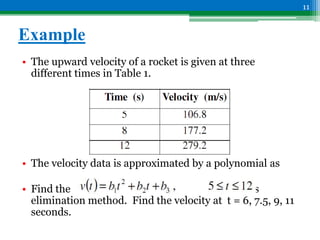
Gaussian elimination is a method for solving systems of linear equations. It involves two main steps: forward elimination and back substitution. Forward elimination reduces the equations to an upper triangular system with one unknown in each equation. Back substitution then solves for the unknowns, starting from the last equation. Partial pivoting may be used to avoid division by zero and reduce rounding errors. It involves row swapping based on the largest element in each column during forward elimination.