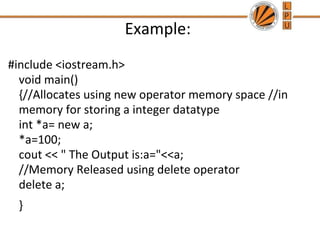
The document summarizes memory management in C++. It discusses dynamic memory allocation using operators like new and delete. New allocates memory at runtime and returns a pointer, while delete frees up memory. Important points are to avoid deleting unallocated pointers and handling null pointers from new. Dynamic constructors can allocate different amounts of memory for each object using new.







![New operator
Dynamic memory allocation in case of arrays can
be done as following:
int* a = new int[x];
a points to a block of memory
containing x ints](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16829memorymanagement2-121212072950-phpapp01/85/16829-memory-management2-9-320.jpg)







![# include <iostream.h>
# include <conio.h>
# include <string.h>
class str
{
char *name;
int len;
public:
str()
{
len=0;
name=new char[len+1];
}
str(char *s)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16829memorymanagement2-121212072950-phpapp01/85/16829-memory-management2-18-320.jpg)
![void str::join(str &a,str &b)
{
len=a.len+b.len;
delete name;
name=newchar[len+1];
strcpy(name,a.name);
strcat(name,b.name);
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16829memorymanagement2-121212072950-phpapp01/85/16829-memory-management2-19-320.jpg)
