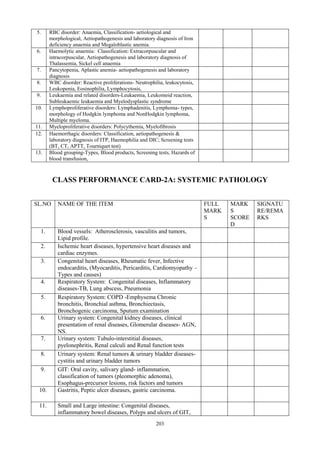
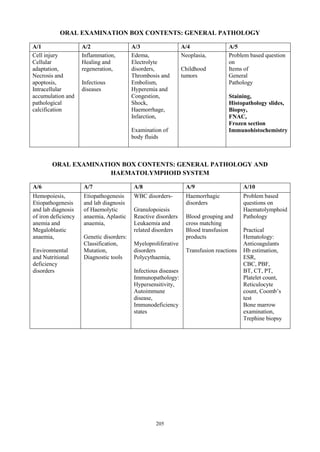
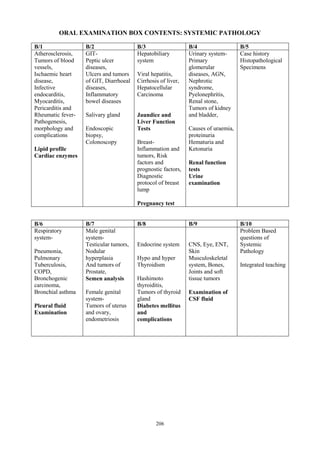
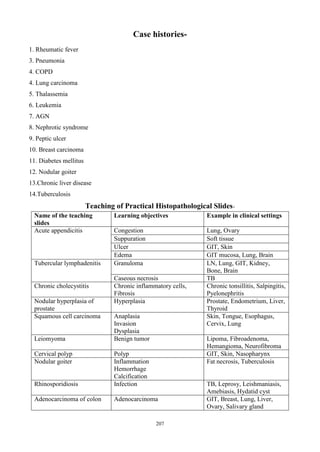
The document outlines the departmental objectives and course contents for an undergraduate pathology course. The objectives are to enable students to explain disease mechanisms, correlate clinical and pathological findings, plan investigations, interpret laboratory results, and develop skills in microscopic examination and laboratory tests. The course covers general pathology topics like cell injury, inflammation, and healing processes. It aims to provide students with 155 hours of lectures, 94 hours of tutorials and 34 hours of practical sessions to achieve the learning objectives.