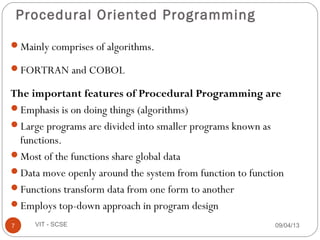
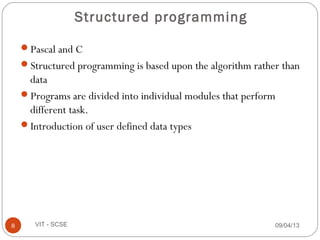
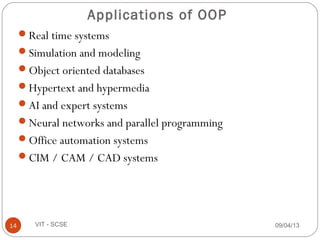
This document outlines the syllabus for the CSE 219 Object Oriented Paradigm and Programming course taught by G.SasiKumar at VIT University. The course will use the textbook "Mastering C++" and will include homework, CAT exams, quizzes, presentations, and a final exam. Key topics will include an introduction to programming languages, object oriented programming concepts, advantages and applications of OOP.