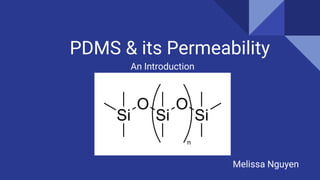
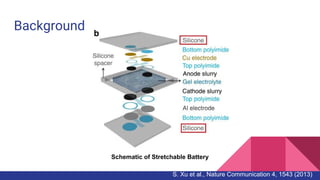
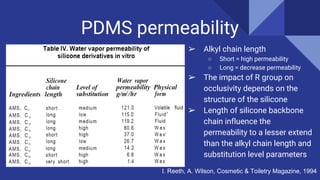
PDMS, or poly(dimethylsiloxane), is an optically clear, inert, non-toxic, and non-flammable material that is elastic at low temperatures and viscoelastic at high temperatures. It is used in flexible electronics and gas/liquid separations due to its flexibility and low cost. Permeability measures the intrinsic permeation rate of a species through a material and is determined by the diffusion coefficient and solubility coefficient. PDMS permeability can be modified by changing the degree of substitution, silicone backbone chain length, structure, and alkyl chain length - with shorter alkyl chains and longer backbones increasing permeability. Further research aims to figure out reaction mechanisms to add more hydrocarbon chain length and decrease PDMS permeability