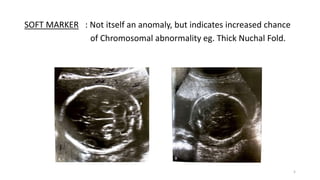
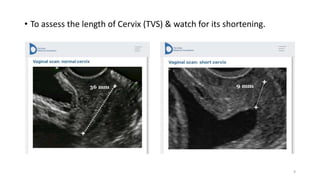
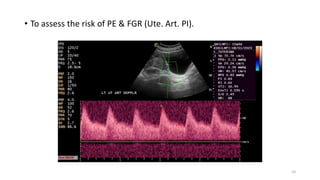
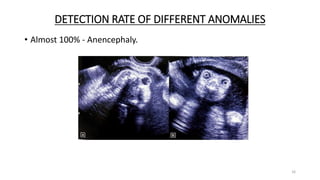
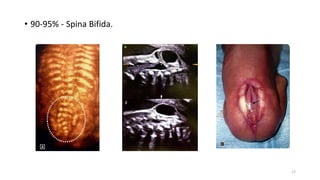
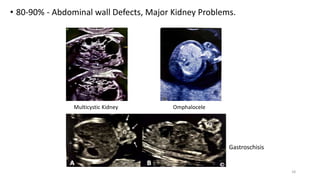
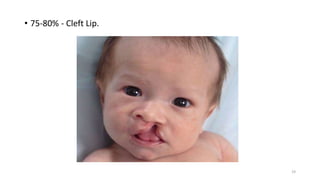
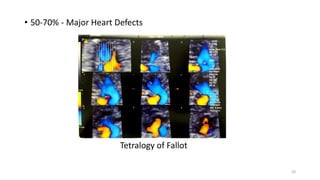
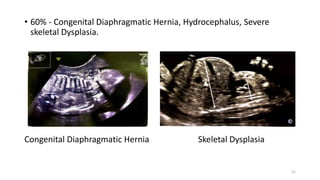
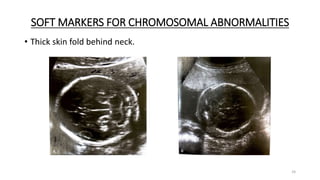
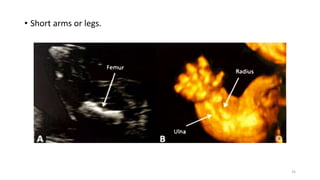
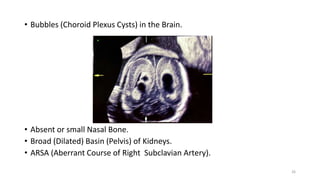
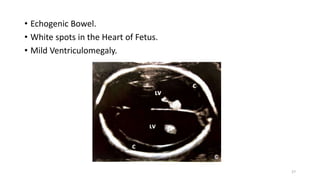
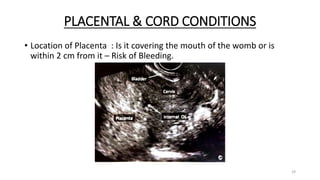
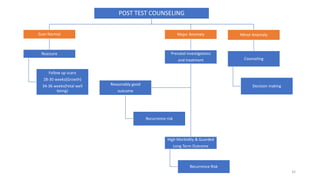
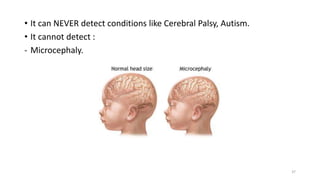
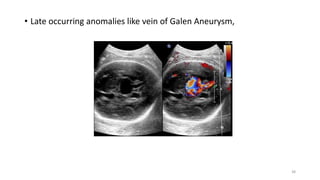
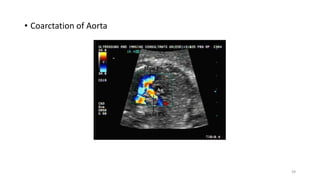
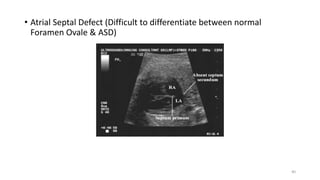
The document discusses the importance and details of the 18-22 weeks anomaly scan by Dr. Nisheeth M. Oza, highlighting its purpose to identify fetal anomalies, structural abnormalities, and soft markers of chromosomal issues. It outlines the screening criteria, procedural steps, detection rates of various anomalies, and pre- and post-test counseling for expecting parents. Furthermore, it emphasizes the necessity of the scan for all pregnant women while explaining risk factors and limitations associated with anomaly detection.