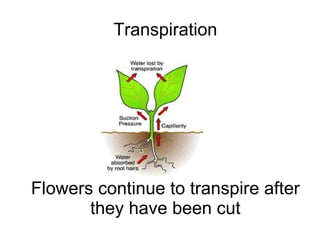
The document provides information about conditioning carnations for floral design. It defines conditioning as the process of preparing flowers for shipment, storage, or arrangement using a solution to prolong flower life. Carnations are described as having fragrant, long-lasting flowers available in many colors. Conditioning involves replacing the water in cut flowers every few days using warm water and a preservative solution to prevent deterioration and maximize absorption. The document outlines best practices for receiving and preparing new cut flowers like removing any damaged blooms, recutting stems, and allowing time to rehydrate in conditioned water.