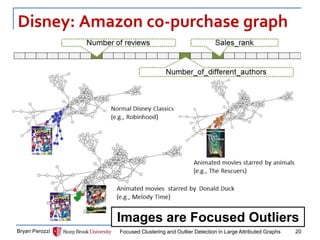
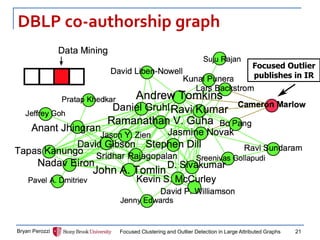
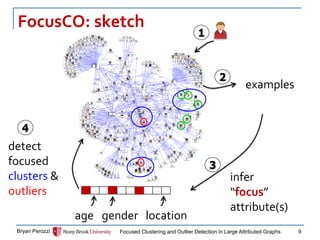
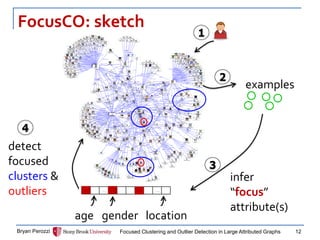
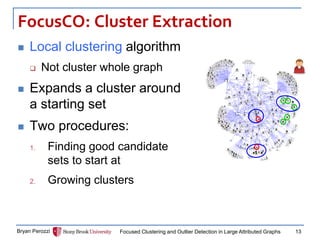
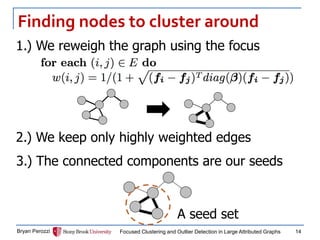
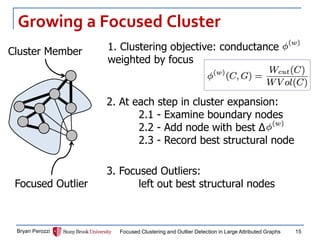
The document presents a new approach called FocusCO for focused clustering and outlier detection in large attributed graphs. FocusCO infers the most relevant attributes (called the "focus") based on examples provided by the user, and uses this focus to extract dense clusters that are coherent in the focused attributes. It can also detect outliers that deviate from the inferred focus. The experiments on synthetic and real-world graphs show that FocusCO outperforms other methods in identifying clusters aligned with different user-specified focuses and detecting outliers corresponding to each focus.

![Distance Metric Learning
Bryan Perozzi
Focused Clustering and Outlier Detection in Large Attributed Graphs
11
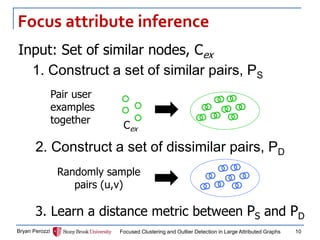
nodes
attributes
Feature Matrix
PS and PD intermixed
nodes
attributes
[Xing, et al 2002]
Focused Attribute Vector
PS closer together](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-kdd-focusedclustersandoutliers-perozzi-141201172459-conversion-gate01/85/Focused-Clustering-and-Outlier-Detection-in-Large-Attributed-Graphs-11-320.jpg)
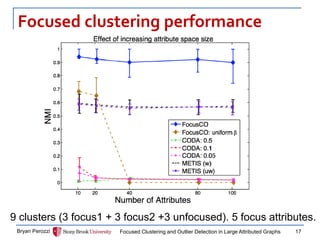
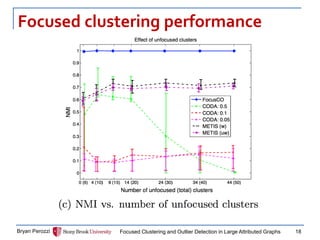
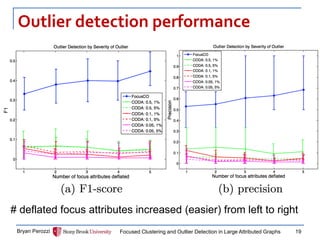
![Experiment set up
Synthetic and Real World Graphs
Performance measures:
Cluster quality: NMI
Outlier accuracy: precision, F1
Compared to:
CODA [Gao+’10]
METIS (no outlier detection) [Karypis+’98]
Bryan Perozzi
Focused Clustering and Outlier Detection in Large Attributed Graphs
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14-kdd-focusedclustersandoutliers-perozzi-141201172459-conversion-gate01/85/Focused-Clustering-and-Outlier-Detection-in-Large-Attributed-Graphs-16-320.jpg)