
The document discusses various advanced packaging and assembly technologies, emphasizing 2D and 3D packaging processes, including chip-to-chip assembly and wafer-level packaging (WLP). It examines the advantages and disadvantages of these methods, such as increased functionality and reduced size, as well as challenges like heat management and die alignment issues. It also highlights tools and materials used in the packaging process, detailing workflows for both fan-in and fan-out WLP.