Here are the key steps to configure Spring MVC in the lab:
1. Configure the ContextLoaderListener in web.xml to initialize the root application context. This loads the common beans.
2. Define the contextConfigLocation parameter pointing to the common spring configuration files.
3. Configure the DispatcherServlet in web.xml. This is the front controller that handles all web requests.
4. Give the DispatcherServlet a unique name and set its contextConfigLocation to load web-specific beans, separate from the root context.
5. Add spring-mvc configuration files defining the component-scan, view resolver, etc.
6. Add Controllers and Views (JSP

![Runtime Environment
1. Development Environment Setup
2. Development Environment Practice
3. Runtime Environment Practice
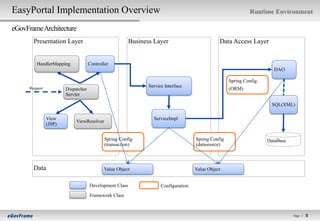
[LAB2-0] easyPortal Implementation Overview
[LAB2-1] IoC Container (Based on XML)
[LAB2-2] IoC Container (Based on Annotation)
[LAB2-3] AOP
[LAB2-4] Data Access
[LAB2-5] Spring MVC
Page l 2 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-2-320.jpg)


![[Lab 2-1] IoC Container (Based on XML) (1/3) Runtime Environment
Practice XML based IoC Contanier
Step 1-1. Define Interface and Method (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.NotificationService)
public Map<String, Object> selectNotificationList(NotificationVO searchVO) throws Exception;
public void insertNotification(NotificationVO notification) throws Exception;
public NotificationVO selectNotification(NotificationVO searchVO) throws Exception;
public void updateNotification(NotificationVO notification) throws Exception;
public void deleteNotification(NotificationVO notification) throws Exception;
Step 1-2. Define a Service implementation class (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationServiceImpl)
- Implement a NotificationService which is a service interface, and check the implementation of interface methods(defined in Step 1-1)
- Extends AbstractServiceImpl which is provided by eGovFrame (It’s compulsory)
Ex: public class NotificationServiceImpl extends AbstractServiceImpl implements NotificationService {
Step 1-3. Check a DAO implementation class (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationDAO)
- Check current DAO handling style (Providing necessary data in the form of ArrayList)
※ Do not need to add extra code or modify
Page l 7 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-7-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-1] IoC Container (Based on XML) (2/3) Runtime Environment
Practice XML based IoC Contanier
Step 1-4. Configure a XML and define services (src/test/resources/egovframework/spring/context-service.xml)
- Configure a Service bean
Ex:
<bean id="notificationService" class="egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationServiceImpl“ />
- Configure DAO dependency injection(DI)
Ex:
<bean id="notificationService" class="egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationServiceImpl">
<property name="dao" ref="notificationDao" />
</bean>
Step 1-5. Define a test class (src/test/java/egovframework.gettingstart.guide.XMLServiceTest)
- Create an ApplicationContext instance
Ex:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String[] {"/egovframework/spring/context-service.xml"}
);
- Call a service
Ex:
NotificationService service = (NotificationService)context.getBean("notificationService");
Page l 8 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-8-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-1] IoC Container (Based on XML) (3/3) Runtime Environment
Practice XML based IoC Contanier
Step 1-6. Run test
- Run test : Select XMLServiceTest class -> Run As -> Java Application
Test Result
- Display the number of notificationService list data (selectNotificationData)
Page l 9 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-9-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-2] IoC Container (Based on Annotation) (1/3) Runtime Environment
PracticeAnnotation based IoC Contanier
Step 2-1. Assign @Repository (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationDAO)
- Assign a Spring bean in a DAO class as using @Repository annotation
- assign bean id with “NotificationDAO”
Ex: @Repository("NotificationDAO“)
Step 2-2. Assign @Service (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationServiceImpl)
- Make ServiceImpl class to a Spring bean as using @Service annotation
- assign bean id with “NotificationService”
Ex: @Service("NotificationService“)
Step 2-3. Assign @Resource (to use an object with DI (Dependency Injection) mechanism)
(egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationServiceImpl)
- Call a notificationDao object(bean) as using @Resource annotation to notificationDao variable
- assign @Resource annotation name with bean(@Repository) id (“NotificationDAO”) which is matched to a target object that want to use
Ex: @Resource(name="NotificationDAO")
private NotificationDAO notificationDao;
Page l
10
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-10-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-2] IoC Container (Based on Annotation) (2/3) Runtime Environment
PracticeAnnotation based IoC Contanier
Step 2-4. Configure component-scan (src/test/resources/egovframework/spring/context-component.xml)
- Create annotation based beans(@Controller, @Service, @Repository) through component-scan configuration
- base-package describes the scan target package and classes which are below the base-package are scanned
Ex: <context:component-scan base-package="egovframework.gettingstart" />
Step 2-5. Create TestCase (egovframework.gettingstart.guide. AnnotationServiceTest)
- Assign @Resource annotation to notificationService variable to call a bean with DI
- make @Resource annotation name field with bean(@Service) id which is “NotificationService”
Ex:
@Resource(name = "NotificationService")
NotificationService notificationService;
Page l
11
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-11-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-2] IoC Container (Based on Annotation) (3/3) Runtime Environment
PracticeAnnotation based IoC Contanier
Step 2-6. Run TestCase
- Run TestCase : Select AnnotationTest Class -> Run As -> JUnit Test
Test results
- Run AnnotationTest class’s testSelectList method (comparing the number of list)
Page l
12
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-12-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-3] AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming) (1/2) Runtime Environment
PracticeAOP
Step 3-1. Check Advice class (egovframework.gettingstart.aop.AdviceUsingXML)
- Advice is a class about processing crosscutting concerns which are scattered in several classes
Step 3-2. Configure Advice bean (src/test/resources/egovframework/spring/context-advice.xml)
- Configure Advice (Id = “adviceUsingXML” , class is “egovframework.gettingstart.aop.AdviceUsingXML”)
Ex : <bean id="adviceUsingXML" class="egovframework.gettingstart.aop.AdviceUsingXML" />
Step 3-3. Check AOP configuration (src/test/resources/egovframework/spring/context-advice.xml)
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="targetMethod"
expression="execution(* egovframework..impl.*Impl.*(..))" />
<aop:aspect ref="adviceUsingXML">
<aop:before pointcut-ref="targetMethod" method="beforeTargetMethod" />
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="targetMethod"
method="afterReturningTargetMethod" returning="retVal" />
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="targetMethod"
method="afterThrowingTargetMethod" throwing="exception" />
<aop:after pointcut-ref="targetMethod" method="afterTargetMethod" />
<aop:around pointcut-ref="targetMethod" method="aroundTargetMethod" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
Page l
13
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-13-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-3] AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming) (2/2) Runtime Environment
PracticeAOP
Step 3-4. Modify TestCase (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.AnnotationServiceTest)
- Modify @ContextConfiguration’s location field. Add context-advice.xml like below (Because value is an array, separated by ",”)
Ex:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {
"classpath*:/egovframework/spring/context-component.xml",
"classpath*:/egovframework/spring/context-advice.xml"
})
Step 3-5. Run TestCase
- Run test : select AnnotationTest class -> Run As -> JUnit Test
- Check the result on console window
Page l
14
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-14-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-4] Data Access (1/4) Runtime Environment
Practice iBatis
Step 4-1. Check sqlMapClient configuration and configure configLocations (src/main/resources/spring/context-sqlMap.xml)
- Configure sqlMapClient for interoperation between iBatis(As a Query service, SQL is separated from Java code) and Spring
- iBatis is composed of SqlMapConfig.xml and SqlMap.xml (file name can be given arbitrarily), and assign ‘SqlMapConfig.xml’ to ‘configLocations’
property in sqlMapClient
-Assign ‘/sqlmap/config/*.xml’ to property, named configLocations (List type) in this practice
Ex:
<property name="configLocations">
<list>
<value>classpath:/sqlmap/config/*.xml</value>
</list>
</property>
Step 4-2. Configure SqlMapConfig(src/main/resources/sqlmap/config/ sql-map-config-guide-notification.xml)
- SqlMapConfig.xml includes SqlMap.xml files which contains executable query as resource property
- Assign ‘sqlmap/sql/guide/Notification_SQL_Hsqldb.xml’ as a resource in this practice
Ex: <sqlMap resource="/sqlmap/sql/guide/Notification_SQL_Hsqldb.xml"/>
Step 4-3. Inherit ‘EgovAbstractDAO’ class (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationDAO)
- In order to apply iBatis, a sqlMapClient should be called and ready to use through DI(Dependency Injection)
- But simply if DAO class inherits EgovAbstractDAO, it’s done.
Ex: public class NotificationDAO extends EgovAbstractDAO {
Page l
15
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-15-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-4] Data Access (2/4) Runtime Environment
Practice iBatis
Step 4-4. Check SqlMap file (src/main/resources/sqlmap/sql/guide/Notification_SQL_Hsqldb.xml)
- Create query through <select ../>, <insert ../>, <update ../>, etc
- Define input(parameterClass) and output(resultClass or resultMap) for each statement
- It is possible to handle various conditions through dynamic query
- Statements are called by query id in DAO
Ex (DAO call):
public List<NotificationVO> selectNotificationList(NotificationVO vo) throws Exception {
return list("NotificationDAO.selectNotificationList", vo);
}
Step 4-5. Write DAO (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.impl.NotificationDAO)
- Remove static part which randomly created data
- Process data access through superclass EgovAbstractDAO’s method (list, selectByPk, insert, update, delete) for each method
Ex :
return list("NotificationDAO.selectNotificationList", vo);
...
return (Integer)selectByPk("NotificationDAO.selectNotificationListCnt", vo);
...
return (String)insert("NotificationDAO.insertNotification", notification);
...
return (NotificationVO)selectByPk("NotificationDAO.selectNotification", searchVO);
...
update("NotificationDAO.updateNotification", notification);
...
delete("NotificationDAO.deleteNotification", notification);
...
return list("NotificationDAO.getNotificationData", vo);
Page l
16
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-16-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-4] Data Access (3/4) Runtime Environment
Practice iBatis
Step 4-6. Run HSQL DB (DATABASE/db)
- Select /DATABASE/db folder in the project
- Select context menu(click mouse right button)
- Select Path Tools -> Command Line Shell menu
- On command window run HSQL : runHsqlDB.cmd
Page l
17
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-17-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-4] Data Access (4/4) Runtime Environment
Practice iBatis
Step 4-7. Run TestCase
-Run test: Select DataAccessTest class -> Run As -> JUnit Test
Test Result
- Run testSelectList method in DataAccessTest class (comparing the number of list)
Page l
18
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-18-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-5] Spring MVC (1/7) Runtime Environment
Practice Spring MVC
Step 5-1. Configure ContextLoaderListener (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml)
- In order to apply Spring MVC, create ApplicationContext through ContextLoaderListener configuration
- ContextLoaderListener is set through Servlet’s <listener> tag
- <listener-class> is defined with org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
Ex:
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
Step 5-2. Define contextConfigLocation context-param (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml)
- When configuring ContextLoaderLister, it is assigned through contextConfigLocation which is for ApplicationContext’s meta information xml
- ContextLoaderListener only defines Persistence and Business field configuration
- Presentation is defined in DispatchServlet which will be configured in Step 5-3 (Inherit ContextLoaderListener’s ApplicationContext and have
separate WebApplicationContext for each presentation area)
- Define "classpath*:spring/context-*.xml“ in this practice
Ex :
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
classpath*:spring/context-*.xml
</param-value>
</context-param>
Page l
19
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-19-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-5] Spring MVC (2/7) Runtime Environment
Practice Spring MVC
Step 5-3. Configure DispatcherServlet (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/web.xml)
- Assign a separate Front Controller to process user request through Spring IoC container
- <servlet-class> is defined with ‘org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet’
- DispatcherServlet defines ApplicationContext’s meta data through separate contextConfigLocation configuration
- Assign “/WEB-INF/config/springmvc/common-*.xml” in this practice
Ex:
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/config/springmvc/common-*.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
Step 5-4. Define HandlerMapping (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/config/springmvc/common-servlet.xml)
- Spring MVC’s HanlderMapping finds a controller that carry out user request’s business logic
- Basic HandlerMaapping is ‘DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping’ and map the user request(which is URL) to the URL which defined Controller’s
@RequestMapping annotation
- HandlerMapping is defiend through <bean> tag (org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping)
Ex :
<bean id="annotationMapper"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping">
<property name="interceptors">
<list>
<ref bean="localeChangeInterceptor" />
</list>
</property>
</bean>
Page l
20
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-20-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-5] Spring MVC (3/7) Runtime Environment
Practice Spring MVC
Step 5-5. Assign a Controller (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.web.NotificationController)
- Controller is assigned as configuring @Controller annotation to the class
Ex:
@Controller
public class NotificationController {
Step 5-6. Configure @RequestMapping (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.web.NotificationController)
- Assign HandlerMapping as configuring @RequestMapping annotation to a Conroller’s specific method
-Assign URL ‘/guide/selectNotificationList.do’ to the method ‘selectNotificationList’
Ex:
@RequestMapping("/guide/selectNotificationList.do")
public String selectNotificationList(HttpSession session, Locale locale,
Step 5-7. pass and process model data (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.web.NotificationController)
- In order to pass model data from a Controller to a View, use ModelMap, etc that is defined as a parameter in the method
Ex:
model.addAttribute("result", vo);
Step 5-8. Call a service method (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.web.NotificationController)
- Change 7 parts(methods) in a Controller. Each method should call a Service’s implemented method
Page l
21
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-21-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-5] Spring MVC (4/7) Runtime Environment
Practice Spring MVC
Step 5-9. Select and process View (egovframework.gettingstart.guide.service.web.NotificationController)
- Call a view as providing View information from a Controller, using methods such as return, etc
- A real view is called through ViewResolver configuration that converts a provided view name(logical view) to real view(physical view)
- Return “guide/notificationList” view name in the end of method ‘selectNotificationList’
Ex:
return "guide/notificationList";
Step 5-10. Configure ViewResolver (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/config/springmvc/common-servlet.xml)
- Call a real view(ex: JSP, etc) as providing view in a controller through ViewResolver configuration
- In case of using JSP as a view, register ‘UrlBasedViewResolver’ as a <bean>
- At this moment, assign the actual called jsp through using prefix and suffix configuration in the front and back of the logical view name
Ex:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.UrlBasedViewResolver" p:order="1"
p:viewClass="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView"
p:prefix="/WEB-INF/jsp/" p:suffix=".jsp"/>
Step 5-11. Use JSP model (src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/jsp/guide/notificationDetail.jsp)
- Display model data in a JSP, as using EL(Expression Language)
- Additionally, utilize JSTL’s core tag libraries
- Display notificationSubject attribute of ‘result’ model data that is added in Step 5-7 through <c:out ../> tag in this practice
Ex:
<c:out value=“${result.notificationSubject}" />
Page l
22
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-22-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-5] Spring MVC (5/7) Runtime Environment
Practice Spring MVC
Step 5-12. Select Servers View
- Select ‘Window -> Show View’ menu and select ‘Servers’
Step 5-13. Configure Tomcat
- Click right mouse button -> New -> Server
Select gettingstart
Start a server
Page l
23
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-23-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-5] Spring MVC (6/7) Runtime Environment
Practice Spring MVC
Step 5-14. Start Tomcat
- Select “Tomcat v6.0 Server at localhost” and then choose “▶” at the top-right corner
Start
Step 5-15. Call a web browser
- http://localhost:8080/lab201
Page l
24
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-24-320.jpg)
![[Lab 2-5] Spring MVC (7/7) Runtime Environment
Practice Spring MVC
Step 5-16. UI Customizing
- Copy UI applied files(jsp, css) : copy lab201/UI/design/main/webapp directory to lab201/src/main/webapp directory
( or when run ‘copy-design’ task in lab201/build.xml(Ant Script), UI applied files are copied to the target directory.)
Step 5-17. Run the application
- Right button click on the project lab201 -> Run As -> Run on Server and check the URL(http://localhost:8080/lab201) on a web browser
Page l
25
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-runtimeenvironmentworkshopen-121115083337-phpapp01/85/04-egovFrame-Runtime-Environment-Workshop-25-320.jpg)