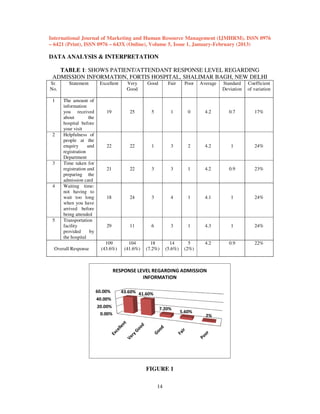
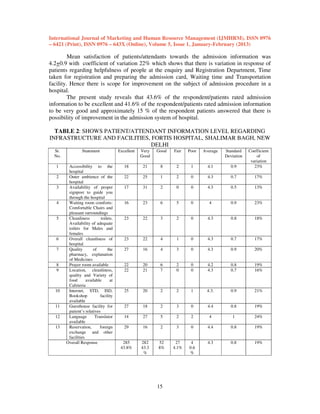
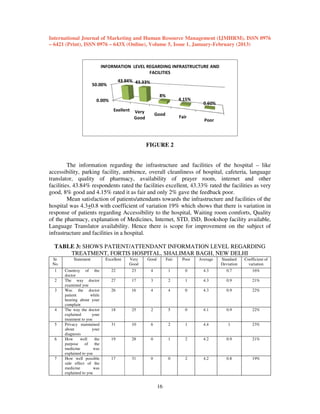
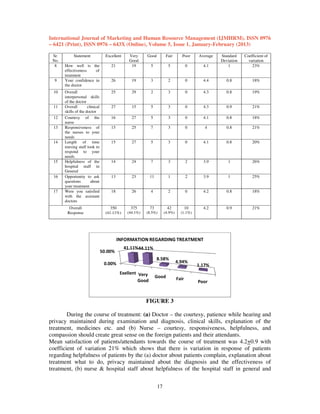
This document is from the International Journal of Marketing and Human Resource Management and discusses several previous studies on medical tourism. It provides an abstract of a study that analyzes why developing countries like India attract foreign patients for medical treatment and evaluates patient satisfaction levels at a hospital in New Delhi. The document also summarizes 6 previous reviews on medical tourism that examined topics like definitions of medical tourism, what motivates medical tourists, ethical issues, and the benefits and consequences of medical tourism for developing and developed countries. Overall, the studies concluded that countries can benefit economically from medical tourism but must ensure quality care and avoid creating dual healthcare systems.