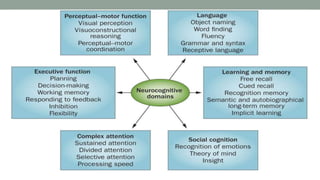
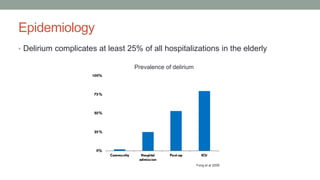
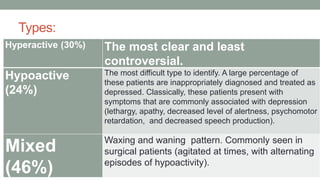
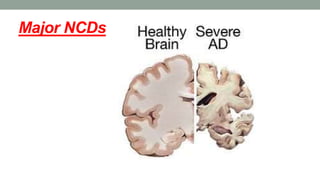
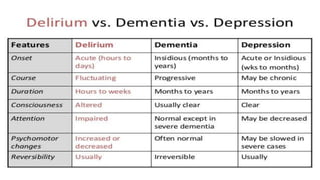
This document discusses neurocognitive disorders including delirium, major neurocognitive disorders such as dementia and amnestic syndrome, mild neurocognitive disorder, epilepsy, and traumatic brain injury. It provides details on the diagnostic criteria, clinical features, epidemiology, treatment, and prognosis of these conditions. Case studies are also presented to illustrate delirium and complex partial seizures.