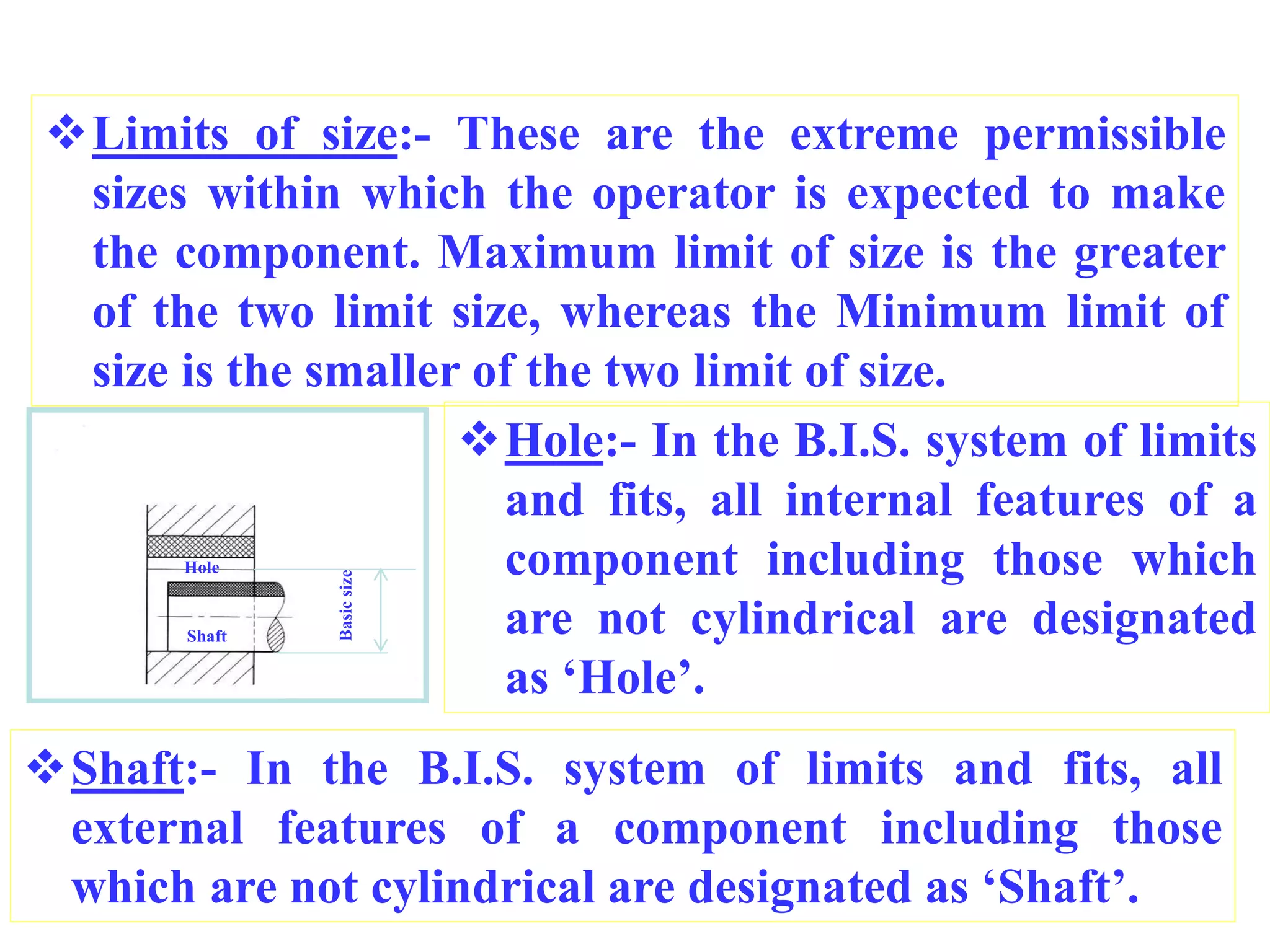
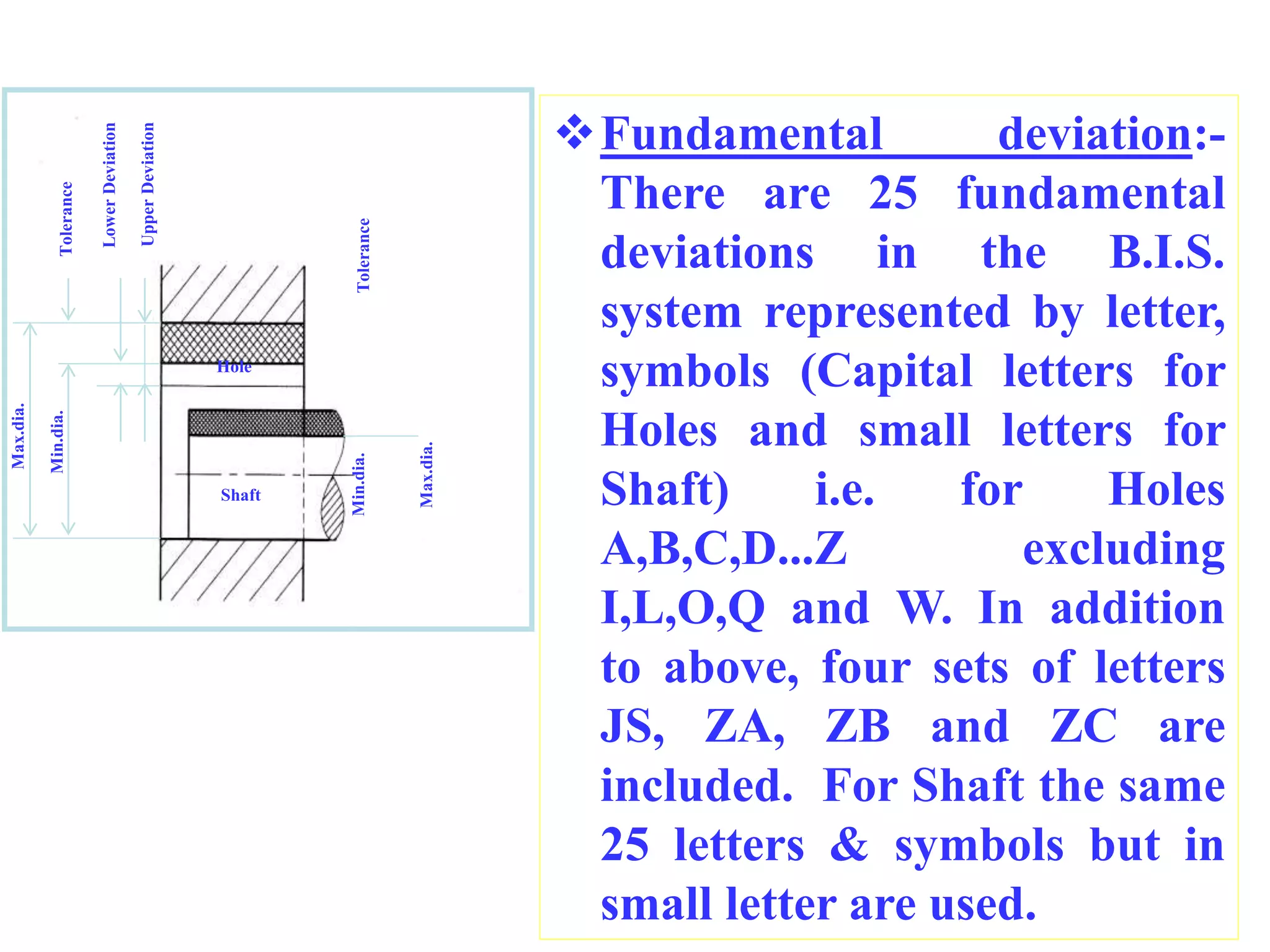
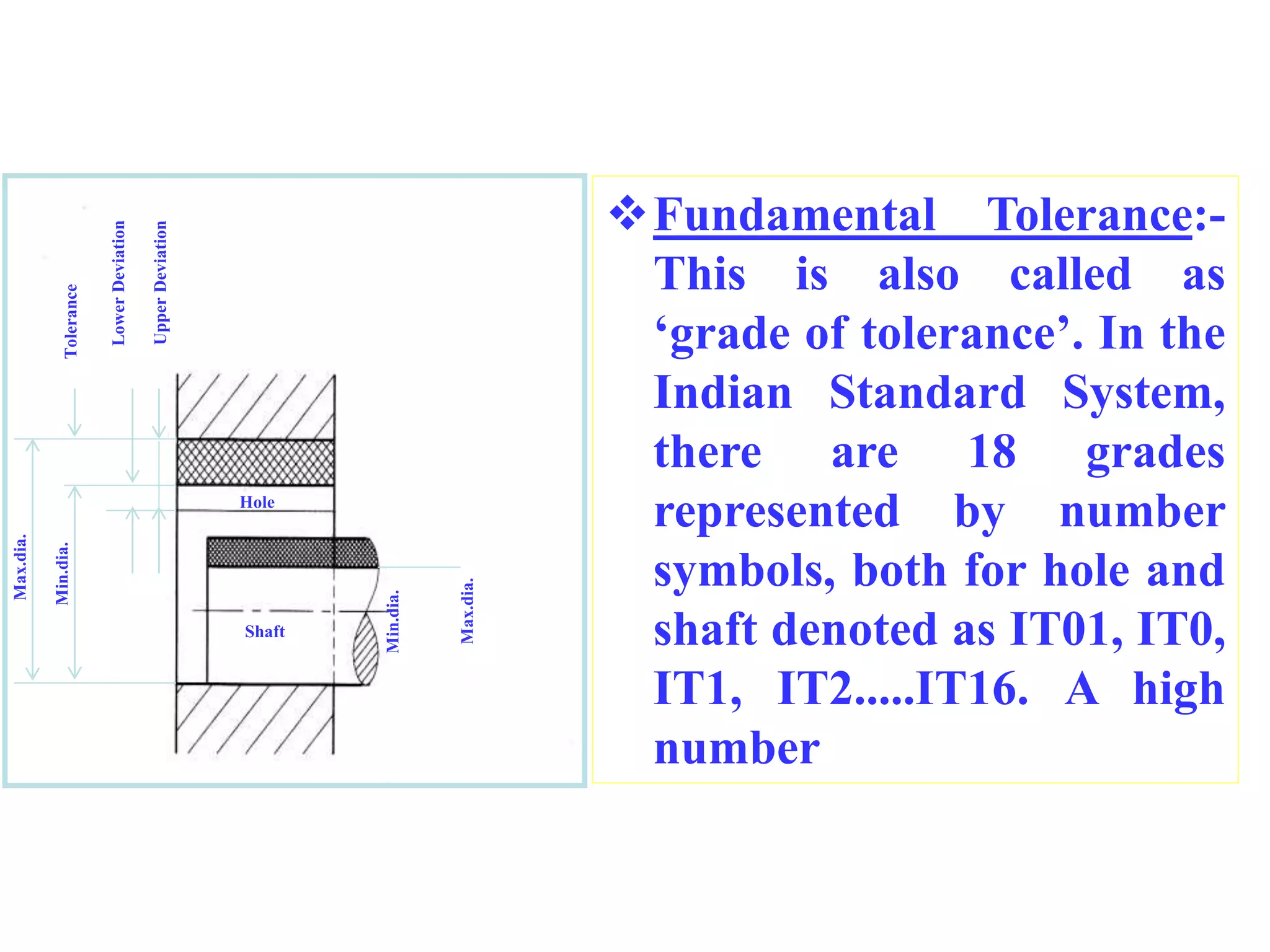
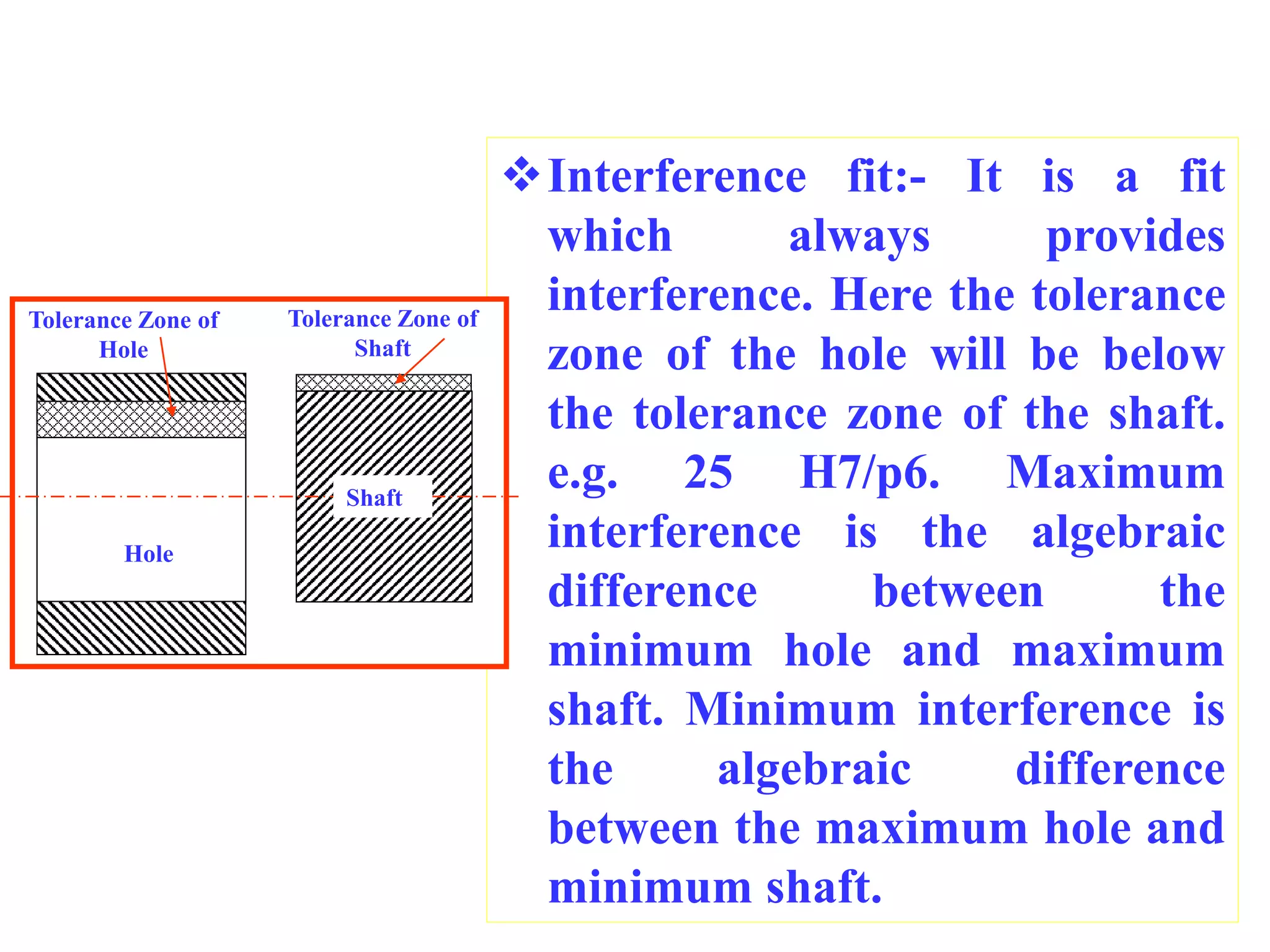
This document defines key terminology used in limits, fits and tolerances including: size, basic size, actual size, limits of size, deviations (upper, lower, actual), tolerance, fundamental deviations, and fundamental tolerances. It describes three types of fits between holes and shafts: clearance fits which always provide clearance, interference fits which always provide interference, and transition fits which may provide either clearance or interference depending on the actual sizes of the hole and shaft. Mass production is also defined as the production of a part or component in large numbers.