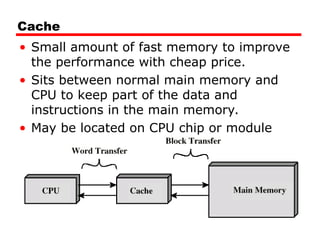
Cache memory is a smaller, faster memory component that stores frequently used data and instructions, acting as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory (RAM). This speeds up access to data and instructions, improving overall system performance.
Key Concepts:
Purpose:
To reduce the time it takes for the CPU to access data by storing frequently used data in a faster, smaller memory.
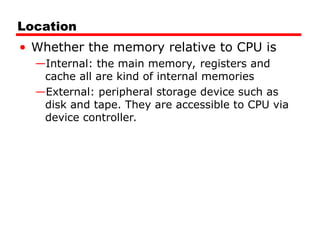
Location:
Situated between the CPU and RAM, often located on the CPU chip itself or on the motherboard.
Types:
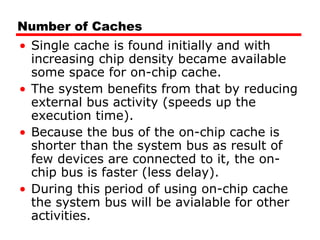
Level 1 (L1) Cache: Fastest and smallest, located within the CPU core.
Level 2 (L2) Cache: Larger and slightly slower than L1, often located on the CPU chip.
Level 3 (L3) Cache: Largest and slowest, located on the CPU chip or motherboard.
Speed and Size:
Cache memory is significantly faster than RAM, but it has a smaller capacity.
Function:
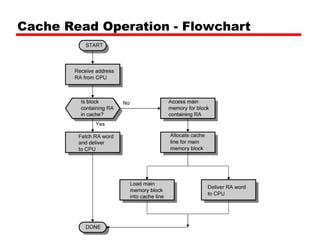
When the CPU needs data, it first checks the cache. If the data is found (a "cache hit"), it's accessed quickly. If not (a "cache miss"), the CPU retrieves the data from RAM, which takes longer.
Benefits:
Faster Data Access:
By storing frequently accessed data, cache memory reduces the need to access slower RAM, leading to faster processing speeds.
Improved Performance:
Reduced waiting times for data access translates to quicker application loading, smoother website browsing, and overall improved system responsiveness.
Energy Efficiency:
In some cases, reduced CPU workload due to cache memory can contribute to lower power consumption and longer battery life, especially in laptops.
Cache memory is a smaller, faster memory component that stores frequently used data and instructions, acting as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory (RAM). This speeds up access to data and instructions, improving overall system performance.
Key Concepts:
Purpose:
To reduce the time it takes for the CPU to access data by storing frequently used data in a faster, smaller memory.
Location:
Situated between the CPU and RAM, often located on the CPU chip itself or on the motherboard.
Types:
Level 1 (L1) Cache: Fastest and smallest, located within the CPU core.
Level 2 (L2) Cache: Larger and slightly slower than L1, often located on the CPU chip.
Level 3 (L3) Cache: Largest and slowest, located on the CPU chip or motherboard.
Speed and Size:
Cache memory is significantly faster than RAM, but it has a smaller capacity.
Function:
When the CPU needs data, it first checks the cache. If the data is found (a "cache hit"), it's accessed quickly. If not (a "cache miss"), the CPU retrieves the data from RAM, which takes longer.
Benefits:
Faster Data Access:
By storing frequently accessed data, cache memory reduces the need to access slower RAM, leading to faster processing speeds.
Improved Performance:
Reduced waiting times for data access translates to quicker application loading, smoother website browsing, and overall improved system responsiveness.
Energy Efficiency:
In some cases, reduced CPU workload due to cache memory can con





















![Direct Mapping
Address Structure
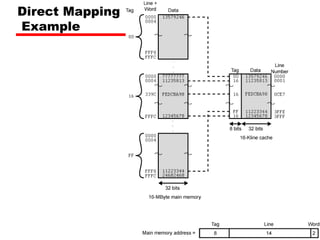
Tag s-r Line or Slot r Word w
8 14 2
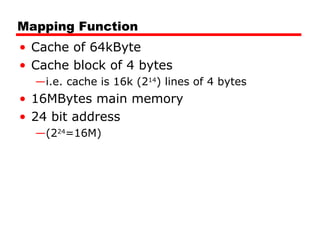
• 24 bit address
• 2 bit word identifier (4 byte block)
• 22 bit block identifier
— 8 bit tag (=22-14) [N.B. the no. of lines in the cache are 214
=
16 K lines]
— 14 bit slot or line
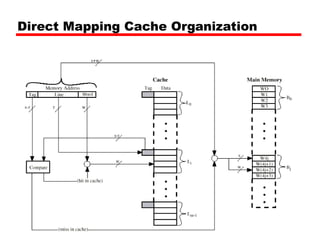
• No two blocks in the same line have the same Tag field
• Check contents of cache by finding line and checking Tag](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04cachememory-cust-250428144205-44d6df8d/85/04_Cache_Memory-cust-memori-memori-memori-ppt-30-320.jpg)





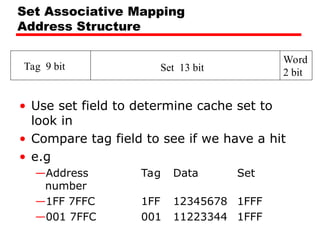
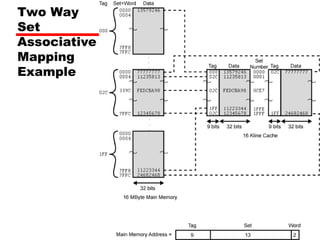

![Set Associative Mapping Summary
• If number of sets (v) = number of lines
(m) [i.e. number of lines for each set
k=1], the set associative technique will
convert to direct mapping.
• If k=m, v=1 (set associative will be fully
associative)
• The most common choice (v=m/2 and
k=2).
• Four way set associative means (k= 4 and
v=v/4).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04cachememory-cust-250428144205-44d6df8d/85/04_Cache_Memory-cust-memori-memori-memori-ppt-47-320.jpg)