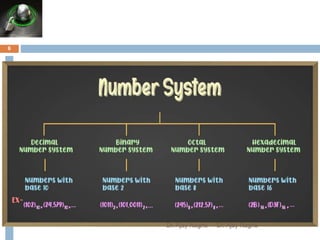
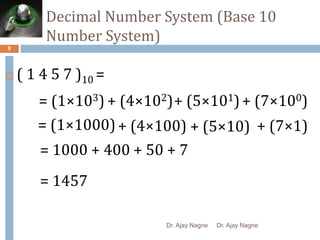
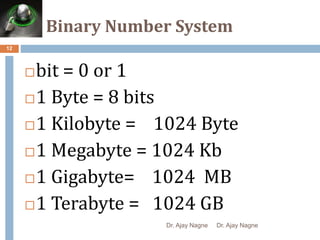
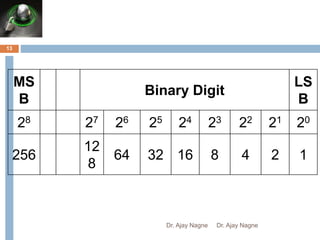
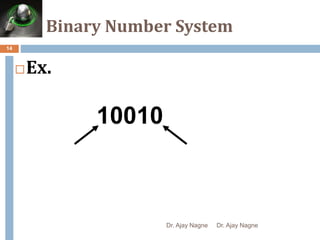
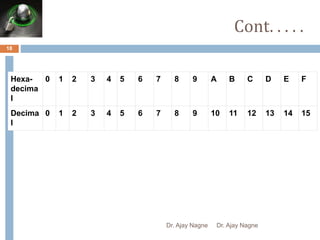
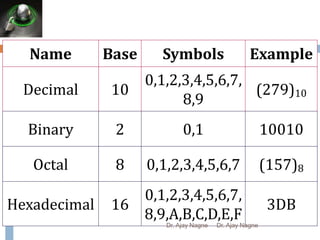
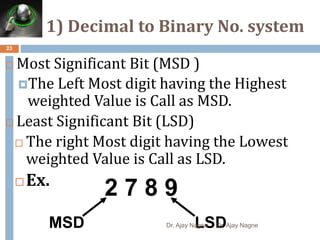
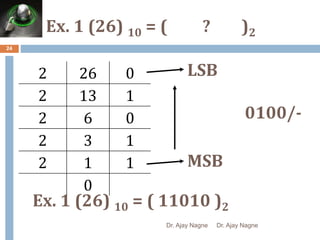
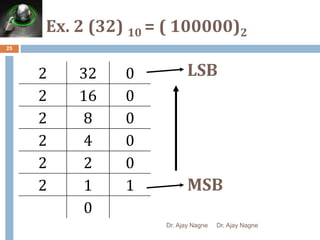
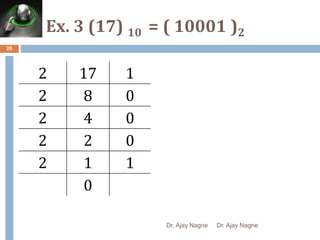
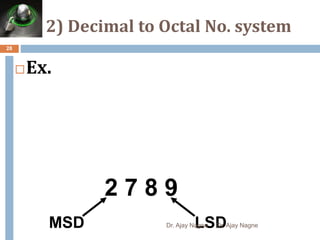
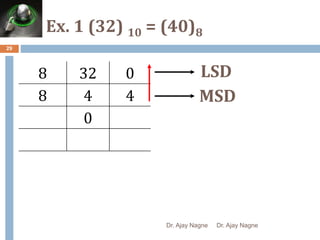
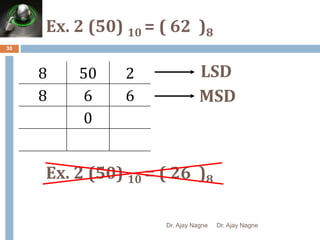
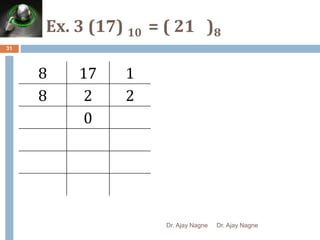
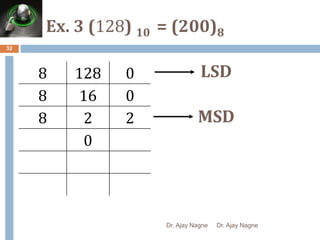
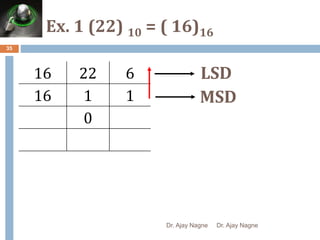
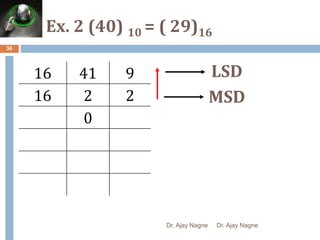
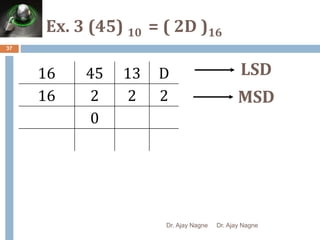
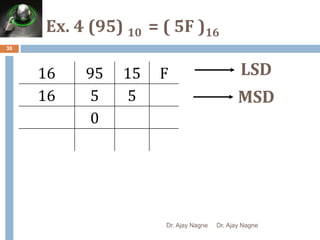
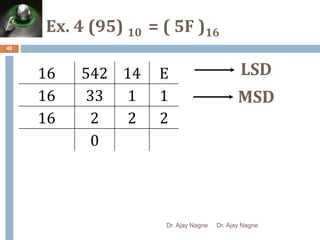
The document discusses different number systems, including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. It explains that a number system allows numbers to be represented using symbols in a consistent way and defines the base of each system. Conversion between number systems is demonstrated through examples, such as converting the decimal number 32 to the binary number 100000 or converting 95 from decimal to the hexadecimal 5F. Key aspects like most/least significant bits or digits and place values are also outlined.