1) The document provides instructions to examiners for evaluating answers to questions on a Contract and Accounts exam. It emphasizes understanding over exact wording and allows for variation in figures as long as the key components are included.
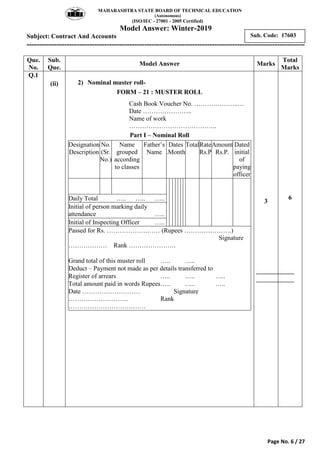
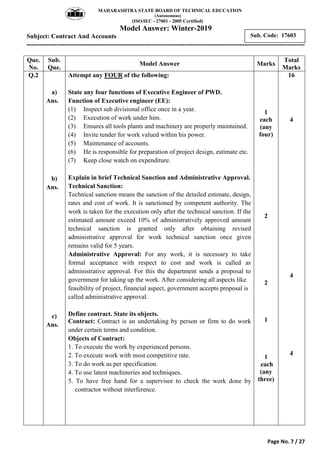
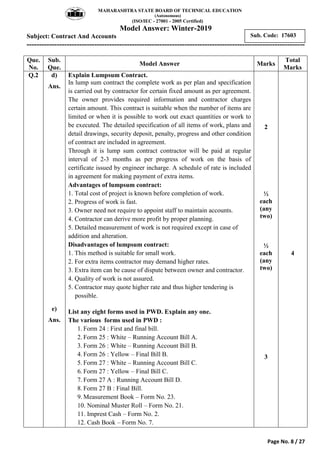
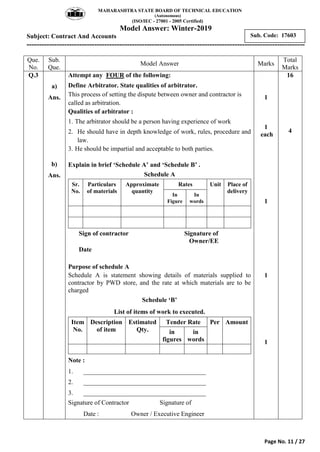
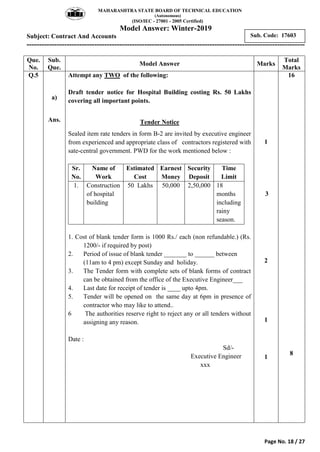
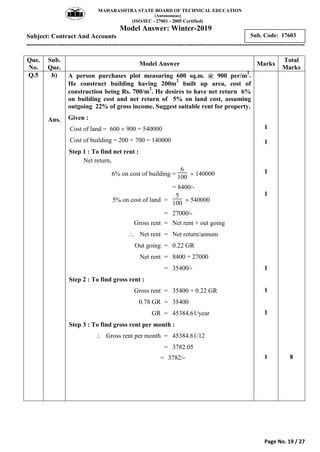
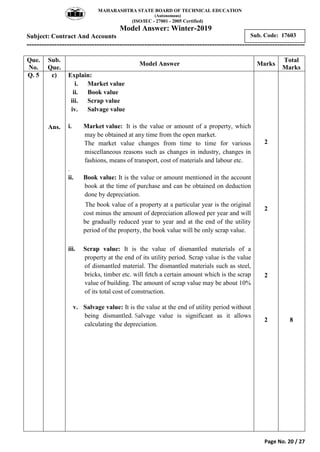
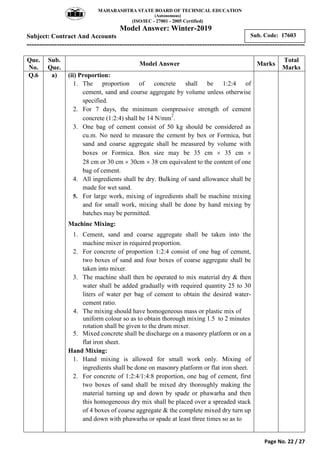
2) It includes a sample exam with questions on construction contract methods, contract requirements, contract types, tender notices, and key contract terms.
3) Model answers are provided for each question explaining the requested topics in detail with examples.