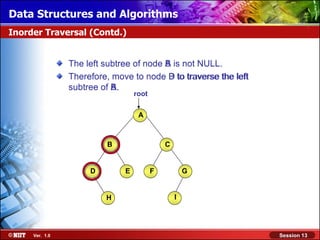
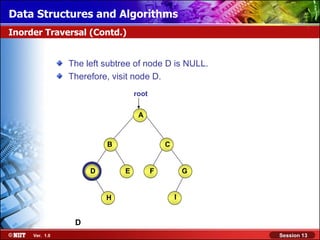
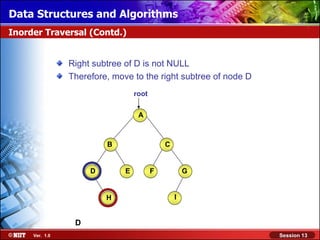
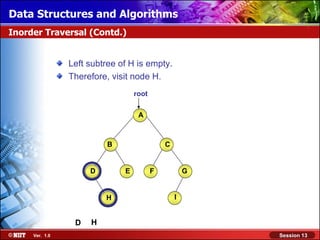
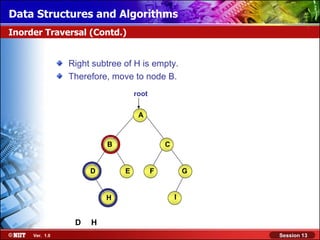
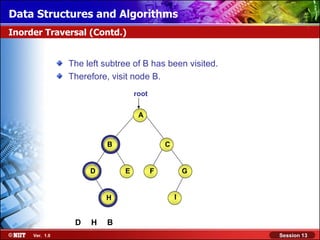
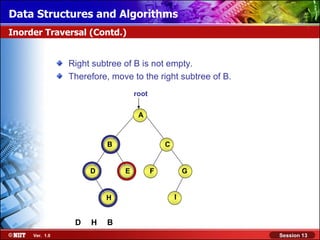
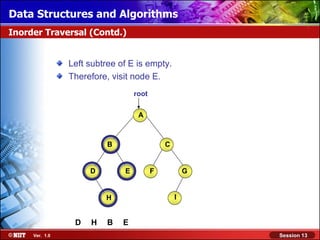
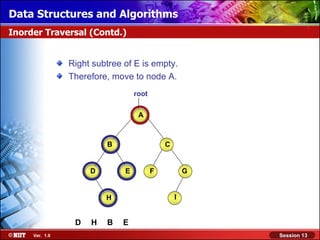
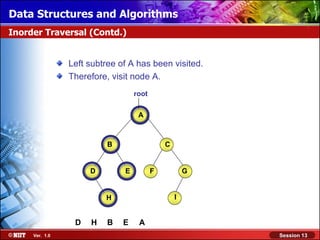
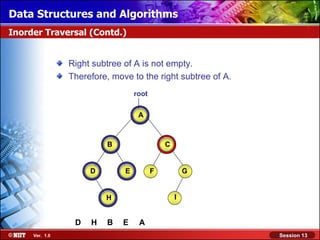
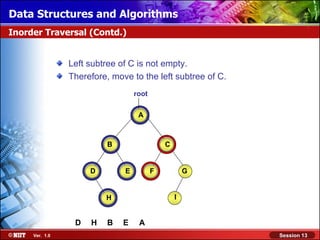
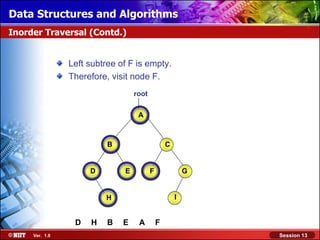
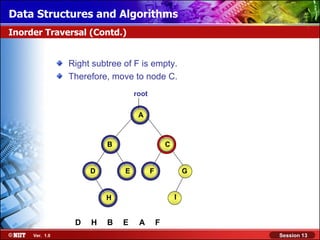
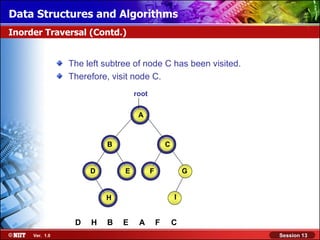
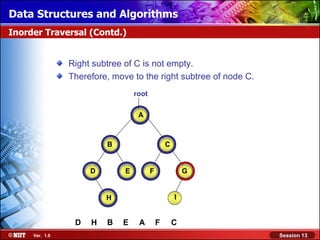
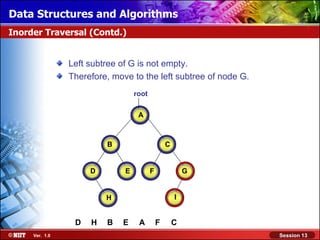
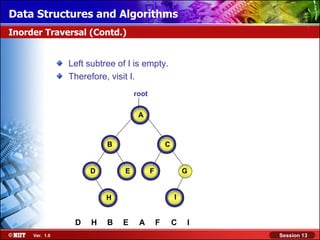
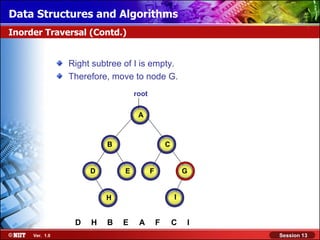
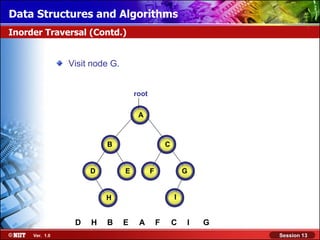
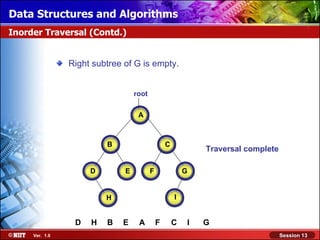
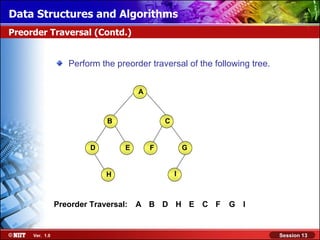
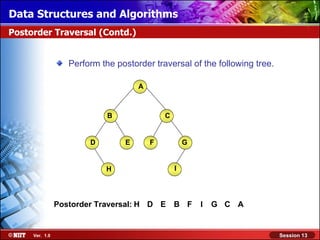
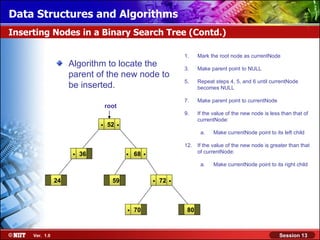
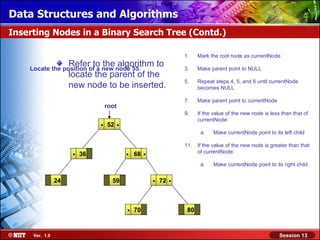
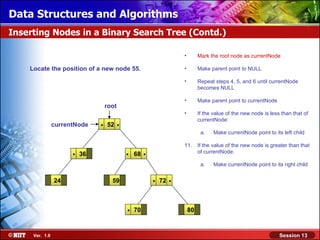
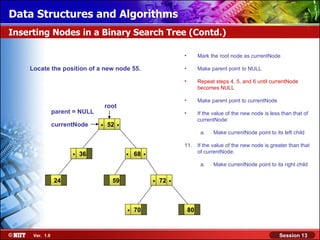
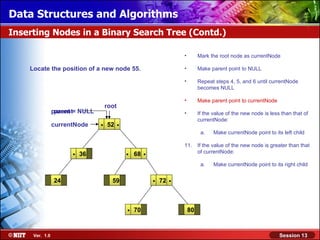
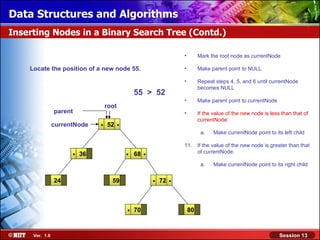
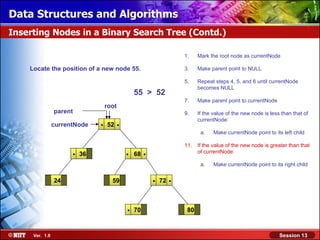
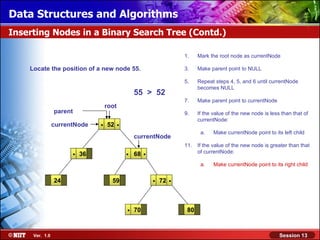
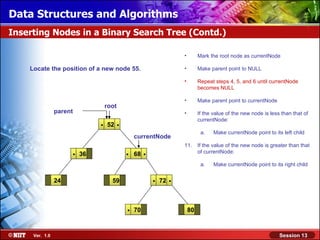
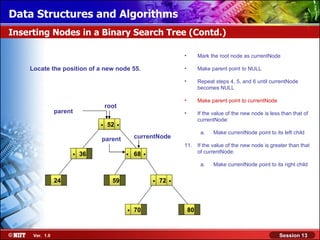
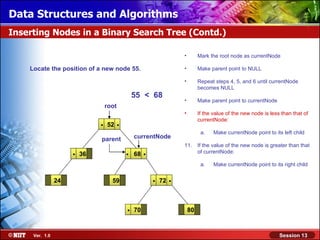
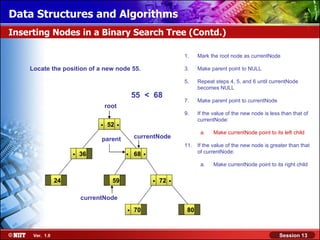
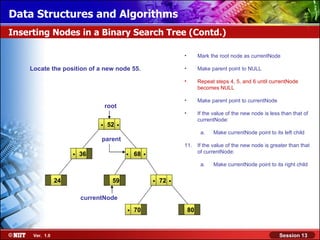
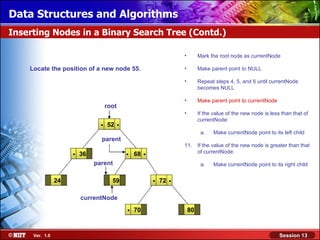
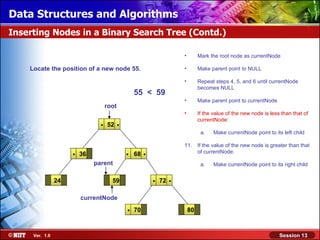
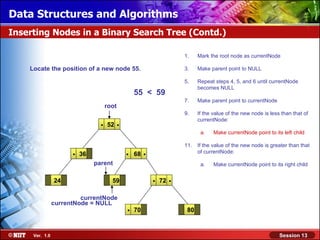
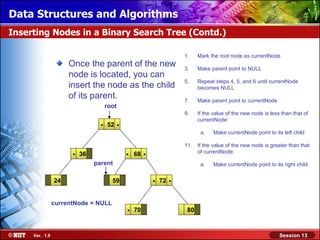
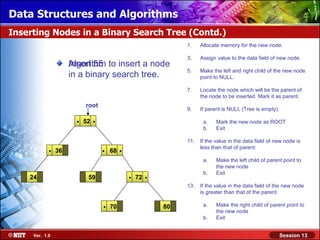
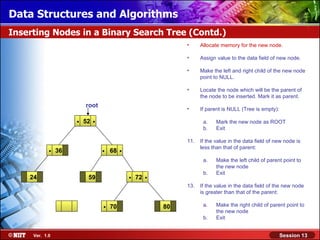
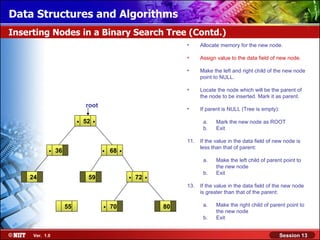
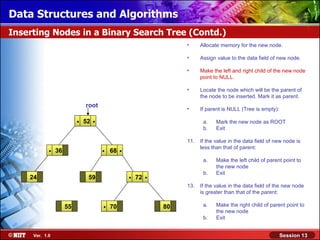
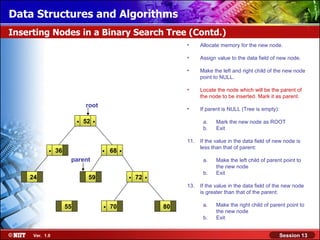
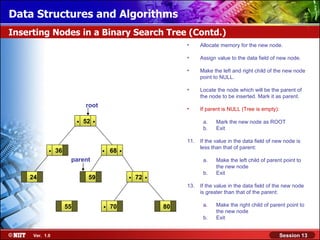
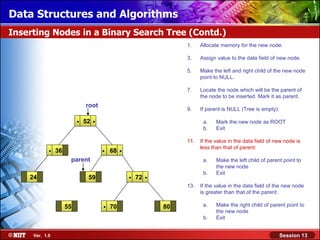
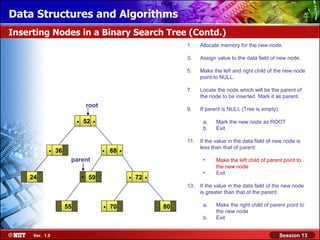
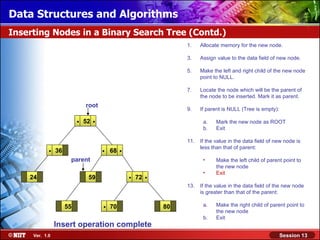
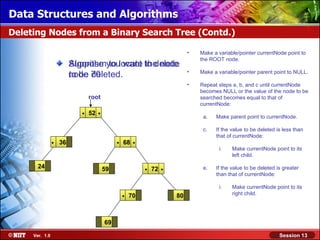
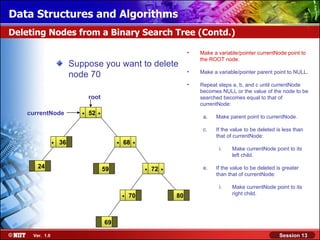
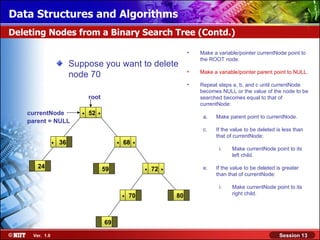
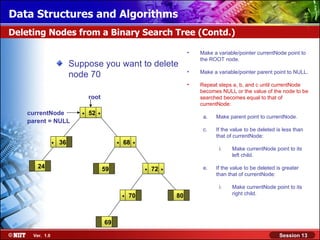
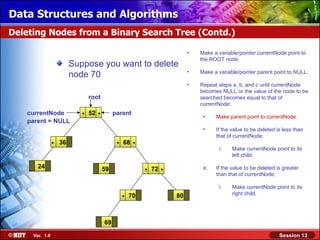
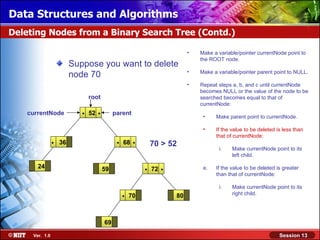
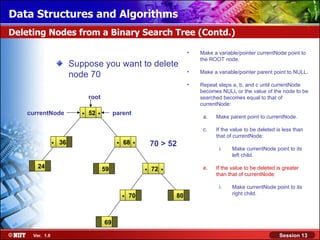
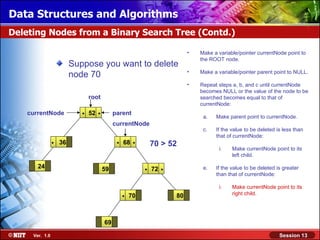
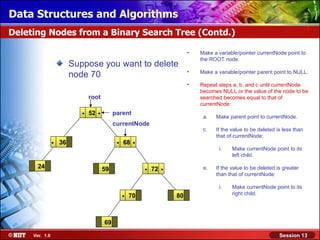
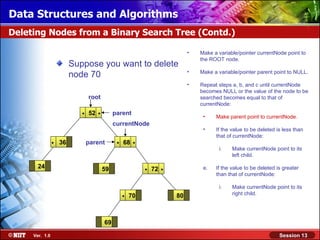
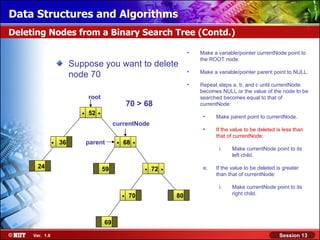
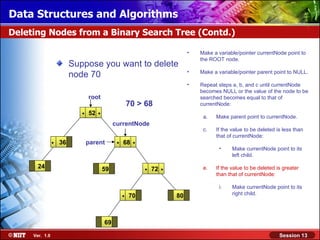
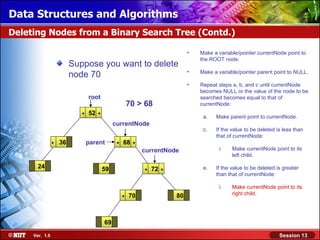
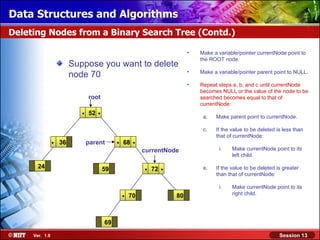
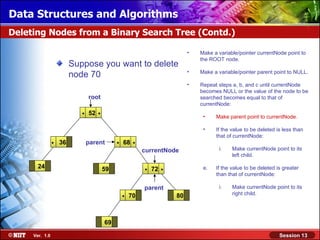
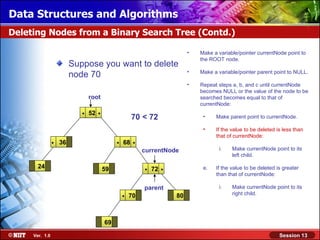
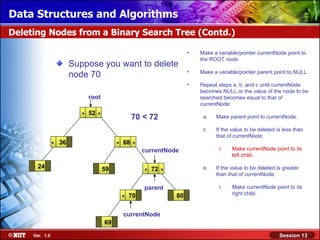
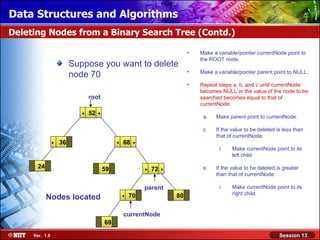
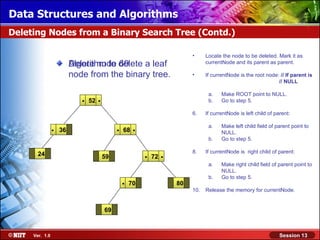
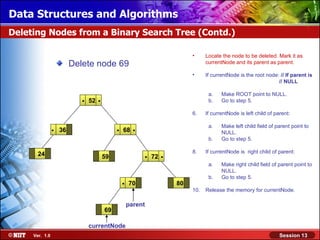
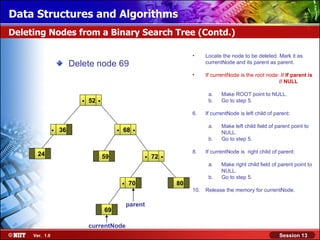
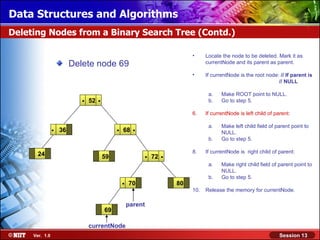
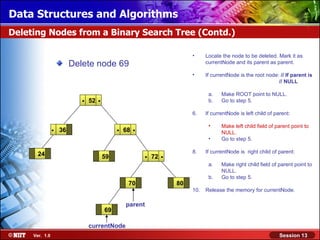
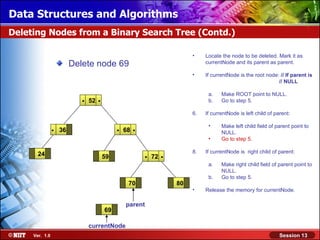
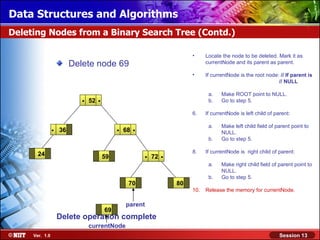
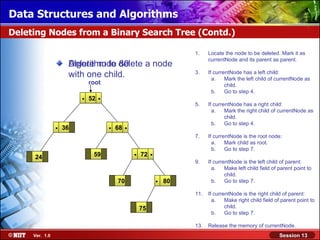
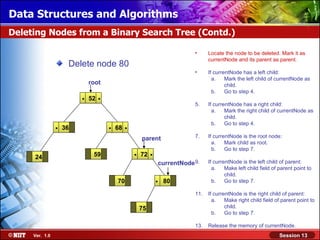
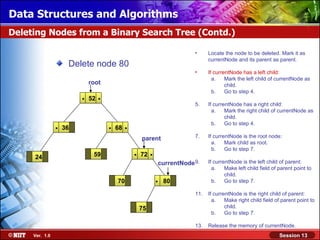
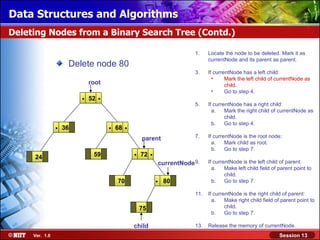
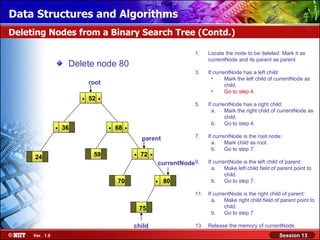
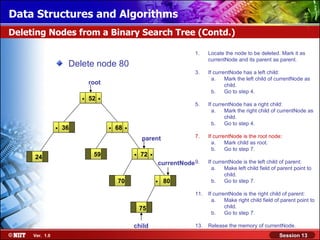
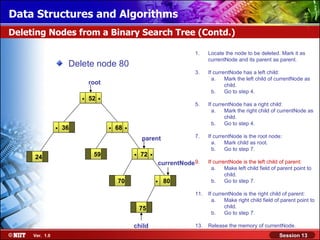
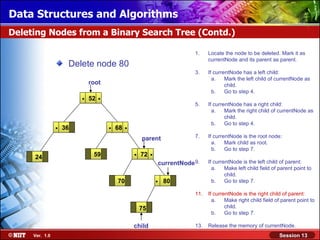
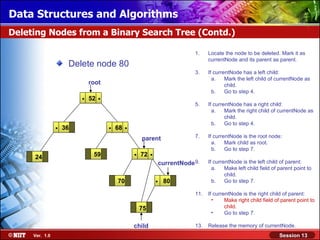
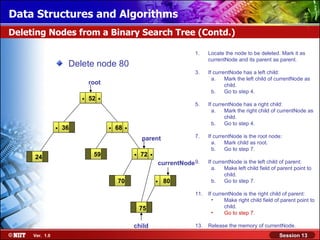
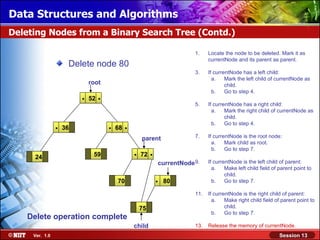
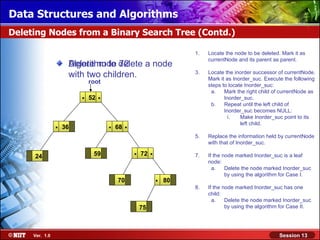
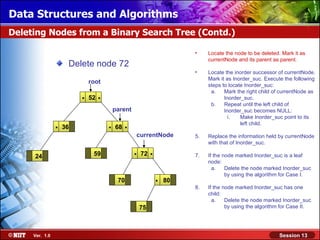
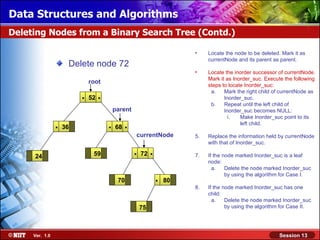
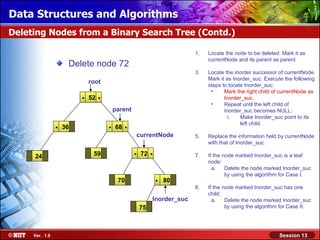
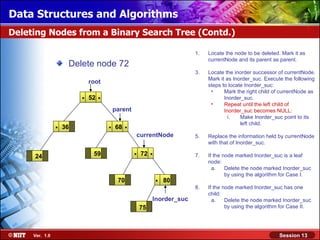
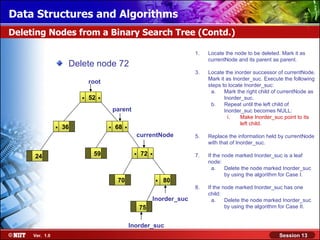
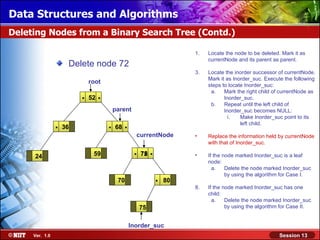
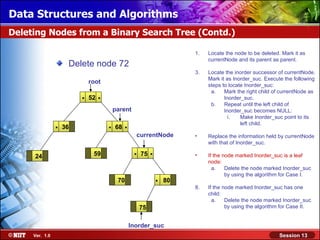
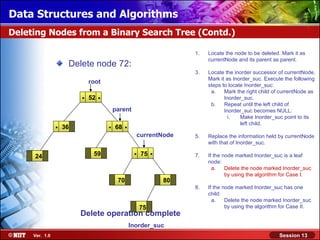
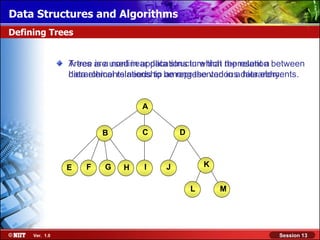
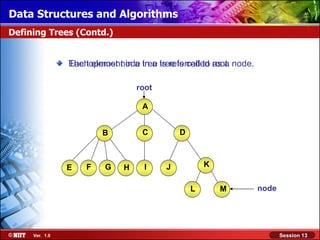
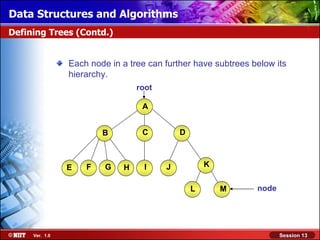
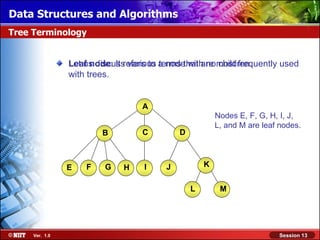
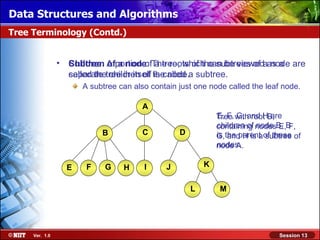
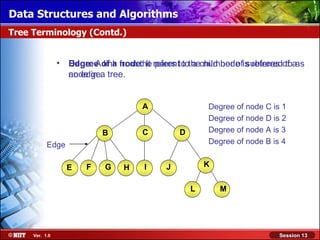
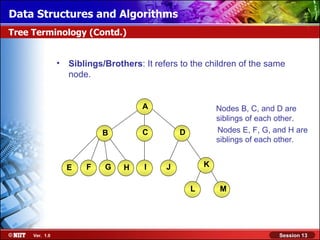
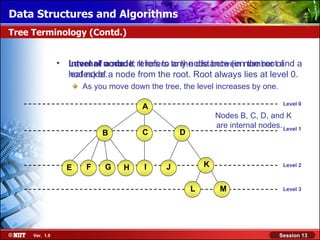
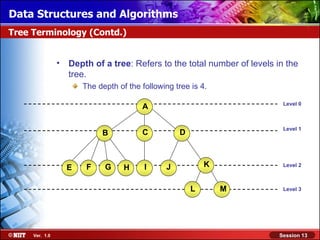
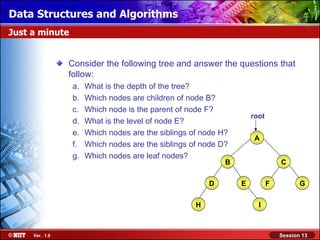
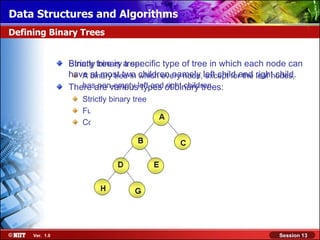
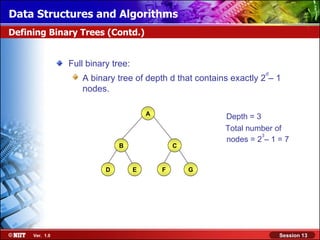
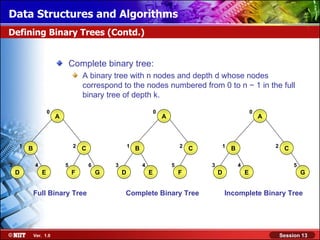
This document discusses binary trees and their terminology. It introduces binary trees as a type of tree where each node has at most two children, namely a left child and a right child. The document then defines various binary tree types and provides examples to illustrate tree terminology such as root, leaf nodes, subtrees, siblings, levels, and depth.


![Data Structures and Algorithms
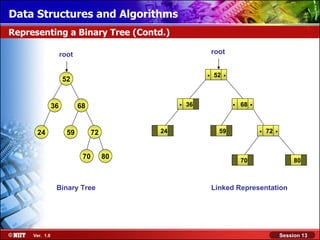
Representing a Binary Tree
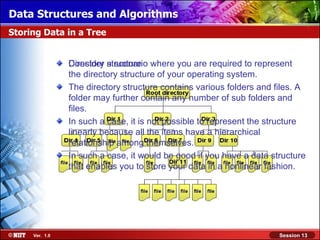
Array representation of binary trees: If there are n nodes in a binary
All the nodes are represented as the elements for any node with index
tree, then of an array.
i, where 0 < i < n – 1:
Parent of i is at (i – 1)/2.
A [0] Left child of i is at 2i + 1:
– If 2i + 1 > n – 1, then
B [1] the node does not
0 have a left child.
C [2]
Right child of i is at 2i + 2:
A
– If 2i + 2 > n – 1, then
D [3]
the node does have a
1 2 right child.
E [4]
B C
3 4 5 6 F [5]
D E F G
G [6]
Binary Tree Array Representation
Ver. 1.0 Session 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/09dsandalgorithmsession13-120424161937-phpapp02/85/09-ds-and-algorithm-session_13-17-320.jpg)