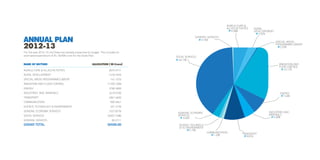
This document summarizes the key points from a speech given by the Chief Minister of Gujarat, Narendra Modi, at the Annual Plan Discussion in the Planning Commission in New Delhi on June 1, 2012. It discusses Gujarat's strong economic growth over the past decade, priorities for the upcoming 12th Five Year Plan, and achievements and priorities in sectors like health, education, and women and child development. The 12th Plan size is proposed to be Rs. 2,51,000 crore, almost double the 11th Plan size, to support continued high growth, improved human development, and balanced regional development.