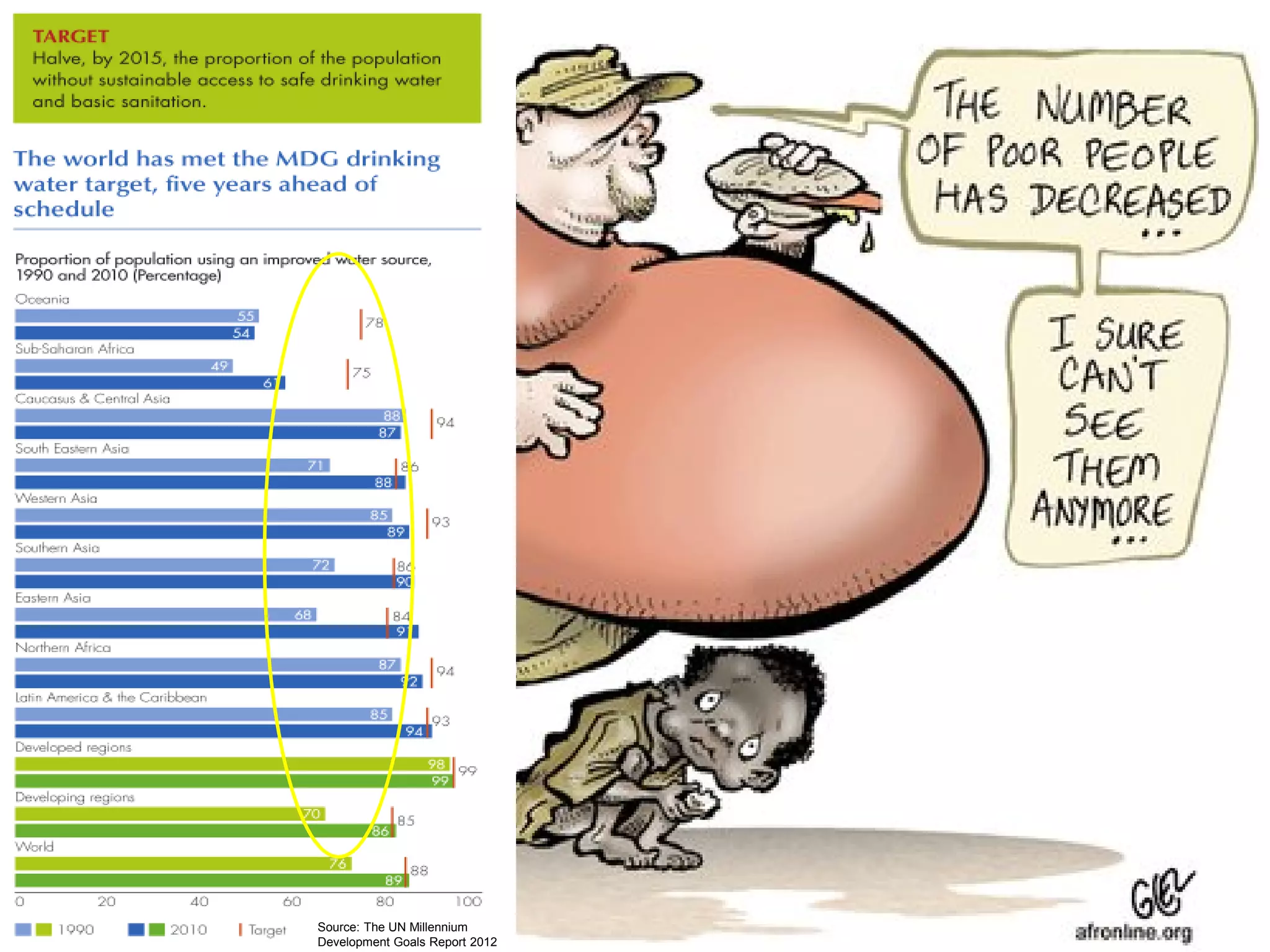
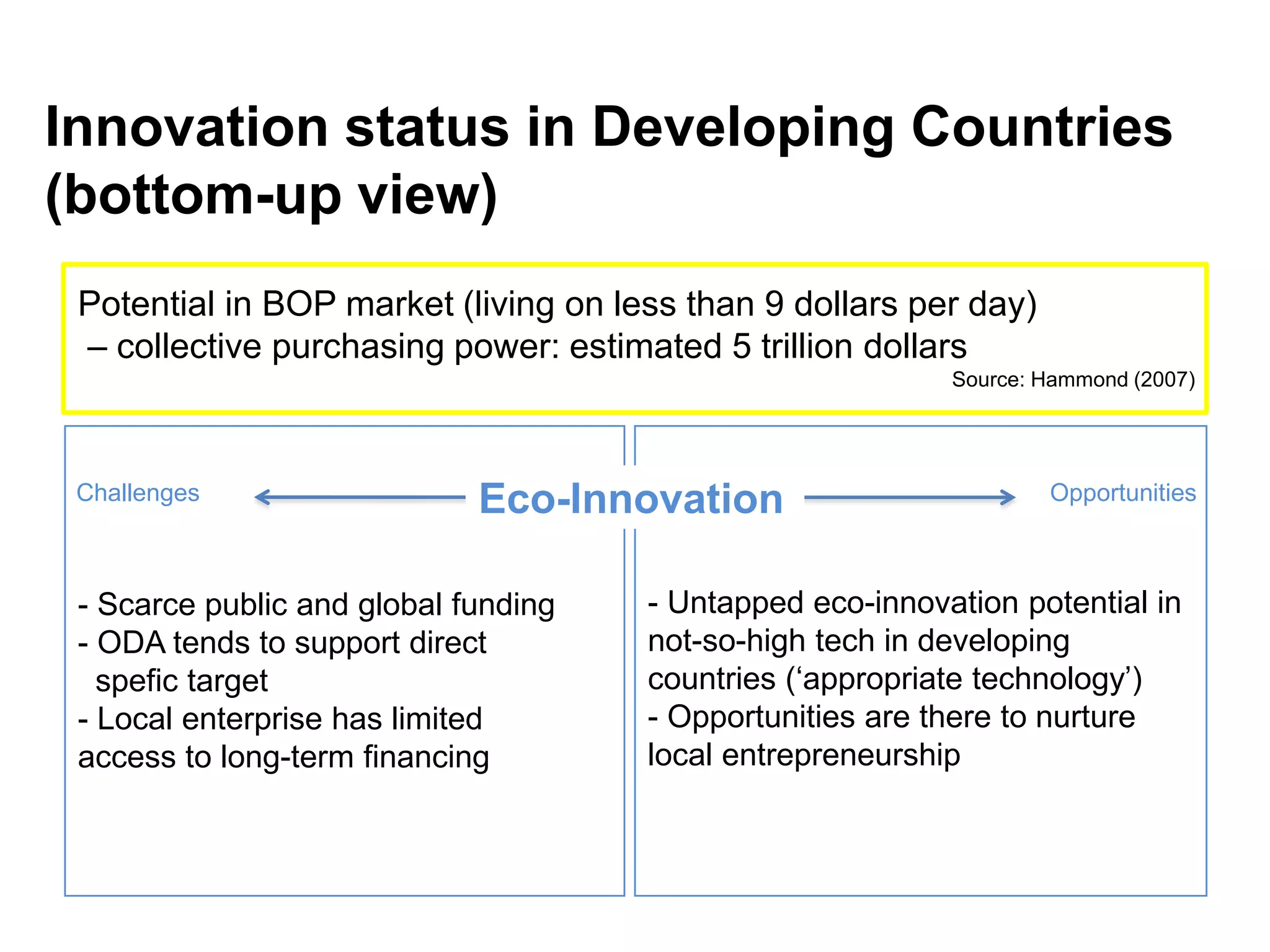
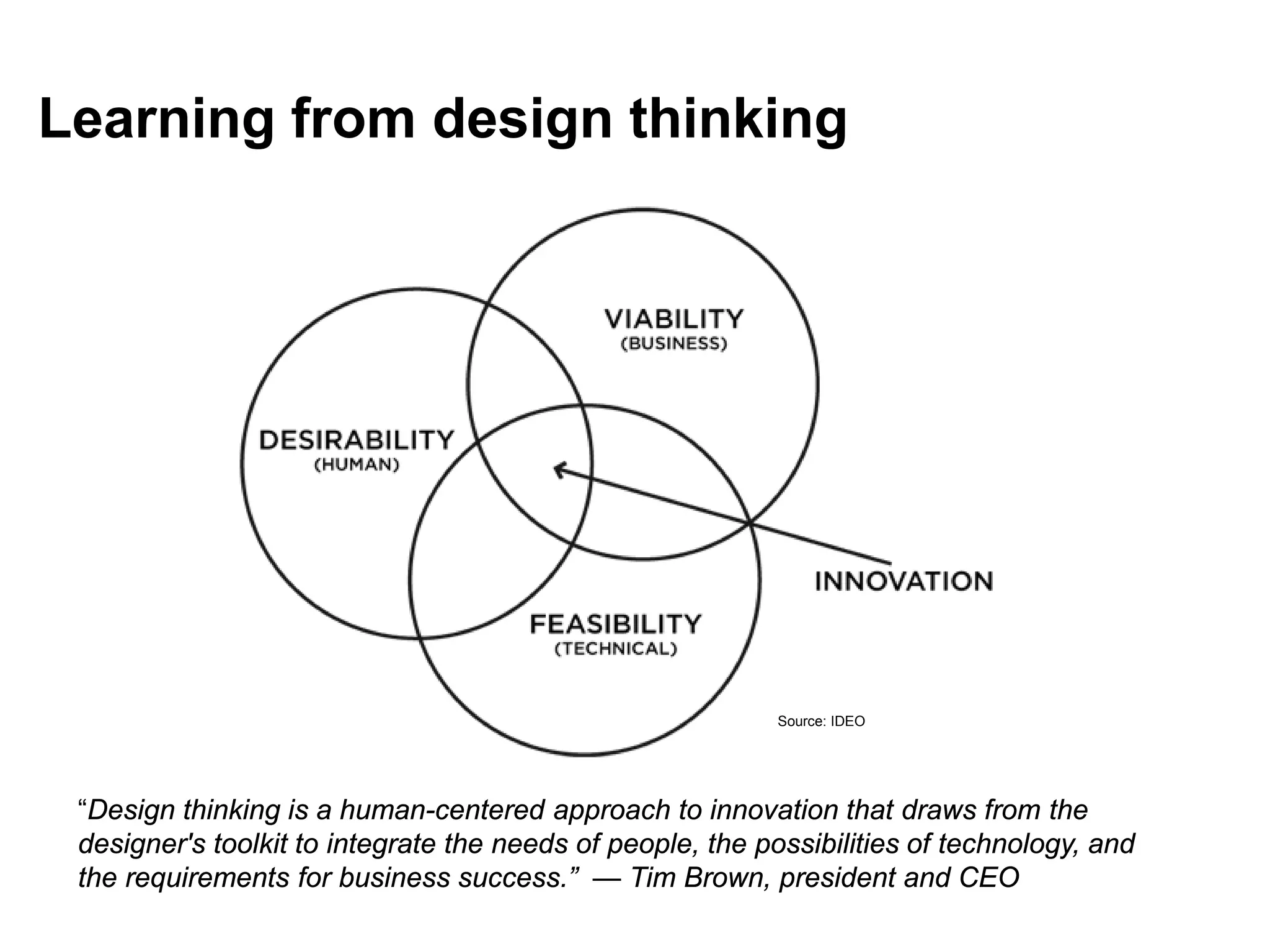
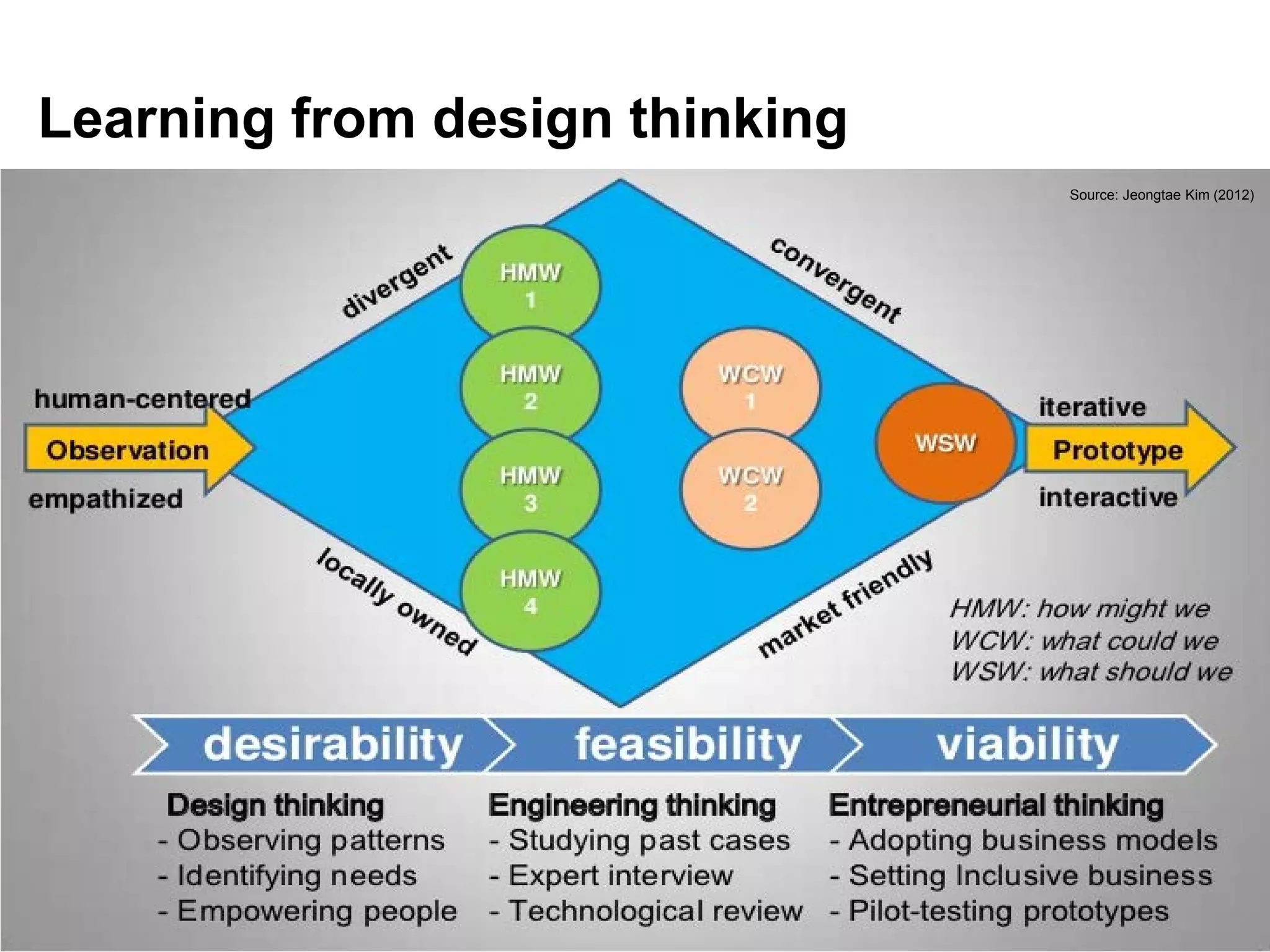
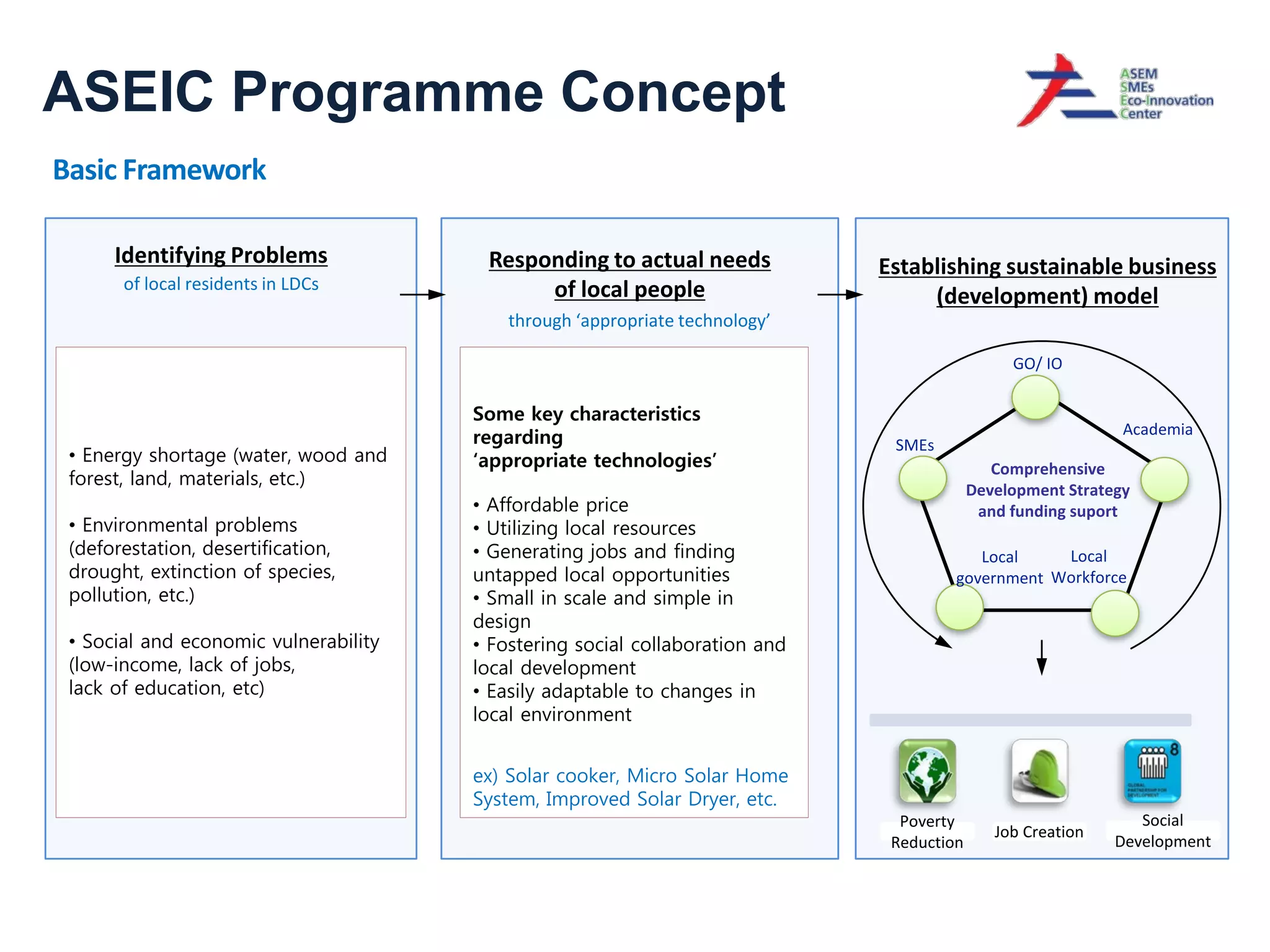
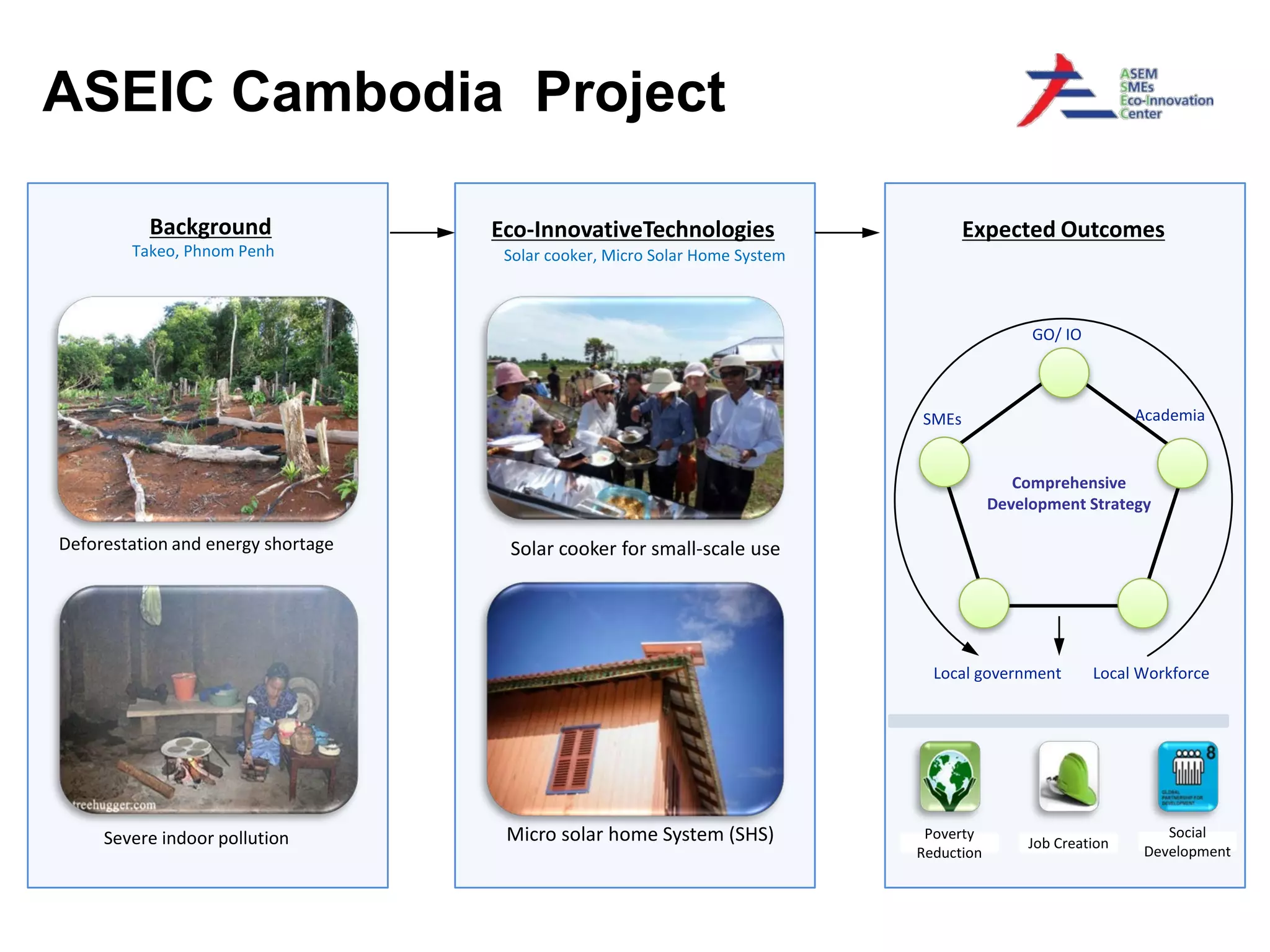
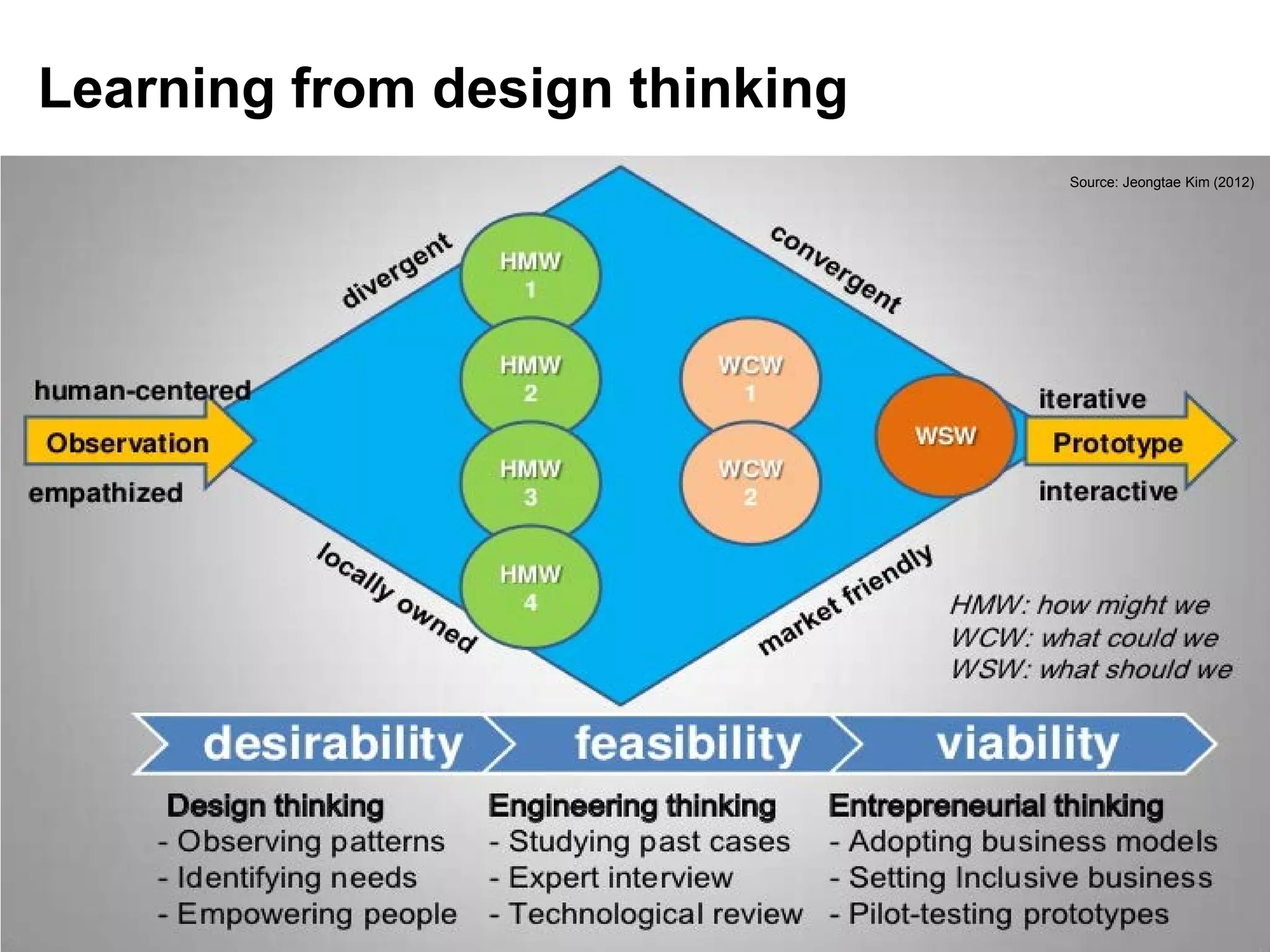
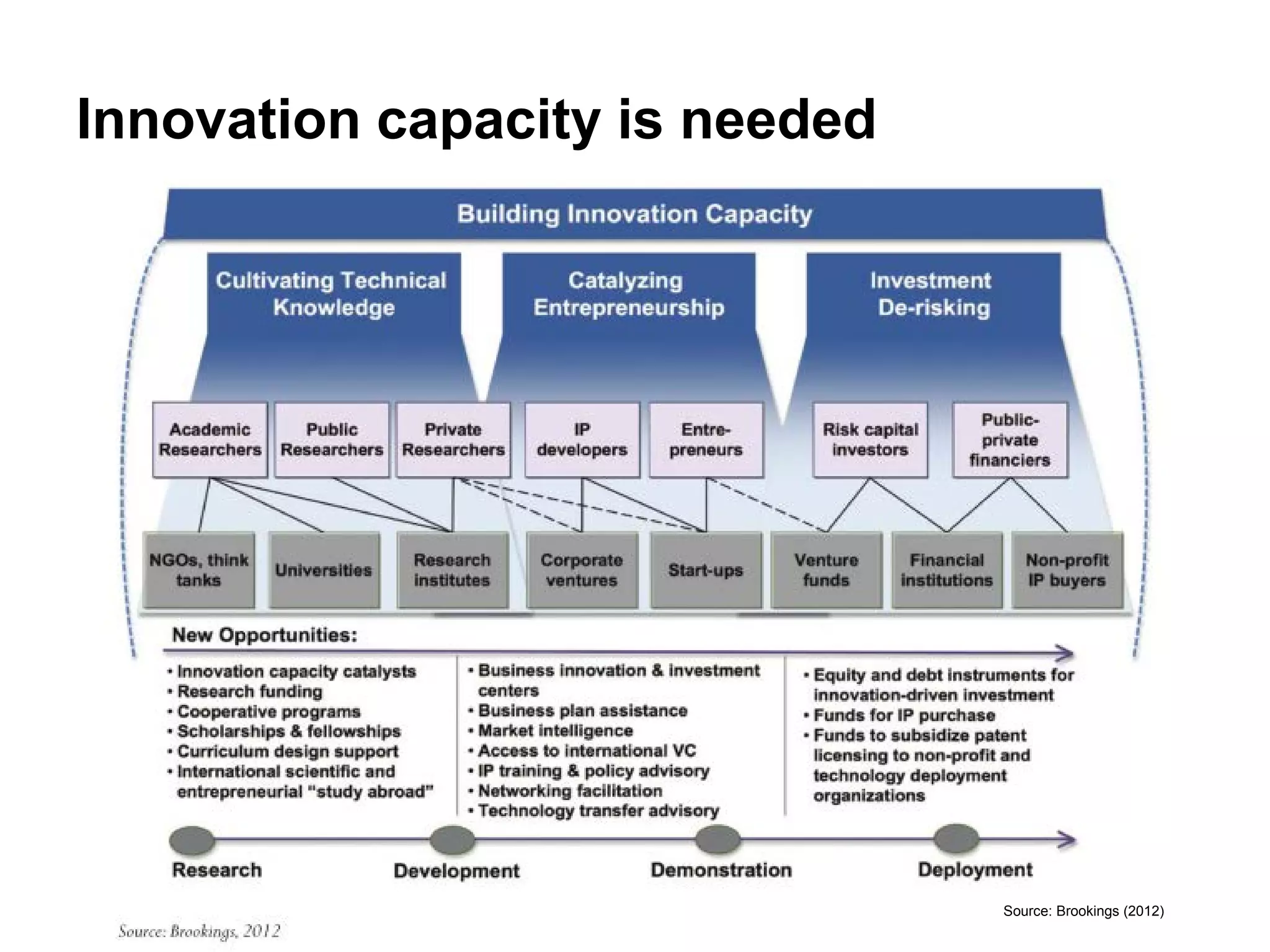
This document discusses sustainable development goals and green growth through bottom-up eco-innovation. It outlines challenges in developing countries related to insufficient innovation capacity and lack of support. Case studies from Cambodia demonstrate how appropriate technologies like solar cookers can meet local needs while creating jobs and reducing environmental impacts. The conclusion emphasizes that green growth requires innovative solutions and dedicated funding is needed to build innovation capacity in least developed countries through demonstration projects and technology sharing.