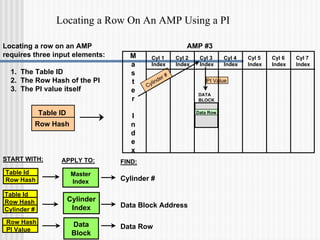
The hashing algorithm and hash map are used to locate rows by primary index (PI) values. The hash map associates a destination selection word from the row hash with an AMP. Within each AMP, the master index and cylinder indexes are used to locate the data block containing a row, given its table ID, row hash, and PI value. A row ID, consisting of the row hash and a uniqueness value, is needed to uniquely identify rows that may have the same PI value or hash to the same value.