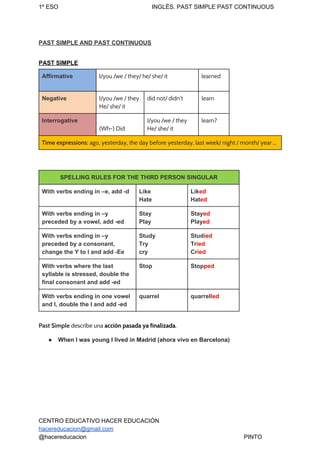
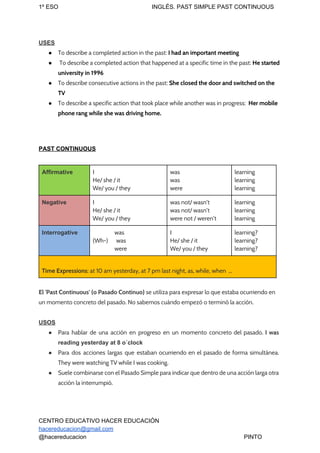
The document provides information on the past simple and past continuous tenses in English. It defines each tense and how they are formed affirmatively, negatively, and interrogatively. It also discusses the differences between the two tenses and provides examples of their common uses, including describing completed actions in the past versus ongoing actions at a specific time in the past. It concludes with exercises for students to practice using the correct past tense based on the context.