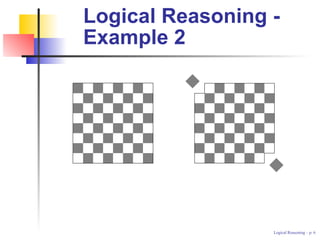
This document discusses logical reasoning and provides 3 examples of problems solved through logical reasoning. Logical reasoning involves breaking down problems into logical steps and using techniques like deduction and contradiction to arrive at solutions. The first example asks if 44 silver dollars can be distributed into 10 pockets with each pocket containing a different number of dollars. The second example asks if a notched checkerboard with squares removed can still be covered with the remaining dominoes. The third example asks if the equation x2 + y2 = 3(u2 + v2) has any integral solutions other than (0, 0, 0, 0). The document concludes by listing references on problem solving strategies and mathematical methods.