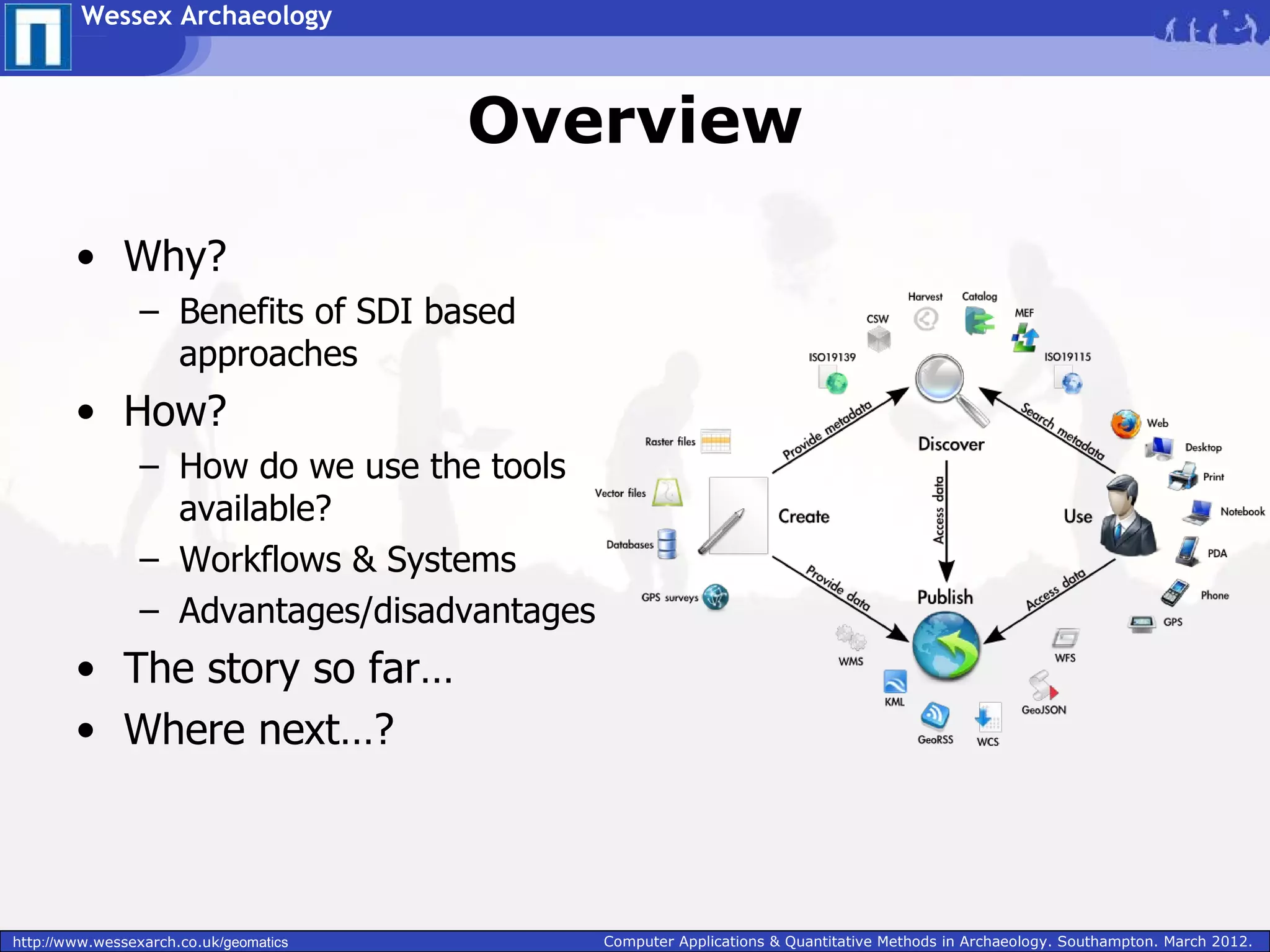
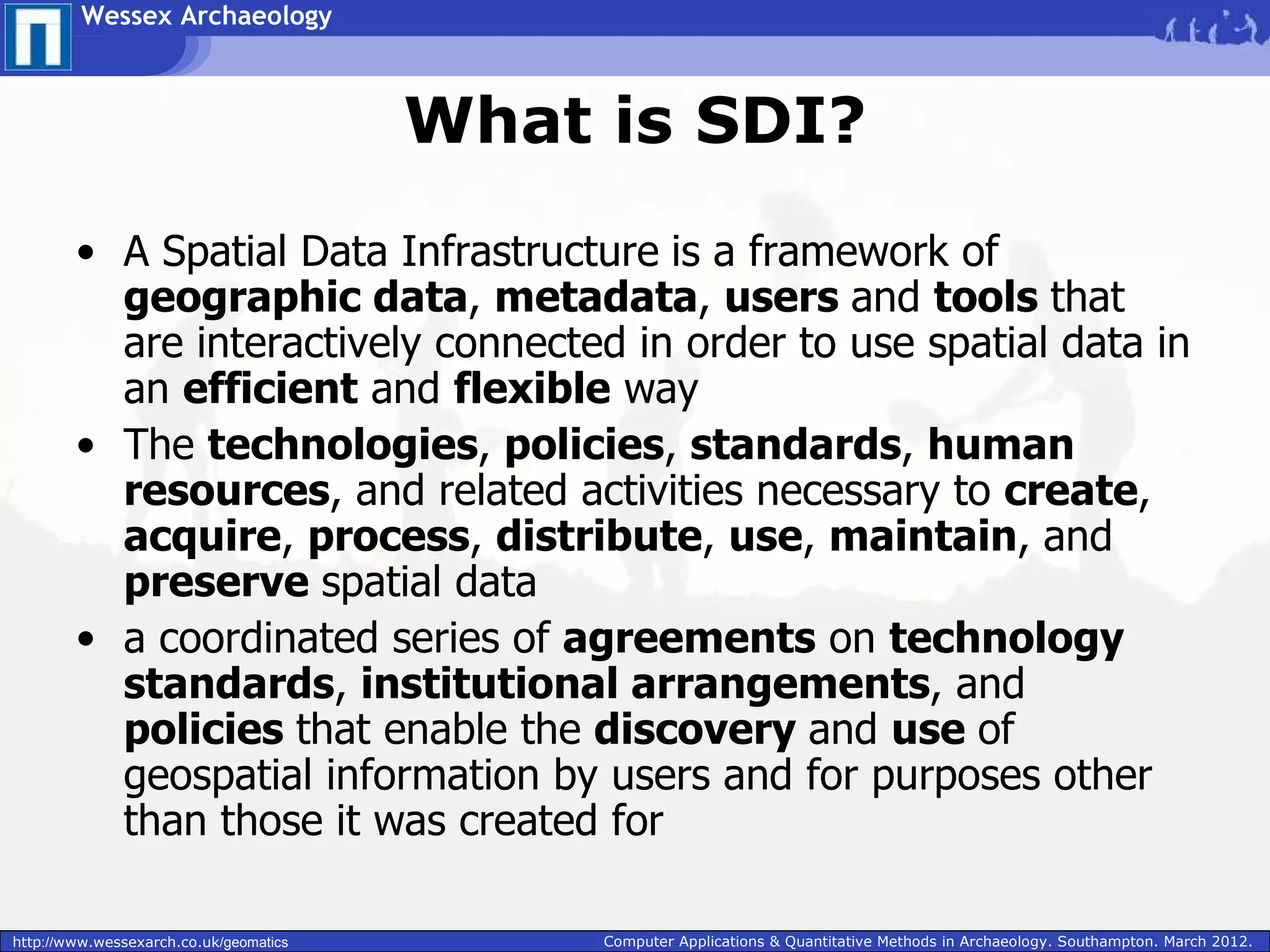
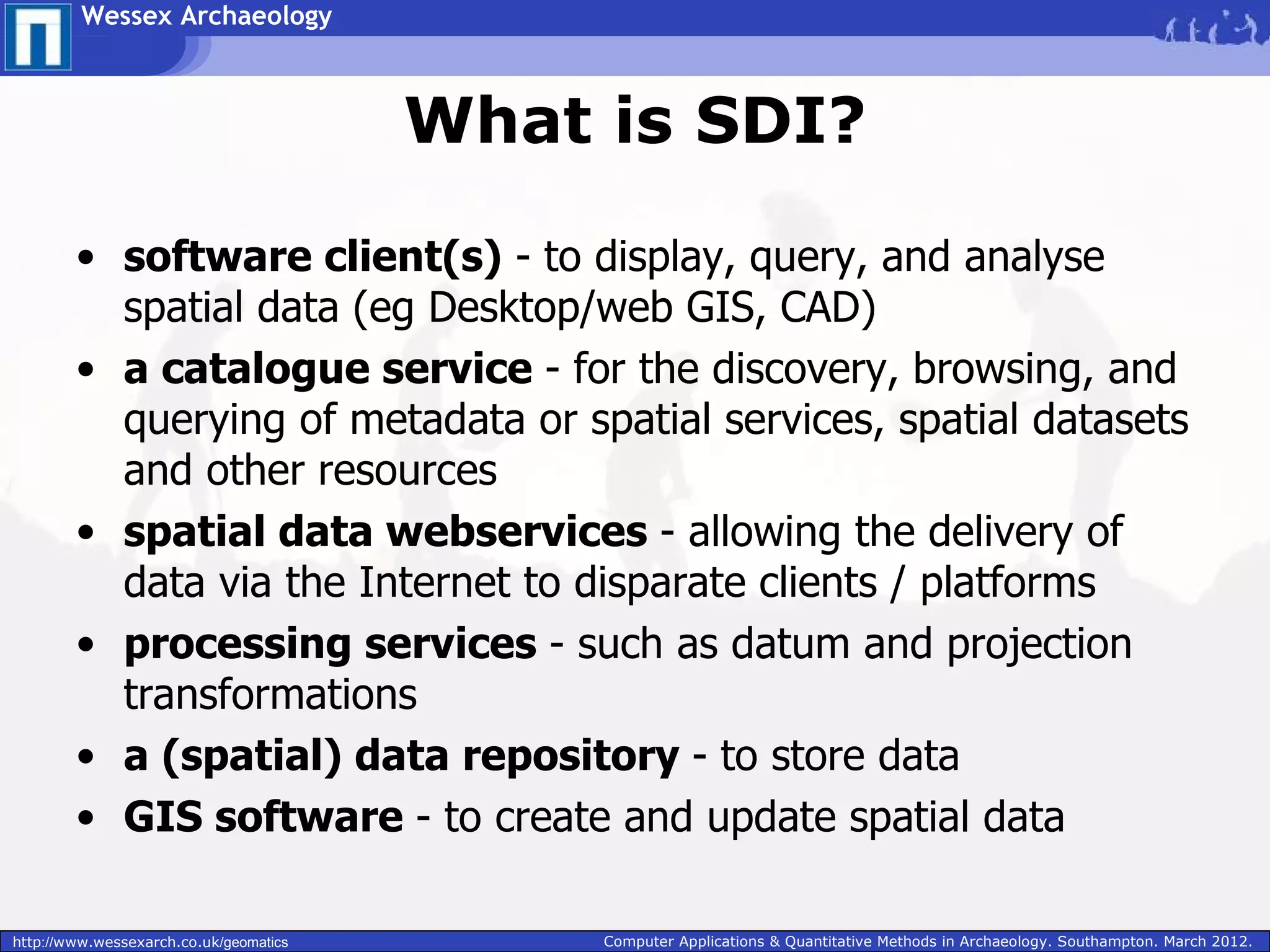
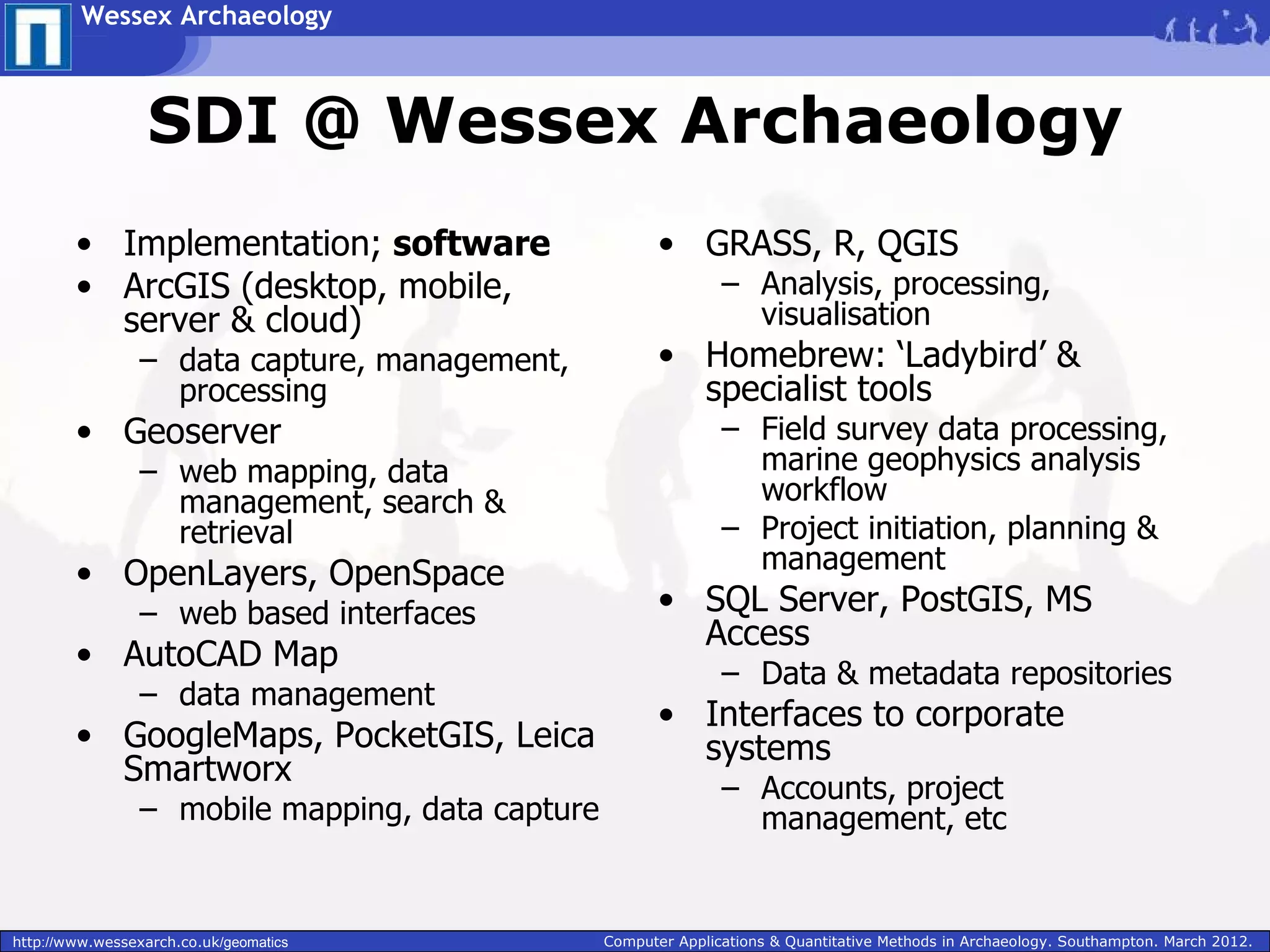
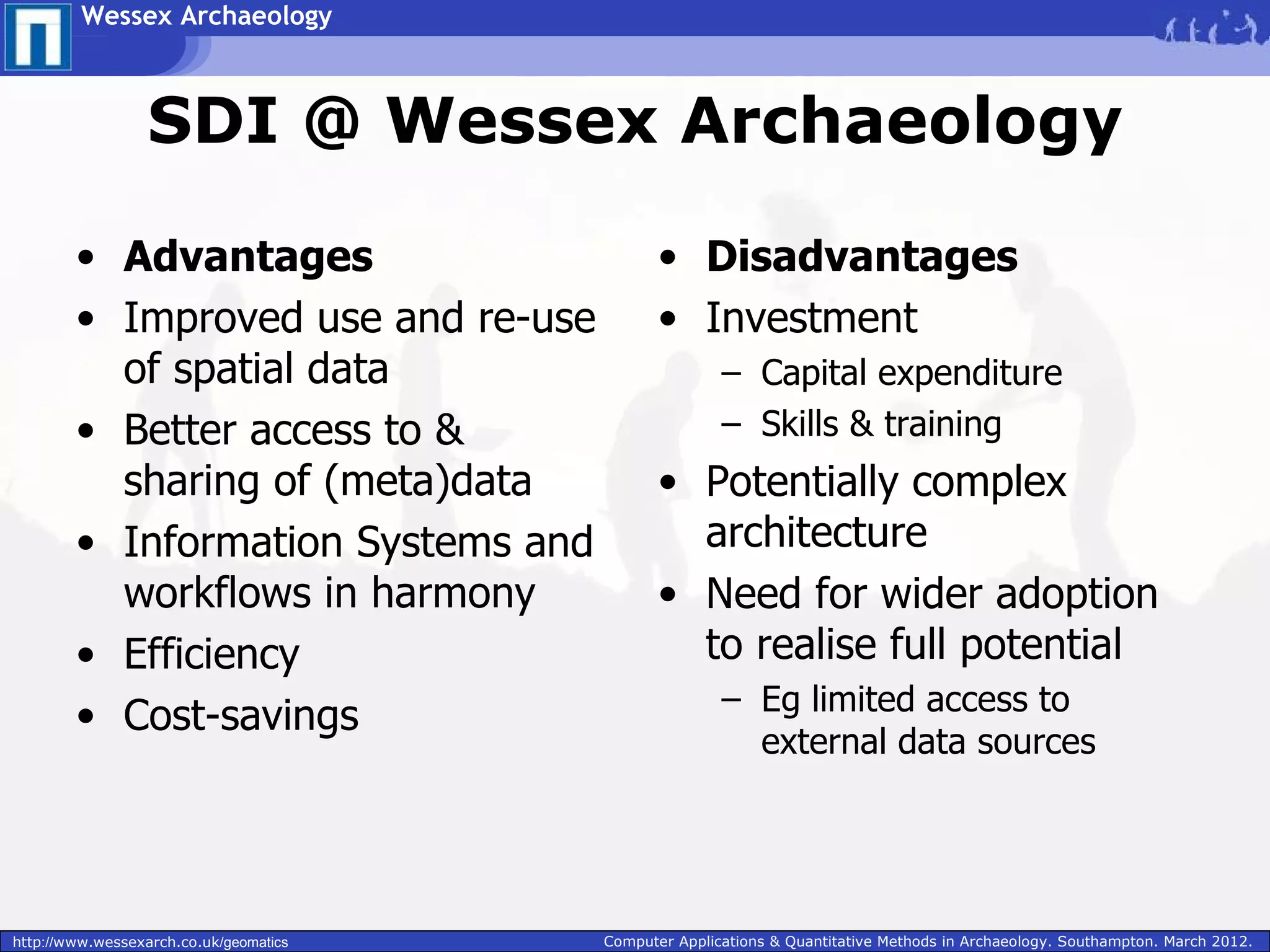
Wessex Archaeology is exploring the benefits of implementing a Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) to better manage their large volumes of spatial archaeological data. An SDI would improve data quality, accessibility, and efficiency by integrating disparate resources through common technology standards and policies. Wessex Archaeology has begun implementing an SDI using tools like ArcGIS, QGIS and GeoServer to capture, store, analyze and share spatial data both internally and with external partners and databases. Further adoption of SDI approaches across the heritage sector could maximize data sharing and reuse.