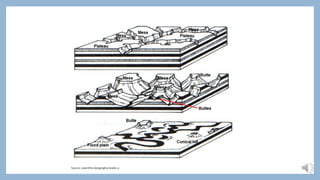
The document discusses various geological features and processes involved in the formation of hilly landscapes, basaltic plateaus, canyon landscapes, and karoo terrains. It explains how strata, erosion, climate, and rock types influence these landscapes, highlighting specific formations such as mesas, buttes, and badlands. The processes of tectonic uplift, cap rock formation, and scarp retreat are also examined in relation to landscape evolution.