Software testing terms are defined to standardize the testing process. Some key terms include:
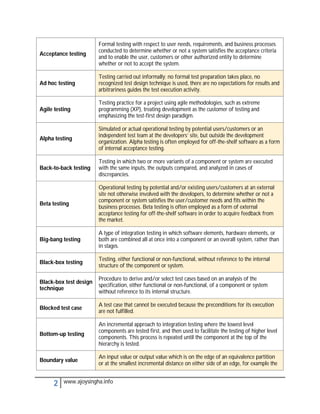
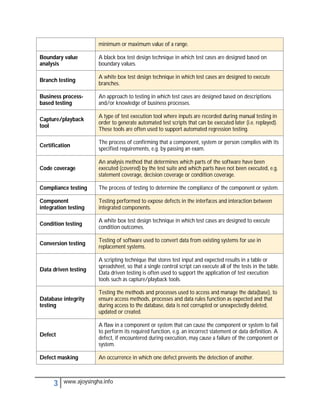
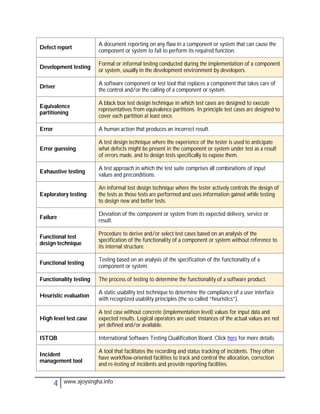
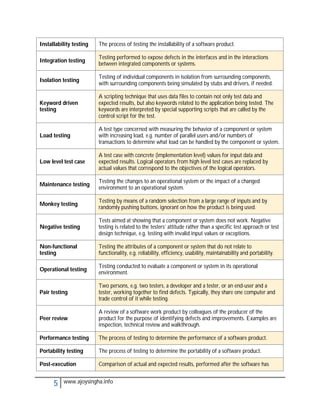
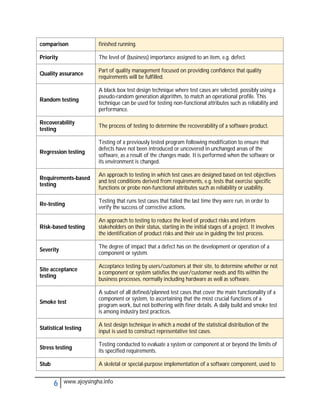
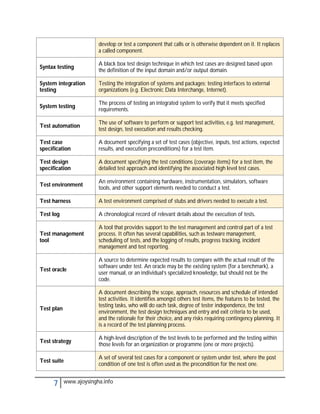
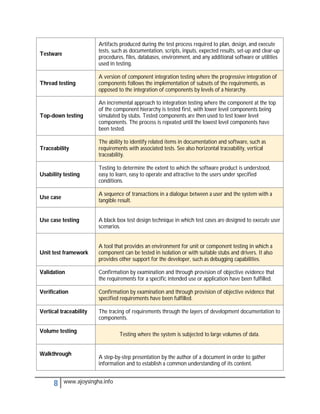
- Acceptance testing determines if a system meets requirements for acceptance.
- Integration testing checks for defects at the interfaces between integrated components.
- Regression testing ensures modifications haven't introduced new defects in unchanged areas.
- Usability testing determines if a system is easy to use under specified conditions.
- Validation and verification confirm requirements have been met through objective evidence.