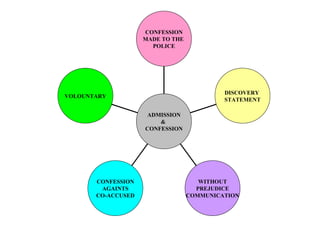
This document discusses admissions and confessions under Sections 17-31 of the Evidence Act 1950 in Malaysia. It defines an admission as a statement that suggests an inference about a fact in question, while a confession is an admission stating or suggesting that the accused committed the offense. A confession is considered a type of admission, and both are exceptions to the hearsay rule because they are declarations against interest. The document also discusses the meaning of "statement" in this context, the circumstances in which admissions can be made, and distinguishes admissions from confessions. It analyzes in detail the meaning of confession, including the plenary vs. non-plenary distinction, and discusses the Anandagoda objective test for determining what constitutes a confession











![Continue…
• However, any doubt about the inferential aspect of the
statement constituting a confession in the (b) part of the
definition was laid to rest by the Privy Council in the Sri
Lankan case of Anandagoda v The Queen [1962] 1
MLJ 289 where the appellant with two others were tried
together with conspiracy to murder and with the murder
of the deceased, One Adeline, by running her over with
a car. The appellant was found guilty of murder.
• The facts are as follows late at night on March 14, 1959,
the dead body of a woman was discovered lying at
Timbiriwewa near the 27th mile-post on the road
between Puttalam and Anuradhapura. A post-mortem
examination conducted on March 16, 1959, revealed
that the woman was between 20 and 25 years of age,
that she had been about seven months advanced in
pregnancy, and that her body bore numerous injuries
consistent with her having been run over by a motor-car.
The case for the prosecution was that the dead body was
that of Adeline Vitharana, that her death had been
caused by a motorcar being deliberately driven over her
dead body at least twice, that the consequent injuries
were the cause of her death.
• Besides what appeared to be strong evidence, the
prosecution adduced evidence by a police officer who
said that the appellant made certain admissions to him
while in his charge at the police station on March 22,
1959.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-13-320.jpg)

![Continue…
• Reception of the Anandagoda objective test by the Malaysian
Federal Court
• The Federal Court in Lemanit v PP [1965] 2 MLJ 26 where in
this case, the appellant was convicted of the offence of using an
arm, to wit by causing a bomb to explode with intent to cause
physical injury to persons and property. The evidence established
an intent to injure property but did not establish a clear intent to
injure persons. The prosecution relied on a confession made by
the appellant and recorded by a magistrate. One of the principal
grounds of appeal was that the statement was not a confession
and should not have been admitted in evidence.
• Held:
• (1) the failure to prove both the intents that is the intent to cause
physical injury to person and property is not fatal to a conviction
under section 4 of the Arms Offences Ordinance as proof of
either intent would suffice and no substantial miscarriage of
justice could be said to have occurred in this respect as far as the
trial judge's direction to the jury was concerned;
• (2) the statement made by the appellant in this case was clearly
inculpatory and therefore the statement was rightly recorded and
admitted in evidence as a confession. (Inculpatory evidence is a
legal term used to describe evidence that shows, or tends to
show, a person's involvement in an act, or evidence that can
establish guilt).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-15-320.jpg)
![Continue…
• Reception of the Anandagoda objective test by the
Malaysian Federal Court & Singapore Cases
• The Anandagoda objective test was again followed in Abdul
Khalid Bin Abdul Hamid [1995] 1 MLJ 692.
• A Series of Singapore cases which have a similar provision as
the Malaysian provision i.e. section 17 (2) of the Evidence Act,
further confirmed this test.
• In Suradet v PP [1993] 3 SLR 265, the court held that the
words “suggesting the inference that he committed the offence”
in section 17 (2) of the Singaporean Evidence Act clearly
demands a wider interpretation than that placed by the Indian
Supreme Court in Pakala Narayana Swami v E.
• In Tong Chee Kong v PP [1998] 2 SLR 843 it was held that for
a statement to amount to a confession, it need not be of a plenary
or unqualified nature; it can also be of non-plenary nature so
long as the statement connected the accused in some way with
the offense.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-16-320.jpg)
![Continue…
• A statement that does not amount to a confession can be used as an admission.
• The Privy Council in a appeal from India held in Ghulam Hussain v R [1950]
LR 77 IA 65 state that a statement made under section 164 of the Code of
Criminal procedure (similar to our section 115 Criminal Procedure Code) which
does not amount to a confession can be used against the maker as an admission.
This question has been raised in courts in India and it has been answered in the
affirmative.
• See Golam Mohammad Khan v The King Emperor [1924] ILR 4 Pat 327, Abdul
Rahim v The King Emperor [1925] AIR Cal 926 and Muhammad Bakhsh v
King Emperor [1941] AIR Sind 129.
• An admission is substantive evidence of the fact admitted and is admissible as
an exception to the hearsay rule. Per Augustine Paul J in PP v Dato’ Seri
Anwar Bin Ibrahim (No.3) [1999] 2 MLJ 1 states:
“A party's own statements are in all cases admissible against himself (see
Slatterie v Pooley 6 M & W 664). Thus, s 21 provides, inter alia, that admission
are relevant and may be proved as against the person who makes them. An
admission is treated as an exception to the hearsay rule and thus admissible. As
Sarkar on Evidence (14th Ed) Vol I says at p 309: The ordinary idea of hearsay
is what is heard out of court from a non-witness, and admissions are therefore
generally treated as exceptions to the hearsay rule”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-17-320.jpg)
![Continue…
• The statement must either be accepted or rejected as a whole.
In Pika Bewa v Emperor (1912) ILR 39 Cal 855 Holmwood and Sharfuddin
JJ. held that:
“where the only evidence of an offence is a statement by the accused and it is
relied on by the prosecution as evidence thereof it must be taken as a whole,
and nothing must be read into it which is not contained therein. As they said,
"it is all the evidence we have; and when the accused's own statement is to be
relied upon, it must be taken as a whole”.
• An admission must be based on personnel knowledge.
Per Lord Hodson in Compt of Customs v Western Letric [1965] 3 All ER
599 states:
“The appellant accordingly seeks to restore the conviction of the respondents
because of their admission that the origin of the goods has been wrongly
declared. Their Lordships are of the opinion that the conviction ought not to be
allowed to rest on the admission alone. If a man admits something of which he
knows nothing it is of no real evidential value. In this case, the admission made
by the respondents’ agent was an admission made on reading the marks and
labels on the goods and was of no more evidential value than those marks and
labels themselves”.
The Evidential value of an admission was explained by Desai J in Ramji
Dayawala v Invest Import AIR 1981 SC 2085 states that :
“Admission, unless explained, furnishes the best evidence”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-18-320.jpg)
![Continue…
• Issue: Can plead of guilty (admission) be admitted as piece of evidence
against the accused.
• In Noor Mohamed v Palanivelu [1956] 1 MLJ 114, the plaintiff, suing
through his next friend, brought this action for damages against the defendants
for personal injuries sustained by him while he was riding on a bicycle along
Batu Road after his day's, work at the Customs Office at Kuala Lumpur. He
collided with a lorry and fell off his bicycle. The vehicle was driven by the first
defendant, a learner driver, at whose side sat R. an instructor, at a school for
learner drivers owned by the 2nd defendant. The first defendant was a registered
pupil at the school. The plaintiff as a result of that accident sustained injuries
though no serious disfigurement but during his period of incapacitation he did
not suffer any financial loss. The plaintiff alleged that the first defendant
overtook him from the rear swerved to the left across his path and without
giving a signal stopped suddenly. The plaintiff swerved to the right to avoid
knocking into the back of the lorry and in so doing he hit the rear right side of
the lorry, lost his balance and another motor vehicle which was following
knocked him. The plaintiff was corroborated by P.W. 3, the driver of the
following motor vehicle. The first defendant and R., the instructor, however,
denied negligence. The first defendant however had pleaded guilty to a charge
of inconsiderate driving before a Magistrate -- for which he was convicted.
• Held: the plea of guilty to the inconsiderate driving was admissible as against
the first defendant. Plead of guilty is relevant under section 17 (1), 18, and 21 of
EA 1950. But as for the verdict it is not admissible as it is not relevant.
• See Hollington v Hewthorn & Co (1943) 1 KB 587, where at p. 600, Goddard
L.J. said: “In the present case, had the defendant before the magistrates pleaded
guilty or made some admission in giving evidence that would have supported
the plaintiff's case, this could have been proved, but not the result of the trial”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-19-320.jpg)

![Confession: The issue voluntary
• A confession is irrelevant if it does not satisfy the requirements
enumerated in the section.
• Per Sarkaria J in Veera Ibrahim v Maharashtra [1976] 3 SCR 672
states:
“To attract the prohibition enacted in section 24, Evidence Act, these
facts must be established:
a) that the statement in question is a confession;
b) that such confession has been made by an accused person;
c) that it has been made to a person in authority;
d) that the confession has been obtained by reason of any inducement,
threat or promise proceeding from a person in authority;
e) such inducement, threat or promise, must have reference to the charge
against the accused person; and
f) the inducement, threat or promise must in the opinion of the court be
sufficient to give the accused person grounds, which would appear to
him reasonable, for supposing that by making it he would gain any
advantage or avoid any evil of a temporal nature in reference to the
proceeding against him.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-21-320.jpg)
![• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• In the celebrated case of Dato’ Mokhtar Hashim v PP [1983] 2
MLJ 232, Abdoolcader FJ said that:
“No statement by an accused is admissible in evidence against him
unless it is shown by the prosecution to have been a voluntary
statement [Ibrahim v R [1914] AC 599, 609 per Lord Sumner)].
• This test was accepted by the House of Lords as the correct
approach in Director of Public Prosecutions v Ping Ling [1975] 3
All ER 175, [1976] AC 574 in which the House said that is not
necessary before a statement is held to be inadmissible because it is
not shown to have been voluntary, that it should be thought or held
that there was impropriety in the conduct of the person to whom the
statement was made, and that what has to be considered is whether a
statement is shown to have been voluntary rather than one brought
about in one of the ways referred to.
• It appears from the decision in Ping Lin (ante) that the classic test
of the admissibility of an accused's confession that the prosecution
must establish beyond reasonable doubt that it was voluntary, in the
sense that it was not obtained from him either by fear or prejudice or
hope of advantage created by a person in authority, or by opression,
should be applied in a manner which is part objective, part
subjective.
Confession: The issue voluntary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-22-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• In the Privy Council in Wong Kam-Ming v The Queen
[1980] AC 247 PC Lord Hailsham of St. Marylebone
said (at page 261):
“... any civilized system of criminal jurisprudence must
accord to the judiciary some means of excluding
confessions or admissions obtained by improper
methods. This is not only because of the potential
unreliability of such statements, but also, and perhaps
mainly, because in a civilized society it is vital that
persons in custody or charged with offences should not
be subjected to ill-treatment or improper pressure in
order to extract confessions. It is therefore of very great
importance that the courts should continue to insist that
before extra-judicial statements can be admitted in
evidence the prosecution must be made to prove beyond
reasonable doubt that the statement was not obtained in a
manner which should be reprobated and was therefore in
the truest sense voluntary”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-23-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• In R v Wilson [1981] 1 NZLR 316 the New Zealand
Court of Appeal held that confessions obtained by
overbearing the will of a person in custody by tactics
amounting to compulsion should not be received in
evidence and that whether a case is of that kind is a
question of fact and degree. The defendant in that case
had been subjected to prolonged interrogation in the
confinement of a small room which was unfair and
oppressive and it was held that there was accordingly
oppression and the means employed must be regarded
as themselves involving a miscarriage of justice.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-24-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• Sharma J, in the useful case of PP v Law Say Seck
[1971] 1 MLJ 199 where is it decided that it is left to
the court entirely to form its own opinion as to whether
an inducement, threat or promise held out in any
particular case was sufficient to lead the person to
suppose that he would gain an advantage of a temporal
nature. In doing so the mind of the person making the
statement has to be judged rather than that of the person
in authority. In scrutinizing a case of this kind the court
has to perform a threefold function: It has to determine
the sufficiency of inducement, threat or promise; it has
to clothe itself with the mentality of the accused to see
whether the grounds would appear to the accused
reasonable for a supposition mentioned in section 24 of
the Evidence Ordinance; lastly
it has to judge as a court if the confession appears to
have been caused in consequence of any inducement,
threat or promise.
• See also Md Desa Bin Hashim v PP [1996] 1 AMR 59](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-25-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• In Aziz Muhamad Din v PP [1997] 1 CLJ Supp 523:
“Thus what is important is the effect that the inducement,
threat or promise has on the accused”.
• In this respect Brennan J in speaking for the Federal Court
of Australia in Collins v R (1980) 31 ALR 257 said at p
307:
“ So the admissibility of the confession as a matter of law
(as distinguished from discretion, later to be discussed) is
not determined by reference to the propriety or otherwise
of the conduct of the police officers in the case, but by
reference to the effect of their conduct in all the
circumstances upon the will of the confessionalist. The
conduct of police before and during an interrogation
fashions the circumstances in which confessions are made
and it is necessary to refer to those circumstances in
determining whether a confession is voluntary.
“ The principle, focusing upon the will of the person
confessing, must be applied according to the age,
background and psychological condition of each
confessionalist and the circumstances in which the
confession is made. Voluntariness is not an issue to be
determined by reference to some hypothetical standard; it
requires a careful assessment of the effect of the actual
circumstances of a case upon the will of the particular
accused.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-26-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• It is therefore clear that the inducement, threat or
promise must have 'caused' the person to make the
statement.
• In the Indian Supreme Court case of Pyare Lal v State
of Rajasthan AIR 1963 SC 1094 Subba Rao J said
that to determine involuntariness the mere existence of
the threat, inducement or promise is not enough.
• As Sharma J said in PP v Law Say Seck & Ors
[1971] 1 MLJ 199 one should be able to say that
without it the person would not have made a statement.
It follows that an inducement, threat or promise per se
is insufficient to render the confession inadmissible.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-27-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• In the light of the foregoing an accused is obliged to testify
in the trial within the trial in order to effectively challenge
the admissibility of his statement.
• Lord Edmund – Davies in Wong Kam-Ming v R [1979] 1
All ER 939 states:
“As already been observed, an accused seeking to challenge
the admissibility of a confession may for all practical
purposes be obliged to testify in the voir dire if his
challenge is to have any chance of succeeding”.
• See also R v Brophy [1981] 2 All ER 705](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-28-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• From the case of Hasibullah Bin Mohd Ghazali v PP
[1993] 3 MLJ 321:
(a) in deciding the issue of admissibility of a confession
made by an accused person, the onus is not on the accused
to show involuntariness but on the prosecution to prove
beyond any reasonable doubt that the confession was
voluntary. The judge in this case had reversed the onus
and disregarded the requirement that the prosecution must
prove beyond any reasonable doubt that the confession
was voluntary;
(b) in deciding whether or not a statement made by an
accused person was obtained from him by fear of
prejudice or hope of advantage exercised or held out by a
person in authority, the cardinal point is not so much the
state of mind of the police officer but that of the accused.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-29-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• In Ibrahim v R [1914] AC 599, the appellant, a private in
the Indian Army, was convicted of the murder of a native
officer. Shortly after the murder the commanding officer
went to see the appellant, who was in custody, and said to
him: "Why have you done such a senseless act?" The
appellant replied: "Some three or four days he has been
abusing me; without a doubt I killed him." No threat or
inducement was offered to the appellant before he made this
statement. At the trial evidence of this conversation was
admitted.
• Held: without deciding whether or not the answer made by a
person in custody to a question put to him by a person with
authority over him was admissible in evidence, the general
circumstances of the case were such, and the preponderance
of unquestioned evidence so great, that it was unlikely that
the jury were substantially influenced by the disputed
evidence, and there was, therefore, no substantial
miscarriage of justice as would justify interference by the
Board.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-30-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• In DPP v Ping Lin [1975] 3 All ER 175, police officers
discovered the appellant smoking heroin in his flat in the
company of two friends. Substantial quantities of Chinese
heroin were found in the flat. The appellant and his two friends
were taken into custody. On the following day, after a caution
had been administered, the appellant was questioned by a
detective superintendent. At first the appellant maintained that
he was not a dealer but only a smoker of the drug. He admitted
that he had obtained the heroin from 'a man in Gerrard Street'.
• The appellant then said: 'You let me go, and I find you man
plenty heroin.' The superintendent replied: 'That can't be done',
and continued his interrogation of the appellant. The
superintendent suggested to the appellant that he had habitually
dealt with drugs in a big way. The appellant then admitted in
effect that he was a dealer on a retail scale by saying: 'Yes. All
right. But I don't sell much.' He added: 'Let me out, and I'll get
you a man with a big packet.' The superintendent again said
'That can't be done'. The appellant then said: 'If I help police,
can you help me?'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-31-320.jpg)

![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Accused’s statement must be voluntary
• PP v Scott Allen Hazlett [2005] 4 MLJ 564 where four
accused were jointly charged, and tried under s 302 of the
Penal Code for the murder of an elderly woman, one
Mdm Seow Saw Poh @ Siew Siaw Poh, on the night of
27 December 1998 at Jalan Tebrau 1, Ukay Heights, Hulu
Kelang, District of Gombak, Selangor. They were
originally tried before Kang Hwee Gee J on 17 January
2000. The learned judge heard the case only partially.
Subsequently, the first accused died while under remand
in prison. With the consent of the prosecution and the
defence, the case against the remaining three accused was
ordered be heard de novo (from the beginning).
• The prosecution, in its endeavour to establish a prima
facie case of the offence of murder against all the three
accused, relied mainly on the evidence of the
prosecution’s key witness, one Haikal Shah bin
Muhammad Kamal (‘PW3 ’), who claimed to be an eye-
witness as well as an accomplice to the alleged crime. The
defence sought to impeach the credit of PW3. There were
also issues on the voluntariness of the oral cautioned
statement of the first and second accused. The prosecution
sought to adduce the oral cautioned statement of the
second accused through a woman police (PW14).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-33-320.jpg)


![Continue…
(6) R v Kingston (1830) 4 C & P 587:
“You had better tell all you know”.
(7) R v Barker (1941) 28 Cr App R 52:
“Offer of non-prosecution”
(8) R v Gills (1866) 11 Cox CC 69:
“Immunity from prosecution”.
(9) R v Luckhurst (1853) 23 LJMC 18:
“If you don’t tell me, I will give in charge of the police till you do
tell me”.
(10) PP v Naikan [1961] MLJ 147:
“You had better tell the truth”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-36-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Cases where expressions used were not held to have an involuntary effect
(1) R v Court (1876) 7 C & P 486:
“Be sure to tell the truth”.
(2) R v Reave and Hancock (1872) LR 1 CCR 362:
“You had better, as good boys, tell the truth”.
(3) R v Reason (1872) 12 Cox CC 228:
“I must know more about it”.
(4) R v Sleeman (1853) 6 Cox CC 245:
“Don’t run your soul into more sin, but tell the truth”.
(5) PP v Ramasamy [1991] 1 MLJ 75:
“You better tell the truth”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-37-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• The issue of oppression
• Oppression has gained momentum as an
additional factor to render a confession as
involuntary.
• It can be traced to the pen of Abdoolcader FJ in
Dato’ Mokhtar Bin Hashim v PP [1983] 2 MLJ
232 where his Lordship said at page 273:
“It appears from the decision in Ping Lin (ante) that
the classic test of the admissibility of an accused's
confession that the prosecution must establish
beyond reasonable doubt that it was voluntary, in
the sense that it was not obtained from him either
by fear or prejudice or hope of advantage created
by a person in authority, or by oppression, should
be applied in a manner which is part objective, part
subjective”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-38-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• The issue of oppression
• Per Faiza Thamby Chik JC in PP v Chan Choon Keong
[1989] 2 MLJ 427 states:
“The other point is whether the cautioned statement was
obtained under oppressive circumstances. The relevant facts
to be looked at and considered to show what are called
'oppressive circumstances' negativing voluntariness are:
(1) characteristics of the accused;
(2) period of time during which he was questioned;
(3) length of time during which he was in custody;
(4) whether or not he was given opportunities of rest and
refreshment. I find these 'wrongful manners of exercise of
authority' by the recording officer and other officers as
improper, following R v Fulling [1987] 2 All ER 65 where it
was stated at p 69: 'This in turn leads us to believe that
'oppression' ... should be given its ordinary dictionary
meaning.
“The Oxford English Dictionary had its third definition of
the word 'oppression' and runs as follows Exercise of
authority or power in a burdensome, harsh or wrongful
manner. Unjust or cruel treatment of subjects, inferiors, etc.
The imposition of unreasonable or unjust burden. As it was
said in R v Priestley (1966) 50 Cr App R 183 'oppression
means something which leads to sap (undermine) and has
sapped that free will which must exist before a confession is
voluntary”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-39-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• The issue of oppression
• In PP v Chong Boo See [1988] 3 MLJ 292, Edgar Joseph
Jr J said that the test of oppression would depend upon
subjective considerations such as his age, health, sex and
personality.
• Abdoolcader FJ said in Dato’ Mokhtar Bin Hashim v PP
[1983] 2 MLJ 232 that
“As to the long and odd hours of interrogation stated in the
station diaries this would appear to be suggestive of
oppression within the definition by Sachs J in R v Priestly
which was adopted in R v Prager”.
• PP v Tan Gong Wai [1985] 1 MLJ 355, the accused was
allowed no sleep or refreshments from the time he was
brought into the customs office at 8.00pm on 18 April 1981
until his cautioned statement was recorded from 5.15am to
7.20am on 19 April. Edgar Joseph Jr J said that this
amounted to oppression.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-40-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• The issue of oppression
• In PP v Chan Choon Keong [1989] 2 MLJ 427, the accused was
interrogated from 21 to 24 December 1984, and at one time even
between 12.45am and 1.00am. He was questions for a whole night with
his hands handcuffed behind his back. The statement was recorded from
11.45 am to 2.15 pm. In rejecting the statement as being involuntary,
Faiza Thamby Chik said that the least the recording officer could have
done was to stop recording the statement at lunch time and continue
after lunch.
• In PP v Kamde Bin Raspani [1988] 3 MLJ 289, Zakaria Yatim J
rejected the cautioned statement for the reason that the interrogations
were carried out after 6.30 pm in violation of rule 20 of the Police
(Lock-Up) Rules 1953 which states “Prisoners shall be locked up for the
night by 6.30 pm and shall rise and be dressed by 6.30 am”. (See also PP
v Lee Chee Meng [1991] 1 MLJ 227).
• Handcuffing of an accused while he is making a statement has been held
in some cases to amount to oppression.
• (See PP v Mohd Bin Wan The [1989] 2 CLJ 652, PP v Abdul Rahim
Bin Ibrahim Penang Criminal Trial No 47 (58)-15-86, unreported, and
PP v Mohd Fuzi Bin Wan The [1989] 2 CLJ 652)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-41-320.jpg)



![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Application of the section
a) A case where no attempt was made by the prosecution to prove that the
impression caused by the inducement had been removed.
In Lim Sing Hiaw v PP [1965] 1 MLJ 85, the appellant was tried and
convicted for unlawful control of a firearm in contravention of section 57(1) of
the Internal Security Act, 1960, and for consorting with armed persons in
contravention of section 58(1) of the same Act and was sentenced to death. On
appeal it was argued inter alia: (iv) the confession of the accused should not
have been admitted in evidence. It appeared that prior to the making of the
statement to the police, the accused had been questioned by the Special Branch
and according to him he had given a statement as he was threatened that if he
did not do so he would be taken into the jungle and shot.
Held: (4) the appellant's subsequent statement was wrongly admitted
because there was no evidence to show that the original threat or premises
made to the appellant to make the previous statement had been dissipated
(abandoned) (5) considering the admissible evidence in this case the appeal
must be dismissed because although the statement had been wrongly admitted
there had been no substantial miscarriage of justice.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-45-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Application of the section
b) A case where the impression caused by a promise was held to
have been removed as shown by the answer given by the accused
to the questions asked by the Magistrate.
In Abdullah Bin Awang Bongkok v PP [1956] MLJ 90, the
appellant in this case was convicted of murder and sentenced to
death. The only point which was argued was whether the confession
made by the appellant to a Magistrate should have been admitted in
evidence.
Held: (1) the answers to the further questions put to the appellant by
the Magistrate made it plain beyond any doubt that the statement was
made freely and voluntarily and was properly admitted in evidence
under s.24 of the Evidence Ordinance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-46-320.jpg)


![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Principle and scope
• This section should also be read with section
24 of the Act. It operates as a general rule of
inclusion (addition) and states that if such
confession as is referred to in section 24 is
otherwise relevant, it does not become
irrelevant merely because:
a) under a promise of secrecy (dibuat atas
sesuatu janji akan merahsiakannnya). If a
confession is obtained from a person with a
promise that it would be kept a secret, it
thereby does not become irrelevant.
See R v Thompson [1836] 7 C & P 345.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-49-320.jpg)
![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Principle and scope
b) In consequence of a deception practiced on the
accused person for the purpose of obtaining it (hasil
daripada sesuatu perdayaan yang dilakukan ke atas orang
tertuduh itu bagi maksud hendak mendapatkannya).
This part of the section must be read with the rule that
illegally obtained evidence is admissible. The court is
not concerned with how the evidence was obtained.
However, in such cases the court always has discretion
to disallow evidence if the strict rules of admissibility
would operate unfairly against the accused. Per Chong
Siew Fai CJ in Goi Ching Ang v PP [1999] 1 MLJ 507
states:
“Fairness requires fair trial which, in turn, needs fair
procedure. Fair process requires that the legitimate
interests of both the prosecution and the defence are
adequately provided for.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-50-320.jpg)

![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Principle and scope
c) When he was drunk (apabila dia mabuk). Although a confession made
by a person when he was drunk is admissible the weight to be attached
to it is another matter.
The weight of a confesssion may be affected by the circumstances
under which it was made as in the case of R v Spilsbury 7 Car & P
187, where it was alleged that a constable had made the accused
drunk and that the latter then made a statement. Coleridge, J.
observed:
"A statement made by a prisoner while drunk is not therefore
inadmissible as evidence and to render a statement inadmissible it
must be obtained by hope or fear. This is a matter of observation for
me upon the weight which ought to attach to this statement when it is
considered by the jury.“
See also R v Santokh Singh [1933] MLJ 178.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-52-320.jpg)


![Confession: The issue voluntary
• Principle and scope
e) Because he was not warned that he was not bound to make a confession
and that evidence of it might be given against him. (kerana dia tidak diberi
amaran bahawa dia tidak terpaksa membuat pengakuan salah itu dan bahawa
keterangan mengenai pengakuan salah itu boleh diberikan terhadapnya).
It must be noted that section 24 of the Act to which this section relates
does not require any form of warning to be given. Be that as it may, the
question whether an accused person was warned may become relevant to
enable the court to decide whether the confession was voluntary. A
statement by an accused person is not admissible in evidence against him
unless it is shown by the prosecution to have been a voluntary statement in
the sense that it was not extorted by fear of prejudice or induced by hope
of advantage held put by a person in authority.
See R v Voisin [1918] 1 KB 531 & Soudreau v The King [1949] SCr
262.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-55-320.jpg)

![Confession made to the police
• Principle and scope
• Meaning of the word police officer in the section was
explained by Per Burton ag CJ in the R v Wong Ah
Kin [1935] MLJ 169 “Now, it is perfectly clear to
my mind that when the Evidence Ordinance says
'Police' it means police…The words 'police
officer' must be construed strictly to mean that he
is a member of the Police Force and nothing else”.
In this case, a statement made to An Assistant
Protector of Chinese was held to be admissible on
the ground that he was not a police officer within the
meaning of this section.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-57-320.jpg)
![Continue…
• In Man Woo v R [1951] MLJ 20 where this was a chandu case.
At the hearing the question was raised as to the interpretation of s.
25 of the Evidence Ordinance. In the present case a statement was
made to a Senior Customs Officer. It is true that in a sense the
activities of all Government officers engaged in enforcing the law
are police duties. It is nevertheless, in my opinion, entirely
contrary to the ordinary use of language to describe officers so
engaged as Police officers. Further, the addition of the words
"below the rank of Inspector" can only have reference to that body
ordinarily known as the "Police" and which is governed by the
Police Ordinance
• Per Sharma J in Chua Beow Huat v PP [1970] 2 MLJ 29 states
“I am consequently of the view that a customs officer is not a
"police officer" within the meaning of s. 25 of the Evidence
Ordinance”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-58-320.jpg)
![Confession made to the police
• Principle and scope
• In Public Prosecutor V. Tay Yam Peng [1951] 1 LNS 67 the
Court of Appeal followed Man Woo V. Rex [1951] 1 LNS 50 and
held that the words "police officer" in s. 26 of the Evidence
Ordinance were to be given their ordinary everyday meaning and
that following that test a chandu officer was not a police officer
within the meaning of s. 26 of the Evidence Ordinance”.
• Section 2 of the Police Act 1967 (Act 344) defines him as a
member of the Royal Malaysian Force.
• In PP v Tay Yam Peng [1951] MLJ 144, the Court of Appeal
hold that a Chandu Officer is a not a police officer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-59-320.jpg)
![Continue…
• Per Abdul Aziz J in Koh Jok Sim v PP [1966] 2 MLJ 50 states
“It is fairly well settled that s. 113 of the Criminal Procedure
Code and ss. 25 and 26 of the Evidence Ordinance do not apply
to excise officers and there is nothing in law to prevent the
answers given to an excise officer by a person subsequently
accused of an offence from being used in evidence subject to the
important proviso that the Court is satisfied that the answers
were voluntarily given”.
• Similar decision was made by Wan Suleiman F.J. in Abdul
Ghani bin Jusoh & Anor v Public Prosecutor [1981] 1 MLJ
25 and Barret v PP [1982] 2 MLJ 284 relating to a statement of
an accused person recorded by a Probationary Police Inspector.
A Probationary Police Inspector is regarded as a person
below the rank of an Inspector.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-60-320.jpg)
![Confession made to the police
• Application of the section
a) A report containing a confession made to a
police officer below the rank of an inspector
will be excluded.
See PA Anselam v PP [1941] MLJ 157 where in
the present case it was an admission of a fact which
would tend to prove the guilt of the accused, and
amounted to a confession. Having been made to a
police officer below the rank of Inspector it is
excluded by section 25 of the Evidence Enactment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-61-320.jpg)
![Confession made to the police
• Application of the section
b) In order to render a statement admissible there must be
evidence to show that the officer to whom it was made was not
below the rank of inspector.
In Yee Ya Mang v PP [1972] 1 MLJ 120 where the appellant
was charged under section 9(a) of the Arms Act, 1960 for having
in his possession a pistol and three rounds of ammunition,
without an arms license or an arms permit. The pistol and the
three rounds of ammunition were not found in the house occupied
by the appellant but at a spot in a rubber estate pointed out by the
appellant. In the course of police investigation the appellant said
that he had a revolver. Subsequently he took the police officer to
the spot where the revolver was found.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-62-320.jpg)



![Confession made to the police while in custody
• Principle and scope
• Whilst section 25 of the Act relates to a confession made to a
police officer, this section is concerned with a confession made
by anyone to a third person while he is in the custody of a police
officer. In order to be admissible it must be have been made in the
immediate presence of a sessions court or magistrate. This section
also applies to all categories of police officers.
• In Lee Yew Seng v PP [1967] 1 MLJ 215 the appellants were
charged with robbing a goldsmith's shop. There was ample
evidence at the trial to show that the appellants took active part in
the robbery but at the trial a confession made by the first
appellant while he was in the custody of the police was admitted
in evidence. The appellants were convicted and they appealed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-66-320.jpg)

![Confession made to the police while in custody
• Meaning of the word custody
• In Sambu v R [1947] MLJ 16 where it was held, (1) that the
accused's statement to the police officer that he had taken the
cloth from Godown 14 was improperly admitted in evidence,
contrary to Section 26 of the Evidence Ordinance, as it was a
confession made by him while he was in the custody of a police
officer. Brown J states “There is nothing technical about being in
custody. A person is in custody when he is in a state of being
guarded and watched to prevent his escape. In order to answer the
question of whether the appellant was in custody at the time when
he is alleged to have made the statement it is only necessary to
consider what would have happened if, at that time, he had tried
to run away”.
• (See also PP v Salamah Bte Abdullah [1947] MLJ 178).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-68-320.jpg)
![Confessions made to a magistrate
• Under this section, a confession made to a magistrate is
admissible.
• In Chong Teng v PP [1960] MLJ 153, Held: (1) the
statement in question amounted to a confession and by
reason of section 26 of the Evidence Ordinance a
confession made by a person while in custody is only
admissible if it is made in the immediate presence of a
Sessions Court President or a Magistrate.
• In Muka Bin Musa v PP [1964] 30 MLJ 275, Held: in
the absence at the trial of any evidence to cast doubt upon
the correctness of the appellant's statement it could not be
said that there was any possibility of such substantial
misinterpretation as to destroy the force of the
confession. (Appeal dismissed).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-69-320.jpg)
![Continue…
• It is also not objectionable for a police officer to
inform a person of his right to make a confession
before a magistrate.
• Per Ong CJ in Yap Chai Chai v PP [1973] 1 MLJ
219 states:
“for the mere fact that this appellant was informed by a
senior police officer of the proper way to set about
making his confession by doing so before a magistrate
was by itself not intrinsic evidence of coercion,
inducement, threat or promise, which this appellant
had expressly denied as motivating his decision”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-70-320.jpg)
![Confession made to the police while in
custody
• Application of the section
a) A confession made by a person to a doctor when he is in the
custody of the police is inadmissible under this section. See Eng
Sin v PP [1974] 2 MLJ 168
b) Failure to object to the admissibility of an inadmissible
confession does not render it admissible. See Packiam v PP
[1972] 1 MLJ 247 & Wong Kok Keong v R [1955] MLJ 13 at p
16 at page 16.
c) The effect of the improper admission of a confession. It would
depend on whether there was other evidence to justify a
conviction. See Lee Yew Seng v PP [1967] 1 MLJ 215.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-71-320.jpg)
![Confession made to the police while
in custody
• Section 25 v section 26
• A confession admissible under section 25 of EA 1950 would be
excluded if the provisions of section 26 of the Act apply. Willan CJ
in Tan Shu En v PP [1948] MLJ 196 states “It is also beyond
doubt that, if the confession made to Mr. Kandiah was not
excluded by the provisions of section 25 of the Evidence
Ordinance, it would still be inadmissible under section 26, on the
ground that the second appellant was in “police custody” at the
time of making it”. In this regard, under section 25, the relevant
question is “To whom was the question made?” If the answer is
that it was made to a police officer below the rank of an Inspector,
it is excluded. Under section 26, the question is “Under what
circumstances was the confession made?” If the answer is that the
confession was made while the accused was in police custody, such
confession shall be excluded unless it was made in the immediate
presence of the Session Court Judge or Magistrate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-72-320.jpg)




![Confession & the issue of discovery
statement
• a) The information must have been received from a person accused of an
offence. In other words, the accused himself gave the information
• Per Suffian LP in Chong Soon Koy v PP [1977] 2 MLJ 78 states “It is
submitted that the information supplied by the accused was not
admissible, since he was arrested under s. 73(1) ISA and at the time he
gave the statement he was not "a person accused of any offence" within s.
27. There is no merit in this argument, since these words mean "a person
accused at the time or subsequently of any offence”.
• The prosecution must prove beyond reasonable doubt that the accused
did give the information. As stated in PP v Basri Bin Salihin [1993] 1 CLJ
420 & Krishnan Ramar [1987] CLJ 145)
• The police officer to whom the information was supplied ought to give
evidence of the discovery of the fact before giving evidence of the
information See Tan Hung Song v R [1951] MLJ 181 where the examination
in chief would proceed on these lines: Did the accused speak to you? Yes.
As result of what he said what did you do? I took the accused to his house.
What did you find? I found this knife which was concealed in the roof)
The police officer should not merely state that in consequence of what the
accuse told him he did so and so (See Tham Fatt v R [1954] MLJ 172).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-77-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery
statement
• a) The information must have been received from a person accused of
an offence. In other words, the accused himself gave the information
• Even if the information was given involuntarily it is still
admissible under the section: See PP v Er Ah Kiat [1966] 1 MLJ 9;
Thurtell and Hunt (1824), Notable British Trials, pp. 144 and 145 &
Queen v. Murugan Ramasamy [1964] 3 WLR 632 at p. 636. Per Raja
Azlan Shah J also states in Chandrasekaran v PP [1971] 1 MLJ 153
that “Section 27 is a concession to the prosecution. It is the express
intention of the legislature that, even though such a statement is
otherwise hit by the three preceding sections viz., s. 24-26 of the
Evidence Ordinance, any portion thereof is nevertheless
admissible in evidence if it leads to the discovery of a relevant fact.
The reason is that, since the discovery itself provides the acid test,
the truth of the statement that led to the discovery is thereby
guaranteed. Admissibility of evidence under s. 27 is in no way
related to the making of the confession; rather, such evidence is
admitted on clear grounds of relevancy as directly connecting the
accused with the object recovered”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-78-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery statement
• a) The information must have been received from a person accused of an offence. In other words,
the accused himself gave the information
• However, in Md Desa Bin Hashim v PP [1995] 3 MLJ 350, the Federal Court ruled that section
27 is governed by section 24 of the Act. Gopal Sri Ram JCA states that “…to qualify for
admission under s. 27, it must have been made voluntarily. A discovery made in
consequence of a confession extracted by illegitimate means in the sense described in s. 24 is
inadmissible”. In Goi Ching Ang v PP [1999] 1 MLJ 507 a different panel of the Federal Court
re-instated section 27 of the Act as an independent provision. Chong Siew Fai CJ said “It will
thus be seen from the judicial pronouncements that the independence and distinctiveness of
s. 27 of the Evidence Act 1950 and its being regarded as an exception to s. 24 thereof are
deeply rooted in our case-law, and so far as we are aware, has stood unchallenged for
decades”.
• However, due to the lack of language-nexus between s. 27 on the one hand and s. 24 and
comparable provisions in other enactments on the other hand, the apparent intention of the
legislature, and the long line of past decisions of our courts not a few of which were from
eminent members of the appellate and the highest courts, any departure from the
entrenched judicial interpretation laid down in the above quoted and other numerous cases
would be a policy decision and should, in our view, be left to the legislature. (See also
Francis Anthonysamy vPP [2005] 2 CLJ 481)
• However in PP v Krisna Rao a/l Gurumurthi [2000] 1 MLJ 274 Kang Hwee Gee J states “the
law is clear where the presiding judge is vested with the discretion whether to admit or not
to admit any evidence, he is bound to exercise his discretion by applying the test whether
the prejudicial effect of its admission would outweigh its probative value”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-79-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery statement
• b) Such person must have been in the custody of a police officer at
the time of giving the information
• The meaning of the word “custody” is not restricted to custody of
a person after formal arrest. The effect of information given
before a person is taken into custody: The general rule under this
section is that when the information is given the accused must
have been in custody of the police. However, even where a person
is not in the actual custody of the police at the time of giving the
information he may be deemed to have submitted himself to such
custody when he gave the information. In the Indian Supreme
Court case of State of UP v Deoman Upadhyaya [1961] 1 SCR 14
Shah J said “When a person not in custody approaches a police
officer investigating an offence and offers to give information
leading to discovery of a fact, having a bearing on the charge
which may be made against him he may appropriately be deemed
to have surrendered himself to the police”. This argument is
rationale of the Federal Court’s decision in Soh Ten Seng v PP
[1964] MLJ 380 where information received from the accused
through the telephone when he was not in the actual custody of the
police was held to be the information for the purposes of section
27.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-80-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery statement
• c) A fact must be deposed to as having been discovered in consequence of such information
• What is the fact discovered?: The fact discovered is not the item (the murder weapon for
example) but more towards a psychological fact that the accused had knowledge of the place
where the object was found. In Pulukuri Kottaya case, the court said that the fact thereby discovered
was the place where the object was found and the accused’s knowledge as to this. Sir John Beaumont in
Pulukuri Kottaya’s case gave the rationale for including the knowledge of the accused person when he
said: “It is fallacious to treat the fact discovered within the section as equivalent to the object
produced; the fact discovered embraces the place from which the object is produced, and the
knowledge of the accused as to this, and the information given must relate distinctly to this fact.
Suffian LP in Chong Soon Koy v PP states “What was the fact discovered? The fact discovered
embraces the place from which the pistol and ammunition were produced and the knowledge of
the accused as to this”.
• There must be proof of some fact discovered as a result of the information given by the accused
before the section can be invoked: Per Murray-Aynsley CJ in Hamiron Bin Mat Udin v PP [1948]
MLJ 50 states “It was claimed by the prosecution that it was as a result of the statements made by
accused that the body was found; and also that it was because of accused's statement that the
Police Inspector was able to identify the body by the rope round the neck. It is to be observed,
however, that there is no evidence on the record to suggest that the body was found at the place
which was pointed out by the second accused - indeed there was no evidence at all as to where the
body was found or by whom. Moreover the body was identified by both the second and fourth
prosecution witnesses without reference to the rope round the neck. …So section 27 has no
application”. See also PP v Tan Ngak Phiew [1990] 2 CLJ 843](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-81-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery statement
• c) A fact must be deposed to as having been discovered in consequence of such
information
• Where there is discovery without any evidence of information within the
meaning of the section then the section has no application: Per Ong J in
Gurusamy v PP [1965] 1 MLJ 245 states “Section 27 clearly had no application
in this case. Evidence of the discovery of the stolen property was admissible
without having to invoke the section, the only purpose of which is to render
self-incriminatory statements admissible if such statements can properly be
regarded as information relating distinctly to the fact thereby discovered. The
appellant was never alleged to have made any statement. Hence, negative
evidence on this point must necessarily be held in his favour, because had he
given any information, such information should have been given in evidence
by the police officer who heard it”.
• Whether the thing recovered must have been hidden: The use of the word
discovered in section 27 of the Act would appear to suggest that the thing
recovered should in the first place have had the characteristic feature of having
been hidden. In MP State v Dhannalal Moruji [1961] 2 Cr LJ 238, Krishnan J said
that “…the discovery…should be the finding of something which had been
partly or wholly concealed and which might not have been found out, at least
at that time, except as a consequence of the statement. When there is no
concealment obviously there is no discover”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-82-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery statement
• c) A fact must be deposed to as having been discovered in consequence of such
information
• If the police had prior knowledge of the existence of the thing discovered then
the section has no application: As was appropriately stated in the Indian case
of Amin v. State AIR [1958] All 293 that the recovery of the articles cannot be
described as a discovery under s. 27 where they are not recovered from any
hidden place and if in the normal course of investigations the investigating
agency is bound to see them and take them in possession without the accused
making any statement of pointing them out. It has become a normal device of
the investigating agency to turn an ordinary recovery into a discovery to
utilize the provision of s. 27 against the accused. See also PP v. Liew Sam
Seong [1982] 1 MLJ 223 & Md Desa Hashim v PP [1995] 3 MLJ 350.
• PP v Basri Bin Salihin [1994] 2 MLJ 476 Visu Sinnadurai J considered the
question of what constitutes prior knowledge of the fact by the police and said
that it would appear that in most cases any prior knowledge by the police that
the accused had in his possession or had hidden drugs in a particular place,
though the exact and specific location had not been identified, would make the
subsequent confession of the accused inadmissible under section 27 in so far as
to the fact relates to the accused’s knowledge of the drugs or the place where
the drugs were found.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-83-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery statement
• d) Admissibility of information upon proof of requirements of
section
• Upon proof of the elements discussed above then so much of such
information, whether it amounts to a confession or not, as relates
distinctly to the fact thereby discovered may be proved.
• Under this section only the information which relates distinctly to
the discovery of the fact is admissible: Per Hashim Yeop A Sani J
in PP v Toh Ah Keat [1977] 2 MLJ 87 states “Section 27 of the
Evidence Act however deals with a very special type of statement
which even if self-incriminatory is nonetheless admissible under
that section provided that the conditions prescribed are strictly
complied with”. The law on s. 27 of the Evidence Act was dealt
with conclusively by the Privy Council in P Kottaya v. Emperor
AIR 1947 PC. In that case the statement challenged was, "I
stabbed with a spear. I hid the spear in a yard in my village. I will
show you the place." The Privy Council held that the whole of the
statement was admissible except the first part. Meaning of the
word distinctly in the section: Per Sharma J in Yee Ya Mang v PP
[1972] 1 MLJ 120 states “The word distinctly in section 27 of the
Evidence Ordinance is important. It means that only that part of
the statement which leads directly to the recovery is admissible”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-84-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery
statement
• Evidential value of fact discovered under this section: The
evidentiary value of a fact discovered under this section
could range from evidence of mere knowledge to evidence
of possession of the fact discovered depending on the
information supplied and the circumstances of the case.
Sharma J states in Yee Ya Mang v PP [1972] 1 MLj 120 “A
good deal depends upon whether the production was
accompanied by information given by the accused in
custody as would be admissible under s. 27 of the
Evidence Ordinance. Such information can be relied on
by the prosecution as incriminating evidence against the
accused along with the production or discovery of the
articles in question but the mere production of such
articles by itself would not necessarily prove his
possession.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-85-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of discovery
statement
• Evidentiary value of information admitted under this section: In
an appropriate case the information will constitute sufficient
evidence for the prosecution to establish a prima facie case against
the accused. In Chong Soon Koy v Public Prosecutor [1977] 2 MLJ
78, the Federal Court held that the statement relating to the
discovery of the firearm and ammunition was rightly admitted in
evidence under section 27 of the Evidence Act. In that case the
Appellant, who had been arrested by the Police, gave a police
officer "information with regard to a firearm and some
ammunition which he had hidden in the Berapit Hills in Bukit
Mertajam." According to the evidence of the Police Officer, as a
result of this information, the Police went to the place led by the
Appellant and there the Appellant recovered the firearm and
ammunition. The Federal Court ruled that this evidence alone was
sufficient to justify the conviction of the Appellant by the trial
judge. (See also PP v Lau Kee Hoo [1984] 1 MLJ 110)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-86-320.jpg)

![Confession & the issue of confession
of co-accused
• Principle and scope
• This section is an exception to the general rule that a confession
only affects the party making it. Under this section where one or
more persons than one are being tried for the same offence, a
confession made by one of them can be used against the other.
• The explanation to the section
• Explanation - "offence" as used in this section includes the
abetment of or attempt to commit the offence. In Joygun Bibi v.
State PLD [1966] SC (Pak) 313 clearly illustrates the application
of the explanation to s. 30. The appellant was convicted of abetting
the murder of her husband committed by one Majid. Majid had
confessed to the murder and at the same time implicated the
appellant. The Court there said that, such a confession could be
admitted under s. 30, merely as a matter to be taken into
consideration. See also Goh Joon Tong v PP [1995] 3 SLR 305 & R
v Amrita Govinda 10 Bom HC 497.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-88-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of confession
of co-accused
• Requirements of the section
• a) The person must be tried jointly for the same offence.
• The term ‘tried jointly’ has been judicially defined to mean legally tried jointly,
with the confessing accused for the same offence. For example in an old leading
Indian case Dengo Kandero v. Emperor AIR [1937] Sind. 94 it was ruled that a
confession of a person who is dead and has never been brought to trial is not
admissible under s. 30 as the confession of the co-accused. In this case Dengo,
Amin and one Haji were charged with conspiracy to murder one Rahimbux (the
deceased). The prosecution case was that Dengo had incited Amin and Haji to
murder Rahimbux. They sought to put in the confession of Haji who implicated
Dengo with the offence charged. But Haji died before he could be tried. It was held
that this confession was not admissible under s. 30 as Haji and the accused were
not tried jointly.
• On the other hand in Ram Sarup Singh v. Emperor AIR [1937] Cre. 39 where J
was tried jointly with L for conspiracy to cheat, and the trial proceeded for some
time, and when about six months before the delivery of the judgment, when the
trial had proceeded for more than a year, J died and before his death his confession
was put on record, it was held that J’s confession implicating the accused was
admissible in evidence as there was a joint trial when the confession was
made.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-89-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of confession
of co-accused
• Requirements of the section
• a) The person must be tried jointly for the same offence.
• An essential requirement for the application of s. 30 is the joint trial in for the same
offence. The expression ‘same offence’ means ‘identical offence’. Thus the ‘same
offence’ means the identical offence and not the offence of the same kind. It means
the same specific offence. The test whether the accused are tried for the same
offence is whether the two persons are accused of the same offence of the same
definition arising out of a single transaction; it is only then that the confession of
one may be used against the other though it inculpates (incriminate/blame) himself
through acts separable from those ascribed to his accomplice and capable therefore
of constituting a separate offence from those of the accomplice. So in PP v. Lai Pong
Yuen & Ors. [1968] 1 MLJ 12, where the three respondents were charged with
bribery and corruption under the Prevention of Corruption Act and the Penal
Code, and where one of them made a self-inculpatory confession implicating one of
the co-accused, Ismail Khan J held that this confession was inadmissible under s. 30
because all the three respondents were charged for offences under s. 9(ii) of the
Prevention of Corruption Act. The offences alleged against the first and second
respondents were on different dates. Moreover there were charges in the
alternative under ss. 161 and 165 of the Penal Code against the first two
respondents. There was therefore no joint trial for the same offence for the purpose
of s. 30 of the Evidence Act."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-90-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of confession
of co-accused
• Requirements of the section
• a) The person must be tried jointly for the same offence.
• An essential requirement for the application of s. 30 is the joint trial in for the same
offence. The expression ‘same offence’ means ‘identical offence’. Thus the ‘same
offence’ means the identical offence and not the offence of the same kind. It means
the same specific offence. The test whether the accused are tried for the same
offence is whether the two persons are accused of the same offence of the same
definition arising out of a single transaction; it is only then that the confession of
one may be used against the other though it inculpates (incriminate/blame) himself
through acts separable from those ascribed to his accomplice and capable therefore
of constituting a separate offence from those of the accomplice.
• In Hakim Ali v. State PLD [1960] 31, the Court emphasised that one of the
requisites of applying s. 30 is that the persons must have been tried jointly for the
‘same offence’. The expression ‘same offence’ means the identical offence and not
an offence of the same kind. Where therefore Hakim and Rafique, the two accused
in the above case were jointly tried for the same kind of offence, (namely under s.
411 Penal Code), but the property in respect of which they were charged was
different in the case of each accused (i.e., Hakim being charged under s. 411 Penal
Code for being in possession of currency notes and other articles, Rafique being
charged separately under s. 411 Penal Code for being in possession of stolen
property) it was held that the confession of Rafique though it implicated Hakim,
could not be taken into consideration at all against Hakim.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-91-320.jpg)


![Confession & the issue of confession
of co-accused
• The value of co-accused’s confession under section 30: Further
reference can be made to the Privy Council case of Bhuboni Sahu
v The King AIR 1949 PC 257 where Sir John Beaumont said at
page 257 “Confession of co-accused is obviously evidence of a very
weak type. It does not indeed come within the definition of
evidence contained in section 3, it is not required to be given on
oath, nor in the present of the accused, and it cannot be tested by
cross-examination”. Confession of co-accused can be used only in
support of other evidence and cannot be made the foundation of
conviction. Sir John Beaumont further stated “.. .. Clearly there
must be other evidence. The confession is only one element in the
consideration of all the facts proved in the case; it can be put into
the scale and weighed with the other evidence. Their Lordships
think that the view which has prevailed in most of the High Courts
in India, namely, that the confession of a co-accused can be used
only in support of other evidence and cannot be made the
foundation of a conviction, is correct ....”. See also Surif v PP
[1965] 1 MLJ 36).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-94-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of confession
of co-accused
• Gopal Sri Ram JCA in Juraimi Bin Husin v PP [1998] 1 MLJ 537 states “The way
in which the section must be applied has been fairly worked out in the decided
cases. The evidence against an accused must be first marshalled, putting aside the
confession of the co-accused. If the court is prepared to convict on the other
evidence, it may pray in aid the co-accused's confession to lend assurance to the
conclusion of guilt already arrived at. This was also the view taken by the Federal
Court in Herchun Singh v PP [1969] 2 MLJ 209 i.e. to lend assurance.
• The Singapore courts have now interpreted this section in a different way. In
Ramachandran a/l Suppiah v PP [1993] 2 SLR 671, the Court of Appeal had held
that the section should be construed such as that, as against an accused person, the
confession of a co-accused could only play a supportive role and cannot itself form
the basis of a conviction. In Chin Seow Noi v PP [1994] 1 SLR 135 the Court of
Appeal said that since section 3 defines evidence as includes instead of means and
includes like in Indian Evidence Act, it should be extensive to include evidence
confessions of co-accused. This interpretation has now been consistently followed
by the courts in Singapore (See Abdul Rashid v PP [1994] 1 SLR 119; Lee Yuan
Kwang v PP [1995] 2 SLR 349; & PP v Rozmaan Bin Jusoh [1999] 2 SLR 181). In
Malaysia, interesting to note that there are one case had accept this view like the
case of Indran v PP [1985] 2 MLJ 408 “statements of the co-accused were credible
evidence to commit the applicants for trial”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-95-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of confession
of co-accused
• Do we need corroboration?
• In PP v Yeoh Teck Chye [1981] 2 MLJ 176 the Federal Court said
that the evidence of a co-accused is not similar to the evidence of
an accomplice and that the rule relating to corroboration does not
apply to it. “It is well settled law that where prisoners are tried
jointly, and one of them gives evidence on his own behalf
incriminating a co-prisoner, the prisoner who has given the
incriminating evidence is not placed in the position of an
accomplice, nor does the rule of practice with regard to the
corroboration of an accomplice apply to such a case, for that rule
applies only to witnesses called for the prosecution — see R v
Barnes & Richards 27 Cr App R 154. Section 30 of the Evidence
Act, in substance says the same thing i.e. that the court may take
into account such incriminating evidence against a co-prisoner”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-96-320.jpg)
![Confession & the issue of retracted confession
• In Yap Sow Keong & Anor. v. PP [1947] MLJ 90 the two
appellants were convicted of armed robbery contrary to ss. 392
and 397 of the Penal Code. The sole evidence against the first
appellant was a confession he had made to a magistrative which he
subsequently retracted at the trial, alleging that he had made the
confession because he had been beaten by a detective while in
police custody. He was convicted, the trial Judge obviously
holding that the confession though retracted, was voluntary. On
appeal against his conviction, Willans CJ said that "In our view
the law as to the admissibility of retracted confessions in evidence
is clear, and put shortly it is that an accused person can be
convicted on his own confession, even when it is retracted, if the
Court is satisfied of its truth”.
• In Osman & Anor. v. PP [1967] 1 MLJ 137 the appellants were
convicted of murder. The evidence which had led to their
conviction was again the retracted confessions of the appellants.
The trial Judge after satisfying himself that the appellants’
confession were made voluntarily, convicted them on these
confessions, even though they were later retracted and not
corroborated by other evidence.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-97-320.jpg)

![Admission & the issue of without prejudice communication
privilege
• The "without prejudice" rule is lucidly stated in
a trilogy of local cases. In Malayan Banking Bhd
v. Foo See Mooi [1981] 2 MLJ 17, 18 FC Chong
Min Tat FJ stated that: “It is settled law that
letters written without prejudice are
inadmissible in evidence of the negotiations
attempted. This is in order not to fetter
(restrain) but to enlarge the scope of the
negotiations, so that a solution acceptable to
both sides can be easily reached”. In Oh Kuang
Liang v. Associated Wood Industries Sdn Bhd
[1995] 2 CLJ 961 Justice Abdul Malik Ishak
expressed his considered view that the "'without
prejudice' rule applies generally to exclude all
negotiations genuinely aimed at settlements
whether oral or in writing from being given in
evidence". Four years later in Dusun Desaru
Sdn Bhd v. Wong Ah Yu [1999] 2 CLJ 749, at p
755 the learned judge stated the rule in his own
inimitable lucid style when he said: “… without
prejudice communications can be said to be
privileged or for a better nomenclature
privileged communications”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-99-320.jpg)
![Admission & the issue of without prejudice communication
privilege
• Rationale underlying the rule
• The broad public policy of encouraging litigants
to settle their differences is acknowledged to be
the underlying purpose of the "without
prejudice" rule. In the leading House of Lord's
case of Rush & Thompkins Ltd v. Greater London
Council & Anor, [1998] 3 All ER 737 where Lord
Griffiths (at pp 739-740) aptly observed that the
rule "is founded on the public policy of
encouraging litigants to settle their differences
rather than litigate them to a finish”. It is
nowhere more clearly expressed than in the
judgment of Oliver LJ in Cutts v. Head [1984] 1
All ER 597 at 605-606: “It is that parties should
be encouraged so far as possible to settle their
disputes without resort to litigation and should
not be discouraged by the knowledge that
anything that is said in the course of such
negotiations (and that includes, of course, as
much the failure to reply to an offer as an actual
reply) may be used to their prejudice in the
course of the proceedings”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-100-320.jpg)
![Admission & the issue of without prejudice communication
privilege
• Rationale underlying the rule
• They should, as it was expressed by Clauson J in
Scott Paper Co. v Drayton Paper Works Ltd. [1927]
44 RPC 151 at 157 be encouraged freely and
frankly to put their cards on the table … The
public policy justification, in truth, essentially
rests on the desirability of preventing statements
or offers made in the course of negotiations for
settlement being brought before the court of
trial as admissions on the question of liability”.
• In fact a decade earlier in the English case of
Tramountana Armadora SA v. Atlantic Shipping
Co SA, [1978] 2 All ER 870 Donaldson LJ had
pointed out that it is in the public interest that
there should be a procedure whereby the parties
to a dispute can discuss their differences freely
and frankly to make offers of settlement without
fear of being embarrassed by such exchanges in
case the settlement was not made.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-101-320.jpg)
![Admission & the issue of without prejudice communication
privilege
• The rule is not absolute
• The "without prejudicial" material will be
admissible if the issue is whether or not the
negotiations resulted in an agreed settlement.
The court will not allow the phrase to be
used to exclude an act of bankruptcy (Re
Daintrey, ex p Holt [1893] 2 QB 116, or to
suppress a threat if an offer is not accepted
(Kitcat v Sharp [1882] 48 LT 64). In
certain circumstances, the "without
prejudice" material may be looked at to
determine a question of costs after
judgment has been given (Cutts v Head
[1984] 1 All ER 597), an admission of an
"independent fact" in no way connected
with the merits of the case is admissible
even if made in the course of negotiations
for a settlement (Waldrige v Kennison
[1794] 1 Esp 143).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-102-320.jpg)
![Admission & the issue of without prejudice communication
privilege
• The privilege continues even after a
compromise has been reached unless it
has been waived. Per Vincent J in Boss
s/o Ramasamy v Penang Port Sdn Bhd
[1996] 5 MLJ 511 “I am mindful that
there are many authorities for the legal
proposition that unless expressly or
impliedly waived, the privilege which
(for reasons of public policy that out-of-
court settlements should be encouraged)
attaches to correspondence in the course
of genuine settlement negotiations,
continues to operate even after
negotiations have been concluded and a
settlement reached (see the decision of
the House of Lords in Rush & Tompkins
Ltd v Greater London Council [*517] &
Anor [1989] AC 1280)”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-103-320.jpg)
![Admission & the issue of without prejudice communication
privilege
• When evidence of "Without
Prejudice" communications may
be admissible in evidence. Evidence
of negotiations becomes admissible
when action is taken by the parties
after the conclusion of an
agreement. In Malayan Banking
Bhd v. Foo See Mooi [1981] 2 MLJ
17 where Chang Min Tat FJ had
already clearly stated that: “But it
is also settled law that where the
negotiations conducted without
prejudice lead to a settlement, then
the letters become admissible in
evidence of the terms of the
agreement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-104-320.jpg)
![Admission & the issue of without prejudice communication
privilege
• Does section 23 cover plea negotiations or
bargaining in criminal cases?
• This issue has not been expressly raised in
the Malaysian courts, perhaps for the simple
reason that plea bargaining is not officially
condoned. Neither are there any reported
cases on the issue either from India or Brunei
where s. 23 of their respective Evidence Laws
are in pari materia our s. 23.
• The ground-breaking judgment of the
Singapore High Court PP v. Knight Glenn
Jeyasingam, [1999] 2 SLR 499 addressed this
issue. In this case Yong Pung How CJ had
the opportunity to deliberate on this issue,
and after surveying the relevant state of
the law in USA, Canada, Australia and
England, concluded that in Singapore plea
negotiations too should be accorded the
"without prejudice" privilege against
disclosure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10admission-150301030645-conversion-gate01/85/10-admission-105-320.jpg)
